Sess 11 Oligipoly and Antitrust regulation.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89

CHAPTER 15 OLIGOPOLY Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 1

OUTLINE Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 2

In some markets, there are only a few firms compete. For example, computer chips are made by Intel and Advanced Micro Devices and each firm must pay close attention to what the other firm is doing. How does competition between just two chip makers work? When a market has only a small number of firms, do they operate in the social interest, like firms in perfect competition? Or do they restrict output to increase profit, like a monopoly? The models of perfect competition and monopoly don’t predict the behavior of the firms we’ve just described. To understand how these markets work, we need the richer models. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 3

What Is Oligopoly? Oligopoly is a market structure in which Natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms. < A small number of firms compete. < Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 4
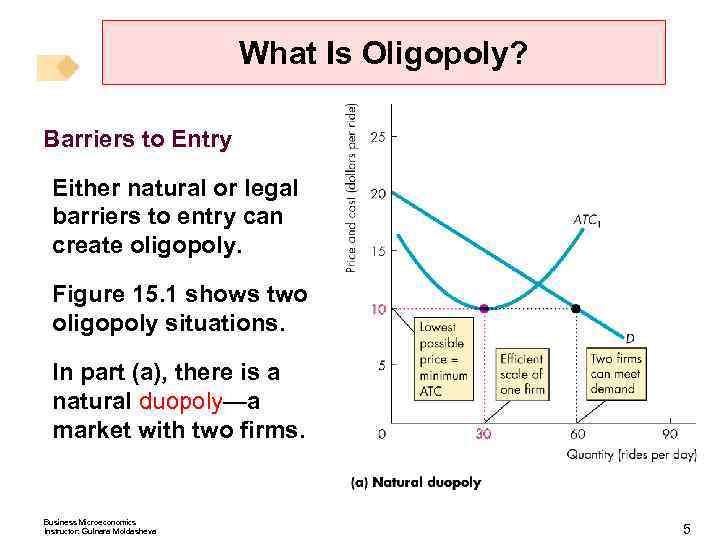
What Is Oligopoly? Barriers to Entry Either natural or legal barriers to entry can create oligopoly. Figure 15. 1 shows two oligopoly situations. In part (a), there is a natural duopoly—a market with two firms. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 5
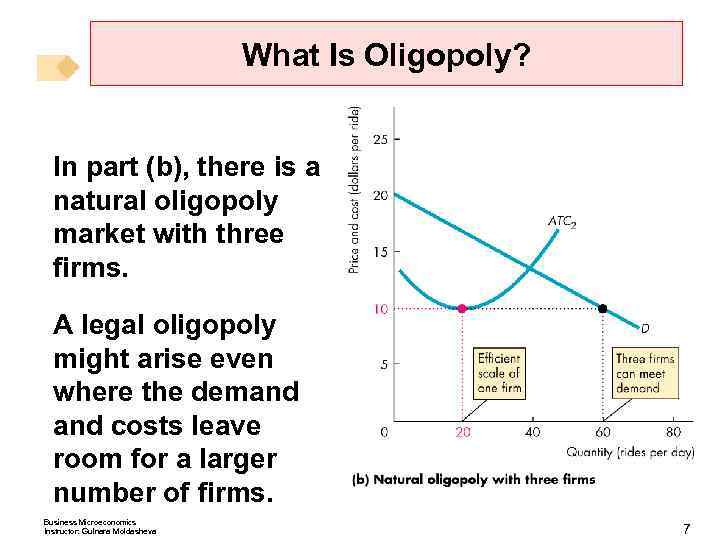
What Is Oligopoly? In part (b), there is a natural oligopoly market with three firms. A legal oligopoly might arise even where the demand costs leave room for a larger number of firms. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 7

What Is Oligopoly? Small Number of Firms Because an oligopoly market has a small number of firms, the firms are interdependent and face a temptation to cooperate. Interdependence: With a small number of firms, each firm’s profit depends on every firm’s actions. Cartel: A cartel and is an illegal group of firms acting together to limit output, raise price, and increase profit. Firms in oligopoly face the temptation to form a cartel, but aside from being illegal, cartels often break down. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 9

Two Traditional Oligopoly Models The Kinked Demand Curve Model In the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly, each firm believes that if it raises its price, its competitors will not follow, but if it lowers its price all of its competitors will follow. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 10
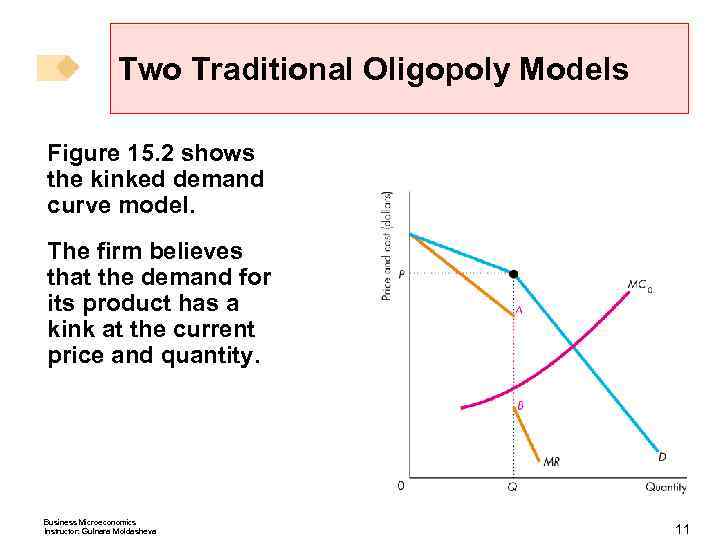
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models Figure 15. 2 shows the kinked demand curve model. The firm believes that the demand for its product has a kink at the current price and quantity. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 11
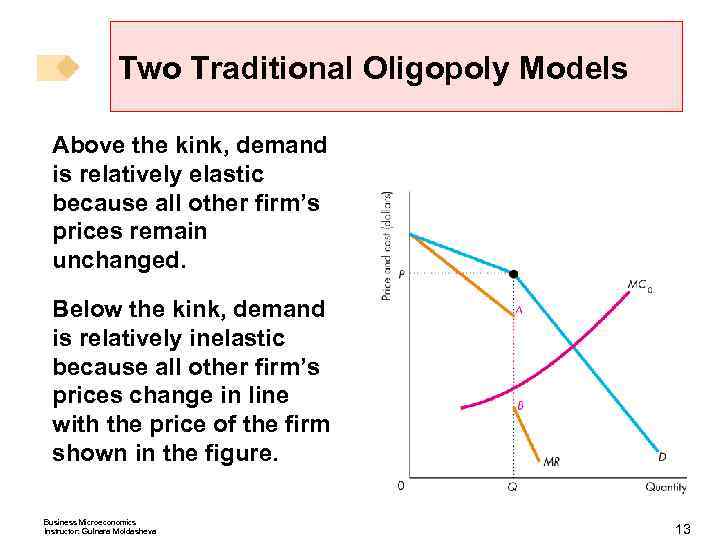
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models Above the kink, demand is relatively elastic because all other firm’s prices remain unchanged. Below the kink, demand is relatively inelastic because all other firm’s prices change in line with the price of the firm shown in the figure. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 13
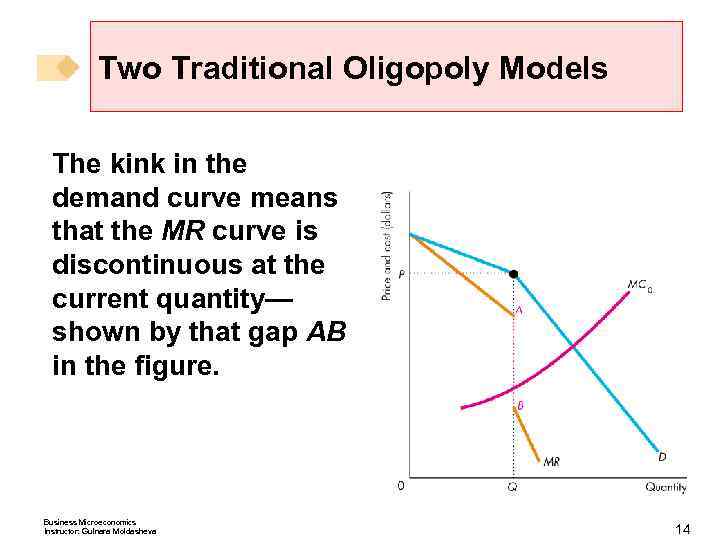
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models The kink in the demand curve means that the MR curve is discontinuous at the current quantity— shown by that gap AB in the figure. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 14
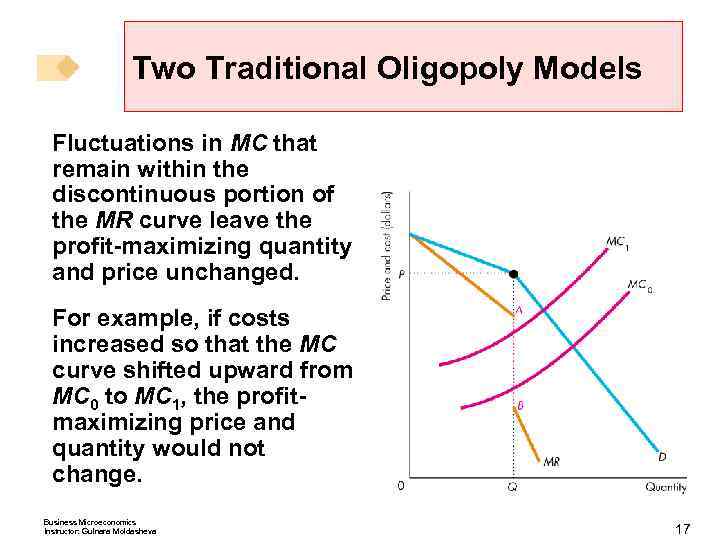
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models Fluctuations in MC that remain within the discontinuous portion of the MR curve leave the profit-maximizing quantity and price unchanged. For example, if costs increased so that the MC curve shifted upward from MC 0 to MC 1, the profitmaximizing price and quantity would not change. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 17
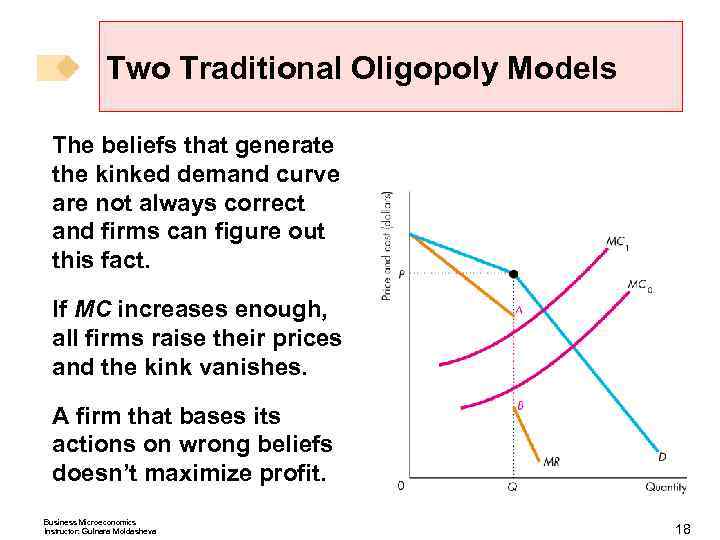
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models The beliefs that generate the kinked demand curve are not always correct and firms can figure out this fact. If MC increases enough, all firms raise their prices and the kink vanishes. A firm that bases its actions on wrong beliefs doesn’t maximize profit. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 18

