d99641b4b2b476d69a84e865d0ab1094.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Chapter 16: Multiagent Systems Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents – Munindar P. Singh and Michael N. Huhns, Wiley, 2005
Chapter 16: Multiagent Systems Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents – Munindar P. Singh and Michael N. Huhns, Wiley, 2005
 Highlights of this Chapter n n n n Chapter 16 Applicability in Service-Based Systems Multiagent Architecture Agent Types Lifecycle Management Consistency Maintenance Modeling Other Agents Cognitive Concepts Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 2
Highlights of this Chapter n n n n Chapter 16 Applicability in Service-Based Systems Multiagent Architecture Agent Types Lifecycle Management Consistency Maintenance Modeling Other Agents Cognitive Concepts Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 2
 Basic Problems of MAS n Distributing control among agents n n Describing, decomposing, distributing tasks Interacting and communicating Representing goals, problem-solving states, and other agents Maintaining consistency, reconciling conflicts Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 3
Basic Problems of MAS n Distributing control among agents n n Describing, decomposing, distributing tasks Interacting and communicating Representing goals, problem-solving states, and other agents Maintaining consistency, reconciling conflicts Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 3
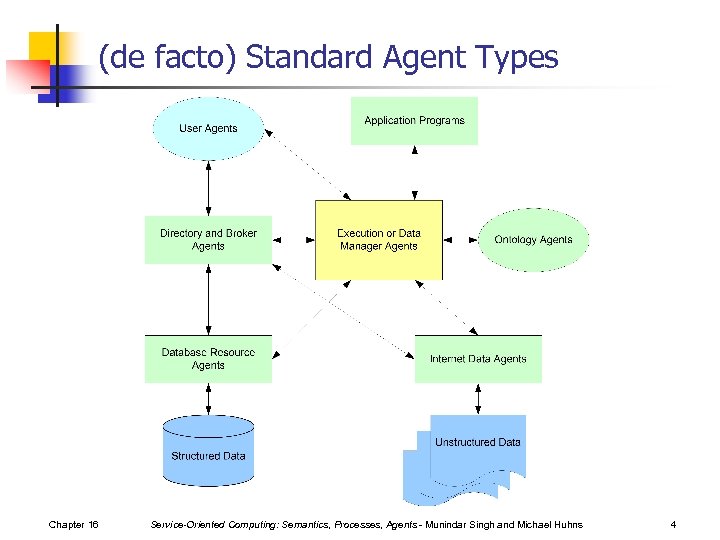 (de facto) Standard Agent Types Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 4
(de facto) Standard Agent Types Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 4
 Brokerage Service n n n Cooperates with a Directory Service Accepts requests from agents to recruit one or more agents who can provide a service Uses knowledge about the requirements and capabilities of registered agents to n n n Identify appropriate agents for an interaction Negotiate with selected agents Potentially learn about the properties of the responses n Chapter 16 Example: Brokerage determines that advertised results from agent X are incomplete and seeks a substitute for X Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 5
Brokerage Service n n n Cooperates with a Directory Service Accepts requests from agents to recruit one or more agents who can provide a service Uses knowledge about the requirements and capabilities of registered agents to n n n Identify appropriate agents for an interaction Negotiate with selected agents Potentially learn about the properties of the responses n Chapter 16 Example: Brokerage determines that advertised results from agent X are incomplete and seeks a substitute for X Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 5
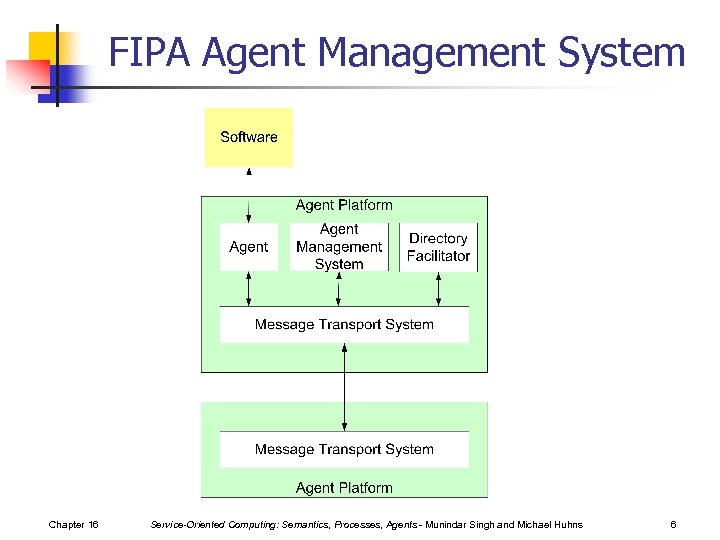 FIPA Agent Management System Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 6
FIPA Agent Management System Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 6
 Agent Management System: 2 n Handles the creation, registration, location, communication, migration, and retirement of agents n White pages, e. g. , agent location and naming (from AMS) n n n Chapter 16 Agent identifiers support social names, transport addresses, name resolution services Yellow pages, e. g. , service location and registration services (from DF) Agent message transport services Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 7
