a6a4327fe09109baa8165df3b6700551.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Chapter 17 War and Terrorism © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 17 War and Terrorism © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
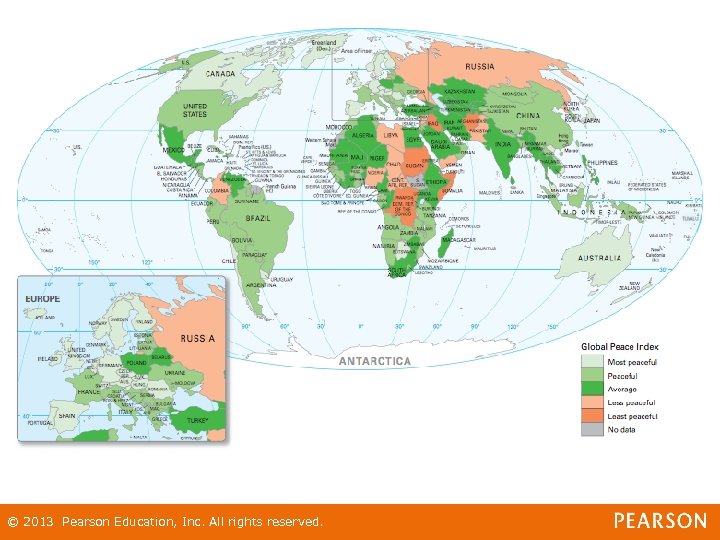
 War and Peace: Basic Definitions • War - violent conflict among nations or organized groups • Peace - absence of violent conflict • Wars have always been part of human history © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
War and Peace: Basic Definitions • War - violent conflict among nations or organized groups • Peace - absence of violent conflict • Wars have always been part of human history © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 War and Peace: Basic Definitions • Over the centuries, the level of war-related violence has increased • During the 20 th century there was no time at which there was not an armed conflict – Occurring somewhere around the world © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
War and Peace: Basic Definitions • Over the centuries, the level of war-related violence has increased • During the 20 th century there was no time at which there was not an armed conflict – Occurring somewhere around the world © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Increasing Destruction of War • Level and destructive nature of war (weaponry) has increased over time • The 20 th century and weapons of mass destruction – Weapons with destructive capacity to kill many thousands of people at the same time © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Increasing Destruction of War • Level and destructive nature of war (weaponry) has increased over time • The 20 th century and weapons of mass destruction – Weapons with destructive capacity to kill many thousands of people at the same time © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Causes of War • 7 factors the promote the outbreak of war: – Perceived threats; Cultural and religious differences; Political objectives – Moral objectives; Wealth, power, and global standing; Social problems – Absence of alternatives © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Causes of War • 7 factors the promote the outbreak of war: – Perceived threats; Cultural and religious differences; Political objectives – Moral objectives; Wealth, power, and global standing; Social problems – Absence of alternatives © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Economic Costs of Militarism • Global military spending exceeds $1. 5 trillion annually • U. S. defense budget for 2012 was $738 billion – Or about $2, 400 for each person in the U. S. • Factors underlying military spending – The cold war era © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Economic Costs of Militarism • Global military spending exceeds $1. 5 trillion annually • U. S. defense budget for 2012 was $738 billion – Or about $2, 400 for each person in the U. S. • Factors underlying military spending – The cold war era © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Economic Costs of Militarism – Post cold war and the world is still a dangerous place • Military-industrial complex – – Political alliance involving federal government, the military, and the defense industries © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Economic Costs of Militarism – Post cold war and the world is still a dangerous place • Military-industrial complex – – Political alliance involving federal government, the military, and the defense industries © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Economic Costs of War • Destruction of the infrastructure of a society – Homes – Workplace – Water systems – Electrical and communication network © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Economic Costs of War • Destruction of the infrastructure of a society – Homes – Workplace – Water systems – Electrical and communication network © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Economic Costs of War • Military spending • U. S. has already spent $60 billion in efforts to rebuild Iraq © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Economic Costs of War • Military spending • U. S. has already spent $60 billion in efforts to rebuild Iraq © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
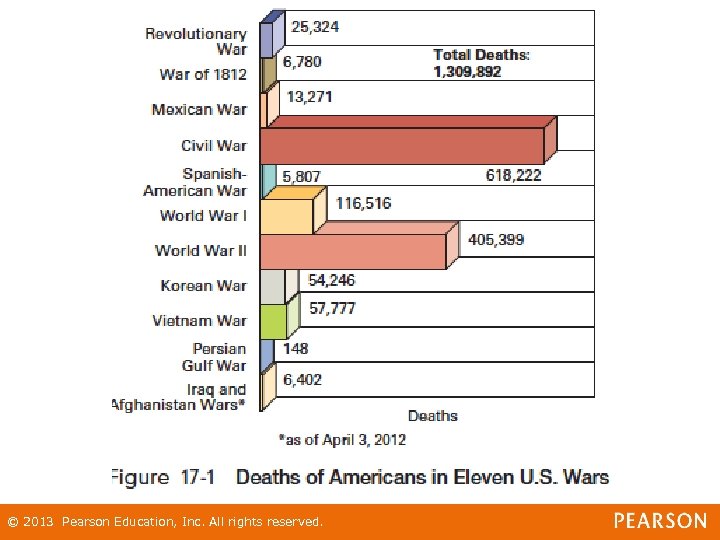