Two Traditional Oligopoly Models Dominant Firm Oligopoly In a dominant firm oligopoly, there is one large firm that has a significant cost advantage over many other, smaller competing firms. The large firm operates as a monopoly, setting its price and output to maximize its profit. The small firms act as perfect competitors, taking as given the market price set by the dominant firm. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 19
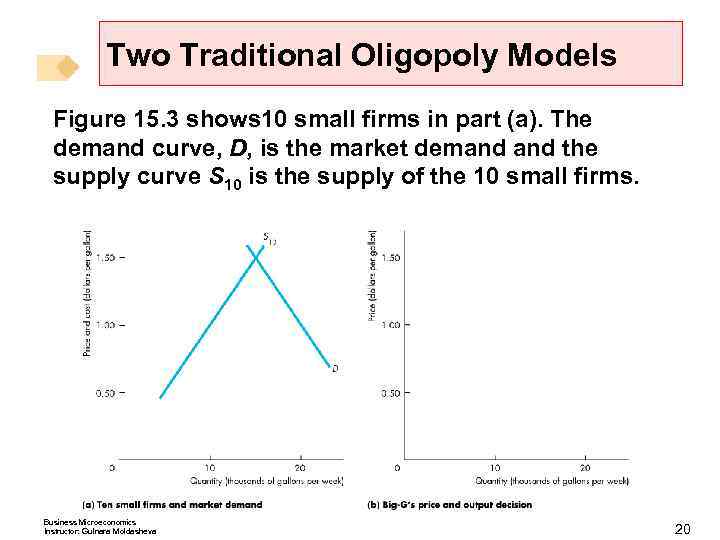
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models Figure 15. 3 shows 10 small firms in part (a). The demand curve, D, is the market demand the supply curve S 10 is the supply of the 10 small firms. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 20
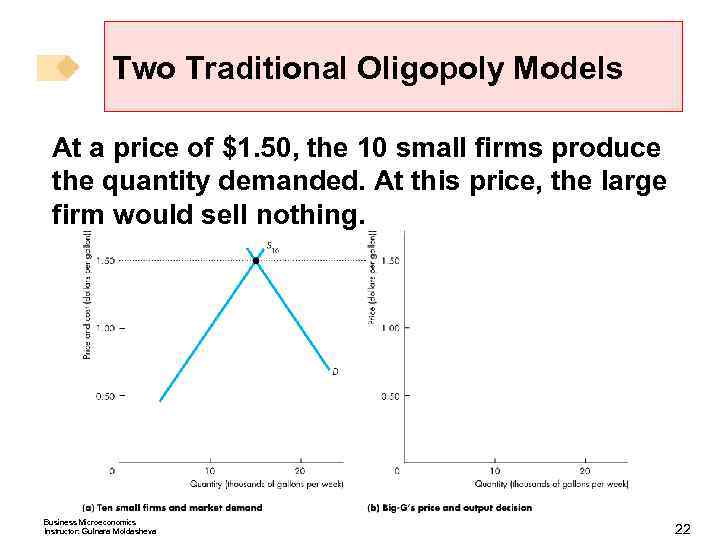
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models At a price of $1. 50, the 10 small firms produce the quantity demanded. At this price, the large firm would sell nothing. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 22
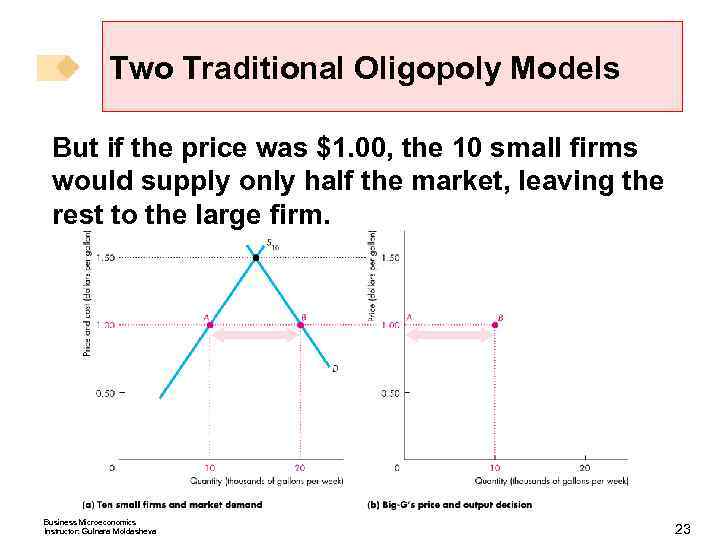
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models But if the price was $1. 00, the 10 small firms would supply only half the market, leaving the rest to the large firm. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 23
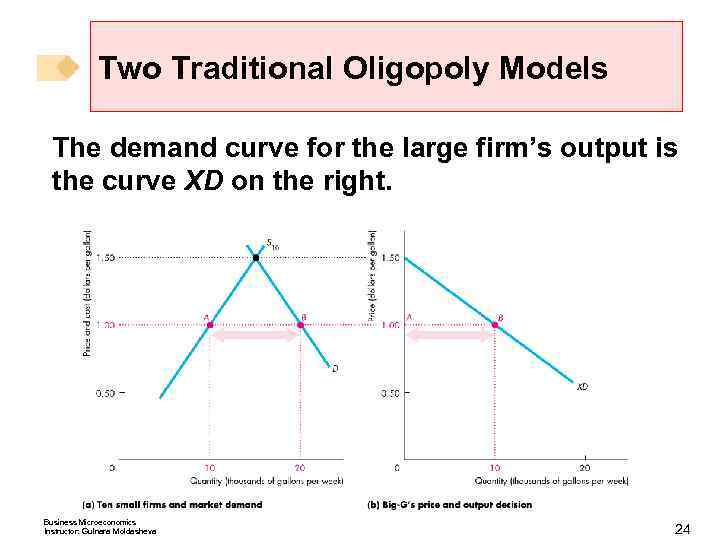
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models The demand curve for the large firm’s output is the curve XD on the right. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 24
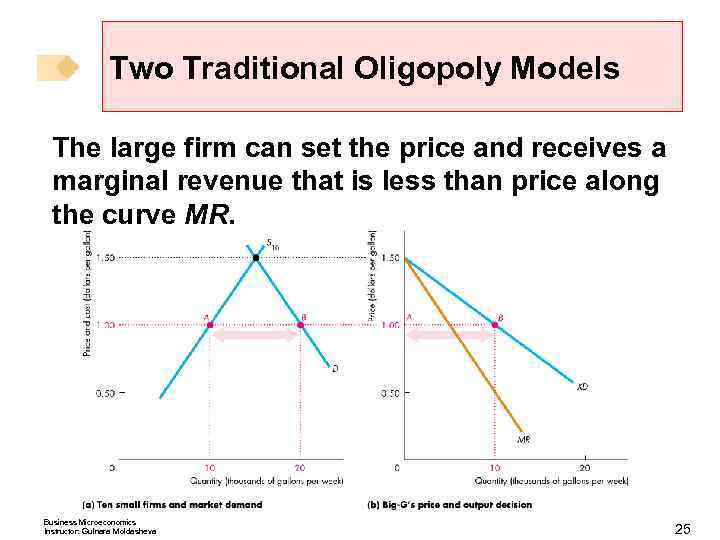
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models The large firm can set the price and receives a marginal revenue that is less than price along the curve MR. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 25
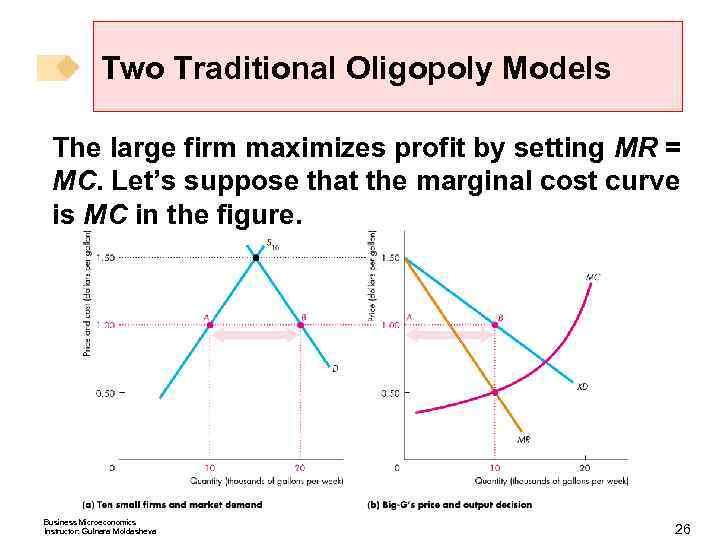
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models The large firm maximizes profit by setting MR = MC. Let’s suppose that the marginal cost curve is MC in the figure. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 26
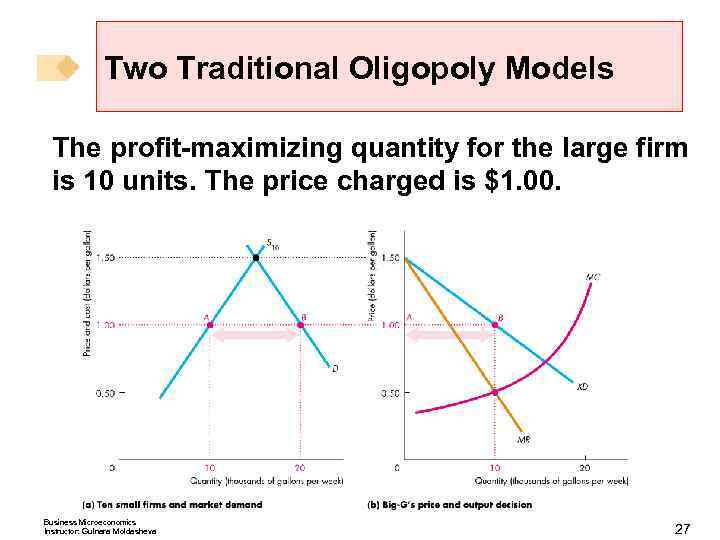
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models The profit-maximizing quantity for the large firm is 10 units. The price charged is $1. 00. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 27
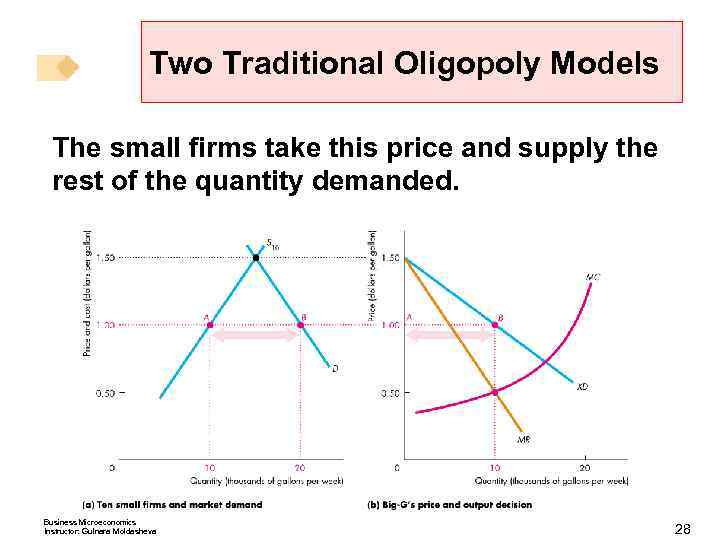
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models The small firms take this price and supply the rest of the quantity demanded. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 28
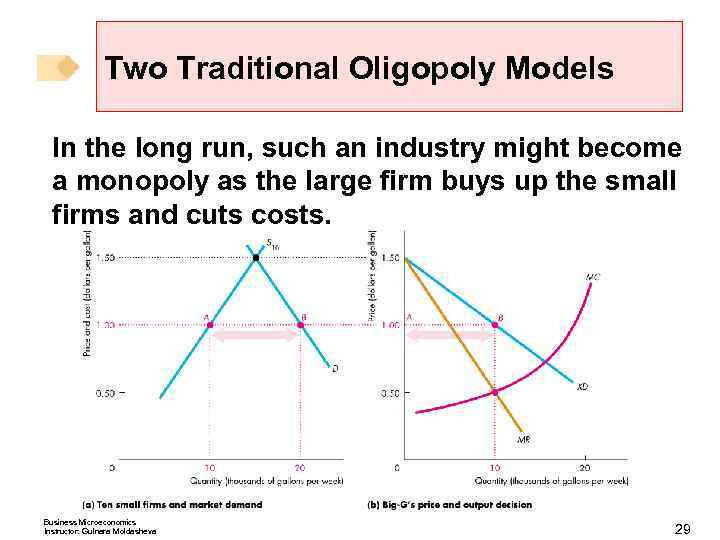
Two Traditional Oligopoly Models In the long run, such an industry might become a monopoly as the large firm buys up the small firms and cuts costs. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 29