Agent Management System: 2 n Handles the creation, registration, location, communication, migration, and retirement of agents n White pages, e. g. , agent location and naming (from AMS) n n n Chapter 16 Agent identifiers support social names, transport addresses, name resolution services Yellow pages, e. g. , service location and registration services (from DF) Agent message transport services Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 7
 Java Agent Development Framework JADE, a popular FIPA-compliant agent framework for multiagent systems: n n Chapter 16 http: //jade. tilab. com/ (FIPA-OS and Zeus having died) Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 8
Java Agent Development Framework JADE, a popular FIPA-compliant agent framework for multiagent systems: n n Chapter 16 http: //jade. tilab. com/ (FIPA-OS and Zeus having died) Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 8
 Consistency Maintenance across Services A truth maintenance system (TMS) helps maintain consistency n Performs a form of propositional deduction n Maintains justifications and explains the results of its deductions n Updates beliefs incrementally when premises change TMSs help us n Deal with atomicity n Maintain modular models Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 9
Consistency Maintenance across Services A truth maintenance system (TMS) helps maintain consistency n Performs a form of propositional deduction n Maintains justifications and explains the results of its deductions n Updates beliefs incrementally when premises change TMSs help us n Deal with atomicity n Maintain modular models Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 9
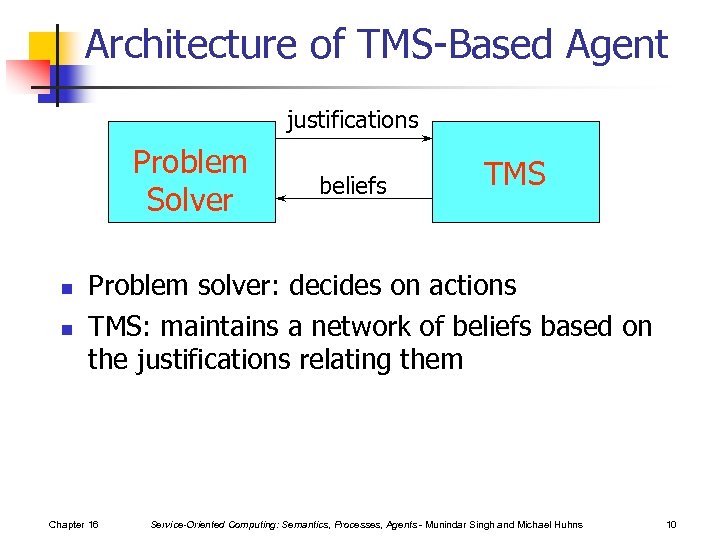 Architecture of TMS-Based Agent justifications Problem Solver n n beliefs TMS Problem solver: decides on actions TMS: maintains a network of beliefs based on the justifications relating them Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 10
Architecture of TMS-Based Agent justifications Problem Solver n n beliefs TMS Problem solver: decides on actions TMS: maintains a network of beliefs based on the justifications relating them Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 10
 Knowledge Base Integrity n Stability: believe everything justified validly; disbelieve everything else n Well-Foundedness: no circular beliefs n Logical consistency: no logical contradictions n Completeness: find a consistent state if one exists, or report failure Problems arise when knowledge is distributed Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 11
Knowledge Base Integrity n Stability: believe everything justified validly; disbelieve everything else n Well-Foundedness: no circular beliefs n Logical consistency: no logical contradictions n Completeness: find a consistent state if one exists, or report failure Problems arise when knowledge is distributed Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 11
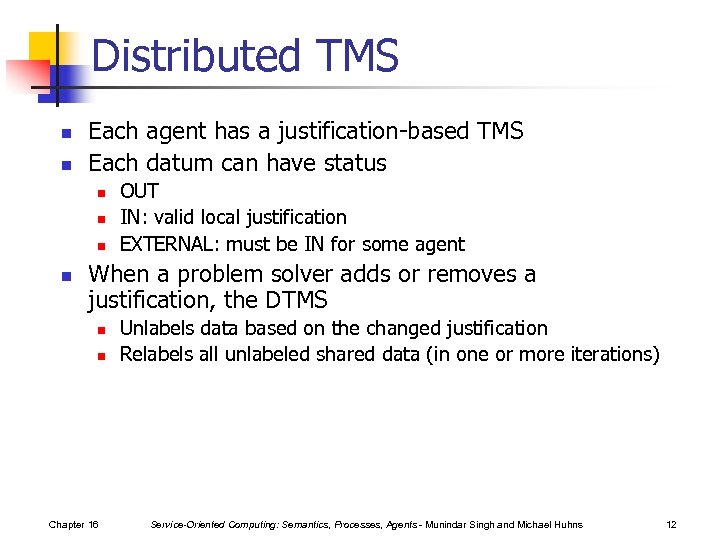 Distributed TMS n n Each agent has a justification-based TMS Each datum can have status n n OUT IN: valid local justification EXTERNAL: must be IN for some agent When a problem solver adds or removes a justification, the DTMS n n Chapter 16 Unlabels data based on the changed justification Relabels all unlabeled shared data (in one or more iterations) Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 12