 The Human Costs of War • Loss of human life has increased with the level of military technology • Total war – – Deadly conflict that targets population centers as well as military targets © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Costs of War • Loss of human life has increased with the level of military technology • Total war – – Deadly conflict that targets population centers as well as military targets © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Human Costs of War • Concentration camps - internment centers for prisoners confined for purposes of: – State security, exploitation, punishment, or execution • War Crimes - offense against the law of war as established by: – International agreements and international law © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Costs of War • Concentration camps - internment centers for prisoners confined for purposes of: – State security, exploitation, punishment, or execution • War Crimes - offense against the law of war as established by: – International agreements and international law © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Human Costs of War • WWII and the Geneva Convention recognized 3 categories of war crimes: • Crimes against peace – starting or preparing to go to war against another nation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Costs of War • WWII and the Geneva Convention recognized 3 categories of war crimes: • Crimes against peace – starting or preparing to go to war against another nation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Human Costs of War • Conventional war crimes – murder, rape, torture or ill treatment of people in any occupied territory • Crimes against humanity – genocide • War-Related Disabilities © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Costs of War • Conventional war crimes – murder, rape, torture or ill treatment of people in any occupied territory • Crimes against humanity – genocide • War-Related Disabilities © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Human Costs of War • Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) • Illness and disability • War and Children – Loss life – Orphaned © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Human Costs of War • Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) • Illness and disability • War and Children – Loss life – Orphaned © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Social Class and the Military • Draft ended in 1973 - now all-voluntary military • Primarily working-class people looking to the military for a job © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Social Class and the Military • Draft ended in 1973 - now all-voluntary military • Primarily working-class people looking to the military for a job © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Mass Media and War • Mass media not only report events, but frame them • Operates to provide selective information on armed conflicts to worldwide audience – Power to shape reality © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Mass Media and War • Mass media not only report events, but frame them • Operates to provide selective information on armed conflicts to worldwide audience – Power to shape reality © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
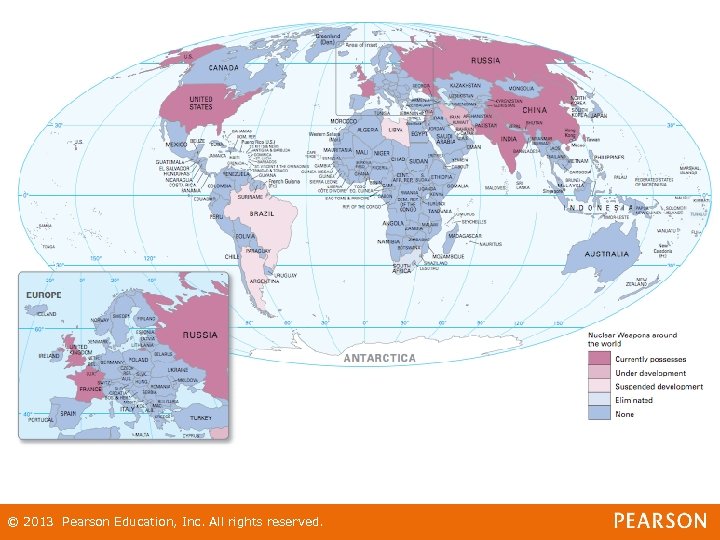
 War in the Nuclear Age • Nuclear weapons – – Bombs that use nuclear reactions to generate enormous destructive force • The Increase and Spread of Nuclear Weapons • Major nuclear powers during Cold War – United States & Russia © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
War in the Nuclear Age • Nuclear weapons – – Bombs that use nuclear reactions to generate enormous destructive force • The Increase and Spread of Nuclear Weapons • Major nuclear powers during Cold War – United States & Russia © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 War in the Nuclear Age • The increase and spread of nuclear weapons, or nuclear proliferation • Other countries with nuclear weapons – Great Britain, France, Israel, India, Pakistan, People’s Republic of China © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
War in the Nuclear Age • The increase and spread of nuclear weapons, or nuclear proliferation • Other countries with nuclear weapons – Great Britain, France, Israel, India, Pakistan, People’s Republic of China © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
© 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 War in the Nuclear Age • The Effects of Nuclear War • Destruction of human life • Nuclear winter and the destruction of the ecosystem – Decline in temperature – Semi-darkness © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
