 Chapter 17 The Foreign Exchange Market
Chapter 17 The Foreign Exchange Market
 Definitions n Exchange Rate: The price of one currency in terms of another currency. Foreign Exchange Market: A market in which trading of currency and bank deposits denominated in particular currencies takes place. Currency Appreciation: the increase in its value. n Currency Depreciation: the fall in its value. n n
Definitions n Exchange Rate: The price of one currency in terms of another currency. Foreign Exchange Market: A market in which trading of currency and bank deposits denominated in particular currencies takes place. Currency Appreciation: the increase in its value. n Currency Depreciation: the fall in its value. n n
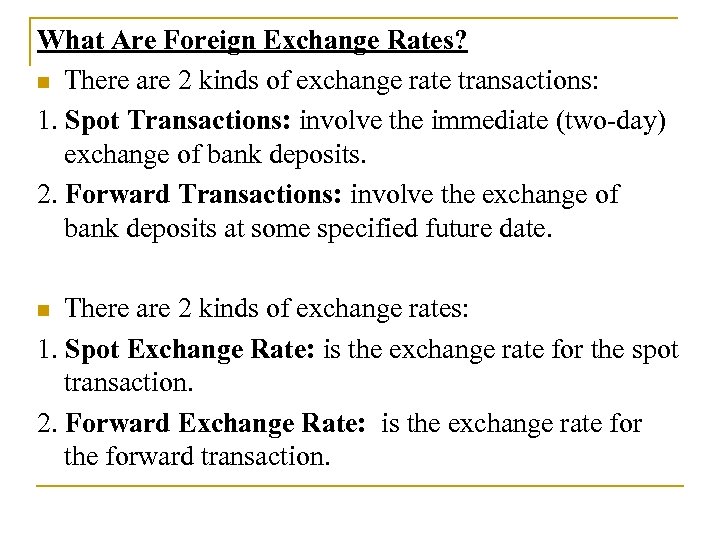 What Are Foreign Exchange Rates? n There are 2 kinds of exchange rate transactions: 1. Spot Transactions: involve the immediate (two-day) exchange of bank deposits. 2. Forward Transactions: involve the exchange of bank deposits at some specified future date. There are 2 kinds of exchange rates: 1. Spot Exchange Rate: is the exchange rate for the spot transaction. 2. Forward Exchange Rate: is the exchange rate for the forward transaction. n
What Are Foreign Exchange Rates? n There are 2 kinds of exchange rate transactions: 1. Spot Transactions: involve the immediate (two-day) exchange of bank deposits. 2. Forward Transactions: involve the exchange of bank deposits at some specified future date. There are 2 kinds of exchange rates: 1. Spot Exchange Rate: is the exchange rate for the spot transaction. 2. Forward Exchange Rate: is the exchange rate for the forward transaction. n
 How is Foreign Exchange Traded? n The foreign exchange market is organized as an over the counter market. n There are several hundred dealers (mostly banks) stand ready to buy and sell deposits denominated in foreign currencies.
How is Foreign Exchange Traded? n The foreign exchange market is organized as an over the counter market. n There are several hundred dealers (mostly banks) stand ready to buy and sell deposits denominated in foreign currencies.
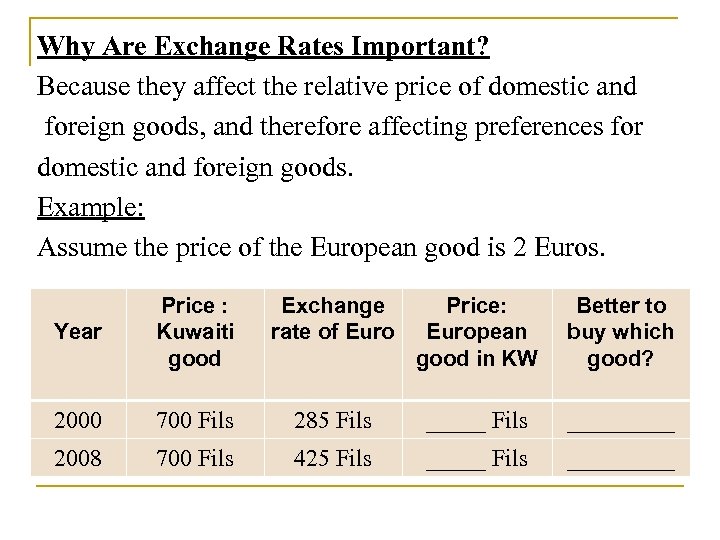 Why Are Exchange Rates Important? Because they affect the relative price of domestic and foreign goods, and therefore affecting preferences for domestic and foreign goods. Example: Assume the price of the European good is 2 Euros. Price : Exchange Price: Better to Year Kuwaiti rate of European buy which good in KW good? 2000 700 Fils 285 Fils _________ 2008 700 Fils 425 Fils _________
Why Are Exchange Rates Important? Because they affect the relative price of domestic and foreign goods, and therefore affecting preferences for domestic and foreign goods. Example: Assume the price of the European good is 2 Euros. Price : Exchange Price: Better to Year Kuwaiti rate of European buy which good in KW good? 2000 700 Fils 285 Fils _________ 2008 700 Fils 425 Fils _________
 Conclusion: n n n When currency appreciates, the country's goods abroad (its exports) become more expensive and foreign goods in that country (its imports) become cheaper. ↑ in EXR → ↓ Exports and ↑ Imports When currency depreciates, the country's goods abroad (its exports) become cheaper and foreign goods in that country (its imports) become more expensive. ↓ in EXR → ↑ Exports and ↓ Imports Result: Net Exporting countries prefer low EXR, while net importing countries prefer high EXR.
Conclusion: n n n When currency appreciates, the country's goods abroad (its exports) become more expensive and foreign goods in that country (its imports) become cheaper. ↑ in EXR → ↓ Exports and ↑ Imports When currency depreciates, the country's goods abroad (its exports) become cheaper and foreign goods in that country (its imports) become more expensive. ↓ in EXR → ↑ Exports and ↓ Imports Result: Net Exporting countries prefer low EXR, while net importing countries prefer high EXR.
 Factors Affecting Exchange Rates in the Long Run 1. Relative Price Level A rise in a country's price level (relative to the foreign price level) causes its currency to depreciate. 2. Trade Barriers (Tariffs and Quotas) Tariffs and quotas cause a country's currency to appreciate in the long run.
Factors Affecting Exchange Rates in the Long Run 1. Relative Price Level A rise in a country's price level (relative to the foreign price level) causes its currency to depreciate. 2. Trade Barriers (Tariffs and Quotas) Tariffs and quotas cause a country's currency to appreciate in the long run.
 3. Preferences for Domestic versus Foreign Goods n Increased demand for imports causes the domestic currency to depreciate. n Increased demand for a country's exports causes its currency to appreciate. 4. Productivity As a country becomes more productive (relative to the other country) its currency appreciates.
3. Preferences for Domestic versus Foreign Goods n Increased demand for imports causes the domestic currency to depreciate. n Increased demand for a country's exports causes its currency to appreciate. 4. Productivity As a country becomes more productive (relative to the other country) its currency appreciates.
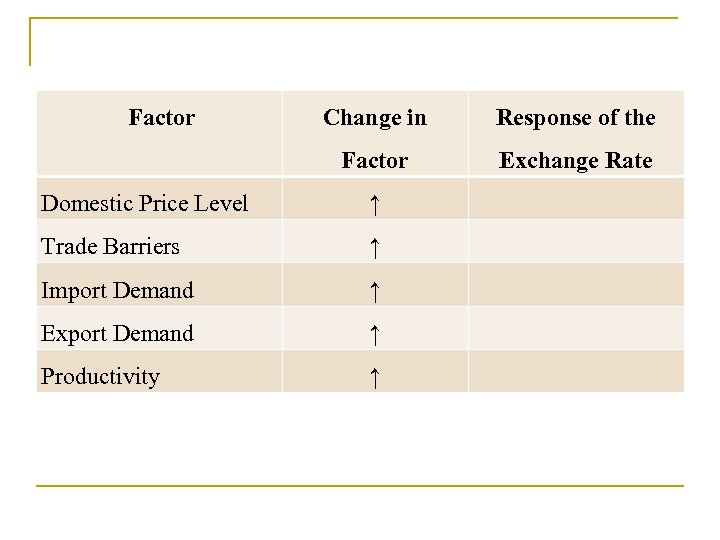 Factor Change in Response of the Factor Exchange Rate Domestic Price Level ↑ Trade Barriers ↑ Import Demand ↑ Export Demand ↑ Productivity ↑
Factor Change in Response of the Factor Exchange Rate Domestic Price Level ↑ Trade Barriers ↑ Import Demand ↑ Export Demand ↑ Productivity ↑
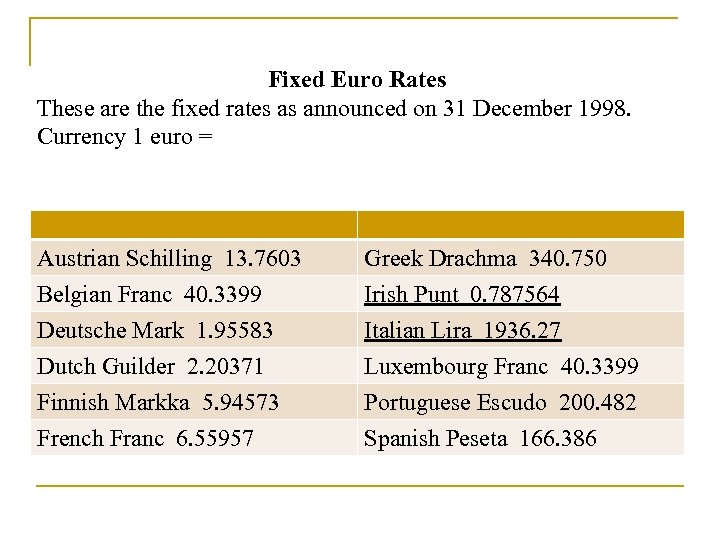 Fixed Euro Rates These are the fixed rates as announced on 31 December 1998. Currency 1 euro = Austrian Schilling 13. 7603 Belgian Franc 40. 3399 Deutsche Mark 1. 95583 Greek Drachma 340. 750 Irish Punt 0. 787564 Italian Lira 1936. 27 Dutch Guilder 2. 20371 Finnish Markka 5. 94573 French Franc 6. 55957 Luxembourg Franc 40. 3399 Portuguese Escudo 200. 482 Spanish Peseta 166. 386
Fixed Euro Rates These are the fixed rates as announced on 31 December 1998. Currency 1 euro = Austrian Schilling 13. 7603 Belgian Franc 40. 3399 Deutsche Mark 1. 95583 Greek Drachma 340. 750 Irish Punt 0. 787564 Italian Lira 1936. 27 Dutch Guilder 2. 20371 Finnish Markka 5. 94573 French Franc 6. 55957 Luxembourg Franc 40. 3399 Portuguese Escudo 200. 482 Spanish Peseta 166. 386
 Exchange Rate of the Euro vs the Dollar (2004 -2008)
Exchange Rate of the Euro vs the Dollar (2004 -2008)