ac765501c518034bebb169f3ce56eb5e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 CHAPTER 16 Neural Computing Applications, and Advanced Artificial Intelligent Systems and Applications 1
CHAPTER 16 Neural Computing Applications, and Advanced Artificial Intelligent Systems and Applications 1
 Neural Computing Applications, and Advanced Artificial Intelligent Systems and Applications n n Several Real-World Applications of ANN Technology Advanced AI Systems – Genetic Algorithms – Fuzzy Logic – Qualitative Reasoning n Integration (Hybrids) 2 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Neural Computing Applications, and Advanced Artificial Intelligent Systems and Applications n n Several Real-World Applications of ANN Technology Advanced AI Systems – Genetic Algorithms – Fuzzy Logic – Qualitative Reasoning n Integration (Hybrids) 2 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Areas of ANN Applications: An Overview Representative Business ANN Applications n n n Accounting Finance Human Resources Management Marketing Operations 3 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Areas of ANN Applications: An Overview Representative Business ANN Applications n n n Accounting Finance Human Resources Management Marketing Operations 3 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Credit Approval with Neural Networks n Increases loan processor productivity by 25 to 35 % over other computerized tools n Also detects credit card fraud 4 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Credit Approval with Neural Networks n Increases loan processor productivity by 25 to 35 % over other computerized tools n Also detects credit card fraud 4 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 The ANN Method n Data from the application and into a database n Preprocess applications manually n Neural network trained in advance with many good and bad risk cases 5 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
The ANN Method n Data from the application and into a database n Preprocess applications manually n Neural network trained in advance with many good and bad risk cases 5 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Neural Network Credit Authorizer Construction Process n Step 1: Collect data n Step 2: Separate data into training and test sets n Step 3: Transform data into network inputs n Step 4: Select, train, and test network n Step 5: Deploy developed network application 6 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Neural Network Credit Authorizer Construction Process n Step 1: Collect data n Step 2: Separate data into training and test sets n Step 3: Transform data into network inputs n Step 4: Select, train, and test network n Step 5: Deploy developed network application 6 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Bankruptcy Prediction with Neural Networks Concept Phase n Paradigm: Three-layer network, back-propagation n Training data: Small set of well-known financial ratios n Data available on bankruptcy outcomes n Supervised network n Training time not to be a problem 7 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Bankruptcy Prediction with Neural Networks Concept Phase n Paradigm: Three-layer network, back-propagation n Training data: Small set of well-known financial ratios n Data available on bankruptcy outcomes n Supervised network n Training time not to be a problem 7 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
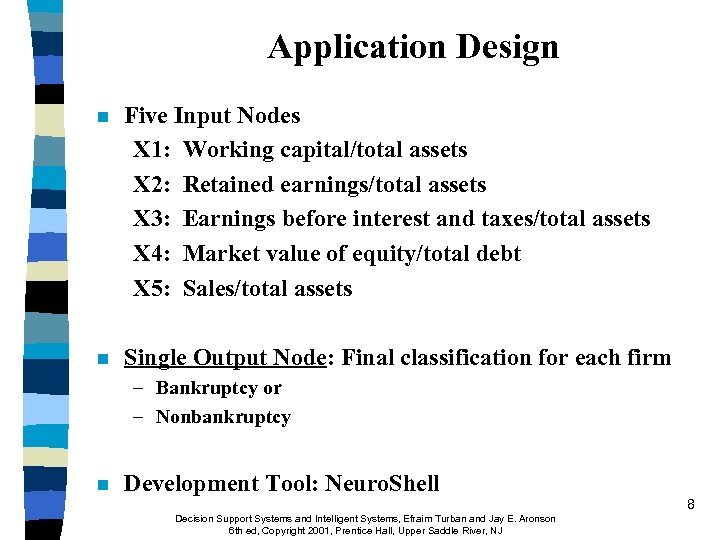 Application Design n Five Input Nodes X 1: Working capital/total assets X 2: Retained earnings/total assets X 3: Earnings before interest and taxes/total assets X 4: Market value of equity/total debt X 5: Sales/total assets n Single Output Node: Final classification for each firm – Bankruptcy or – Nonbankruptcy n Development Tool: Neuro. Shell Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ 8
Application Design n Five Input Nodes X 1: Working capital/total assets X 2: Retained earnings/total assets X 3: Earnings before interest and taxes/total assets X 4: Market value of equity/total debt X 5: Sales/total assets n Single Output Node: Final classification for each firm – Bankruptcy or – Nonbankruptcy n Development Tool: Neuro. Shell Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ 8
