745c06f2c13651fe17ff8b7183dae3a3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Chapter 17: IR to Infectious Disease • In BIOL 304, we examined how pathogens can establish an infection in a susceptible host • Re: the 7 components of pathogenicity!! • On the other hand, humans are defended by: • • • Physical barriers of epithelia and skin Surface chemicals, enzymes, acids Competitive flora Complement and s. Ig Phagocytic cells Specific/Adaptive IR
Chapter 17: IR to Infectious Disease • In BIOL 304, we examined how pathogens can establish an infection in a susceptible host • Re: the 7 components of pathogenicity!! • On the other hand, humans are defended by: • • • Physical barriers of epithelia and skin Surface chemicals, enzymes, acids Competitive flora Complement and s. Ig Phagocytic cells Specific/Adaptive IR
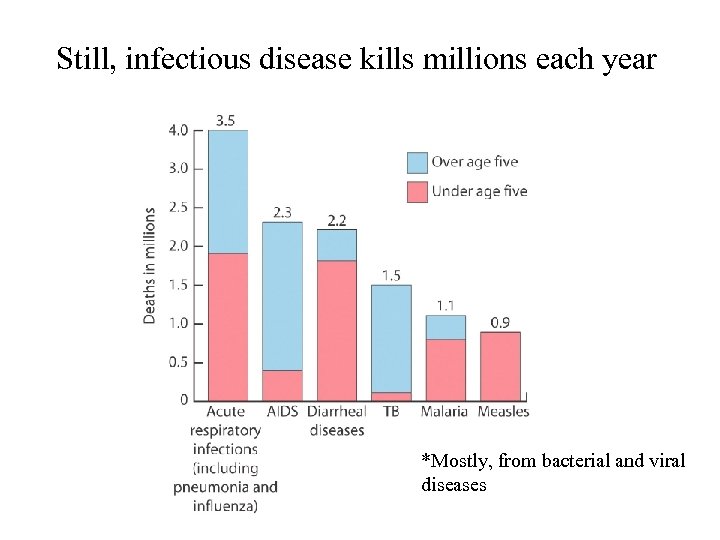 Still, infectious disease kills millions each year *Mostly, from bacterial and viral diseases
Still, infectious disease kills millions each year *Mostly, from bacterial and viral diseases
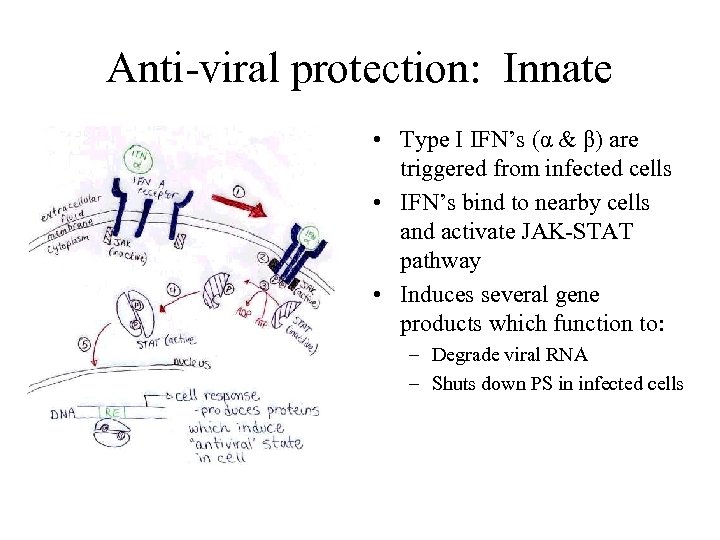 Anti-viral protection: Innate • Type I IFN’s (α & β) are triggered from infected cells • IFN’s bind to nearby cells and activate JAK-STAT pathway • Induces several gene products which function to: – Degrade viral RNA – Shuts down PS in infected cells
Anti-viral protection: Innate • Type I IFN’s (α & β) are triggered from infected cells • IFN’s bind to nearby cells and activate JAK-STAT pathway • Induces several gene products which function to: – Degrade viral RNA – Shuts down PS in infected cells
