9ee3a773c708a49268ec1ad2f93bccb2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 103

Chapter 15: The Civil War Begins Section 1 – Texas Secession The secession of Southern states cause the North and the South to take up arms. Texas becomes one of the early states to secede from the Union and join the Confederacy. Which side had the advantage in the Civil War?

North vs. South in 1861 On a sheet of paper, draw the chart below. After studying the few slides that follow, write in your responses and complete the chart. North South Advantages ? ? Disadvantages ? ?
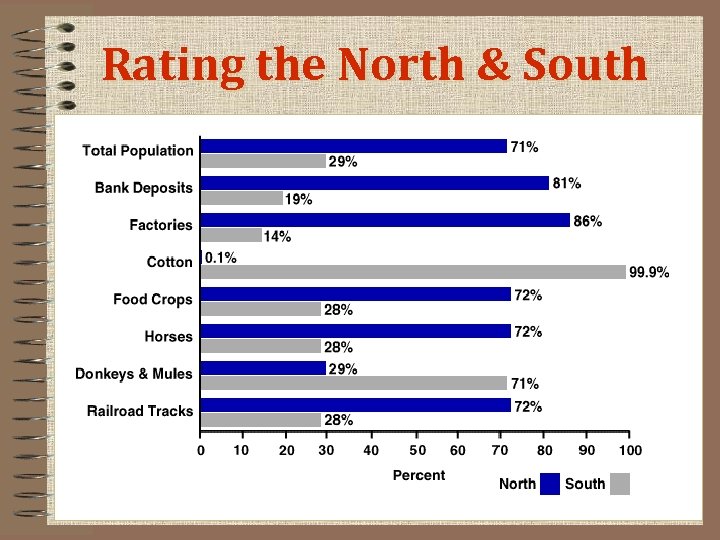
Rating the North & South
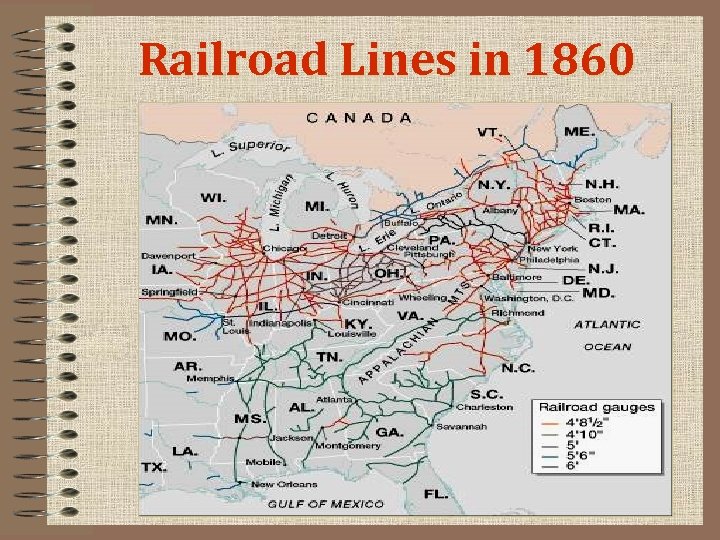
Railroad Lines in 1860
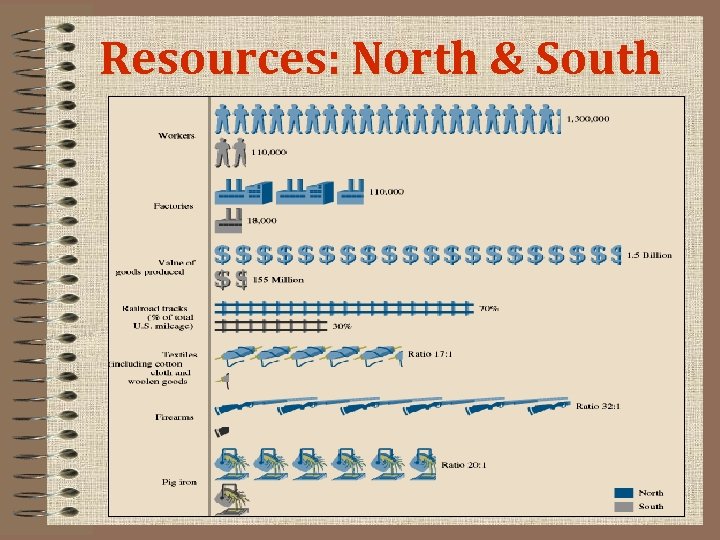
Resources: North & South
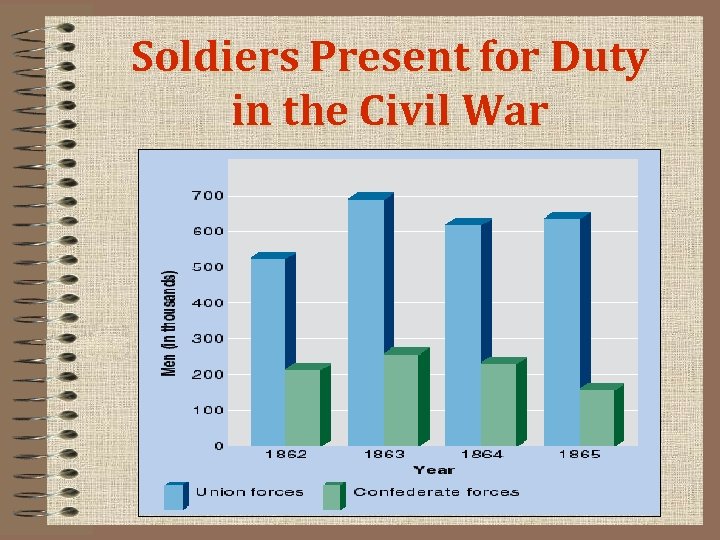
Soldiers Present for Duty in the Civil War
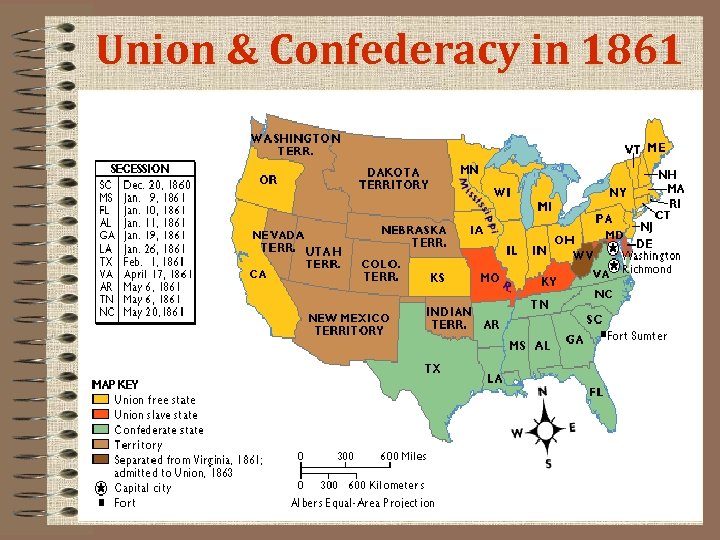
Union & Confederacy in 1861
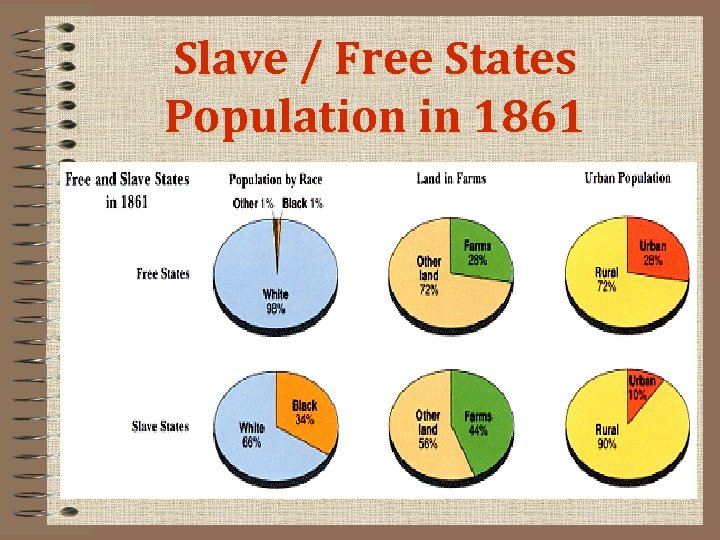
Slave / Free States Population in 1861
The Civil War (1861 -1865) Through Maps, Charts, Graphs & Pictures Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY

Many Issues Divide the Country • 1861 – Texas joined 10 other states to secede from the Union and form the Confederate States of America (CSA). • This action followed years of long-standing differences between the North and the South.

What Issues did the North & South Disagree On? • Tariffs – taxes on imported goods • Distribution of public lands • States’ Rights – states should have more power over what they do and the federal government should have less power over them. • Most of all – the issue of SLAVERY
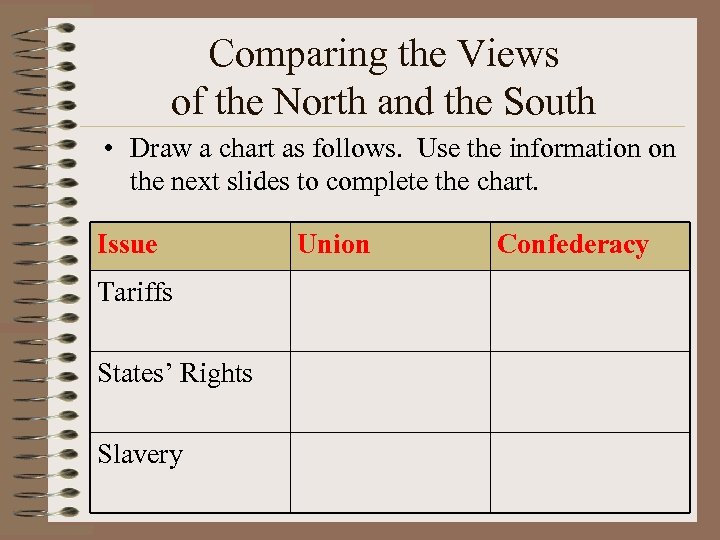
Comparing the Views of the North and the South • Draw a chart as follows. Use the information on the next slides to complete the chart. Issue Tariffs States’ Rights Slavery Union Confederacy

The Republican Party Opposes Slavery • Many Northerners who opposed slavery joined the Republican Party. • Abolitionists – wanted to end ALL slavery. • However, not all Northern whites agreed. The majority of Northern whites were prejudiced against African Americans (free/slave). • BUT…the majority of Northern whites did NOT want slavery to spread westward into new territories.

A Northern/Republican’s View: • Many Northern business leaders and farmers believed that the Southern Democrats were responsible for an economic depression (similar to the Great Depression) of the late 1850 s could be brought back by tariffs, a homestead act, and other internal improvements.

Tariffs Republicans/Northerners believed: • Would boost the economy and bring in much needed money to businesses and farmers.

