99713d4936f8ef0752de323c540c78fa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Chapter 15 Relea se from Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
Chapter 15 Relea se from Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 “parole” definition u the conditional release of an inmate from incarceration after part of the prison sentence has been served u release is typically to a period of supervision in the community u offender must comply with specific behavioral requirements during this Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
“parole” definition u the conditional release of an inmate from incarceration after part of the prison sentence has been served u release is typically to a period of supervision in the community u offender must comply with specific behavioral requirements during this Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 “parole eligibility” definition u the point in a prisoner’s sentence when he/she is first legally able to be released from prison u determined variously, in different jurisdictions u at the end of the minimum term, less good time u at a specific fraction (eg, 1/3 or 1/2) of the minimum or the maximum sentence u “good time” affects eligibility in various ways u offender sees parole board automatically, when eligible (no need to “apply”) Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
“parole eligibility” definition u the point in a prisoner’s sentence when he/she is first legally able to be released from prison u determined variously, in different jurisdictions u at the end of the minimum term, less good time u at a specific fraction (eg, 1/3 or 1/2) of the minimum or the maximum sentence u “good time” affects eligibility in various ways u offender sees parole board automatically, when eligible (no need to “apply”) Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
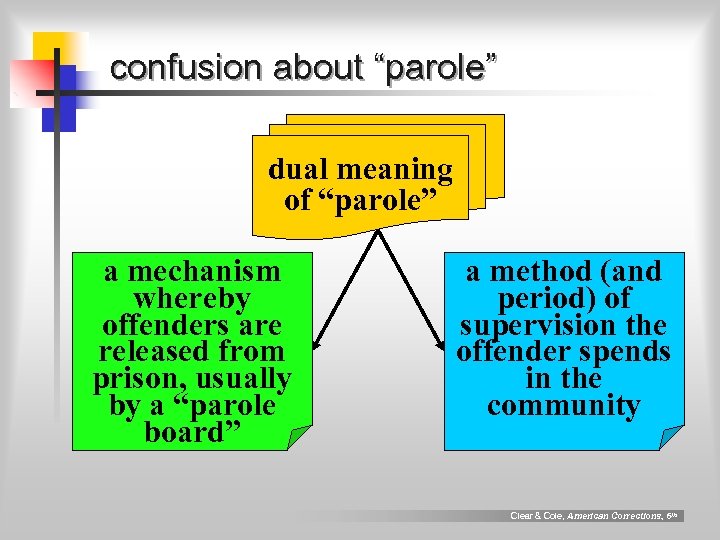 confusion about “parole” dual meaning of “parole” a mechanism whereby offenders are released from prison, usually by a “parole board” a method (and period) of supervision the offender spends in the community Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
confusion about “parole” dual meaning of “parole” a mechanism whereby offenders are released from prison, usually by a “parole board” a method (and period) of supervision the offender spends in the community Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 conceptual basis of parole grace or privilege government extends privilege of release, though offender could be kept in prison “parole” custody contract government enters into agreement with offender, who promises to comply with certain conditions in exchange for being released parole is an extension of correctional programs into the community; offender is still the responsibility of the government Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
conceptual basis of parole grace or privilege government extends privilege of release, though offender could be kept in prison “parole” custody contract government enters into agreement with offender, who promises to comply with certain conditions in exchange for being released parole is an extension of correctional programs into the community; offender is still the responsibility of the government Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 predecessors of parole u historical methods of moving criminals out of prison in England, Ireland, and Australia were responses to: n n n crowding labor shortages cost of incarceration n n conditional pardon apprenticeship by indenture transportation tickets of leave u methods included: Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