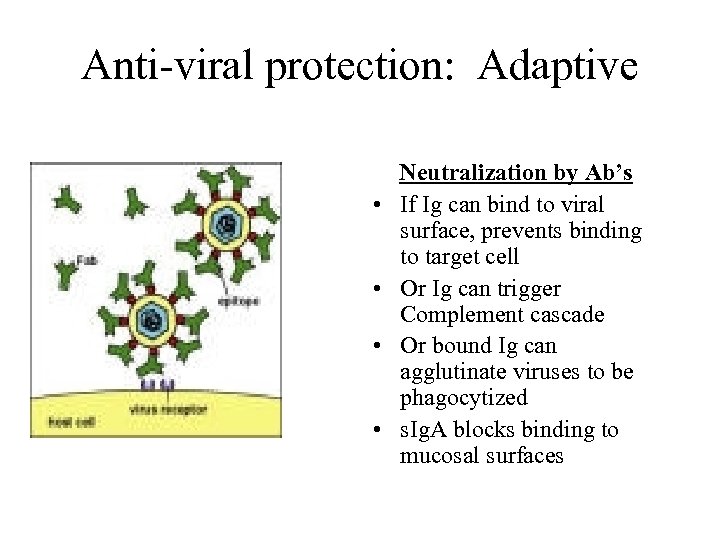 Anti-viral protection: Adaptive • • Neutralization by Ab’s If Ig can bind to viral surface, prevents binding to target cell Or Ig can trigger Complement cascade Or bound Ig can agglutinate viruses to be phagocytized s. Ig. A blocks binding to mucosal surfaces
Anti-viral protection: Adaptive • • Neutralization by Ab’s If Ig can bind to viral surface, prevents binding to target cell Or Ig can trigger Complement cascade Or bound Ig can agglutinate viruses to be phagocytized s. Ig. A blocks binding to mucosal surfaces
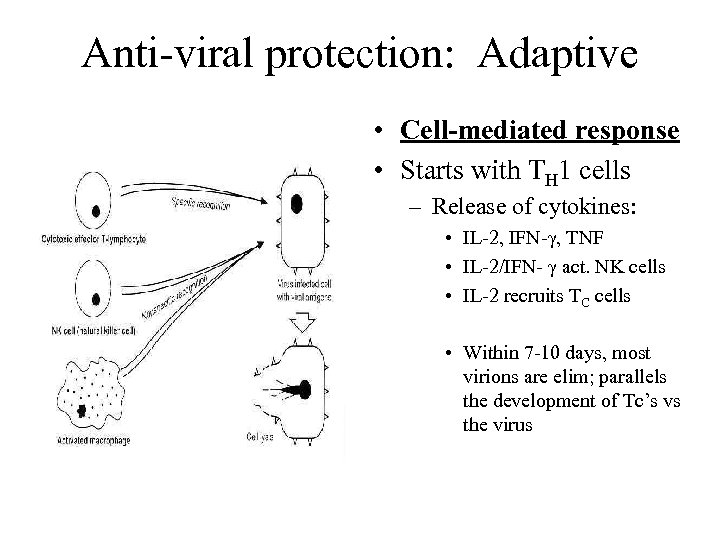 Anti-viral protection: Adaptive • Cell-mediated response • Starts with TH 1 cells – Release of cytokines: • IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF • IL-2/IFN- γ act. NK cells • IL-2 recruits TC cells • Within 7 -10 days, most virions are elim; parallels the development of Tc’s vs the virus
Anti-viral protection: Adaptive • Cell-mediated response • Starts with TH 1 cells – Release of cytokines: • IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF • IL-2/IFN- γ act. NK cells • IL-2 recruits TC cells • Within 7 -10 days, most virions are elim; parallels the development of Tc’s vs the virus
 Evasion of Host defenses • Block intracellular effects of IFN’s (Hep C) • Block TAP function for Ag delivery to MHC I (HSV 1 and 2) prevents lysis by Tc’s • Block formation of MHC I (Adenovirus, CMV) • Block formation of MHC II (CMV, measles, HIV) • Block complement fixation (Vaccinia binds to C 4 b*; HSV binds to C 3 b**) • Antigenic variation (influenza, rhinovirus, HIV) • Imunosuppression thru immune cell infection