Oligopoly Games Game theory is a tool for studying strategic behavior, which is behavior that takes into account the expected behavior of others and the mutual recognition of interdependence. The Prisoners’ Dilemma The prisoners’ dilemma game illustrates the four features of a game. Rules < Strategies < Payoffs < Outcome < Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 30

Oligopoly Games Rules The rules describe the setting of the game, the actions the players may take, and the consequences of those actions. In the prisoners’ dilemma game, two prisoners (Art and Bob) have been caught committing a petty crime. Each is held in a separate cell and cannot communicate with each other. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 31

Oligopoly Games Each is told that both are suspected of committing a more serious crime. If one of them confesses, he will get a 1 -year sentence for cooperating while his accomplice get a 10 -year sentence for both crimes. If both confess to the more serious crime, each receives 3 years in jail for both crimes. If neither confesses, each receives a 2 -year sentence for the minor crime only. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 32

Oligopoly Games Strategies are all the possible actions of each player. Art and Bob each have two possible actions: 1. Confess to the larger crime. 2. Deny having committed the larger crime. With two players and two actions for each player, there are four possible outcomes: 1. Both confess. 2. Both deny. 3. Art confesses and Bob denies. 4. Bob confesses and Art denies. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 33

Oligopoly Games Payoffs Each prisoner can work out what happens to him—can work out his payoff—in each of the four possible outcomes. We can tabulate these outcomes in a payoff matrix. A payoff matrix is a table that shows the payoffs for every possible action by each player for every possible action by the other player. The next slide shows the payoff matrix for this prisoners’ dilemma game. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 34
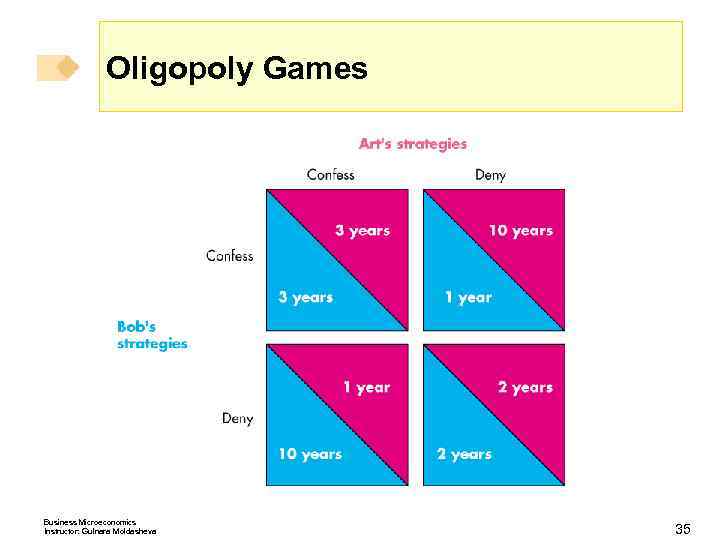
Oligopoly Games Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 35

Oligopoly Games Outcome If a player makes a rational choice in pursuit of his own best interest, he chooses the action that is best for him, given any action taken by the other player. If both players are rational and choose their actions in this way, the outcome is an equilibrium called Nash equilibrium—first proposed by John Nash. Finding the Nash Equilibrium The following slides show to find the Nash equilibrium. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 36
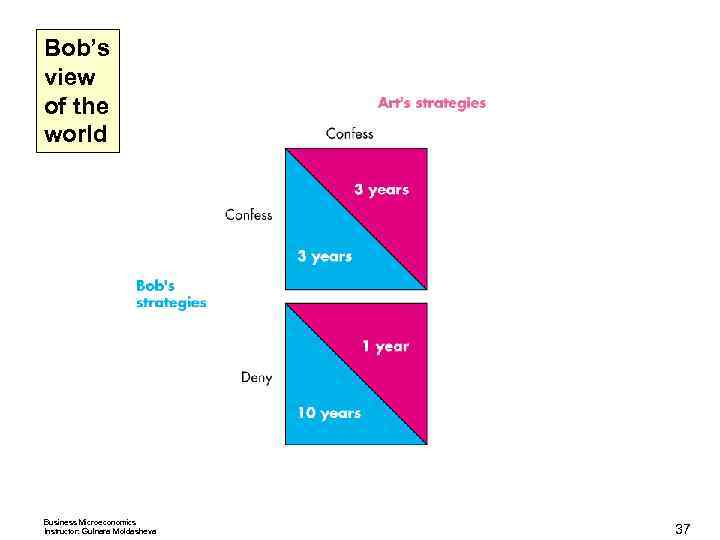
Bob’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 37
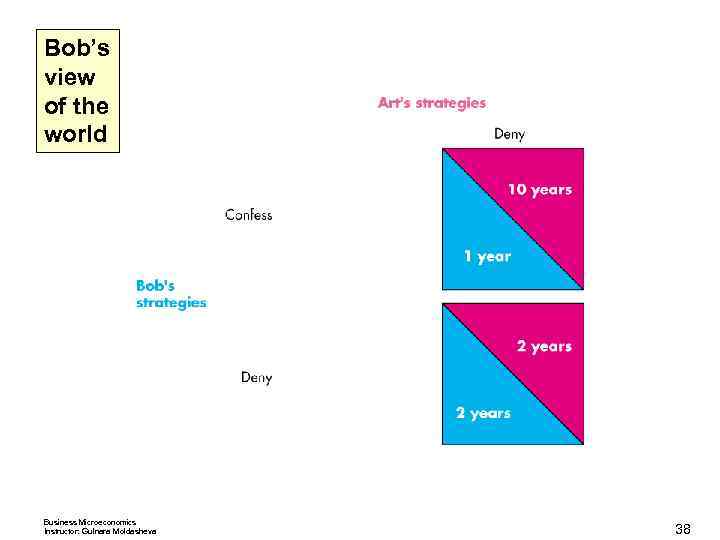
Bob’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 38
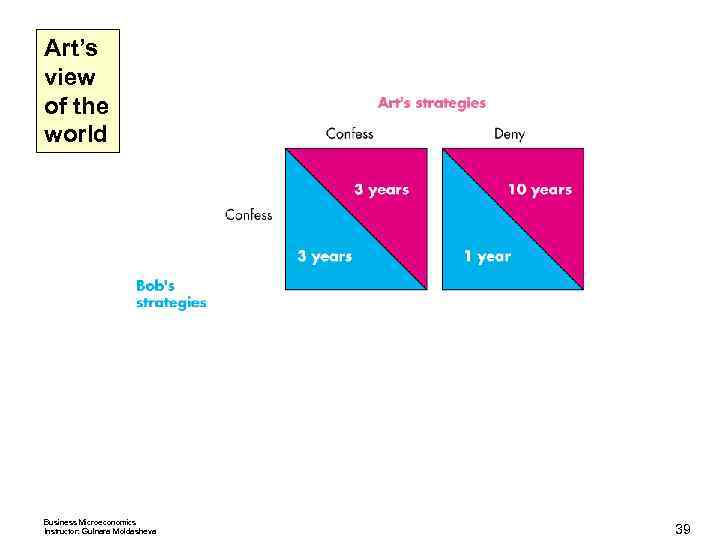
Art’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 39
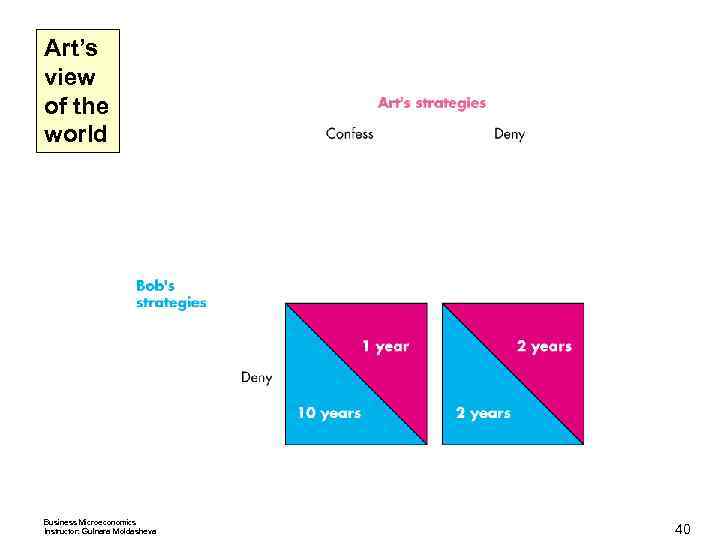
Art’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 40
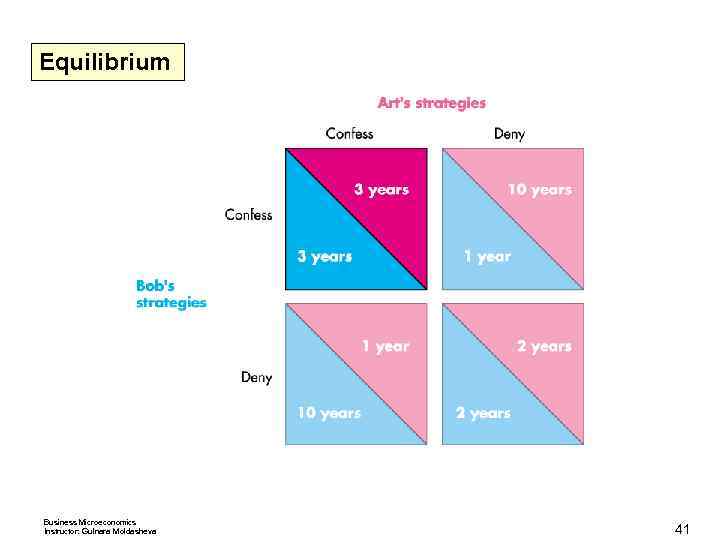
Equilibrium Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 41