States’ Rights Republicans/Northerners believed: • The federal system (under which the U. S. government was formed) allowed for the sharing of powers between the federal government and state governments. • States should NOT have more powers than they were given in the original U. S. constitution. • States had NO RIGHT to secede from the Union.

A Southern/Democrat’s View: • Opposed to ALL of the North’s ideas because they believed the ideas would ONLY benefit the North – not the South. • Believed that victory for the Republican Party would mean the end of slavery and the Southern way of life.
![States’ Rights • [Southern] states are sovereign, meaning they had entered the Union voluntarily States’ Rights • [Southern] states are sovereign, meaning they had entered the Union voluntarily](https://present5.com/presentation/9ee3a773c708a49268ec1ad2f93bccb2/image-18.jpg)
States’ Rights • [Southern] states are sovereign, meaning they had entered the Union voluntarily and they should be able to leave it voluntarily as they see fit.
![Tariffs • As sovereign states, they [Southern states] had the sole authority to set Tariffs • As sovereign states, they [Southern states] had the sole authority to set](https://present5.com/presentation/9ee3a773c708a49268ec1ad2f93bccb2/image-19.jpg)
Tariffs • As sovereign states, they [Southern states] had the sole authority to set or void tariffs as they saw fit.

Southern States Vow to Secede • During the 1860 presidential election, Southern leaders threatened to secede if a Republican (Abraham Lincoln) was elected. • After Lincoln won the 1860 election, 6 states seceded: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, and Louisiana. • Texans call on Governor Sam Houston to organize a convention to consider secession also.

The Convention Votes on Secession • Sam Houston OPPOSED secession. • Houston did not believe that the South could win a war against the North. • He hoped that Texans would rally against a convention and declare such a convention illegal. • Houston refused to call a special session of the legislature and Texans organized a convention and elected delegates to attend - all without Houston’s approval.

Texas Secession Convention • Met in Austin on January 28, 1861. • Adopted a decree called the “Ordinance of Secession. ” Ordinance declared that the U. S. government had abused its power in order to “strike down the interest and prosperity of the people of Texas” …”her citizens are freed from allegiance to the U. S. ” • On February 23, 1861, Texas approved secession from the Union and became the 7 th state to secede from the Union and join the Confederacy.

The Confederacy is Formed • Formed at a convention in Montgomery, Alabama on February 4, 1861. • Called the Confederate States of America (CSA).

Confederate Constitution • Drew up a constitution similar to the U. S. constitution, but with some important differences: • 1. states were given MORE power and the federal government was given LESS power; • 2. this constitution guaranteed the protection of slavery.

The Confederate “White House”

Leaders of the Confederacy Pres. Jefferson Davis VP Alexander Stevens

A Northern View of Jeff Davis

Texas Approves the Confederate Constitution • Texas quickly approved the Confederate constitution. • They prepared a Texas Constitution of 1861. • This constitution replaced references to the “U. S. constitution” with “Confederate constitution. ”

Houston Removed from Office • Texas Secession Convention ordered all state government leaders to take an oath of loyalty to the Confederacy – Houston refused and is removed as Governor. • Lt. Governor Edward Clark replaced Houston as Governor (he took the oath) • This ends Houston’s career in politics and military – he retires to home in Huntsville and dies in 1863.

Lincoln’s View on States’ Secession • Lincoln said that the Union was “perpetual” (continuing forever) and the Southern states had no right to leave it. • He promised to carry out the law of the land (according to the U. S. constitution) in all states, and • Vowed to preserve the nation at all costs.
The War Begins • It starts at Fort Sumter, SC: • Confederate soldiers take over Fort Sumter – Fort Sumter— a Union outpost in the Charleston harbor – Confederates demand surrender of Fort Sumter • First Shots – – Lincoln does not reinforce or evacuate, just sends food For South, no action would damage sovereignty of Confederacy Jefferson Davis chooses to turn peaceful secession into war Orders Confederate soldiers to fire on Sumter April 12, 1861 This is the beginning of the Civil War!

Section 2 – Texans Go to War

Lincoln’s Generals Winfield Scott Irwin Mc. Dowell George Mc. Clellan Joseph Hooker Ambrose Burnside Ulysses S. Grant George Meade George Mc. Clellan, Again!

Mc. Clellan: I Can Do It All!

The Confederate Generals “Stonewall” Jackson Nathan Bedford Forrest George Pickett Jeb Stuart James Longstreet Robert E. Lee
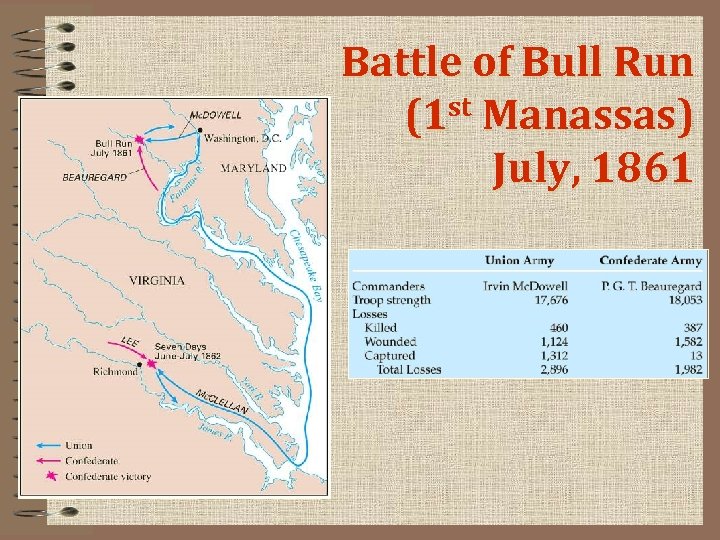
Battle of Bull Run st Manassas) (1 July, 1861

