Oligopoly.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Chapter 15: Oligopoly Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
Chapter 15: Oligopoly Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 1. Two firms make most of the consumer alkaline batteries in the country: Duracell and Energizer. The market for batteries is most likely A. B. C. D. a monopoly. an oligopoly. perfectly competitive. monopolistically competitive. Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
1. Two firms make most of the consumer alkaline batteries in the country: Duracell and Energizer. The market for batteries is most likely A. B. C. D. a monopoly. an oligopoly. perfectly competitive. monopolistically competitive. Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 2. A problem with the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly is that A. firms’ beliefs about the demand curve are not always correct and firms can figure out that these beliefs are not correct. B. it assumes that oligopolists can price discriminate. C. it implies that firms ignore the actions of each other. D. it assumes that the largest firm has a lower average cost than the other firms. Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
2. A problem with the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly is that A. firms’ beliefs about the demand curve are not always correct and firms can figure out that these beliefs are not correct. B. it assumes that oligopolists can price discriminate. C. it implies that firms ignore the actions of each other. D. it assumes that the largest firm has a lower average cost than the other firms. Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 3. The price war was unleashed by Wal-Mart Stores Inc. , the country’s largest retailer, a few years ago. Since then, many grocery stores have followed suit. Drugstore giant Walgreens announced in 2008 it would sell 90 -day supplies of more than 400 medications for $9. 99. Suppose this market is represented by the dominant firm oligopoly model. If Wal. Mart is the dominant firm, which of the following is NOT true? A. Wal-Mart has a big cost advantage over the other firms and produces a large part of the industry output B. The other firms behave like perfect competitors taking Wal-Mart’s price as the market price C. Wal-Mart can retaliate against the other firms if they do not follow Wal-Mart’s pricing strategy D. All firms together produce the market quantity of prescription drugs demanded at Wal-Mart’s price Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
3. The price war was unleashed by Wal-Mart Stores Inc. , the country’s largest retailer, a few years ago. Since then, many grocery stores have followed suit. Drugstore giant Walgreens announced in 2008 it would sell 90 -day supplies of more than 400 medications for $9. 99. Suppose this market is represented by the dominant firm oligopoly model. If Wal. Mart is the dominant firm, which of the following is NOT true? A. Wal-Mart has a big cost advantage over the other firms and produces a large part of the industry output B. The other firms behave like perfect competitors taking Wal-Mart’s price as the market price C. Wal-Mart can retaliate against the other firms if they do not follow Wal-Mart’s pricing strategy D. All firms together produce the market quantity of prescription drugs demanded at Wal-Mart’s price Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 4. In a duopoly game we observe the following payouts: if the two firms collude they will each earn $50, 000. If one firm cheats then he earns $60, 000 and the other firm earns $10, 000. If both firms cheat then they each earn zero economic profit. In this game what is the Nash equilibrium? A. B. C. D. Both firms cheat. Only one firm will cheat. Neither firm will cheat. It is impossible to say. Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
4. In a duopoly game we observe the following payouts: if the two firms collude they will each earn $50, 000. If one firm cheats then he earns $60, 000 and the other firm earns $10, 000. If both firms cheat then they each earn zero economic profit. In this game what is the Nash equilibrium? A. B. C. D. Both firms cheat. Only one firm will cheat. Neither firm will cheat. It is impossible to say. Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 5. In 2008, a former Intel engineer has been charged with stealing trade secrets worth $1 billion. Intel owns 80 percent of the worldwide market for microprocessors, AMD has the rest. Conducting R&D is very expensive so suppose that each of these firms can either steal R&D or develop their own R&D. If both firms develop their own R&D, economic profit will be $50 million each. If one company steals R&D, that firm earns $100 million in economic profit while the other firm earns $10 million. If both firms steal R&D, each firm breaks even. What is the outcome of this game? A. B. C. D. Both firms will conduct R&D Both firms will steal R&D The outcome will be a dominant strategy equilibrium Only one firm will conduct R&D, but we cannot predict which firm will conduct R&D Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
5. In 2008, a former Intel engineer has been charged with stealing trade secrets worth $1 billion. Intel owns 80 percent of the worldwide market for microprocessors, AMD has the rest. Conducting R&D is very expensive so suppose that each of these firms can either steal R&D or develop their own R&D. If both firms develop their own R&D, economic profit will be $50 million each. If one company steals R&D, that firm earns $100 million in economic profit while the other firm earns $10 million. If both firms steal R&D, each firm breaks even. What is the outcome of this game? A. B. C. D. Both firms will conduct R&D Both firms will steal R&D The outcome will be a dominant strategy equilibrium Only one firm will conduct R&D, but we cannot predict which firm will conduct R&D Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 6. In a contestable market the Herfindahl. Hirschman Index is ____ and the market behaves as if it is ____. A. B. C. D. low; perfectly competitive low; a monopoly high; perfectly competitive high; a monopoly Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