Oligopoly Games An Oligopoly Price-Fixing Game A game like the prisoners’ dilemma is played in duopoly. A duopoly is a market in which there are only two producers that compete. Duopoly captures the essence of oligopoly. Cost and Demand Conditions Figure 15. 4 on the next slide describes the cost and demand situation in a natural duopoly. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 42
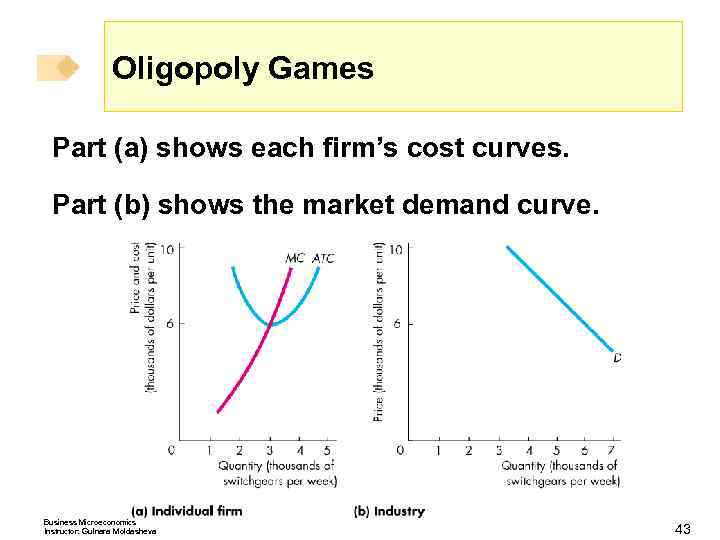
Oligopoly Games Part (a) shows each firm’s cost curves. Part (b) shows the market demand curve. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 43
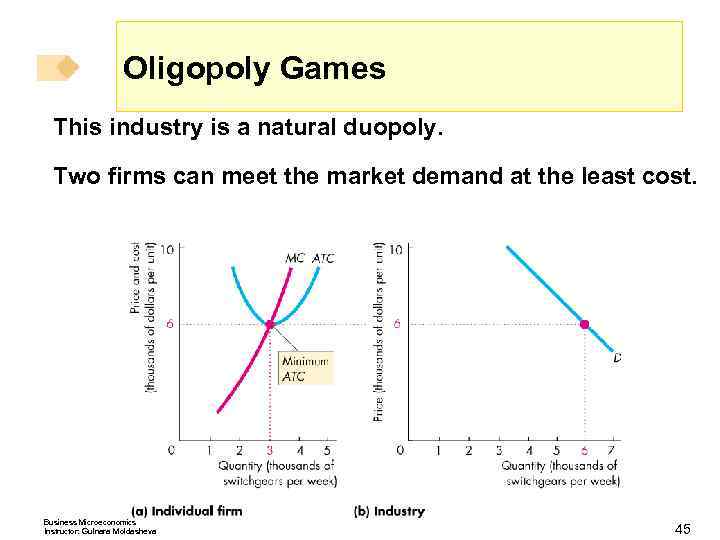
Oligopoly Games This industry is a natural duopoly. Two firms can meet the market demand at the least cost. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 45
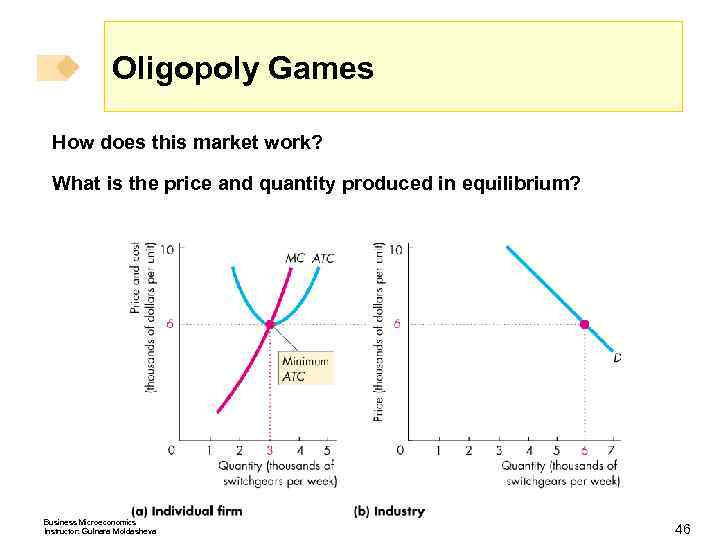
Oligopoly Games How does this market work? What is the price and quantity produced in equilibrium? Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 46

Oligopoly Games Collusion Suppose that the two firms enter into a collusive agreement. A collusive agreement is an agreement between two (or more) firms to restrict output, raise the price, and increase profits. Such agreements are illegal in the United States and are undertaken in secret. Firms in a collusive agreement operate a cartel. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 47