Buy Your Way Out of Military Service

Confederates Fire on Fort Sumter • The Confederacy Takes Control – Confederate soldiers take over government, military installations – Fort Sumter—Union outpost in Charleston harbor – Confederates demand surrender of Fort Sumter • Lincoln’s Dilemma – Reinforcing fort by force would lead rest of slave states to secede – Evacuating fort would legitimize Confederacy, endangering the Union

Confederates Fire on Fort Sumter • First Shots – – Lincoln does not reinforce or evacuate, just sends food For South, no action would damage sovereignty of Confederacy Jefferson Davis chooses to turn peaceful secession into war fires on Sumter April 12, 1861 • Begins the Civil War

Confederates Fire on Fort Sumter • Virginia Secedes – Fall of Fort Sumter unites North; volunteers rush to enlist – Virginia unwilling to fight the South; secedes from Union • This is very important, because Virginia is the most populated state in the South, and Robert E. Lee is from Virginia – antislavery western counties secede from VA, creating the state of West Virginia • Three more states secede; border states remain in Union – Border states are very important. – Lincoln will have to make political decisions that will not agitate the border states.

Americans Expect a Short War • Union and Confederate Strategies – Union advantages: soldiers, factories, food, and railroads – Confederate advantages: cotton profits, generals, motivation • Anaconda plan: Union strategy to conquer South – blockade Southern ports – divide Confederacy in two in west – capture Richmond, Confederate capital • Confederate strategy: defense, invade North if opportunity arises
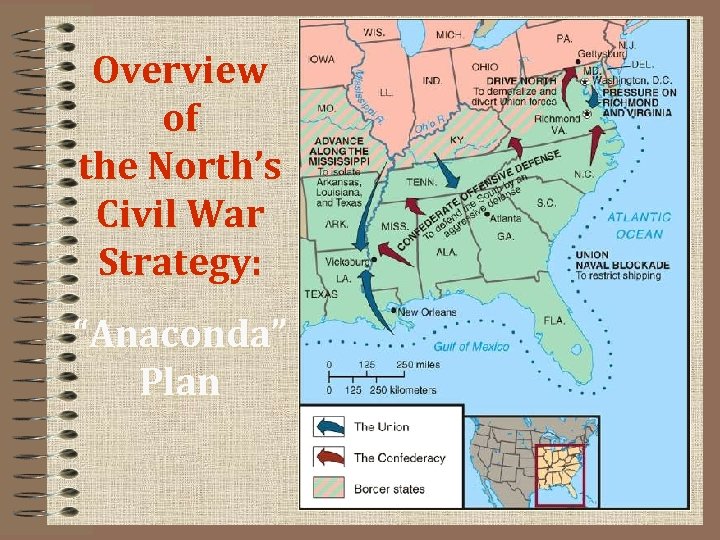
Overview of the North’s Civil War Strategy: “Anaconda” Plan

The “Anaconda” Plan

Americans Expect a Short War • Bull Run – Bull Run—first battle, near Washington, D. C. ; Confederate victory • This battle shows both sides that the war will not be short. – Thomas J. Jackson called Stonewall Jackson for firm stand in battle

Union Armies in the West • Protecting Washington, D. C. – After Bull Run, Lincoln calls for 1 million additional soldiers – Appoints General George Mc. Clellan to lead Army of the Potomac • Forts Henry and Donelson – General Ulysses S. Grant—brave, tough, decisive commander in West – Feb. 1862, Grant captures Confederate Forts Henry, Donelson

Union Armies in the West • Shiloh – March 1862, Confederate troops surprise Union soldiers at Shiloh – Grant counterattacks; Confederates retreat; thousands dead, wounded – Shiloh teaches preparation needed, Confederacy vulnerable in West • Farragut on the Lower Mississippi – David G. Farragut commands fleet that takes New Orleans, April 1862 • Why is New Orleans an important victory for the North – takes Baton Rouge, Natchez

• Pretend that you have been given the task of setting the odds of winning or losing the Civil War. Look at the advantages and disadvantages for both sides and make a prediction and explain your prediction

The War for the Capitals • “On to Richmond” – Mc. Clellan waits to attack Richmond; drills troops for 5 months [Visual] – Spring 1862, Robert E. Lee takes command of Southern army • Lee, Mc. Clellan fight Seven Days’ Battle; Union leaves Richmond area – Lee shows the advantage of military leadership for the Confederacy. – The confederacy in the east is very successful, even though they are outnumber, and outmatched

The War for the Capitals • Antietam • Lee wins the Second Battle of Bull Run; marches into Maryland !!!!!!!!!! • Lee, Mc. Clellan clash at Antietam—bloodiest single-day battle in American History!!!!!!! • Battle a standoff; Confederates retreat; Mc. Clellan does not pursue • Lincoln fires Mc. Clellan

Soldiers Suffer on Both Sides • Lives on the Lines – Lack of sanitation, personal hygiene lead to disease in camp • Soldiers only required to wash their hands and face once a day, and bath once a week. – Diets are unvaried, limited, unappealing