Evasion of Host defenses • Block intracellular effects of IFN’s (Hep C) • Block TAP function for Ag delivery to MHC I (HSV 1 and 2) prevents lysis by Tc’s • Block formation of MHC I (Adenovirus, CMV) • Block formation of MHC II (CMV, measles, HIV) • Block complement fixation (Vaccinia binds to C 4 b*; HSV binds to C 3 b**) • Antigenic variation (influenza, rhinovirus, HIV) • Imunosuppression thru immune cell infection
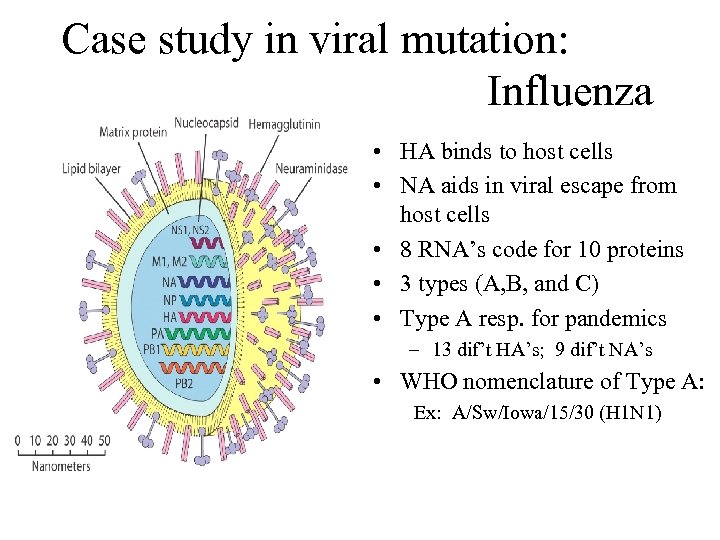 Case study in viral mutation: Influenza • HA binds to host cells • NA aids in viral escape from host cells • 8 RNA’s code for 10 proteins • 3 types (A, B, and C) • Type A resp. for pandemics – 13 dif’t HA’s; 9 dif’t NA’s • WHO nomenclature of Type A: Ex: A/Sw/Iowa/15/30 (H 1 N 1)
Case study in viral mutation: Influenza • HA binds to host cells • NA aids in viral escape from host cells • 8 RNA’s code for 10 proteins • 3 types (A, B, and C) • Type A resp. for pandemics – 13 dif’t HA’s; 9 dif’t NA’s • WHO nomenclature of Type A: Ex: A/Sw/Iowa/15/30 (H 1 N 1)
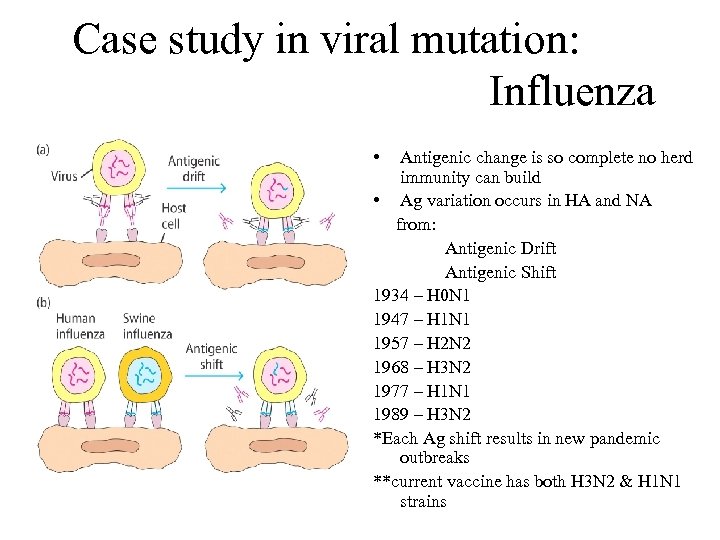 Case study in viral mutation: Influenza • Antigenic change is so complete no herd immunity can build • Ag variation occurs in HA and NA from: Antigenic Drift Antigenic Shift 1934 – H 0 N 1 1947 – H 1 N 1 1957 – H 2 N 2 1968 – H 3 N 2 1977 – H 1 N 1 1989 – H 3 N 2 *Each Ag shift results in new pandemic outbreaks **current vaccine has both H 3 N 2 & H 1 N 1 strains
