14e5db955f54e0a280892171739d9e7f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Chapter 19 -1 Introduction to Ecology Biosphere 2, In Arizona. Cost 150 mil. What could this be used for?
Biosphere -1

space is big; Even at the speed of light it would take us 7 hours to get to Pluto, the fastest things we’ve made were Voyager which is moving at thirty five thousand miles away from us. On a diagram just our Solar system with Earth the size of a Pea, Jupiter would be a thousand feet away, and Pluto would be a mile & a half distant. Proxima Centauri (4. 3 light years away) the nearest start is 10, 000 miles away, That’s from Pittsburgh to Melbourne Australia. To get to Sirius would be another 4. 6 Light years, So complete the trip back from Melbourne. Know one knows, but estimates are that there are 100 -400 billion stars in the Milky way. And the Milky Way is one of 140 Billion estimated Galaxies. So chances for E. T. is good, but even if they are viewing us with great telescopes the light they are receiving left Earth 200 years ago. They’re watching the French Revolution & Thomas Jefferson.

Chapter 19 -1 Objectives • Define Ecology, explain why its important • List & describe 3 human caused environmental problems • I. D. five levels of organization in ecology • Explain theme of interconnectedness Ecosphere: Self contained environment of Shrimp and algae, developed by NASA

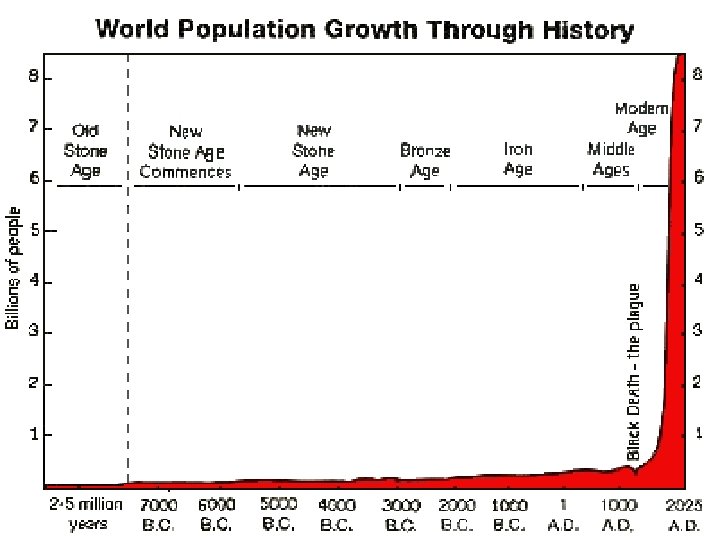
Humans changing the environment • Global population tripled in the 20 th Century. • The lack of space & resources is causing mass extinction • Oikos means house
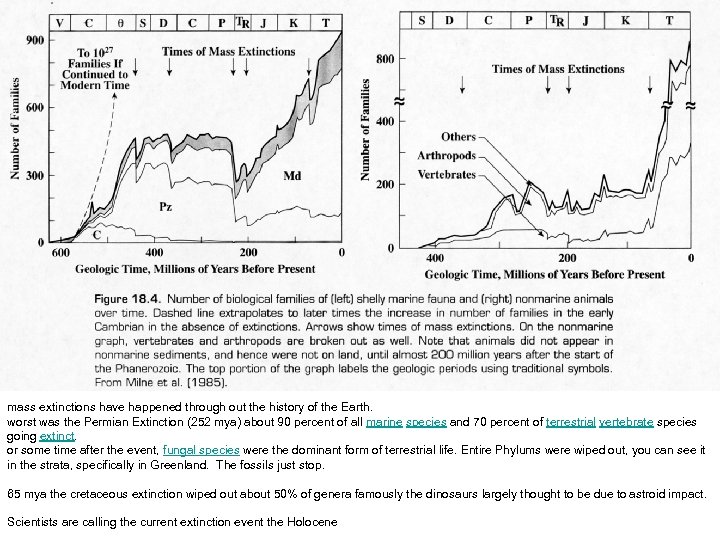
mass extinctions have happened through out the history of the Earth. worst was the Permian Extinction (252 mya) about 90 percent of all marine species and 70 percent of terrestrial vertebrate species going extinct. or some time after the event, fungal species were the dominant form of terrestrial life. Entire Phylums were wiped out, you can see it in the strata, specifically in Greenland. The fossils just stop. 65 mya the cretaceous extinction wiped out about 50% of genera famously the dinosaurs largely thought to be due to astroid impact. Scientists are calling the current extinction event the Holocene