A Revolution in Warfare • Ironclads – What is an Ironclad? – New ironclad ships instrumental in victories of Grant, Farragut – Ironclads splinter wooden ships, withstand cannon, resist burning – March 1862, North’s Monitor, South’s Merrimack fight to a draw • New Weapons – Rifles more accurate, faster loading, fire more rounds than muskets – Minié ball (more destructive bullet), grenades, land mines are used – Fighting from trenches, barricades new advantage in infantry attacks

1864 Copperhead Campaign Poster

African Americans Fight for Freedom • Slave Resistance in the Confederacy – Slaves seek freedom behind Union army lines – On plantations, destroy property, refuse to leave with fleeing owners

Both Sides Face Political Problems • Conscription – Casualties, desertions lead to conscription—draft to serve in army – Both armies allow draftees to hire substitutes to serve for them – Planters with more than 20 slaves exempted – 90% eligible Southerners serve; 92% Northern soldiers volunteer • Draft Riots – White workers fear Southern blacks will come North, compete for jobs – Angry at having to free slaves, mobs rampage through New York City – Also rioted because the rich did not have to fight. (Substitutes)

Britain Remains Neutral • Britain Pursues Its Own Interests – Britain has cotton inventory, new sources; does not need South – Needs Northern wheat, corn; chooses neutrality • The Trent Affair – Confederate diplomats travel on Trent to get British, French support – U. S. Navy arrests them; Lincoln frees them, averts war with Britain • Almost brings Britain into the war.

African Americans Fight for Freedom • African-American Soldiers – African Americans 1% of North’s population, by war’s end 10% of army – Lower pay than white troops for most of war; limits on military rank • Will eventually receive equal pay. – High mortality from disease; POWs killed or returned to slavery – Fort Pillow, TN—Confederates massacre over 200 African. American POWs – Why? !!!!

The Peace Movement: Copperheads Clement Vallandigham
The Southern View of Emancipation

Battle of Antietam “Bloodiest Single Day of the War” September 17, 1862 23, 000 casualties
The Year is 1863… The Civil War is progressing… The fighting is intense and the death toll is climbing… Events are unfolding quickly now…these events will forever change the nation… for better and for worse…
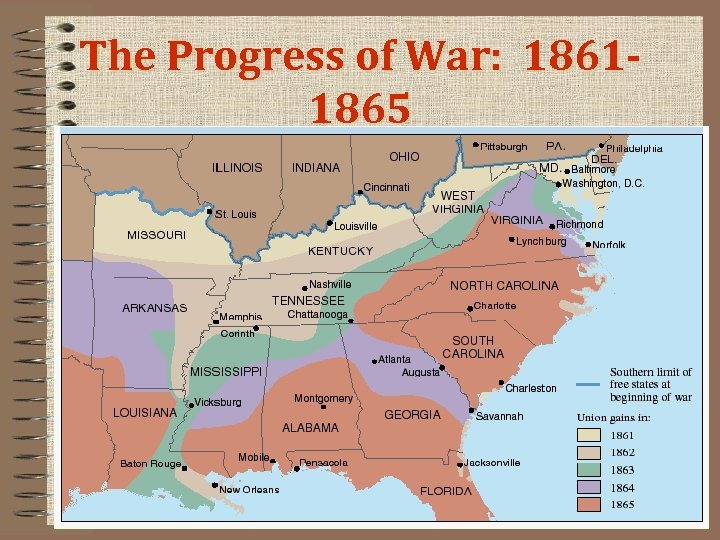
The Progress of War: 18611865

The Emancipation Proclamation

Emancipation Proclamation • • By issuing the Emancipation Proclamation, President Lincoln makes slavery the focus of the war. Terms of the Proclamation: 1) frees slaves in the Confederate states 2) does NOT apply to areas occupied by the Union or states where slavery is permitted in the Union – (such as the border states of Missouri and Kentucky) 3) Discourages Britain from supporting/joining the Confederacy (audio clips of freed slaves)

Proclaiming Emancipation • Lincoln’s View of Slavery 1) Federal government has no power to abolish slavery where it exists 2) Lincoln decides slaves who labor for Confederacy (southern states) CAN BE FREED • The Proclamation brings mixed reactions…
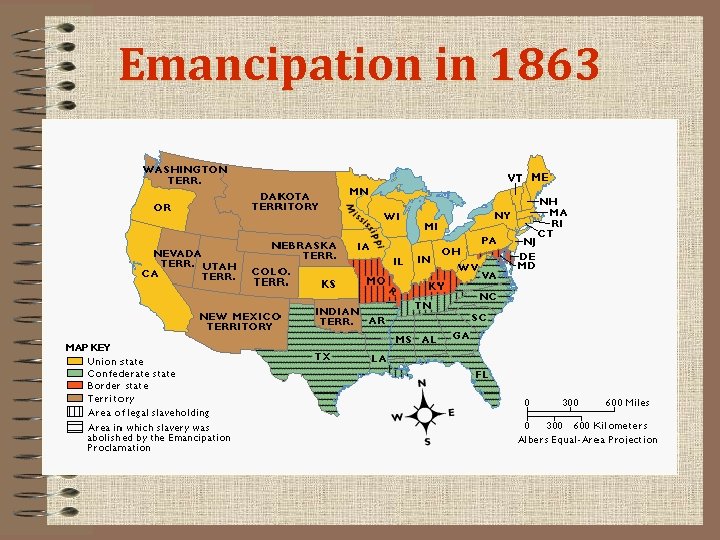
Emancipation in 1863

Some Reactions: • gives war a higher moral purpose • Free blacks can now join Union army and fight against slavery • Northern Democrats claim it will antagonize the South and prolong the war • Confederacy now MORE DETERMINED to fight to keep slavery • No chance of compromise now-one side must Win and the other side must LOSE!