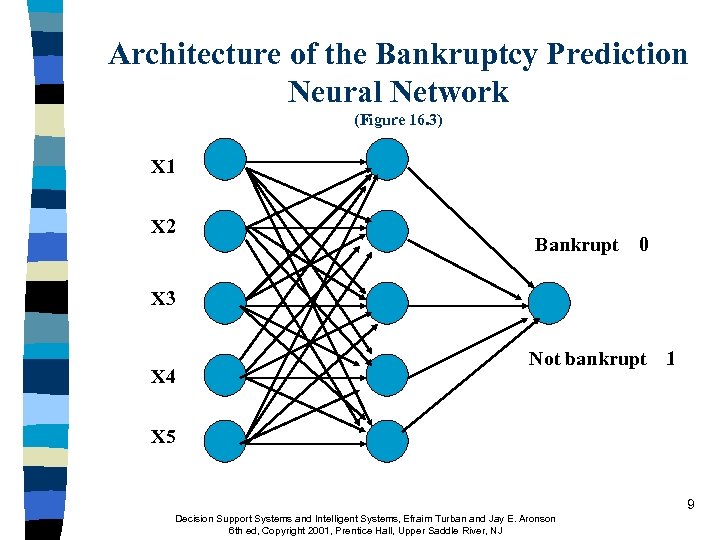 Architecture of the Bankruptcy Prediction Neural Network (Figure 16. 3) X 1 X 2 Bankrupt 0 X 3 X 4 Not bankrupt 1 X 5 9 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Architecture of the Bankruptcy Prediction Neural Network (Figure 16. 3) X 1 X 2 Bankrupt 0 X 3 X 4 Not bankrupt 1 X 5 9 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 n ANN did better predicting 22 out of the 27 actual cases n Discriminant analysis predicted only 16 correctly n Error Analysis – Five bankrupt firms misclassified by both methods – Similar for nonbankrupt firms n Neural network at least as good as conventional n Accuracy of about 80 percent is usually acceptable for neural network applications 10 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
n ANN did better predicting 22 out of the 27 actual cases n Discriminant analysis predicted only 16 correctly n Error Analysis – Five bankrupt firms misclassified by both methods – Similar for nonbankrupt firms n Neural network at least as good as conventional n Accuracy of about 80 percent is usually acceptable for neural network applications 10 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Stock Market Prediction System with Modular Neural Networks n Accurate Stock Market Prediction - Complex Problem n Several Mathematical Models - Disappointing Results n Fujitsu and Nikko Securities: TOPIX Buying and Selling Prediction System 11 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Stock Market Prediction System with Modular Neural Networks n Accurate Stock Market Prediction - Complex Problem n Several Mathematical Models - Disappointing Results n Fujitsu and Nikko Securities: TOPIX Buying and Selling Prediction System 11 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 n Input: Several technical and economic indexes n Several modular neural networks relate past indexes, and buy/sell timing n Prediction system – Modular neural networks – Very accurate 12 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
n Input: Several technical and economic indexes n Several modular neural networks relate past indexes, and buy/sell timing n Prediction system – Modular neural networks – Very accurate 12 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Integrated ANNs and Expert Systems 1. Resource Requirements Advisor 2. Personnel Resource Requirements Advisor 3. Diagnostic System for an Airline 4. Manufacturing Product Liability 5. Oil Refinery Production Scheduling and Environmental Control 13 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Integrated ANNs and Expert Systems 1. Resource Requirements Advisor 2. Personnel Resource Requirements Advisor 3. Diagnostic System for an Airline 4. Manufacturing Product Liability 5. Oil Refinery Production Scheduling and Environmental Control 13 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Genetic Algorithms n n n Goal (evolutionary algorithms): Demonstrate selforganization and adaptation by exposure to the environment System learns to adapt to changes. Example 1: Vector Game – Random trial and error – Genetic algorithm solution n n Process (Figure 16. 9) Example: the game of Master. Mind 14 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Genetic Algorithms n n n Goal (evolutionary algorithms): Demonstrate selforganization and adaptation by exposure to the environment System learns to adapt to changes. Example 1: Vector Game – Random trial and error – Genetic algorithm solution n n Process (Figure 16. 9) Example: the game of Master. Mind 14 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Genetic Algorithm Definition and Process Genetic algorithm: "an iterative procedure maintaining a population of structures that are candidate solutions to specific domain challenges” (Grefenstette, 1982) n Each candidate solution is called a chromosome n Chromosomes can copy themselves, mate, and mutate n Use specific genetic operators - reproduction, crossover and mutation 15 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Genetic Algorithm Definition and Process Genetic algorithm: "an iterative procedure maintaining a population of structures that are candidate solutions to specific domain challenges” (Grefenstette, 1982) n Each candidate solution is called a chromosome n Chromosomes can copy themselves, mate, and mutate n Use specific genetic operators - reproduction, crossover and mutation 15 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Primary Operators of Most Genetic Algorithms n Reproduction n Crossover n Mutation 16 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Primary Operators of Most Genetic Algorithms n Reproduction n Crossover n Mutation 16 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