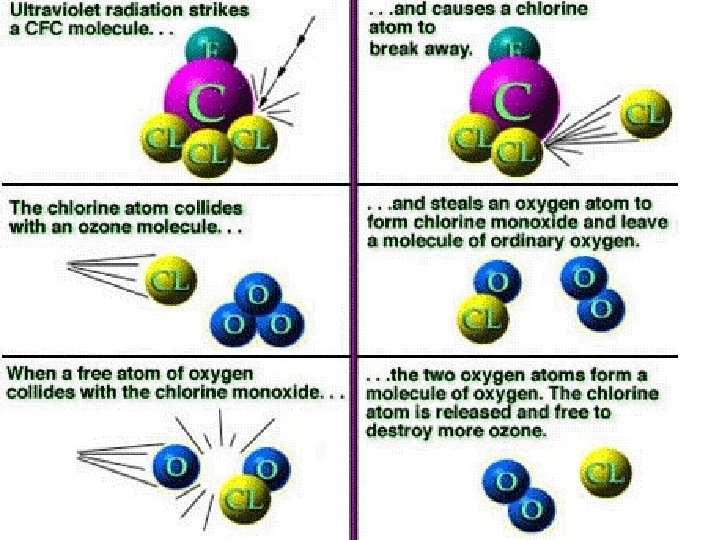
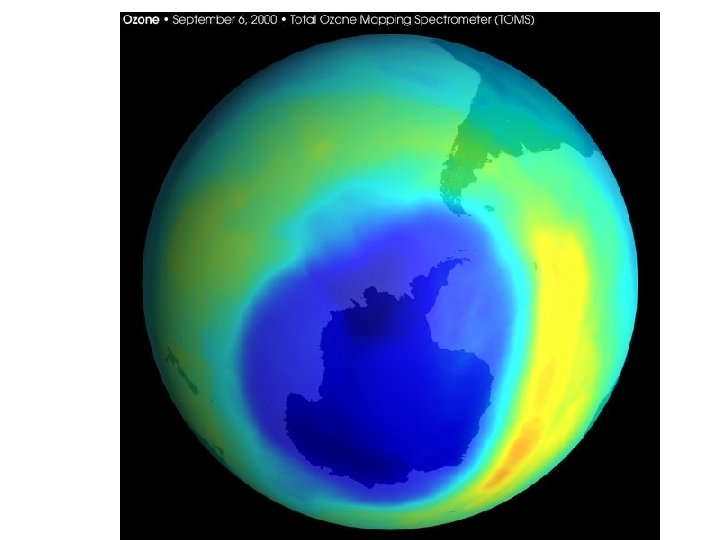
Ozone Layer • A relatively high layer of O 3 absorbs ultraviolet light from the sun • Man-Made Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) & other chemicals react with ozone, decomposing it. • A chlorine atom can disable 100, 000 ozone molecules, before UV radiation

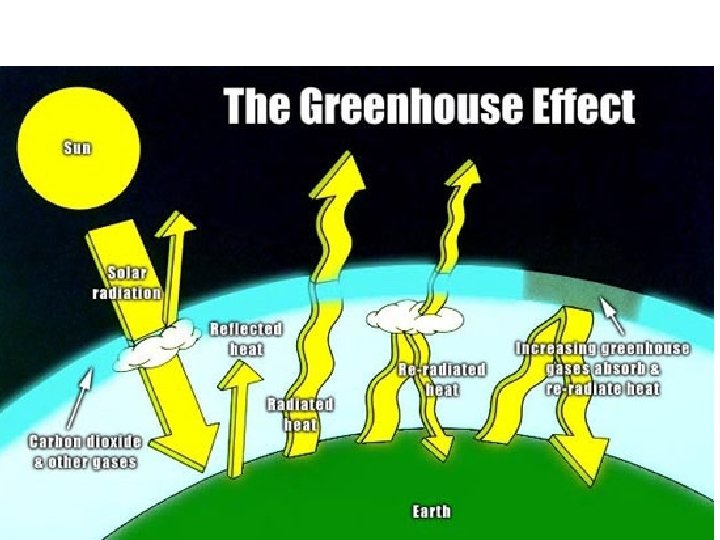
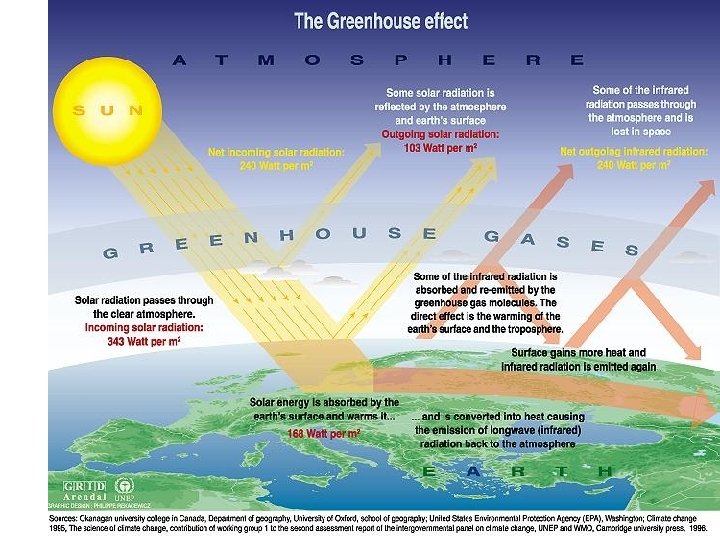
Greenhouse effect • Like any stone the Earth heats up in the sunlight, and then heat escapes in the dark • Carbon Dioxide & water vapor insulates the Earth reflecting escaping heat back • Burning fossil fuels leads to an increase of CO 2 levels rise; warming the globe • Melting the ice caps?