Both Sides Face Political Problems • Dealing with Dissent • Lincoln suspends habeas corpus: – order to bring accused to court, explain charges – (Copperheads – anti-war N Democrats among those arrested) – Seizes telegraph offices to prevent subversion • Davis denounces Lincoln’s action and then suspends habeas corpus in South also • Lincoln’s action in dramatically expanding presidential powers to meet a crisis in wartime “emergency powers” sets precedent for future presidents
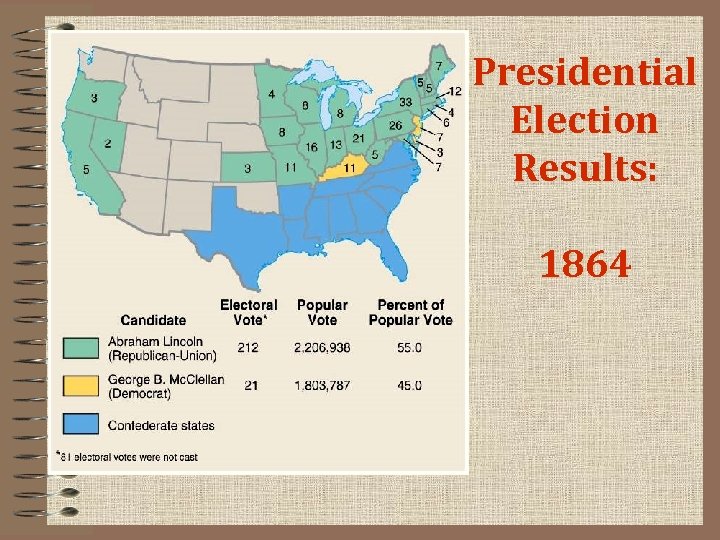
Presidential Election Results: 1864

1864: Life During Wartime • The Civil War brings about dramatic social and economic changes in American society including: 1) 2) 3) African Americans join the Union army to fight (54 th Massachusetts) Other slaves seek freedom behind Union army lines On plantations: some destroy property, others refuse to leave

African-American Recruiting Poster
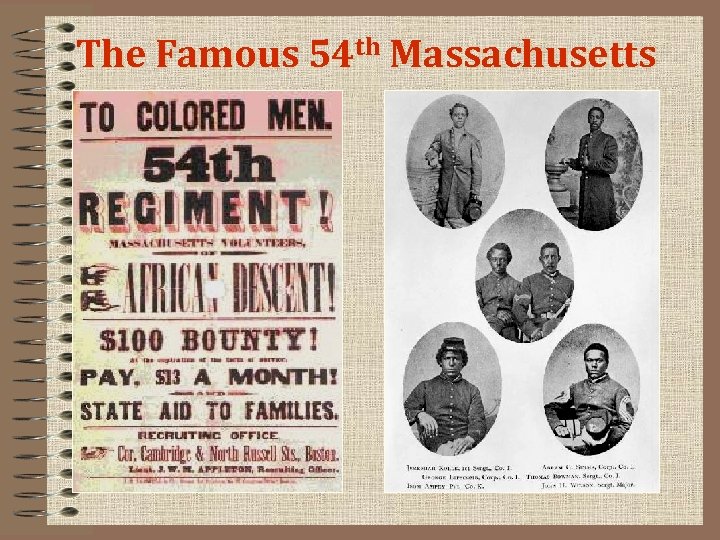
The Famous 54 th Massachusetts

Black Troops Freeing Slaves

The War Affects Regional Economies • FOOD SHORTAGES in the South – Food shortages from lost manpower, Union occupation, loss of slaves – Blockade creates other shortages; some Confederates trade with enemy • ECONOMY BOOM in the North – Industries that supply army boom; some contractors cheat and profit – Wages do not keep up with prices; workers’ standard of living drops – Women replace men on farms, city jobs, government jobs – Congress establishes first income tax on earnings to pay for war
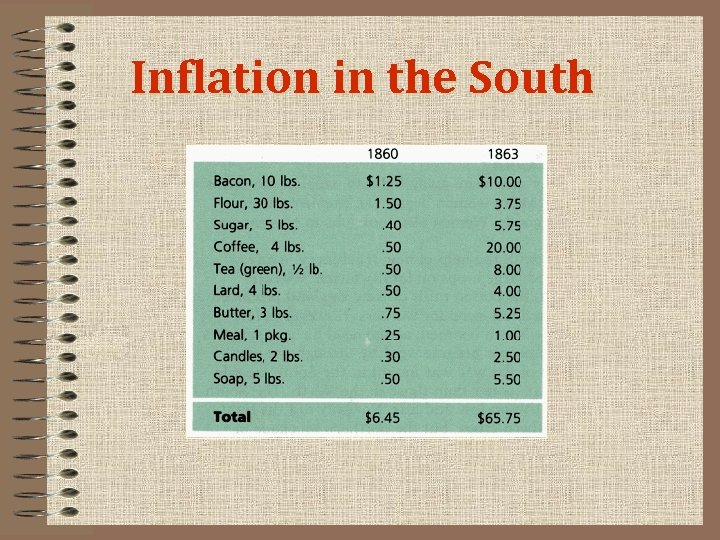
Inflation in the South

Soldiers Suffer on Both Sides • More soldiers died from Dysentery (diarrhea) than were killed in battle • Lived in unsanitary camps, conditions (epidemics easily spread) wash hands 1/day, bathe 1/week • 75% of surgeries were amputations (saw often used on 1 person after another w/o sanitizing) - fingers the most amputated body part