Distributed TMS n n Each agent has a justification-based TMS Each datum can have status n n OUT IN: valid local justification EXTERNAL: must be IN for some agent When a problem solver adds or removes a justification, the DTMS n n Chapter 16 Unlabels data based on the changed justification Relabels all unlabeled shared data (in one or more iterations) Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 12
 Degrees of Logical Consistency n Inconsistency: some agent is individually n Local Consistency: all agents are individually n Local-and-Shared Consistency: agents are inconsistent locally consistent and agree about any data they might share n Global Consistency: agents are globally consistent (union of KBs is consistent) The DTMS maintains local-and-shared consistency and well-foundedness Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 13
Degrees of Logical Consistency n Inconsistency: some agent is individually n Local Consistency: all agents are individually n Local-and-Shared Consistency: agents are inconsistent locally consistent and agree about any data they might share n Global Consistency: agents are globally consistent (union of KBs is consistent) The DTMS maintains local-and-shared consistency and well-foundedness Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 13
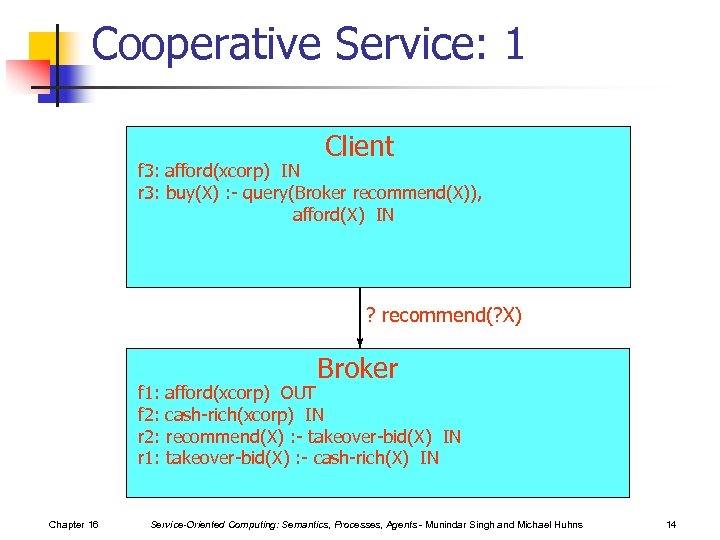 Cooperative Service: 1 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN ? recommend(? X) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) IN r 2: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 1: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 14
Cooperative Service: 1 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN ? recommend(? X) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) IN r 2: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 1: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 14
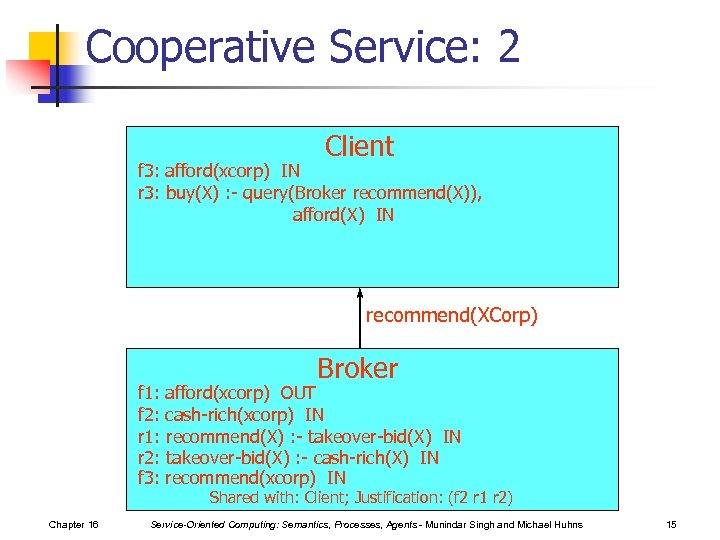 Cooperative Service: 2 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN recommend(XCorp) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) IN r 1: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 2: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN f 3: recommend(xcorp) IN Shared with: Client; Justification: (f 2 r 1 r 2) Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 15
Cooperative Service: 2 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN recommend(XCorp) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) IN r 1: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 2: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN f 3: recommend(xcorp) IN Shared with: Client; Justification: (f 2 r 1 r 2) Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 15
 Cooperative Service: 3 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN f 4: recommend(xcorp) EXTERNAL Shared with: Broker; Justification: ( ) f 5: buy(xcorp) IN Justification: (f 3 f 4 r 3) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) IN r 1: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 2: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN f 3: recommend(xcorp) IN Shared with: Client; Justification: (f 2 r 1 r 2) Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 16