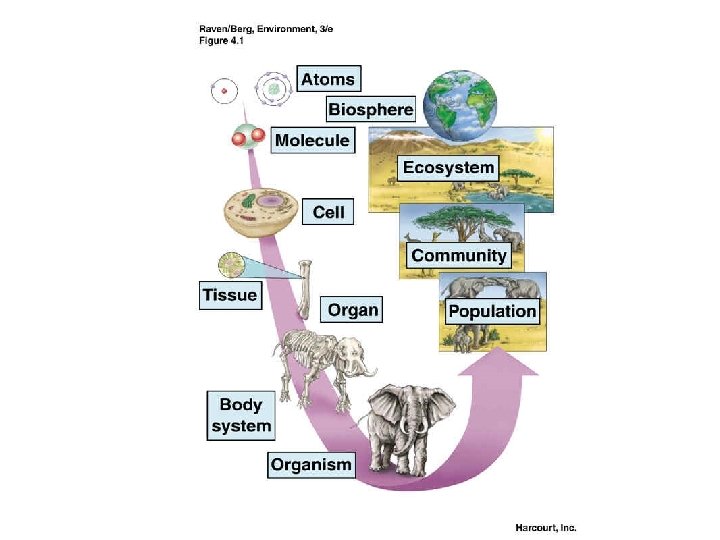
Levels of Organization • Is the whole greater than the sum of the parts? – Emergent Properties: larger groups (of cells, individuals, chemicals) can carry out more complex processes. • Every level influences every other level – Butterfly effect – A butterfly flaps its wings…

The levels of organization 1. Biosphere: part of Earth that supports life 2. Ecosystems: the organisms & non-living environment in a particular place 3. Community: only the organisms in a particular place 4. Population: the members of one species in one place during one stretch of time 5. Organism: The individual
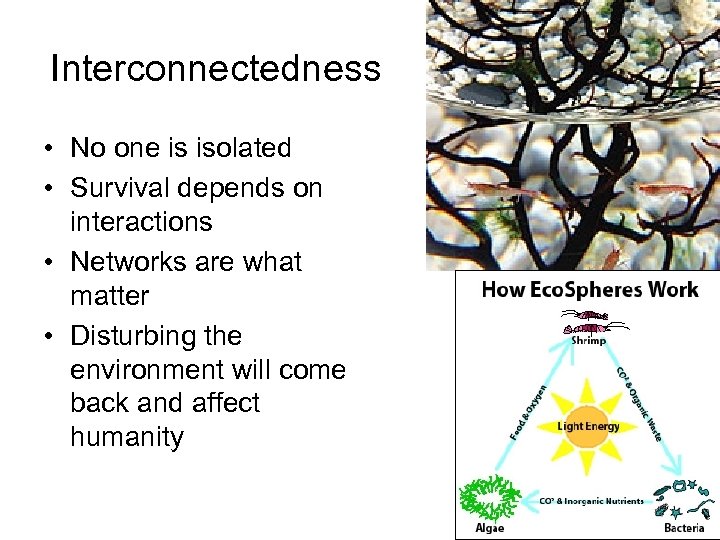
Interconnectedness • No one is isolated • Survival depends on interactions • Networks are what matter • Disturbing the environment will come back and affect humanity
14e5db955f54e0a280892171739d9e7f.ppt