predecessors of parole u historical methods of moving criminals out of prison in England, Ireland, and Australia were responses to: n n n crowding labor shortages cost of incarceration n n conditional pardon apprenticeship by indenture transportation tickets of leave u methods included: Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 Alexander Maconochie u key figure in parole (1787 -1860) u administered British penal colonies in Tasmania/South Pacific/England u offender sentenced to certain number of “marks, ” according to severity of offense u offender could reduce sentence by earning “marks” for work, good behavior u sentence also tied to graduated steps: n n n strict imprisonment labor on chain gang freedom within one area Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
Alexander Maconochie u key figure in parole (1787 -1860) u administered British penal colonies in Tasmania/South Pacific/England u offender sentenced to certain number of “marks, ” according to severity of offense u offender could reduce sentence by earning “marks” for work, good behavior u sentence also tied to graduated steps: n n n strict imprisonment labor on chain gang freedom within one area Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 Walter Crofton u built on Maconochie’s ideas (18151897) u Ireland system (“intermediate system”) period of solitary confinement public work prisons (could earn “marks”) n intermediate stage (after earning enough marks); like halfway house n ticket of leave (conditional release) n n u Crofton added: parolees submitted monthly reports to police n special civilian inspector (Dublin) supervised n Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
Walter Crofton u built on Maconochie’s ideas (18151897) u Ireland system (“intermediate system”) period of solitary confinement public work prisons (could earn “marks”) n intermediate stage (after earning enough marks); like halfway house n ticket of leave (conditional release) n n u Crofton added: parolees submitted monthly reports to police n special civilian inspector (Dublin) supervised n Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 U. S. evolution of parole u Zebulon Brockway released prisoners on parole with NY indeterminate law, 1876 u 1900: 20 states have parole systems u 1910: each federal prison had own parole u 1925: 46 states (not Miss, Va) u 1930: Congress created US Board of Parole u 1942: Mississippi and Virginia joined Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
U. S. evolution of parole u Zebulon Brockway released prisoners on parole with NY indeterminate law, 1876 u 1900: 20 states have parole systems u 1910: each federal prison had own parole u 1925: 46 states (not Miss, Va) u 1930: Congress created US Board of Parole u 1942: Mississippi and Virginia joined Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
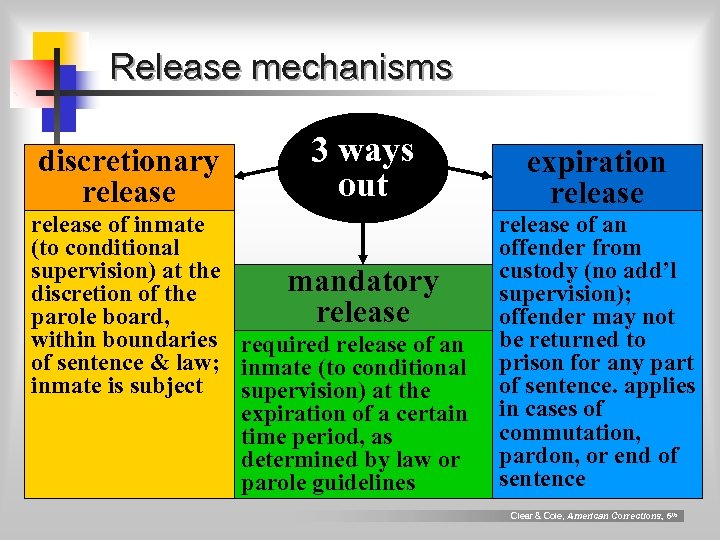 Release mechanisms discretionary release 3 ways out release of inmate (to conditional supervision) at the mandatory discretion of the release parole board, within boundaries required release of an of sentence & law; inmate (to conditional inmate is subject supervision) at the expiration of a certain time period, as determined by law or parole guidelines expiration release of an offender from custody (no add’l supervision); offender may not be returned to prison for any part of sentence. applies in cases of commutation, pardon, or end of sentence Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
Release mechanisms discretionary release 3 ways out release of inmate (to conditional supervision) at the mandatory discretion of the release parole board, within boundaries required release of an of sentence & law; inmate (to conditional inmate is subject supervision) at the expiration of a certain time period, as determined by law or parole guidelines expiration release of an offender from custody (no add’l supervision); offender may not be returned to prison for any part of sentence. applies in cases of commutation, pardon, or end of sentence Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
