f40d3f6113cd3191e23b26a82ff74c74.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Chapter 16 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management 1
Chapter 16 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management 1
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Learning Objectives 1 • Identify management tools for competitiveness 2 • Identify the complexity of international logistics 3 • Identify the importance of international inventory management 4 • Identify materials management and physical distribution concepts 5 • Demonstrate how the infrastructure determines management’s options 2
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Learning Objectives 1 • Identify management tools for competitiveness 2 • Identify the complexity of international logistics 3 • Identify the importance of international inventory management 4 • Identify materials management and physical distribution concepts 5 • Demonstrate how the infrastructure determines management’s options 2
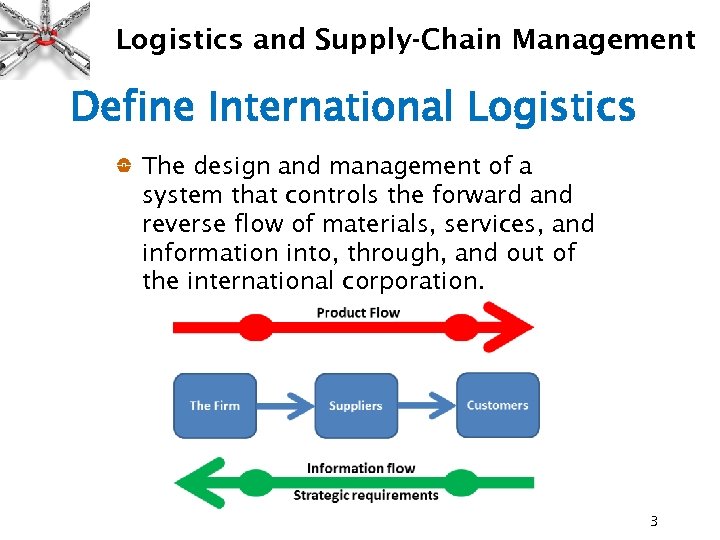 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Define International Logistics The design and management of a system that controls the forward and reverse flow of materials, services, and information into, through, and out of the international corporation. 3
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Define International Logistics The design and management of a system that controls the forward and reverse flow of materials, services, and information into, through, and out of the international corporation. 3
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management International Logistics Through the implementation of international logistics, the firm can implement cost-saving programs such as just-in-time (JIT), electronic data interchange (EDI), and early supplier involvement (ESI). The two phases of the movement of materials include: materials management, or the timely movement of materials, parts, and supplies. physical distribution, or the movement of the firm’s physical product to its customers. 4
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management International Logistics Through the implementation of international logistics, the firm can implement cost-saving programs such as just-in-time (JIT), electronic data interchange (EDI), and early supplier involvement (ESI). The two phases of the movement of materials include: materials management, or the timely movement of materials, parts, and supplies. physical distribution, or the movement of the firm’s physical product to its customers. 4
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Concepts of Business Logistics 1 • Total Cost Concept 2 • Systems Concept 3 • Trade-off Concept 5
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Concepts of Business Logistics 1 • Total Cost Concept 2 • Systems Concept 3 • Trade-off Concept 5
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management The integration of business processes from end user through original suppliers, that provide products, services, and information that add value for customers. Supply-chain management connects a company’s supply side with its demand side. It opens up supplier relationships for companies outside of the buyer’s domestic market. 6
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management The integration of business processes from end user through original suppliers, that provide products, services, and information that add value for customers. Supply-chain management connects a company’s supply side with its demand side. It opens up supplier relationships for companies outside of the buyer’s domestic market. 6
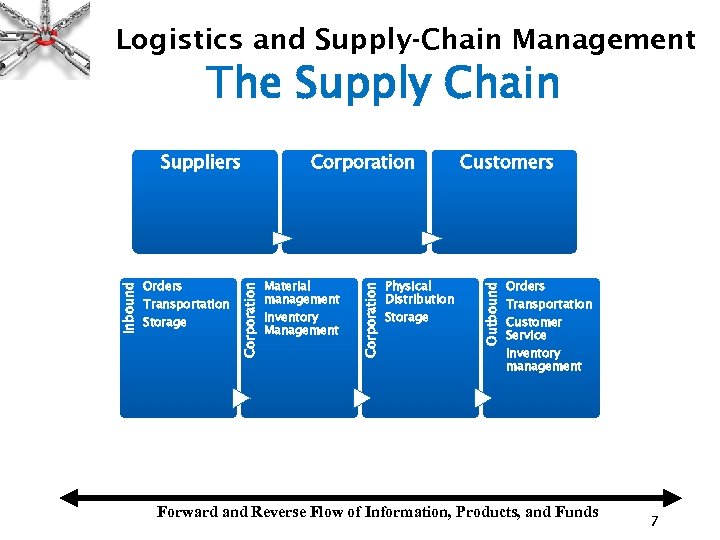 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management The Supply Chain Material management Inventory Management Physical Distribution Storage Customers Outbound Transportation Storage Corporation Orders Corporation Inbound Suppliers Orders Transportation Customer Service Inventory management Forward and Reverse Flow of Information, Products, and Funds 7
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management The Supply Chain Material management Inventory Management Physical Distribution Storage Customers Outbound Transportation Storage Corporation Orders Corporation Inbound Suppliers Orders Transportation Customer Service Inventory management Forward and Reverse Flow of Information, Products, and Funds 7
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Transportation Infrastructure 1 • Determined by a location’s ease and convenience of market reach 2 • Determined by the public sector’s investment 3 • Determined by the manager’s knowledge of existing and planned infrastructure 8
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Transportation Infrastructure 1 • Determined by a location’s ease and convenience of market reach 2 • Determined by the public sector’s investment 3 • Determined by the manager’s knowledge of existing and planned infrastructure 8