Oligopoly Games The strategies that firms in a cartel can pursue are to § Comply § Cheat Because each firm has two strategies, there are four possible combinations of actions for the firms: 1. Both comply. 2. Both cheat. 3. Trick complies and Gear cheats. 4. Gear complies and Trick cheats. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 48
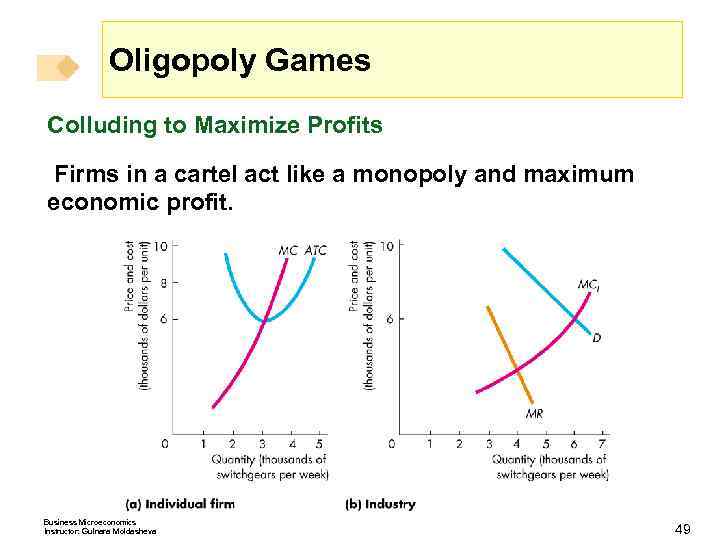
Oligopoly Games Colluding to Maximize Profits Firms in a cartel act like a monopoly and maximum economic profit. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 49
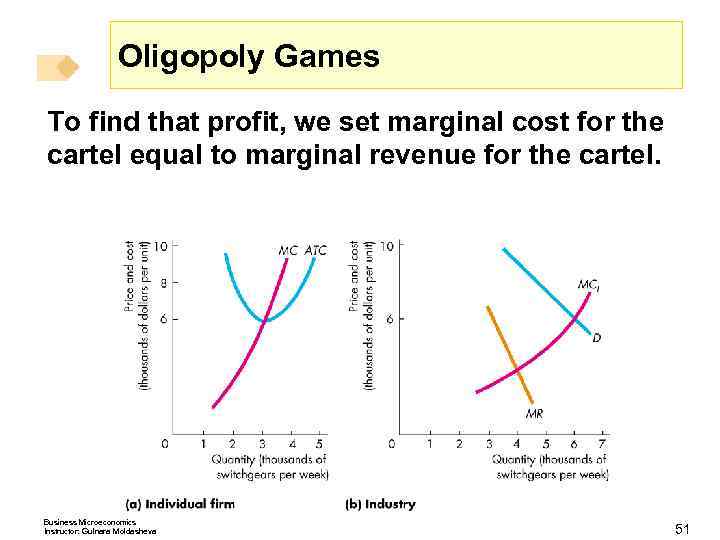
Oligopoly Games To find that profit, we set marginal cost for the cartel equal to marginal revenue for the cartel. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 51
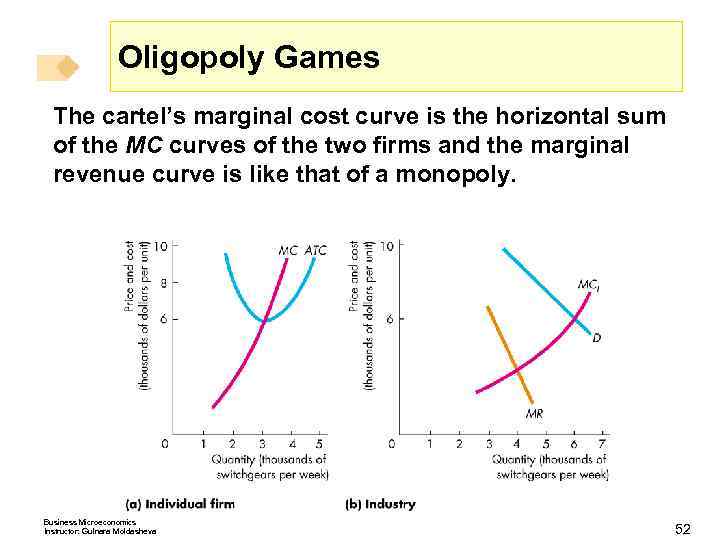
Oligopoly Games The cartel’s marginal cost curve is the horizontal sum of the MC curves of the two firms and the marginal revenue curve is like that of a monopoly. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 52
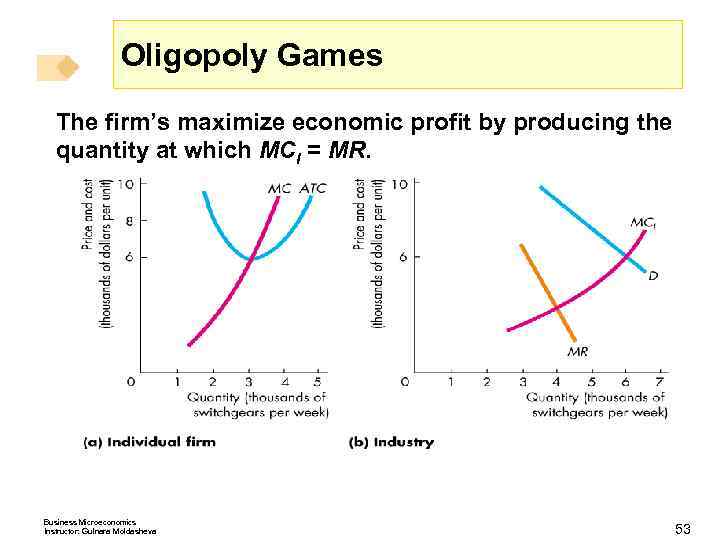
Oligopoly Games The firm’s maximize economic profit by producing the quantity at which MCI = MR. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 53
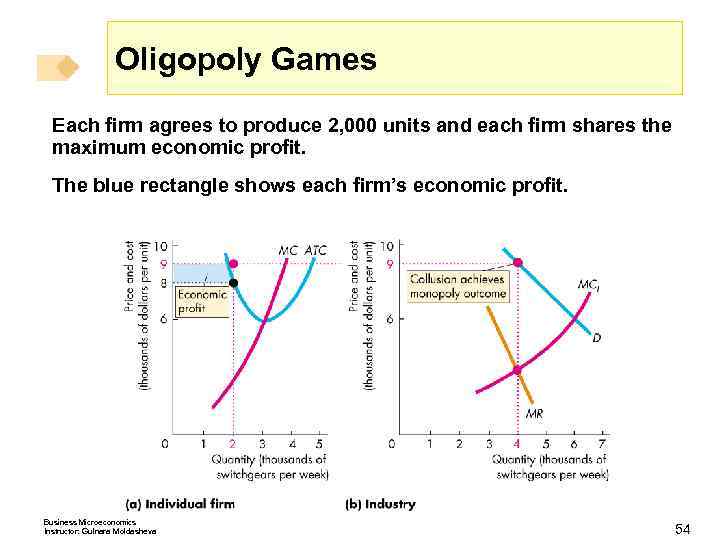