Soldiers Suffer on Both Sides • Prisons – Andersonville—worst Confederate prison (in Georgia) – Conditions so bad that Major (warden) Henry Wirz is tried, convicted, hanged for war crimes from Andersonville – no shelter, sanitation, little food – 1/3 of prisoners die – Northern prisons more space, food, shelter Major

The North Takes Charge • UNION army is wearing down the CONFEDERACY • KEY VICTORIES for Union: 1) Vicksburg, and 2) Gettysburg

Armies Clash at Gettysburg • Prelude to Gettysburg In May 1863, South defeats North at Chancellorsville – Stonewall Jackson mistakenly shot by own troops – dies 8 days later of pneumonia

Armies Clash at Gettysburg • Three-day battle at Gettysburg devastates/cripples the South… 1) Union (Meade) and Confederate (Lee) 2) vicious artillery fire 3) on 3 rd day, Lee retreats and Meade stays behind • Staggering losses on both sides • This is the turning point in the war
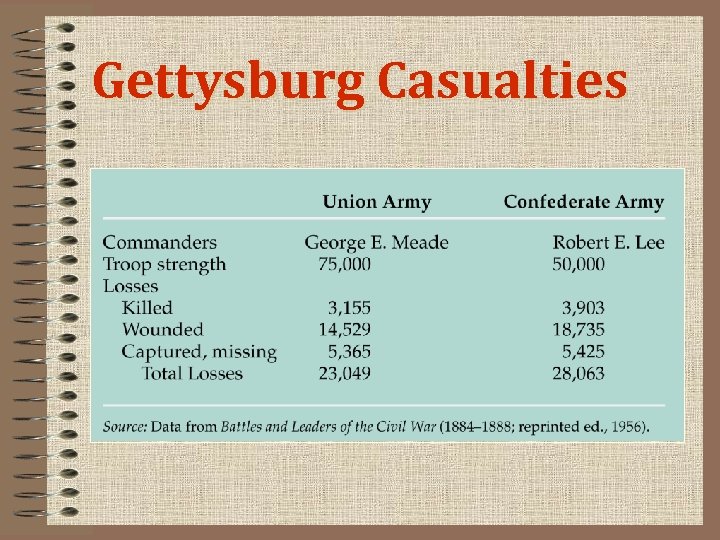
Gettysburg Casualties

Vicksburg Under Siege • Grant Wins at Vicksburg – Confederate Vicksburg prevents Union from controlling Mississippi – Spring 1863, Union destroys MS rail lines, sacks Jackson – Grant begins siege in May – Starving Confederates surrender on July 4 – Confederacy completely divided
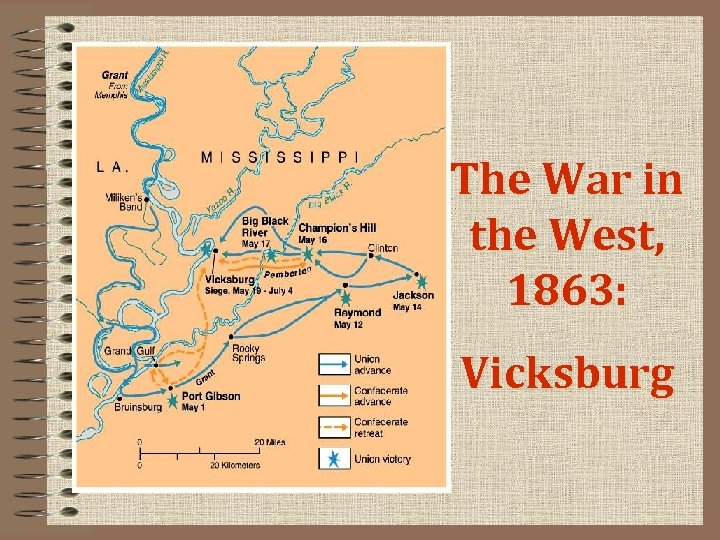
The War in the West, 1863: Vicksburg

The Gettysburg Address • The Memorial Ceremony – November 1863, ceremony held to dedicate cemetery in Gettysburg and honors dead soldiers – Edward Everett, noted speaker, gives flowery twohour speech – Lincoln’s two-minute Gettysburg Address asserts unity of U. S. – Speech calls for living to dedicate selves to preserving the Union and freedom

The Confederacy Wears Down • Confederate Morale – South unable to attack; hopes to get armistice – Civilian morale plummets – Discord in government • Grant Appoints Sherman – March 1864, Lincoln appoints Grant commander of all Union armies – Grant appoints William Tecumseh Sherman commander of Mississippi division [West] Grant, Sherman believe in total war to destroy South’s will to fight

The Confederacy Wears Down • Grant and Lee in Virginia • Grants’s strategy: 1) immobilize Lee in Virginia while Sherman raids Georgia 2) May 1864 -April 1865, Grant and Lee fight many battles - heavy losses on both sides - North can replace soldiers – South cannot!
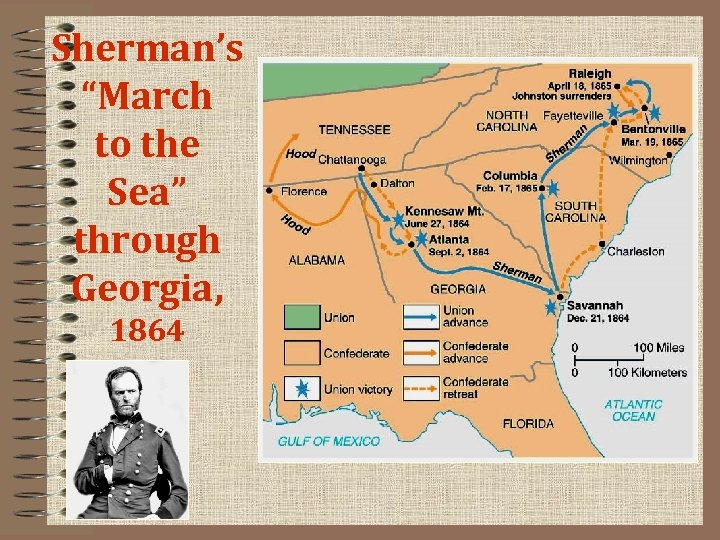
Sherman’s “March to the Sea” through Georgia, 1864