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Ocean Shipping options Bulk Service Tramp Service Liner Service 9
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Ocean Shipping options Bulk Service Tramp Service Liner Service 9
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Airfreight Shipping Option 40 % Percentage of the world’s manufactured Products travel by air 10
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Airfreight Shipping Option 40 % Percentage of the world’s manufactured Products travel by air 10
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Selecting a Mode of Transport Transit Time Noneconomic Factors ? Predictability Cost 11
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Selecting a Mode of Transport Transit Time Noneconomic Factors ? Predictability Cost 11
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Export Documentation A bill of lading is a contract between the exporter and the carrier indicating that the carrier has accepted responsibility for the goods and will provide transportation in return for payment A commercial invoice is a bill for the goods stating basic information about the transaction, including a description of the merchandise, total cost of the goods sold, addresses of the shipper and seller, and delivery and payment terms 12
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Export Documentation A bill of lading is a contract between the exporter and the carrier indicating that the carrier has accepted responsibility for the goods and will provide transportation in return for payment A commercial invoice is a bill for the goods stating basic information about the transaction, including a description of the merchandise, total cost of the goods sold, addresses of the shipper and seller, and delivery and payment terms 12
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management International Inventory Issues Inventories tie up a major portion of corporate funds, therefore proper inventory policies should be a major concern to the international logistician. Just-in-time inventory policies minimize the volume of inventory by making it available only when needed. The purpose of establishing inventory systems are: to maintain product movement in the delivery pipeline to have a cushion to absorb demand fluctuations 13
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management International Inventory Issues Inventories tie up a major portion of corporate funds, therefore proper inventory policies should be a major concern to the international logistician. Just-in-time inventory policies minimize the volume of inventory by making it available only when needed. The purpose of establishing inventory systems are: to maintain product movement in the delivery pipeline to have a cushion to absorb demand fluctuations 13
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management What Affects Inventory Level? Order Cycle Time Use of Inventories as a Strategic Tool Desired Customer Service Levels 14
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management What Affects Inventory Level? Order Cycle Time Use of Inventories as a Strategic Tool Desired Customer Service Levels 14
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management International Packaging Issues Packaging is instrumental in getting the merchandise to the destination in a safe, presentable condition. Considerations include • Environmental conditions and weight • Inter-modal containers • Cost attention 15
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management International Packaging Issues Packaging is instrumental in getting the merchandise to the destination in a safe, presentable condition. Considerations include • Environmental conditions and weight • Inter-modal containers • Cost attention 15
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Storage Facilities A stationary period is involved when merchandise becomes inventory stored in warehouses. The location decision addresses how many distribution centers to have and where to locate them. Storage facilities abroad can differ in availability and quality. The logistician should analyze international product sales and then rank order products according to warehousing needs. 16
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Storage Facilities A stationary period is involved when merchandise becomes inventory stored in warehouses. The location decision addresses how many distribution centers to have and where to locate them. Storage facilities abroad can differ in availability and quality. The logistician should analyze international product sales and then rank order products according to warehousing needs. 16
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Special Trade Zones Foreign trade zones areas where foreign goods may be held or processed and then reexported without incurring duties. In export processing zones, special rules apply that are different in other regions of the country. Example The maquiladoras of Mexico Example The special economic zones of China 17