6. In a contestable market the Herfindahl. Hirschman Index is ____ and the market behaves as if it is ____. A. B. C. D. low; perfectly competitive low; a monopoly high; perfectly competitive high; a monopoly Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 7. Russia and Qatar made the first serious moves in October 2008 toward forming an OPEC–style cartel on natural gas. The two strategies these countries face are to comply with the cartel agreement or to cheat on the cartel agreement. If all countries comply, the economic profit for both will be $140 million. If one country cheats, that country earns $200 million in economic profit and the other country has an economic loss of $10 million. If all countries cheat, they break even. What is the likely outcome of this game if it is repeated as a tit -for-tat game? A. B. C. D. If there are periods of cheating and colluding, then profits will be less than profits will be lower than if they always colluded If the countries never collude, the outcome will be the monopoly outcome If there are periods of cheating and colluding, then profits will be less than profits will be higher than if they always colluded If the countries always collude, the outcome will be the perfectly competitive outcome Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
7. Russia and Qatar made the first serious moves in October 2008 toward forming an OPEC–style cartel on natural gas. The two strategies these countries face are to comply with the cartel agreement or to cheat on the cartel agreement. If all countries comply, the economic profit for both will be $140 million. If one country cheats, that country earns $200 million in economic profit and the other country has an economic loss of $10 million. If all countries cheat, they break even. What is the likely outcome of this game if it is repeated as a tit -for-tat game? A. B. C. D. If there are periods of cheating and colluding, then profits will be less than profits will be lower than if they always colluded If the countries never collude, the outcome will be the monopoly outcome If there are periods of cheating and colluding, then profits will be less than profits will be higher than if they always colluded If the countries always collude, the outcome will be the perfectly competitive outcome Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 8. The main purpose of antitrust law is to A. prohibit monopoly practices such as restricting output. B. regulate advertising. C. encourage the formation of cartels. D. regulate the stock and bond markets. Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
8. The main purpose of antitrust law is to A. prohibit monopoly practices such as restricting output. B. regulate advertising. C. encourage the formation of cartels. D. regulate the stock and bond markets. Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 9. Under U. S. law, it’s a crime for competitors to collaborate on production or prices. However, many farm groups and cooperatives are allowed to work together under the 1922 Capper-Volstead Act. The act was originally meant to help small farms bargain with big processors but has now led to collusion and price fixing. What U. S. law (or set of laws) makes it a crime for competitors to collaborate on production or prices? A. B. C. D. The Sherman Act of 1890 The Clayton Act of 1914 The Antitrust Act of 1882 The Parkin Anti-Collusion act of 1907 Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
9. Under U. S. law, it’s a crime for competitors to collaborate on production or prices. However, many farm groups and cooperatives are allowed to work together under the 1922 Capper-Volstead Act. The act was originally meant to help small farms bargain with big processors but has now led to collusion and price fixing. What U. S. law (or set of laws) makes it a crime for competitors to collaborate on production or prices? A. B. C. D. The Sherman Act of 1890 The Clayton Act of 1914 The Antitrust Act of 1882 The Parkin Anti-Collusion act of 1907 Parkin Microeconomics, Ninth Edition © 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 10. Which of the following is a distinguishing characteristic of oligopoly? A) A small number of firms compete. B) No one firm's actions directly affect the actions of the other firms. C) Firms are free to enter and exit the industry. D) Natural barriers cannot prevent the entry of new firms.
10. Which of the following is a distinguishing characteristic of oligopoly? A) A small number of firms compete. B) No one firm's actions directly affect the actions of the other firms. C) Firms are free to enter and exit the industry. D) Natural barriers cannot prevent the entry of new firms.
 11. When producers agree to restrict output, raise the price, and increase profits, the agreement is called ____. A) a pricing agreement B) an oligopoly agreement C) a collusive agreement D) a monopoly agreement
11. When producers agree to restrict output, raise the price, and increase profits, the agreement is called ____. A) a pricing agreement B) an oligopoly agreement C) a collusive agreement D) a monopoly agreement
 12. Game theory is applicable to oligopoly behavior because oligopolists A) use strategic behavior. B) ignore rival firms. C) are price takers. D) can only be profitable if they collude.
12. Game theory is applicable to oligopoly behavior because oligopolists A) use strategic behavior. B) ignore rival firms. C) are price takers. D) can only be profitable if they collude.
 13. The simplest prisoners' dilemma is a game that, in part, requires A) two players who are able to communicate with each other. B) two players who are unable to communicate with each other. C) monopolistic competition. D) an oligopoly with one very large firm.
13. The simplest prisoners' dilemma is a game that, in part, requires A) two players who are able to communicate with each other. B) two players who are unable to communicate with each other. C) monopolistic competition. D) an oligopoly with one very large firm.
