502251322566a970ee2472a58743c078.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 >>>> Chapter 17 The Financial System
>>>> Chapter 17 The Financial System
 g Goals Learnin 1 Outline the structure and importance of the financial system. List the various types of securities. 5 Discuss the organization and functioning of financial institutions. 6 Explain the functions of the Federal Reserve System and the tools it uses to control the supply of money and credit. 2 3 Define financial market, and distinguish between primary and secondary financial markets. 7 Describe the characteristics of the major stock exchanges. 4 Evaluate the major features of regulations and laws affecting the financial system. 8 Describe the global financial system.
g Goals Learnin 1 Outline the structure and importance of the financial system. List the various types of securities. 5 Discuss the organization and functioning of financial institutions. 6 Explain the functions of the Federal Reserve System and the tools it uses to control the supply of money and credit. 2 3 Define financial market, and distinguish between primary and secondary financial markets. 7 Describe the characteristics of the major stock exchanges. 4 Evaluate the major features of regulations and laws affecting the financial system. 8 Describe the global financial system.
 l System Financia he T The financial system is the process by which money flows from savers to users.
l System Financia he T The financial system is the process by which money flows from savers to users.
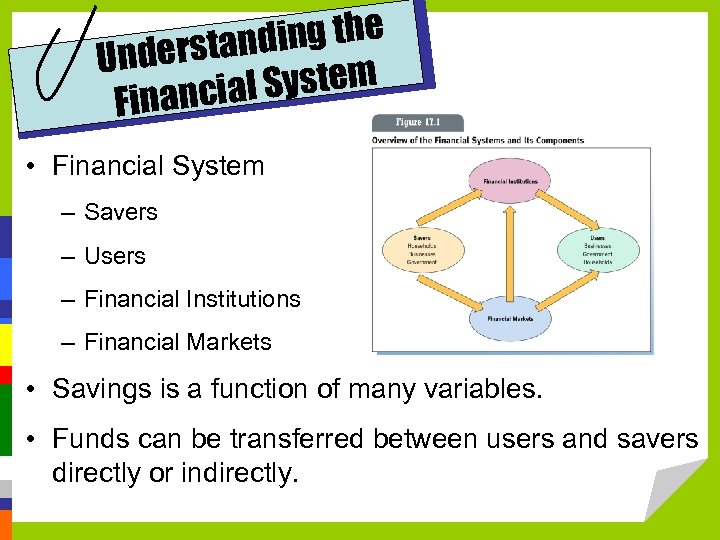 ing the derstand Un System inancial F • Financial System – Savers – Users – Financial Institutions – Financial Markets • Savings is a function of many variables. • Funds can be transferred between users and savers directly or indirectly.
ing the derstand Un System inancial F • Financial System – Savers – Users – Financial Institutions – Financial Markets • Savings is a function of many variables. • Funds can be transferred between users and savers directly or indirectly.
 urities s of Sec Type • Securities – Financial instruments – Obligations on the part of the issuer • Businesses and Governments – Provide rate of return to purchasers • Money Market Instruments • Bonds • Stock
urities s of Sec Type • Securities – Financial instruments – Obligations on the part of the issuer • Businesses and Governments – Provide rate of return to purchasers • Money Market Instruments • Bonds • Stock
 ey Market Mon struments In • Short-term Debt Securities – Issued by governments, financial institutions and corporations • Investors are paid interest for the use of their funds. • Generally low-risk • U. S. Treasury bills, commercial paper, and bank certificates of deposit
ey Market Mon struments In • Short-term Debt Securities – Issued by governments, financial institutions and corporations • Investors are paid interest for the use of their funds. • Generally low-risk • U. S. Treasury bills, commercial paper, and bank certificates of deposit
 Bonds • Government Bonds – Bonds sold by the U. S. Department of the Treasury. • Municipal Bonds – Bonds issued by state or local governments • Revenue bonds are used toward a project that will produce revenue, General Obligation Bonds are not.
Bonds • Government Bonds – Bonds sold by the U. S. Department of the Treasury. • Municipal Bonds – Bonds issued by state or local governments • Revenue bonds are used toward a project that will produce revenue, General Obligation Bonds are not.
 Ratings Bond • Price is determined by risk and interest rate. • Several firms rate bonds – Standard & Poor’s (S&P) – Moody’s • Investment-grade • Speculative/Junk
Ratings Bond • Price is determined by risk and interest rate. • Several firms rate bonds – Standard & Poor’s (S&P) – Moody’s • Investment-grade • Speculative/Junk
 Stocks • Common stock – ownership claims in corporations. – Vote on major company decisions – Cash dividends – Price appreciation • Preferred stock – stockholders with preference in the payment of dividends.