Case study in viral mutation: Influenza • Antigenic change is so complete no herd immunity can build • Ag variation occurs in HA and NA from: Antigenic Drift Antigenic Shift 1934 – H 0 N 1 1947 – H 1 N 1 1957 – H 2 N 2 1968 – H 3 N 2 1977 – H 1 N 1 1989 – H 3 N 2 *Each Ag shift results in new pandemic outbreaks **current vaccine has both H 3 N 2 & H 1 N 1 strains
 Anti-bacterial protection • Bacterial infections are controlled by different IR’s (just as in viral infections) • The type of IR centers on: • Amount of inoculum • Degree of virulence • Extra- vs intra-cellular infection • MO’s enter mostly through mucosal surfaces (resp/g. i tract/g. u. tract) • Cuts/breaks in skin
Anti-bacterial protection • Bacterial infections are controlled by different IR’s (just as in viral infections) • The type of IR centers on: • Amount of inoculum • Degree of virulence • Extra- vs intra-cellular infection • MO’s enter mostly through mucosal surfaces (resp/g. i tract/g. u. tract) • Cuts/breaks in skin
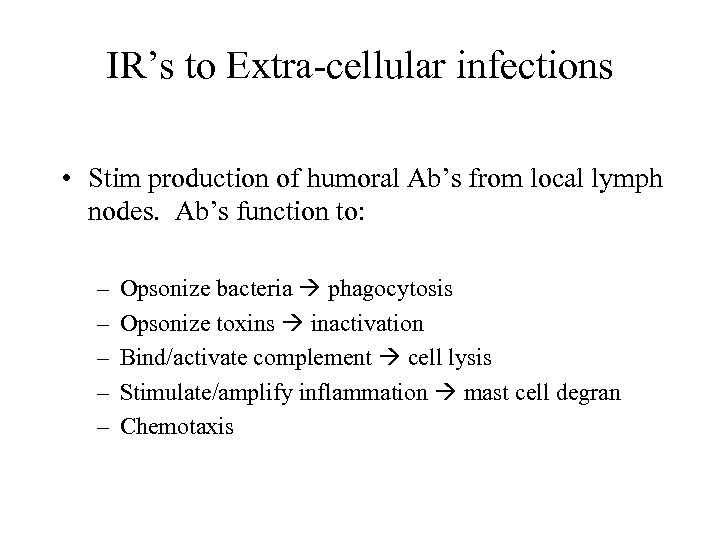 IR’s to Extra-cellular infections • Stim production of humoral Ab’s from local lymph nodes. Ab’s function to: – – – Opsonize bacteria phagocytosis Opsonize toxins inactivation Bind/activate complement cell lysis Stimulate/amplify inflammation mast cell degran Chemotaxis
IR’s to Extra-cellular infections • Stim production of humoral Ab’s from local lymph nodes. Ab’s function to: – – – Opsonize bacteria phagocytosis Opsonize toxins inactivation Bind/activate complement cell lysis Stimulate/amplify inflammation mast cell degran Chemotaxis