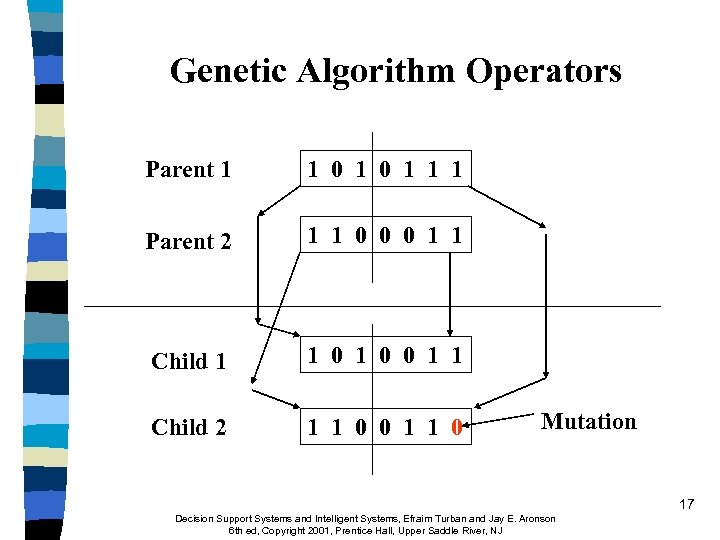 Genetic Algorithm Operators Parent 1 1 0 1 1 1 Parent 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 Child 1 1 0 0 1 1 Child 2 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 Mutation 17 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Genetic Algorithm Operators Parent 1 1 0 1 1 1 Parent 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 Child 1 1 0 0 1 1 Child 2 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 Mutation 17 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 GA Example: The Knapsack Problem n n n n n Item: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Benefit: 5 8 3 2 7 9 4 Weight: 7 8 4 10 4 6 4 Knapsack holds a maximum of 22 pounds Fill it to get the maximum benefit Solutions take the form of a string of 1’s Solution: 1 1 0 0 Means choose items 1, 2, 5. Weight = 21, Benefit = 20 Evolver solution in Figure 16. 10 18 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
GA Example: The Knapsack Problem n n n n n Item: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Benefit: 5 8 3 2 7 9 4 Weight: 7 8 4 10 4 6 4 Knapsack holds a maximum of 22 pounds Fill it to get the maximum benefit Solutions take the form of a string of 1’s Solution: 1 1 0 0 Means choose items 1, 2, 5. Weight = 21, Benefit = 20 Evolver solution in Figure 16. 10 18 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Genetic Algorithm Application Areas n n n Dynamic process control Induction of rule optimization Discovering new connectivity topologies Simulating biological models of behavior and evolution Complex design of engineering structures Pattern recognition Scheduling Transportation Layout and circuit design Telecommunication Graph-based problems 19 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Genetic Algorithm Application Areas n n n Dynamic process control Induction of rule optimization Discovering new connectivity topologies Simulating biological models of behavior and evolution Complex design of engineering structures Pattern recognition Scheduling Transportation Layout and circuit design Telecommunication Graph-based problems 19 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Business Applications n Channel 4 Television (England) to schedule commercials Driver scheduling in a public transportation system Jobshop scheduling Assignment of destinations to sources Trading stocks Productivity in whisky making is increased n Often genetic algorithm hybrids with other AI methods n n n 20 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Business Applications n Channel 4 Television (England) to schedule commercials Driver scheduling in a public transportation system Jobshop scheduling Assignment of destinations to sources Trading stocks Productivity in whisky making is increased n Often genetic algorithm hybrids with other AI methods n n n 20 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Representative Commercial Packages n n n Evolver (Excel spreadsheet add-in) Genetic Algorithm User Interface (GAUI) OOGA (Object-Oriented GA for industrial use) Xper. Rule Genasys (ES shell with an embedded genetic algorithm) Sugal Genetic Algorithm Simulator 21 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Representative Commercial Packages n n n Evolver (Excel spreadsheet add-in) Genetic Algorithm User Interface (GAUI) OOGA (Object-Oriented GA for industrial use) Xper. Rule Genasys (ES shell with an embedded genetic algorithm) Sugal Genetic Algorithm Simulator 21 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Fuzzy Logic n Fuzzy logic deals with uncertainty n Uses the mathematical theory of fuzzy sets n Simulates the process of normal human reasoning n Allows the computer to behave less precisely and logically Decision making involves gray areas and the term maybe 22 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Fuzzy Logic n Fuzzy logic deals with uncertainty n Uses the mathematical theory of fuzzy sets n Simulates the process of normal human reasoning n Allows the computer to behave less precisely and logically Decision making involves gray areas and the term maybe 22 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
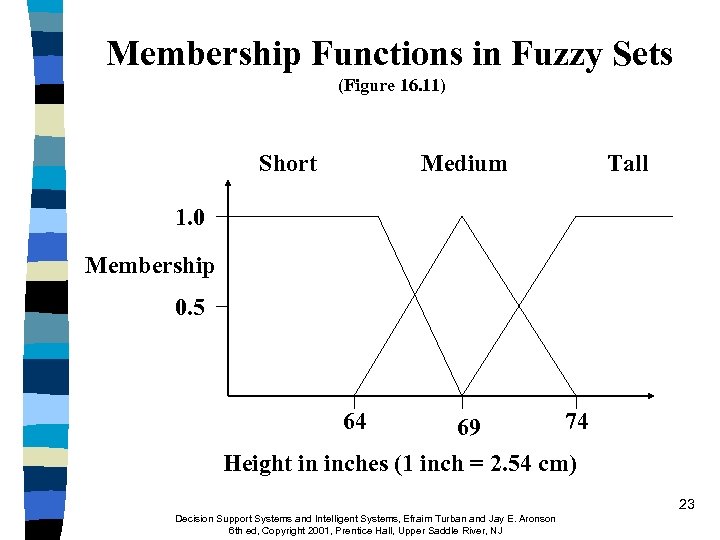 Membership Functions in Fuzzy Sets (Figure 16. 11) Short Medium Tall 1. 0 Membership 0. 5 64 74 69 Height in inches (1 inch = 2. 54 cm) 23 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Membership Functions in Fuzzy Sets (Figure 16. 11) Short Medium Tall 1. 0 Membership 0. 5 64 74 69 Height in inches (1 inch = 2. 54 cm) 23 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Fuzzy Logic Applications and Software n Difficult to apply when people provide evidence n Used in consumer products that have sensors – – – Air conditioners Cameras Dishwashers Microwaves Toasters n Special software packages n Controls applications Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ 24