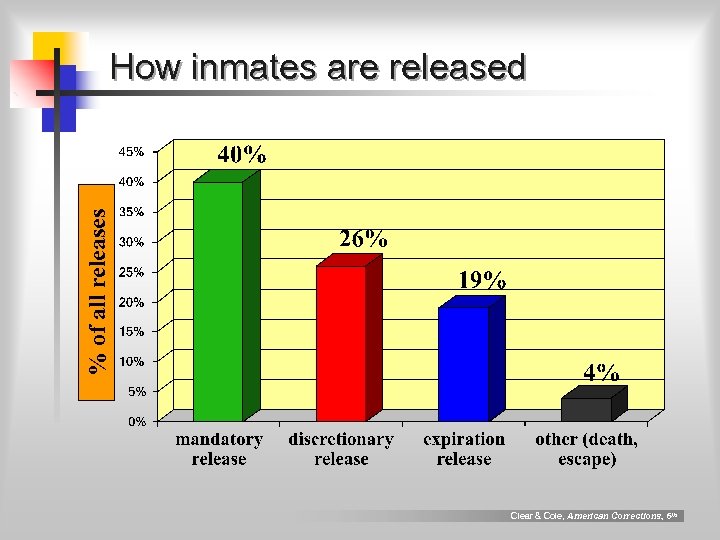 % of all releases How inmates are released Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
% of all releases How inmates are released Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 organization of releasing authorities issues u parole n board consolidated vs. autonomous? F inside dept. of corrections ü more responsive to corrections needs & programs F independent agency of government u field n ü less affected by institutional/dept. pressures services under parole board vs. under corrections? u board members n full vs. part time? n by governor vs. by department? u appointment F who is “qualified” to be on a board? Clear F what makes one “qualified? ” & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
organization of releasing authorities issues u parole n board consolidated vs. autonomous? F inside dept. of corrections ü more responsive to corrections needs & programs F independent agency of government u field n ü less affected by institutional/dept. pressures services under parole board vs. under corrections? u board members n full vs. part time? n by governor vs. by department? u appointment F who is “qualified” to be on a board? Clear F what makes one “qualified? ” & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 criteria for parole release u offense n n severity & attitude toward offense public attitude about offense u criminal record u attitude toward family, victim, authority u institutional behavior, participation, & improvement u history of community adjustment u health (physical, mental, emotional) u insight into causes of behavior u adequacy of parole plan Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
criteria for parole release u offense n n severity & attitude toward offense public attitude about offense u criminal record u attitude toward family, victim, authority u institutional behavior, participation, & improvement u history of community adjustment u health (physical, mental, emotional) u insight into causes of behavior u adequacy of parole plan Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 “parole guidelines” u definition method for structuring decisions of paroling authorities (like sentencing guidelines), by standardizing release decisions according to the objective measurement of relevant criteria along two dimensions: ua “severity scale” rates crimes according to their seriousness u a “salient factor score” measures the offender’s Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
“parole guidelines” u definition method for structuring decisions of paroling authorities (like sentencing guidelines), by standardizing release decisions according to the objective measurement of relevant criteria along two dimensions: ua “severity scale” rates crimes according to their seriousness u a “salient factor score” measures the offender’s Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
 “presumptive parole date” definition u the presumed release date stipulated by parole guidelines, as long as the offender serves his/her time without disciplinary (or other) incidents Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
“presumptive parole date” definition u the presumed release date stipulated by parole guidelines, as long as the offender serves his/her time without disciplinary (or other) incidents Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
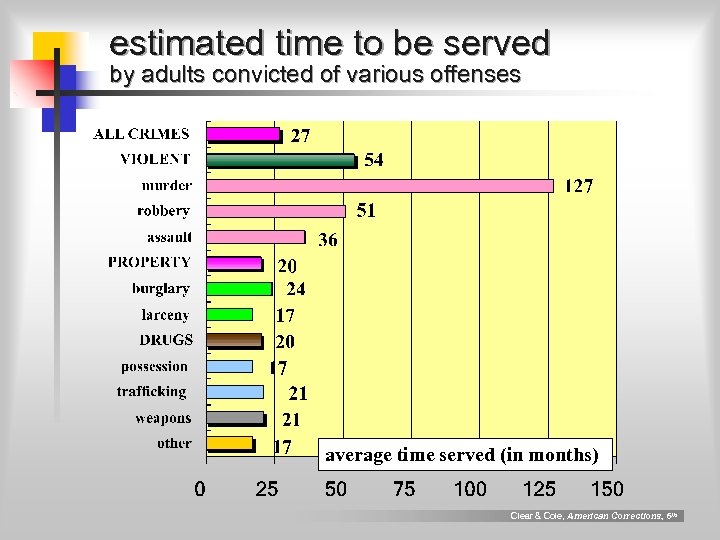 estimated time to be served by adults convicted of various offenses average time served (in months) Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th
estimated time to be served by adults convicted of various offenses average time served (in months) Clear & Cole, American Corrections, 6 th