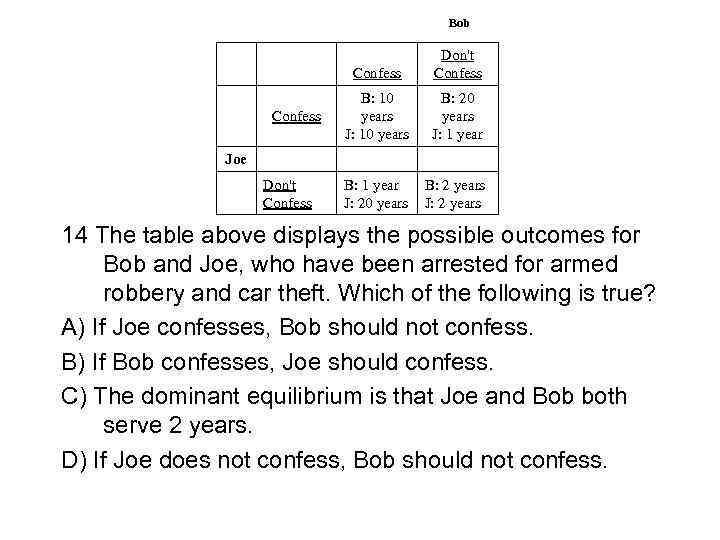 Bob Confess Don't Confess B: 10 years J: 10 years B: 20 years J: 1 year B: 1 year J: 20 years B: 2 years Joe Don't Confess 14 The table above displays the possible outcomes for Bob and Joe, who have been arrested for armed robbery and car theft. Which of the following is true? A) If Joe confesses, Bob should not confess. B) If Bob confesses, Joe should confess. C) The dominant equilibrium is that Joe and Bob both serve 2 years. D) If Joe does not confess, Bob should not confess.
Bob Confess Don't Confess B: 10 years J: 10 years B: 20 years J: 1 year B: 1 year J: 20 years B: 2 years Joe Don't Confess 14 The table above displays the possible outcomes for Bob and Joe, who have been arrested for armed robbery and car theft. Which of the following is true? A) If Joe confesses, Bob should not confess. B) If Bob confesses, Joe should confess. C) The dominant equilibrium is that Joe and Bob both serve 2 years. D) If Joe does not confess, Bob should not confess.
 Disney Thanksgiving release D: $100 F: $80 Christmas release D: $105 F: $95 Fox Christmas release D: $110 F: $100 D: $95 F: $85 15 Disney and Fox must decide when to release their next films. The revenues received by each studio depends in part on when the other studio releases its film. Each studio can release its film at Thanksgiving or at Christmas. The revenues received by each studio, in millions of dollars, are depicted in the payoff matrix above. Which of the following statements correctly describes Fox's strategy given what Disney's release choice may be? A) If Disney chooses a Thanksgiving release, Fox should choose a Christmas release. B) If Disney chooses a Christmas release, Fox should choose a Thanksgiving release. C) Fox should release on Christmas regardless of what Disney does. D) Both answers A and B are correct.
Disney Thanksgiving release D: $100 F: $80 Christmas release D: $105 F: $95 Fox Christmas release D: $110 F: $100 D: $95 F: $85 15 Disney and Fox must decide when to release their next films. The revenues received by each studio depends in part on when the other studio releases its film. Each studio can release its film at Thanksgiving or at Christmas. The revenues received by each studio, in millions of dollars, are depicted in the payoff matrix above. Which of the following statements correctly describes Fox's strategy given what Disney's release choice may be? A) If Disney chooses a Thanksgiving release, Fox should choose a Christmas release. B) If Disney chooses a Christmas release, Fox should choose a Thanksgiving release. C) Fox should release on Christmas regardless of what Disney does. D) Both answers A and B are correct.
 Consider a game with two players who cannot communicate, and in which each player is asked a question. The players can answer the question honestly or lie. If both answer honestly, each receives $100. If one player answers honestly and the other lies, the liar receives $500 and the honest player gets nothing. If both lie, then each receives $50. a. Describe the strategies and payoffs of this game. b. Construct the payoff matrix. c. What is the equilibrium of this game? d. Compare this game to the prisoners’ dilemma. Are the two games similar or different? Explain.
Consider a game with two players who cannot communicate, and in which each player is asked a question. The players can answer the question honestly or lie. If both answer honestly, each receives $100. If one player answers honestly and the other lies, the liar receives $500 and the honest player gets nothing. If both lie, then each receives $50. a. Describe the strategies and payoffs of this game. b. Construct the payoff matrix. c. What is the equilibrium of this game? d. Compare this game to the prisoners’ dilemma. Are the two games similar or different? Explain.