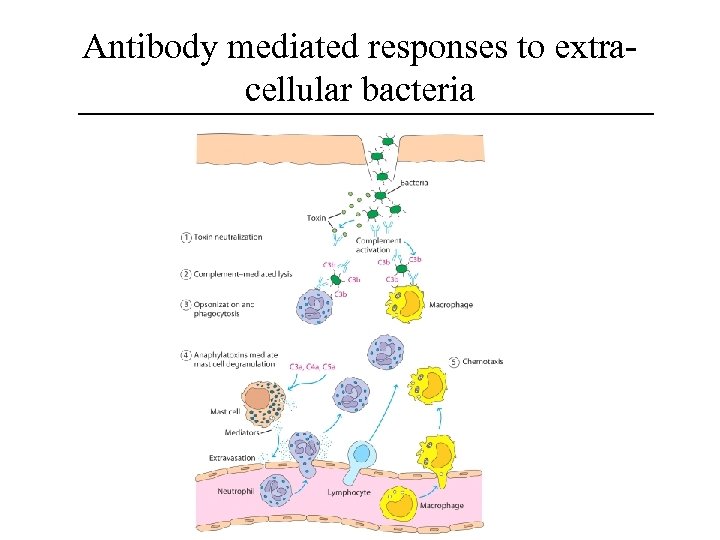 Antibody mediated responses to extracellular bacteria
Antibody mediated responses to extracellular bacteria
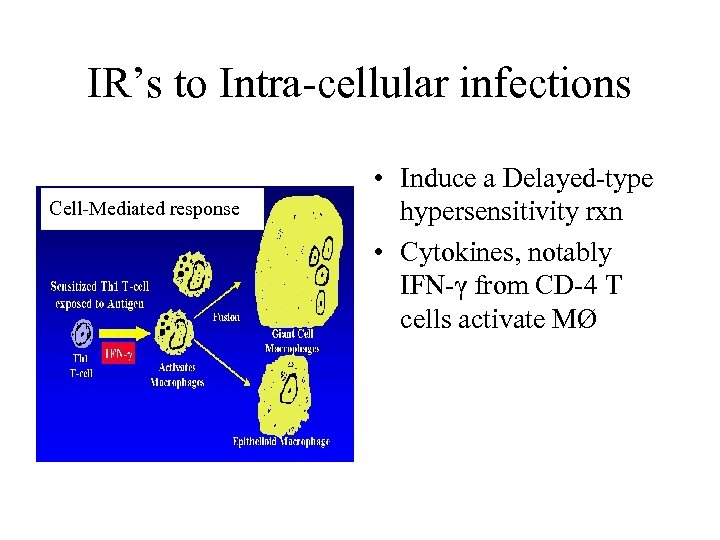 IR’s to Intra-cellular infections Cell-Mediated response • Induce a Delayed-type hypersensitivity rxn • Cytokines, notably IFN-γ from CD-4 T cells activate MØ
IR’s to Intra-cellular infections Cell-Mediated response • Induce a Delayed-type hypersensitivity rxn • Cytokines, notably IFN-γ from CD-4 T cells activate MØ
 Evasion of Host Defenses • Major steps to bacterial infection: – Attachment – Proliferation/growth – Invasion – Toxin-induced damage • Host defenses operate during each one of these steps
Evasion of Host Defenses • Major steps to bacterial infection: – Attachment – Proliferation/growth – Invasion – Toxin-induced damage • Host defenses operate during each one of these steps
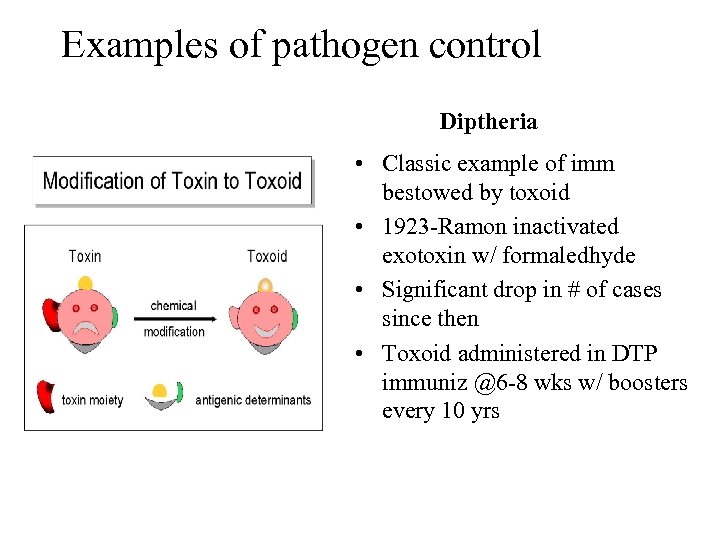 Examples of pathogen control Diptheria • Classic example of imm bestowed by toxoid • 1923 -Ramon inactivated exotoxin w/ formaledhyde • Significant drop in # of cases since then • Toxoid administered in DTP immuniz @6 -8 wks w/ boosters every 10 yrs
Examples of pathogen control Diptheria • Classic example of imm bestowed by toxoid • 1923 -Ramon inactivated exotoxin w/ formaledhyde • Significant drop in # of cases since then • Toxoid administered in DTP immuniz @6 -8 wks w/ boosters every 10 yrs