Oligopoly Games Each firm agrees to produce 2, 000 units and each firm shares the maximum economic profit. The blue rectangle shows each firm’s economic profit. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 54
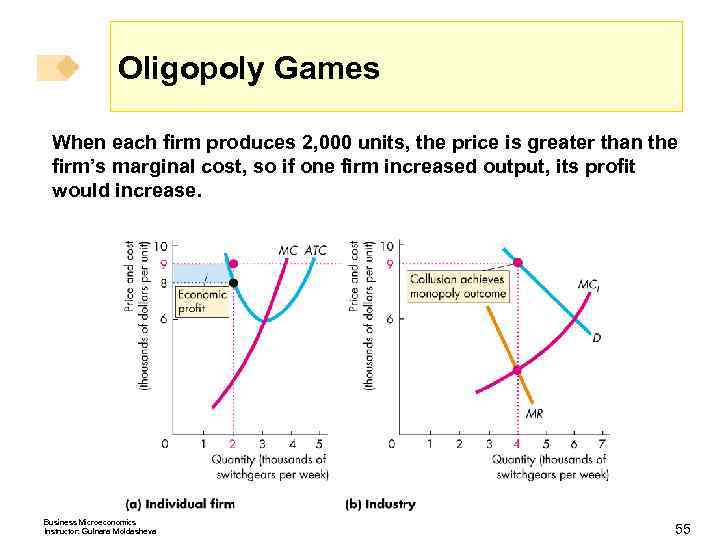
Oligopoly Games When each firm produces 2, 000 units, the price is greater than the firm’s marginal cost, so if one firm increased output, its profit would increase. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 55
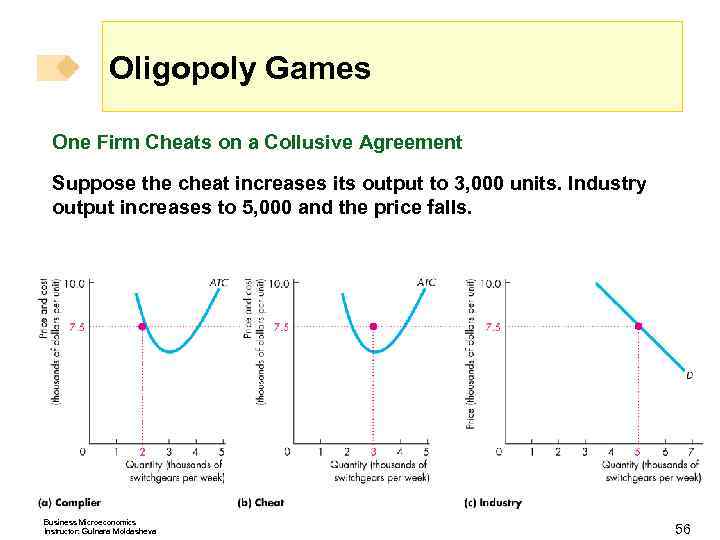
Oligopoly Games One Firm Cheats on a Collusive Agreement Suppose the cheat increases its output to 3, 000 units. Industry output increases to 5, 000 and the price falls. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 56
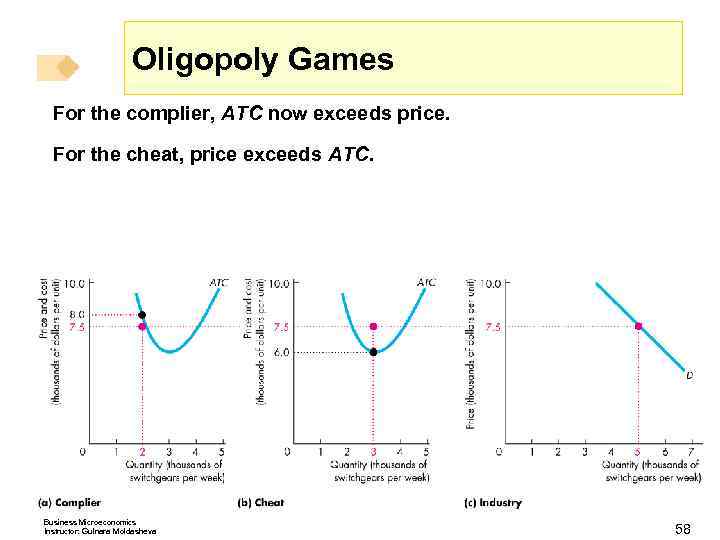
Oligopoly Games For the complier, ATC now exceeds price. For the cheat, price exceeds ATC. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 58
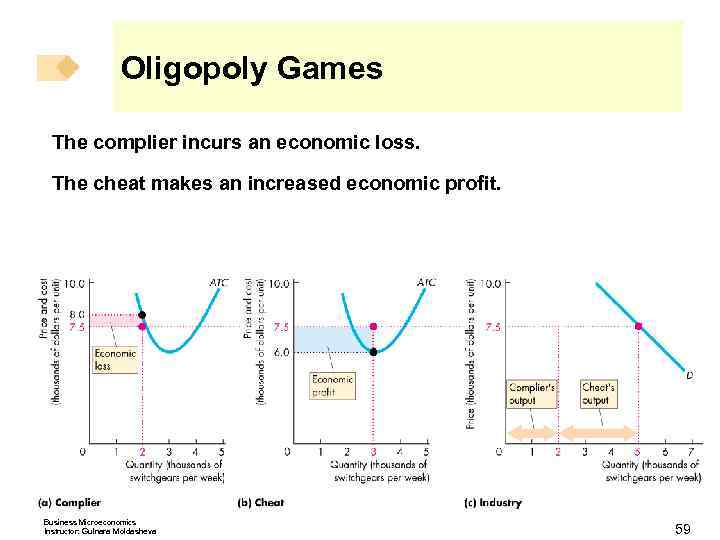
Oligopoly Games The complier incurs an economic loss. The cheat makes an increased economic profit. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 59
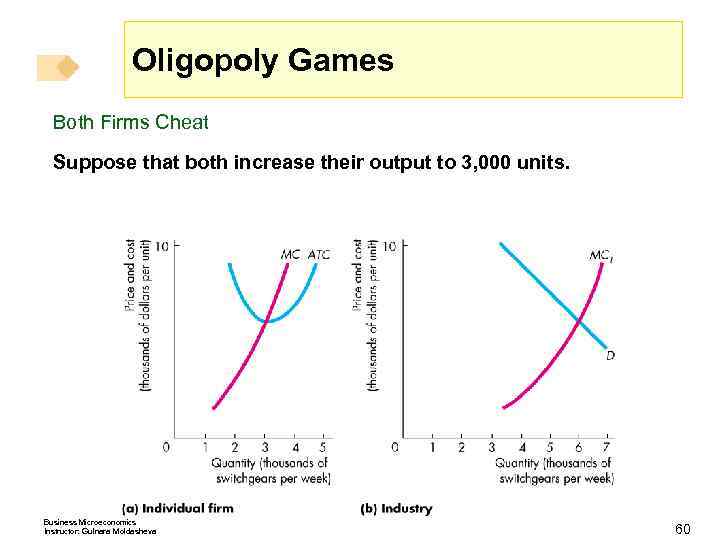
Oligopoly Games Both Firms Cheat Suppose that both increase their output to 3, 000 units. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 60
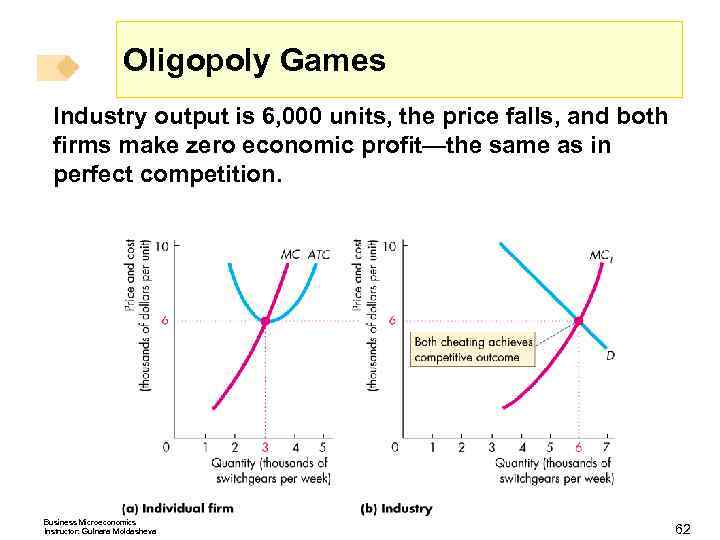