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Special Trade Zones Foreign trade zones areas where foreign goods may be held or processed and then reexported without incurring duties. In export processing zones, special rules apply that are different in other regions of the country. Example The maquiladoras of Mexico Example The special economic zones of China 17
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Type Centralized Decision-making is clear All staff report to one person An objective viewpoint Decentralized Firm responsive to local needs Each unit carries responsibility for its performance 18
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Type Centralized Decision-making is clear All staff report to one person An objective viewpoint Decentralized Firm responsive to local needs Each unit carries responsibility for its performance 18
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Supply Chain Considerations The internet provides a variety of choices Logistics systems and modern transportation systems are often the targets of attacks Since environmental laws and regulations differ across the globe, the firm’s efforts need to be responsive to a wide variety of requirements 19
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Supply Chain Considerations The internet provides a variety of choices Logistics systems and modern transportation systems are often the targets of attacks Since environmental laws and regulations differ across the globe, the firm’s efforts need to be responsive to a wide variety of requirements 19
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Reference Malamed, C. (2015). Visual design solutions: Principles and creative inspiration for learning professionals. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley & Sons. Shah, Amit. 2014. Logistics and supply-chain management. Retrieved from www. siue. edu/~akutan/mba 532/ch 16. ppt 20
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Reference Malamed, C. (2015). Visual design solutions: Principles and creative inspiration for learning professionals. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley & Sons. Shah, Amit. 2014. Logistics and supply-chain management. Retrieved from www. siue. edu/~akutan/mba 532/ch 16. ppt 20
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Color The colors chosen were blue and a touch of red. Due to those with color blindness, red was mostly avoided (Malamed, 2015). These were balanced with the mostly black body type text and white space to make it feel clean and uncluttered. I converted quite a few slides of bullet points to Smart. Art and shapes and used the same color blue which provided great contrast. 21
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Color The colors chosen were blue and a touch of red. Due to those with color blindness, red was mostly avoided (Malamed, 2015). These were balanced with the mostly black body type text and white space to make it feel clean and uncluttered. I converted quite a few slides of bullet points to Smart. Art and shapes and used the same color blue which provided great contrast. 21
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Images The illustrations were helpful to convey the topic and simple in nature so as not to distract (Malamed, 2015). As mentioned in my comments about color, I converted a number of bulleted text slides to more graphics type slides using Smart. Art and rounded corner shapes. I then recolored the shapes the same blue and used a preset effect with rounded edges to add perspective rather than have a flat appearance. The chain on the introduction and master slide conveyed the concept of each link’s importance. 22
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Images The illustrations were helpful to convey the topic and simple in nature so as not to distract (Malamed, 2015). As mentioned in my comments about color, I converted a number of bulleted text slides to more graphics type slides using Smart. Art and rounded corner shapes. I then recolored the shapes the same blue and used a preset effect with rounded edges to add perspective rather than have a flat appearance. The chain on the introduction and master slide conveyed the concept of each link’s importance. 22
 Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Typeface The typeface chosen was Lucinda Sans Unicode. It has a clean look with no curves or ornate markings so it will be easier to read onscreen without any serifs (Malamed, 2015). While the original type did have serifs and was very readable, the decenders (Malamed, 2015) on the letter “g” looked very odd onscreen. 23
Logistics and Supply-Chain Management Typeface The typeface chosen was Lucinda Sans Unicode. It has a clean look with no curves or ornate markings so it will be easier to read onscreen without any serifs (Malamed, 2015). While the original type did have serifs and was very readable, the decenders (Malamed, 2015) on the letter “g” looked very odd onscreen. 23