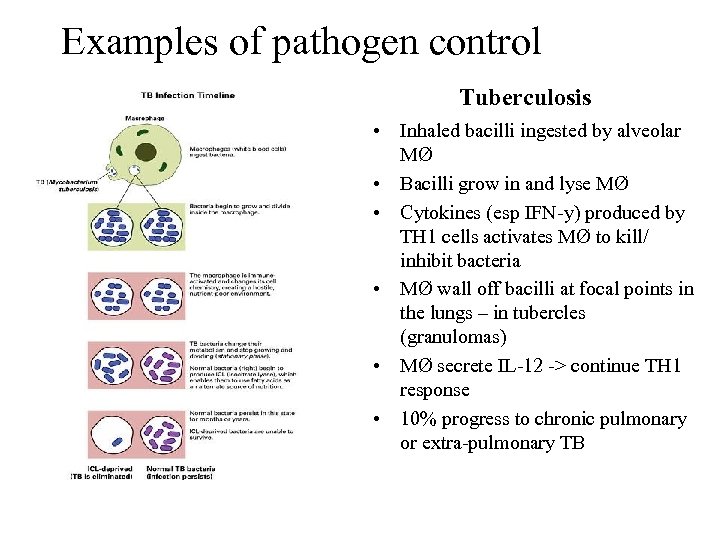 Examples of pathogen control Tuberculosis • Inhaled bacilli ingested by alveolar MØ • Bacilli grow in and lyse MØ • Cytokines (esp IFN-y) produced by TH 1 cells activates MØ to kill/ inhibit bacteria • MØ wall off bacilli at focal points in the lungs – in tubercles (granulomas) • MØ secrete IL-12 -> continue TH 1 response • 10% progress to chronic pulmonary or extra-pulmonary TB
Examples of pathogen control Tuberculosis • Inhaled bacilli ingested by alveolar MØ • Bacilli grow in and lyse MØ • Cytokines (esp IFN-y) produced by TH 1 cells activates MØ to kill/ inhibit bacteria • MØ wall off bacilli at focal points in the lungs – in tubercles (granulomas) • MØ secrete IL-12 -> continue TH 1 response • 10% progress to chronic pulmonary or extra-pulmonary TB
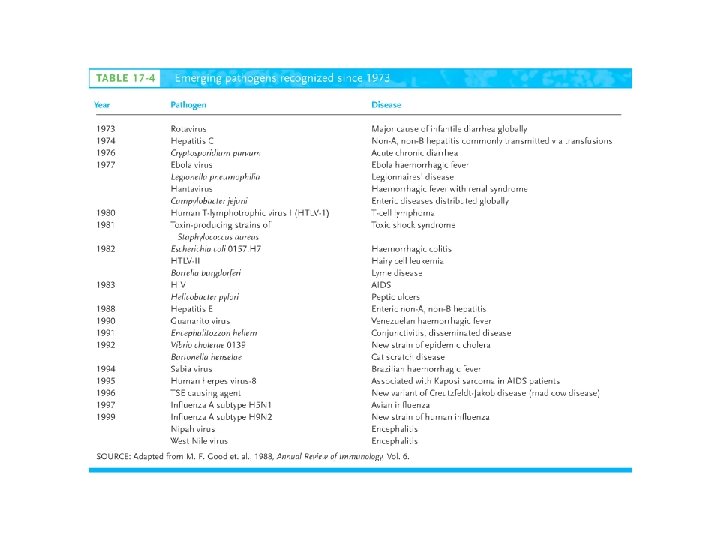
 Emerging Infectious Diseases • Newly described pathogens • Those (which were once under control) showing rapid increases = “re-emerging infectious disease” Ex: TB Diptheria • Causes of emerging/re-emerging diseases: – Overcrowding in cities among lower socioeconomic populations – International travel – Mass distribution of food commodity
Emerging Infectious Diseases • Newly described pathogens • Those (which were once under control) showing rapid increases = “re-emerging infectious disease” Ex: TB Diptheria • Causes of emerging/re-emerging diseases: – Overcrowding in cities among lower socioeconomic populations – International travel – Mass distribution of food commodity