War in the Nuclear Age • The Effects of Nuclear War • Destruction of human life • Nuclear winter and the destruction of the ecosystem – Decline in temperature – Semi-darkness © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Strategies for Peace • Deterrence - strategy to keep peace based on the threat of retaliation – MAD, mutual assured destruction • High-Technology Defense– Use of high technology (satellites and ground installations, to shield the U. S. from attack) – SDI, strategic defense initiative © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Strategies for Peace • Deterrence - strategy to keep peace based on the threat of retaliation – MAD, mutual assured destruction • High-Technology Defense– Use of high technology (satellites and ground installations, to shield the U. S. from attack) – SDI, strategic defense initiative © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Strategies for Peace • Arms Control- international agreements to: – Limit the development, testing, production, and deployment of weapons – SALT-(1970 s)strategic arms limitation talks – START-(1991)strategic arms reduction talk • Resolving Underlying Conflicts – Diplomacy and peace negotiations © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Strategies for Peace • Arms Control- international agreements to: – Limit the development, testing, production, and deployment of weapons – SALT-(1970 s)strategic arms limitation talks – START-(1991)strategic arms reduction talk • Resolving Underlying Conflicts – Diplomacy and peace negotiations © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Terrorism • Terrorism - unlawful and typically random acts of violence or threat of such violence – Employed by an individual, group, or government to achieve a political goal • State sponsored terrorism - government provides money, weapons, and training – For terrorists who engage in violence in another nation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Terrorism • Terrorism - unlawful and typically random acts of violence or threat of such violence – Employed by an individual, group, or government to achieve a political goal • State sponsored terrorism - government provides money, weapons, and training – For terrorists who engage in violence in another nation © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Terrorism • Repressive state terrorism – – Government use of ruthless violence within its own borders to eliminate political opposition © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Terrorism • Repressive state terrorism – – Government use of ruthless violence within its own borders to eliminate political opposition © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Extent of Terrorism • In 2010, there were more than 11, 600 terrorist attacks worldwide • Terrorism: Global Perspective • Irish Republican Army (IRA) • Post WWII and the militant faction of the Zionist movement © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Extent of Terrorism • In 2010, there were more than 11, 600 terrorist attacks worldwide • Terrorism: Global Perspective • Irish Republican Army (IRA) • Post WWII and the militant faction of the Zionist movement © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Extent of Terrorism • Current terrorism is directed towards U. S. interests – Al-Qaeda • • Terrorism in the United States Post-slavery and the Ku Klux Klan Employers and the labor movement Industrial Workers of the World © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Extent of Terrorism • Current terrorism is directed towards U. S. interests – Al-Qaeda • • Terrorism in the United States Post-slavery and the Ku Klux Klan Employers and the labor movement Industrial Workers of the World © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The Extent of Terrorism • Weather Underground group of the 1960 s • Timothy Mc. Veigh • September 11, 2001 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Extent of Terrorism • Weather Underground group of the 1960 s • Timothy Mc. Veigh • September 11, 2001 © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Costs of Terrorism • Loss of life – Tens of thousands of lives lost worldwide in recent years • Psychological cost • Financial cost © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Costs of Terrorism • Loss of life – Tens of thousands of lives lost worldwide in recent years • Psychological cost • Financial cost © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Terrorism as a Type of War • Terrorism differs from conventional war: – The parties in conflict are not clearly known – The objectives of the terrorist groups are not clearly stated – Terrorism is asymmetrical © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Terrorism as a Type of War • Terrorism differs from conventional war: – The parties in conflict are not clearly known – The objectives of the terrorist groups are not clearly stated – Terrorism is asymmetrical © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Strategies for Dealing with Terrorism • Make no concessions – Giving in only produces more terrorism • Prosecute or kill terrorists • Apply economic sanctions – Against nations that sponsor terrorism © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Strategies for Dealing with Terrorism • Make no concessions – Giving in only produces more terrorism • Prosecute or kill terrorists • Apply economic sanctions – Against nations that sponsor terrorism © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Strategies for Dealing with Terrorism • Use Military Force • Defend against terrorism • Address the root causes of terrorism – Examine underlying conflicts and conditions © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Strategies for Dealing with Terrorism • Use Military Force • Defend against terrorism • Address the root causes of terrorism – Examine underlying conflicts and conditions © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Biological Theories of War • Konrad Lorenz – resort to violence to protect territory – instinctual matter of survival • Edward O. Wilson – war results from the innate tendency of aggression and competition © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Biological Theories of War • Konrad Lorenz – resort to violence to protect territory – instinctual matter of survival • Edward O. Wilson – war results from the innate tendency of aggression and competition © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Structural-Functional Analysis: The Functions of Conflict • Functions of war: – Establishing political boundaries – Uniting a population against a common enemy – Improving the status of minorities © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Structural-Functional Analysis: The Functions of Conflict • Functions of war: – Establishing political boundaries – Uniting a population against a common enemy – Improving the status of minorities © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Symbolic-Interaction Analysis: The Meanings of Conflict • Meanings that people attach to war and conflict • Symbols to define the nature of war and enemy – Define enemy as less than human © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Symbolic-Interaction Analysis: The Meanings of Conflict • Meanings that people attach to war and conflict • Symbols to define the nature of war and enemy – Define enemy as less than human © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Social-Conflict Analysis: Inequality and Conflict • War is a function of the struggle for power and wealth – Haves and Have Nots • War evolves out of defending and expanding the capitalist global economy • Strong nations use war to dominate the globe • Powerless use terrorism to fight back © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Social-Conflict Analysis: Inequality and Conflict • War is a function of the struggle for power and wealth – Haves and Have Nots • War evolves out of defending and expanding the capitalist global economy • Strong nations use war to dominate the globe • Powerless use terrorism to fight back © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Conservatives: Strength Means Security • Strong military – Increase military spending • Hard line against terrorists-bring them to justice – Military response © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conservatives: Strength Means Security • Strong military – Increase military spending • Hard line against terrorists-bring them to justice – Military response © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Liberals: The Danger of Militarism • Necessary military force and spending to defend national interests • Impact of military spending on the society – Money could be spent on education, health care, etc. • Diplomacy first © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Liberals: The Danger of Militarism • Necessary military force and spending to defend national interests • Impact of military spending on the society – Money could be spent on education, health care, etc. • Diplomacy first © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Radicals: The Need for Justice • Radicals on the left - root cause of war is inequality – Change the status of the poor people around the world • Move towards social justice around the world © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Radicals: The Need for Justice • Radicals on the left - root cause of war is inequality – Change the status of the poor people around the world • Move towards social justice around the world © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Radicals: The Need for Justice • U. S. is protecting U. S. interests around the world – Keeps corporate profits high © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Radicals: The Need for Justice • U. S. is protecting U. S. interests around the world – Keeps corporate profits high © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.