Oligopoly Games Industry output is 6, 000 units, the price falls, and both firms make zero economic profit—the same as in perfect competition. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 62
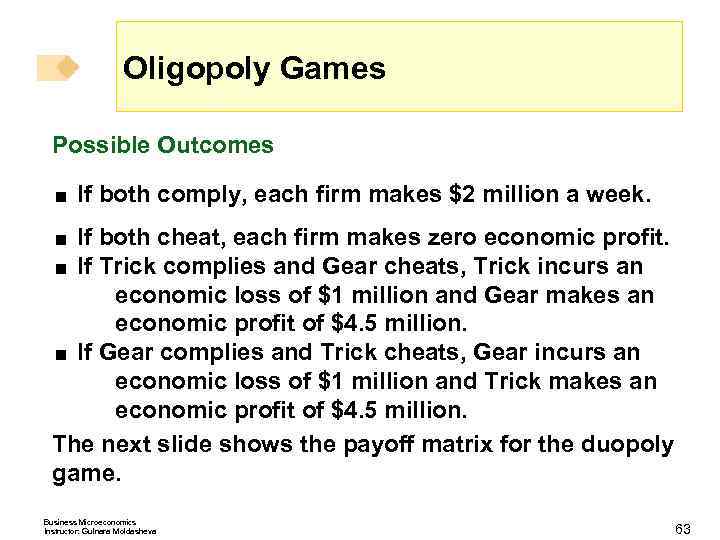
Oligopoly Games Possible Outcomes < If both comply, each firm makes $2 million a week. If both cheat, each firm makes zero economic profit. < If Trick complies and Gear cheats, Trick incurs an economic loss of $1 million and Gear makes an economic profit of $4. 5 million. < If Gear complies and Trick cheats, Gear incurs an economic loss of $1 million and Trick makes an economic profit of $4. 5 million. The next slide shows the payoff matrix for the duopoly game. < Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 63
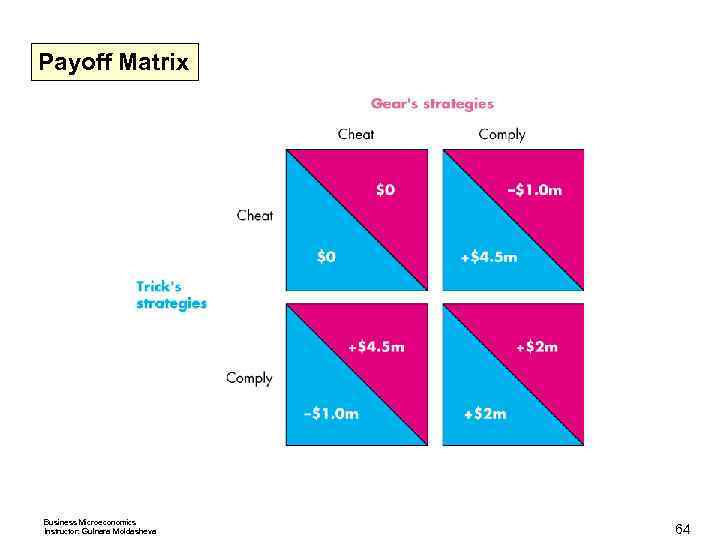
Payoff Matrix Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 64
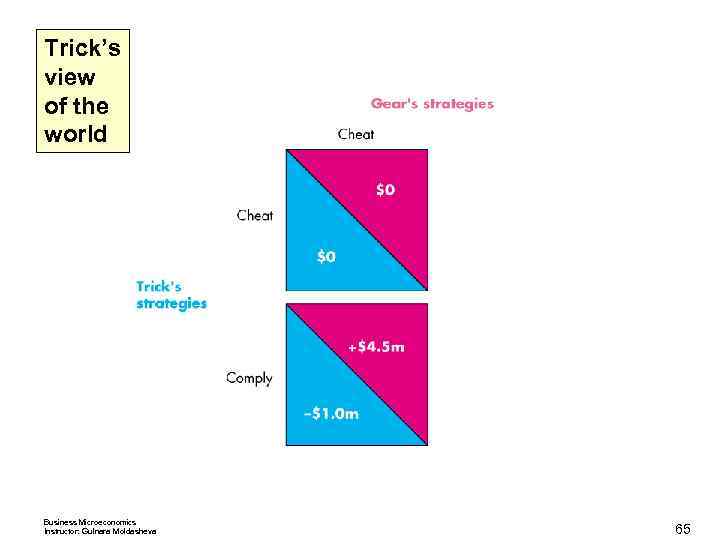
Trick’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 65
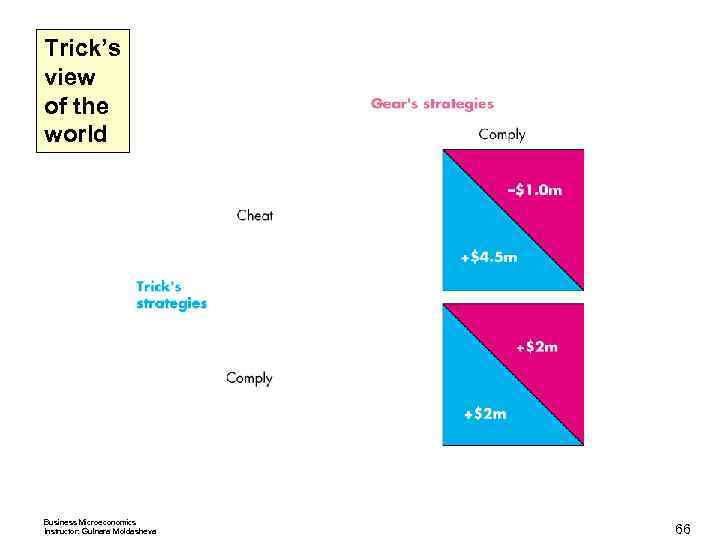
Trick’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 66
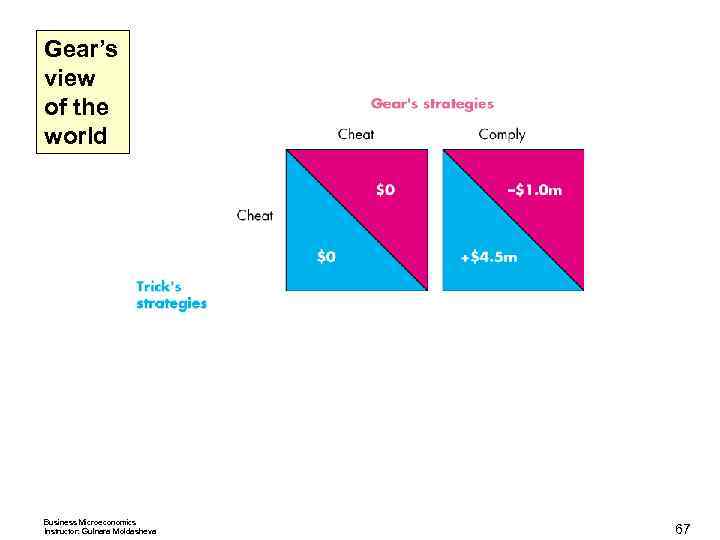
Gear’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 67
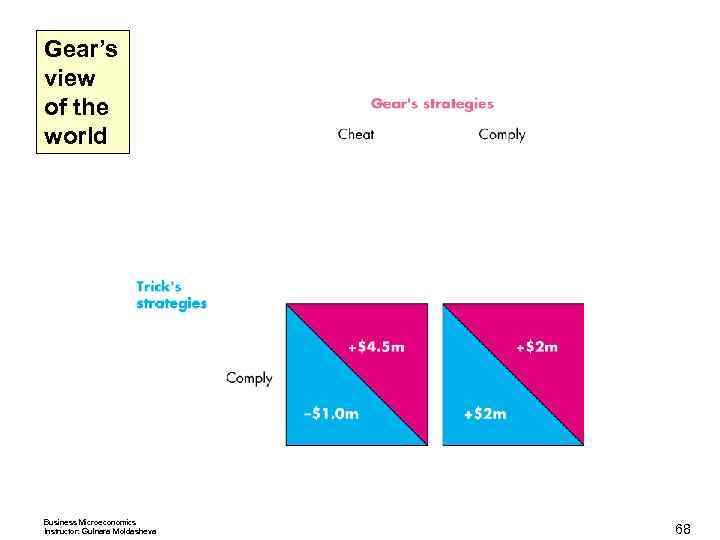
Gear’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 68
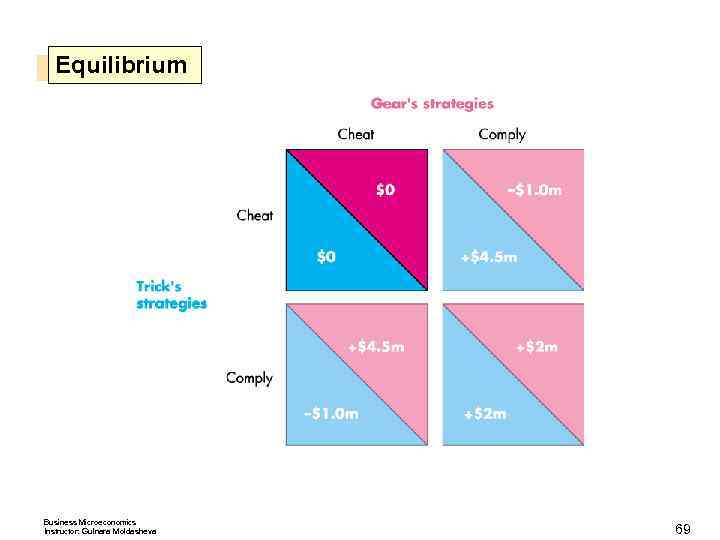
Equilibrium Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 69