Stocks • Common stock – ownership claims in corporations. – Vote on major company decisions – Cash dividends – Price appreciation • Preferred stock – stockholders with preference in the payment of dividends.
 ecurities nvertible S Co Stockholder has the right to exchange the bond or preferred stock for a fixed number of shares of common stock.
ecurities nvertible S Co Stockholder has the right to exchange the bond or preferred stock for a fixed number of shares of common stock.
 arkets nancial M Fi • Primary Market – firms and governments issue securities and sell them initially to the public. – When a firm offers a stock for sale to the general public for the first time. • Secondary Market – collection of financial markets in which previously issued securities are traded among investors.
arkets nancial M Fi • Primary Market – firms and governments issue securities and sell them initially to the public. – When a firm offers a stock for sale to the general public for the first time. • Secondary Market – collection of financial markets in which previously issued securities are traded among investors.
 ding Stock nderstan U Markets Stock market (exchange) – market in which common stocks are traded, such as the New York Stock Exchange.
ding Stock nderstan U Markets Stock market (exchange) – market in which common stocks are traded, such as the New York Stock Exchange.
 changes Stock Ex • The New York Stock Exchange – the Big Board is the most famous and one of the oldest stock markets in the world. More than 3, 000 stocks are listed on NYSE. • The Nasdaq Stock Market – the second largest stock market. Over 5, 000 companies have their stocks listed on Nasdaq but many are smaller firms. • Other U. S. Stock Markets – The American Stock Exchange/AMEX – Regional Stock Exchanges – Foreign Markets
changes Stock Ex • The New York Stock Exchange – the Big Board is the most famous and one of the oldest stock markets in the world. More than 3, 000 stocks are listed on NYSE. • The Nasdaq Stock Market – the second largest stock market. Over 5, 000 companies have their stocks listed on Nasdaq but many are smaller firms. • Other U. S. Stock Markets – The American Stock Exchange/AMEX – Regional Stock Exchanges – Foreign Markets
 ure of The Fut Ns and EC arkets Stock M • ECNs – electronic communication networks – The 4 th Market – Buyers and sellers meet in a virtual market and exchange with one another – Take place on INET or Archipelago • INET and Archipelago have been purchased by Nasdaq and NYSE
ure of The Fut Ns and EC arkets Stock M • ECNs – electronic communication networks – The 4 th Market – Buyers and sellers meet in a virtual market and exchange with one another – Take place on INET or Archipelago • INET and Archipelago have been purchased by Nasdaq and NYSE
 icipation estor Part Inv Markets the Stock in • Investors use brokerage firms, they: 1) Establish an account 2) Enter orders 3) Trade stock • The brokerage firm executes the trade on behalf of the investor, charging a fee for the order – Market Order – Limit Order
icipation estor Part Inv Markets the Stock in • Investors use brokerage firms, they: 1) Establish an account 2) Enter orders 3) Trade stock • The brokerage firm executes the trade on behalf of the investor, charging a fee for the order – Market Order – Limit Order
 nstitutions inancial I F ü Commercial Banks ü Savings Banks and Credit Unions ü Non-depository Institutions
nstitutions inancial I F ü Commercial Banks ü Savings Banks and Credit Unions ü Non-depository Institutions
 Banking ctronic Ele ü An increasing amount of funds move through electronic funds transfer (EFTs). ü Millions of businesses and consumers now pay bills and receive payments electronically. ü Most employees directly deposit employee paychecks. ü Social security and other federal payments are made each year electronically. ü Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) continue to grow in popularity. ü More than 1/3 of American households use some online banking.
Banking ctronic Ele ü An increasing amount of funds move through electronic funds transfer (EFTs). ü Millions of businesses and consumers now pay bills and receive payments electronically. ü Most employees directly deposit employee paychecks. ü Social security and other federal payments are made each year electronically. ü Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) continue to grow in popularity. ü More than 1/3 of American households use some online banking.