The Confederacy Wears Down • Sherman’s March to the Sea • Sept, 1864: 1) Sherman takes Atlanta - not much of a fight, Atlanta mostly vacant 2) Sherman cuts wide path (60 miles) of destruction across Georgia towards Savannah 3) By December, takes Savannah and moves up to SC - even more destruction in SC

1864 Election Pres. Lincoln (R) George Mc. Clellan (D)

The Confederacy Wears Down • The Election of 1864 1) Lincoln re-elected for 2 nd term • IT’S OVER! The Surrender at Appomatox 1) Davis’s government leaves Richmond and burn it to the ground 2) Lee surrenders April 9, 1865 at the Appomattox Courthouse - Lee’s soldiers paroled on generous terms

Surrender at Appomattox April 9, 1865

The Legacy of the War • Civil War settles long-standing disputes over states’ rights and slavery. • Many changes follow….

The War Changes the Nation • Political Changes 1) 2) ends threats of secession increases power of federal government • Economic Changes 1) 2) new federal system of chartered banks Gap between North and South widens - North: industry and commercial agriculture growth - South: industry, farms destroyed

Casualties on Both Sides
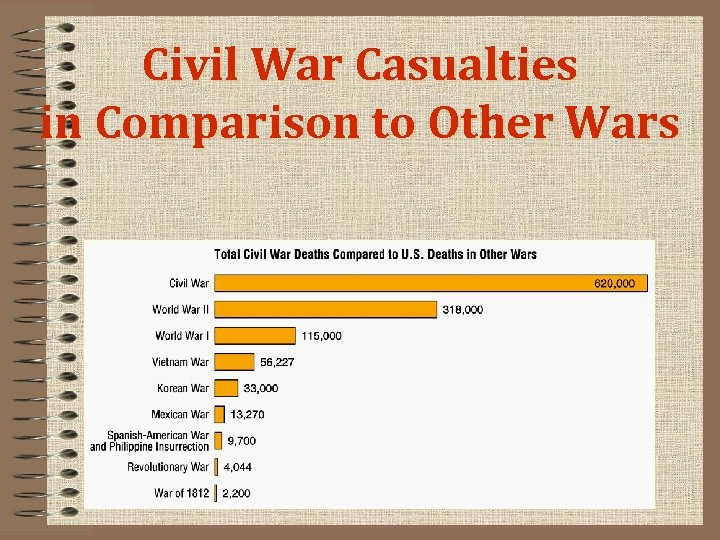
Civil War Casualties in Comparison to Other Wars
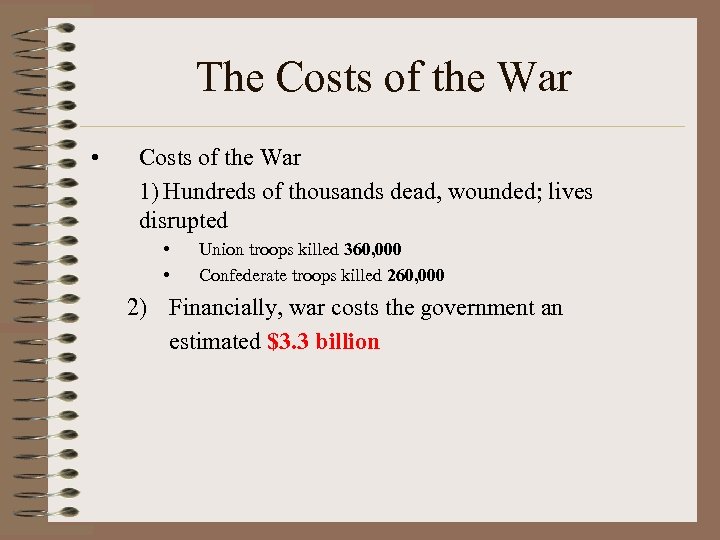
The Costs of the War • Costs of the War 1) Hundreds of thousands dead, wounded; lives disrupted • • Union troops killed 360, 000 Confederate troops killed 260, 000 2) Financially, war costs the government an estimated $3. 3 billion

The War Changes Lives • New Birth of Freedom 1) 1865: 13 th Amendment abolishes slavery in all states • Civilians Follow New Paths 1) Some soldiers stay in army, others are civilians, many go west

Ford’s Theater (April 14, 1865)

The Assassination

The War Changes our Future • Assassination of President Abraham Lincoln 1) 2) April 14, 1865, Lincoln is shot at Ford’s Theatre Assassin John Wilkes Booth escapes, is trapped by Union cavalry and shot 3) 7 million people pay respects to Lincoln’s funeral train

The Assassin John Wilkes Booth

Now He Belongs to the Ages!

WANTED~~!!

The Execution
9ee3a773c708a49268ec1ad2f93bccb2.ppt