Cooperative Service: 3 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN f 4: recommend(xcorp) EXTERNAL Shared with: Broker; Justification: ( ) f 5: buy(xcorp) IN Justification: (f 3 f 4 r 3) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) IN r 1: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 2: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN f 3: recommend(xcorp) IN Shared with: Client; Justification: (f 2 r 1 r 2) Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 16
 Cooperative Service: 4 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN f 4: recommend(xcorp) EXTERNAL Shared with: Broker; Justification: ( ) f 5: buy(xcorp) IN Justification: (f 3 f 4 r 3) relabel recommend(XCorp) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) IN --> OUT r 1: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 2: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN f 3: recommend(xcorp) IN --> OUT Shared with: Client; Justification: (f 2 r 1 r 2) Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 17
Cooperative Service: 4 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN f 4: recommend(xcorp) EXTERNAL Shared with: Broker; Justification: ( ) f 5: buy(xcorp) IN Justification: (f 3 f 4 r 3) relabel recommend(XCorp) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) IN --> OUT r 1: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 2: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN f 3: recommend(xcorp) IN --> OUT Shared with: Client; Justification: (f 2 r 1 r 2) Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 17
 Cooperative Service: 5 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN f 4: recommend(xcorp) OUT Shared with: Broker; Justification: ( ) f 5: buy(xcorp) OUT Justification: (f 3 f 4 r 3) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) OUT r 1: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 2: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN f 3: recommend(xcorp) OUT Shared with: Client; Justification: (f 2 r 1 r 2) Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 18
Cooperative Service: 5 Client f 3: afford(xcorp) IN r 3: buy(X) : - query(Broker recommend(X)), afford(X) IN f 4: recommend(xcorp) OUT Shared with: Broker; Justification: ( ) f 5: buy(xcorp) OUT Justification: (f 3 f 4 r 3) Broker f 1: afford(xcorp) OUT f 2: cash-rich(xcorp) OUT r 1: recommend(X) : - takeover-bid(X) IN r 2: takeover-bid(X) : - cash-rich(X) IN f 3: recommend(xcorp) OUT Shared with: Client; Justification: (f 2 r 1 r 2) Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 18
 Chapter 16 Summary Study multiagent systems because interactions among agents make them interesting n Communication among agents is key, although markets (later chapter) only support implicit communication through prices n Programming environments support agent interactions n Consistency maintenance is a major challenge n Agents must model agents; simple techniques are often adequate; more subtle techniques can require extensive reasoning power Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 19
Chapter 16 Summary Study multiagent systems because interactions among agents make them interesting n Communication among agents is key, although markets (later chapter) only support implicit communication through prices n Programming environments support agent interactions n Consistency maintenance is a major challenge n Agents must model agents; simple techniques are often adequate; more subtle techniques can require extensive reasoning power Chapter 16 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 19