 Deposit Federal nsurance I • Enacted by the Banking Act of 1933 • Restore public confidence in the banking system • Before deposit insurance, runs were common as people rushed to withdraw their money from the bank • Deposit insurance shifts the risk of bank failures from individuals to the FDIC
Deposit Federal nsurance I • Enacted by the Banking Act of 1933 • Restore public confidence in the banking system • Before deposit insurance, runs were common as people rushed to withdraw their money from the bank • Deposit insurance shifts the risk of bank failures from individuals to the FDIC
 nks and avings Ba S dit Unions Cre • Offer a variety of consumer services • 85% of their loans are real estate loans • Credit unions are cooperative financial institutions that are owned by depositors/members. • Credit unions are created to serve consumers. – Insured by National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) which functions the same as the FDIC
nks and avings Ba S dit Unions Cre • Offer a variety of consumer services • 85% of their loans are real estate loans • Credit unions are cooperative financial institutions that are owned by depositors/members. • Credit unions are created to serve consumers. – Insured by National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) which functions the same as the FDIC
 epository Non D titutions ancial Ins Fin ü Insurance Companies ü Pension Funds ü Finance Companies
epository Non D titutions ancial Ins Fin ü Insurance Companies ü Pension Funds ü Finance Companies
 Federal ole of the The R Reserve • Created In 1913 • Central bank of the United States • Regulate commercial banks • Perform banking-related activities for the U. S. Department of Treasury • Providing services for banks • Setting monetary policy
Federal ole of the The R Reserve • Created In 1913 • Central bank of the United States • Regulate commercial banks • Perform banking-related activities for the U. S. Department of Treasury • Providing services for banks • Setting monetary policy
 ion of the Organizat l Reserve Federa • 12 Federal reserve districts – Own federal reserve bank • District banks are run by a nine-member board of directors. • The board of governors is the governing body. • Politically independent • Federal Open Markets Committee (FOMC) sets most policies concerning monetary policy and interest rates.
ion of the Organizat l Reserve Federa • 12 Federal reserve districts – Own federal reserve bank • District banks are run by a nine-member board of directors. • The board of governors is the governing body. • Politically independent • Federal Open Markets Committee (FOMC) sets most policies concerning monetary policy and interest rates.
 k Clearing Chec the Fed and • Americans still write billions of paper checks. • The process by which funds are transferred from the check writer to receiver • The multiple-step process is managed and cleared by the FED. • The Check Clearing for the 21 st Century Act is making this process more electronic.
k Clearing Chec the Fed and • Americans still write billions of paper checks. • The process by which funds are transferred from the check writer to receiver • The multiple-step process is managed and cleared by the FED. • The Check Clearing for the 21 st Century Act is making this process more electronic.
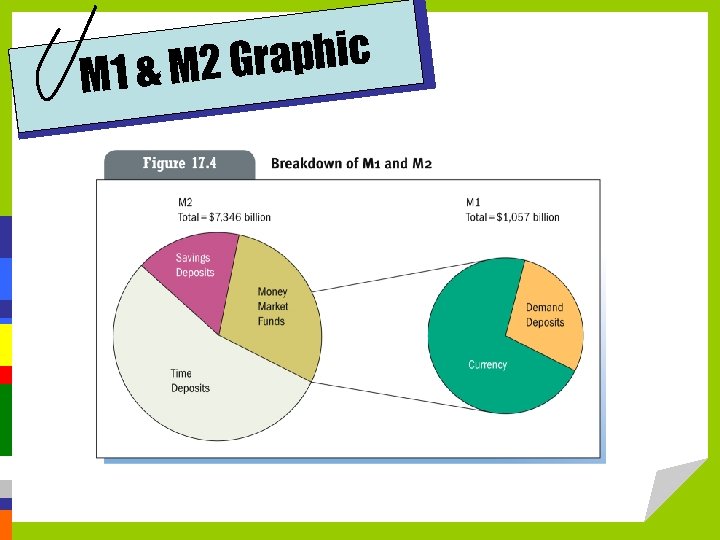
 ry Policy Moneta • Supply of money and credit • Measures of the money supply: M 1 & M 2 • The FED requires banks to maintain reserves. • Set the discount rate • Open Market Operations
ry Policy Moneta • Supply of money and credit • Measures of the money supply: M 1 & M 2 • The FED requires banks to maintain reserves. • Set the discount rate • Open Market Operations
 Graphic M 1 & M 2
Graphic M 1 & M 2
 on of the Regulati ial System Financ • Bank Regulation • Government Regulation of the Financial Markets • Industry Self-Regulation – Rules of conduct by professional organizations like National Association of Securities Dealers – Market Surveillance
on of the Regulati ial System Financ • Bank Regulation • Government Regulation of the Financial Markets • Industry Self-Regulation – Rules of conduct by professional organizations like National Association of Securities Dealers – Market Surveillance
 al System: The Financi erspective Global P A • The financial system is more connected. • Financial institutions are more global. • Only 3 of the 30 largest banks in the world are US institutions. • Most nations have a central bank.
al System: The Financi erspective Global P A • The financial system is more connected. • Financial institutions are more global. • Only 3 of the 30 largest banks in the world are US institutions. • Most nations have a central bank.