Fuzzy Logic Applications and Software n Difficult to apply when people provide evidence n Used in consumer products that have sensors – – – Air conditioners Cameras Dishwashers Microwaves Toasters n Special software packages n Controls applications Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ 24
 Examples of Fuzzy Logic Example 1: Strategic planning – STRATASSIST - fuzzy expert system that helps small- to medium-sized firms plan strategically for a single product Example 2: Fuzziness in real estate Example 3: A fuzzy bond evaluation system 25 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Examples of Fuzzy Logic Example 1: Strategic planning – STRATASSIST - fuzzy expert system that helps small- to medium-sized firms plan strategically for a single product Example 2: Fuzziness in real estate Example 3: A fuzzy bond evaluation system 25 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Fuzzy Logic Software n n Fuzzy Inference Development Environment (FIDE) Z Search Hyper. Logic Corporation demos Others 26 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Fuzzy Logic Software n n Fuzzy Inference Development Environment (FIDE) Z Search Hyper. Logic Corporation demos Others 26 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Qualitative Reasoning (QR) – Means of representing and making inferences using general, physical knowledge about the world – QR is a model-based procedure that consequently incorporates deep knowledge about a problem domain – Typical QR Logic • “If you touch a kettle full of boiling water on a stove, you will burn yourself” • “If you throw an object off a building, it will go down” 27 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Qualitative Reasoning (QR) – Means of representing and making inferences using general, physical knowledge about the world – QR is a model-based procedure that consequently incorporates deep knowledge about a problem domain – Typical QR Logic • “If you touch a kettle full of boiling water on a stove, you will burn yourself” • “If you throw an object off a building, it will go down” 27 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 n But n No specific knowledge about boiling temperature, just that it is really hot! n No specific information about the building or object, unless you are the object, or you are trying to catch it 28 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
n But n No specific knowledge about boiling temperature, just that it is really hot! n No specific information about the building or object, unless you are the object, or you are trying to catch it 28 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Some Real-World QR Applications n Nuclear plant fault diagnoses n Business processes n Financial markets n Economic systems 29 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Some Real-World QR Applications n Nuclear plant fault diagnoses n Business processes n Financial markets n Economic systems 29 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Intelligent Systems Integration n Combine – – n n Neural Computing Expert Systems Genetic Algorithms Fuzzy Logic Example: International investment management-stock selection Fuzzy Logic and ANN (Fuzzy. Net) to forecast the expected returns from stocks, cash, bonds, and other assets to determine the optimal allocation of assets 30 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Intelligent Systems Integration n Combine – – n n Neural Computing Expert Systems Genetic Algorithms Fuzzy Logic Example: International investment management-stock selection Fuzzy Logic and ANN (Fuzzy. Net) to forecast the expected returns from stocks, cash, bonds, and other assets to determine the optimal allocation of assets 30 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
 Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) n n Hidden value in data Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) 31 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) n n Hidden value in data Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) 31 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Efraim Turban and Jay E. Aronson 6 th ed, Copyright 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ