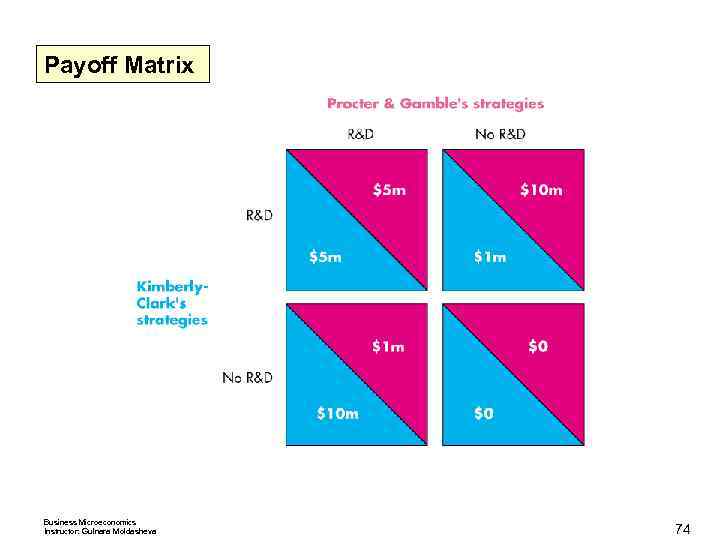
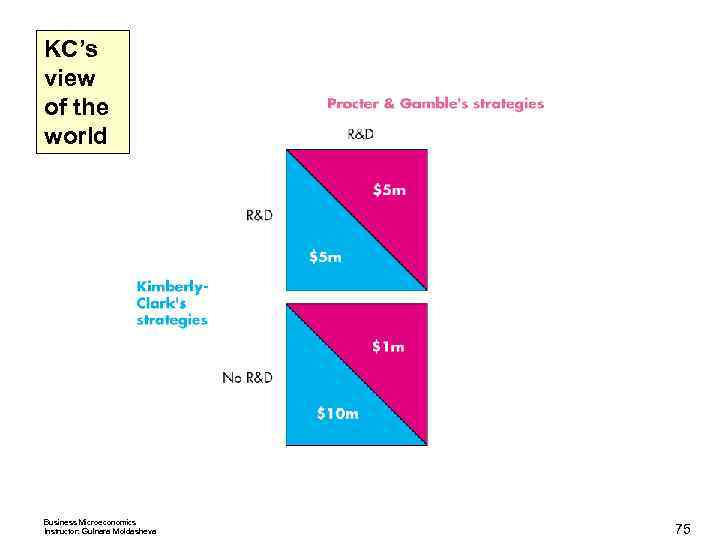
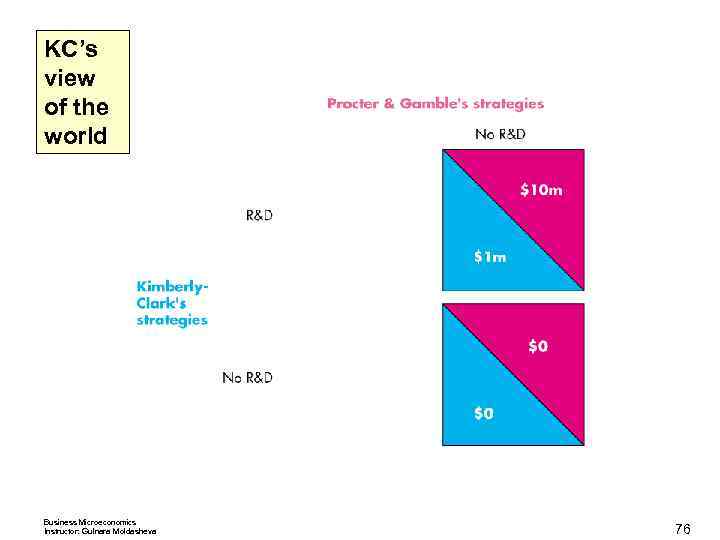
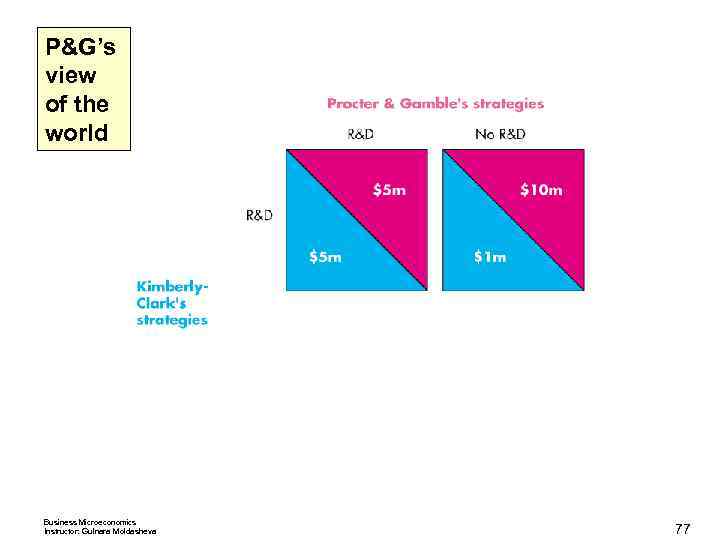
Oligopoly Games Nash Equilibrium in Duopolists’ Dilemma The Nash equilibrium is that both firms cheat. The quantity and price are those of a competitive market, and the firms make zero economic profit. Other Oligopoly Games Advertising and R&D games are also prisoners’ dilemmas. An R&D Game Procter & Gamble and Kimberley Clark play an R&D game in the market for disposable diapers. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 70
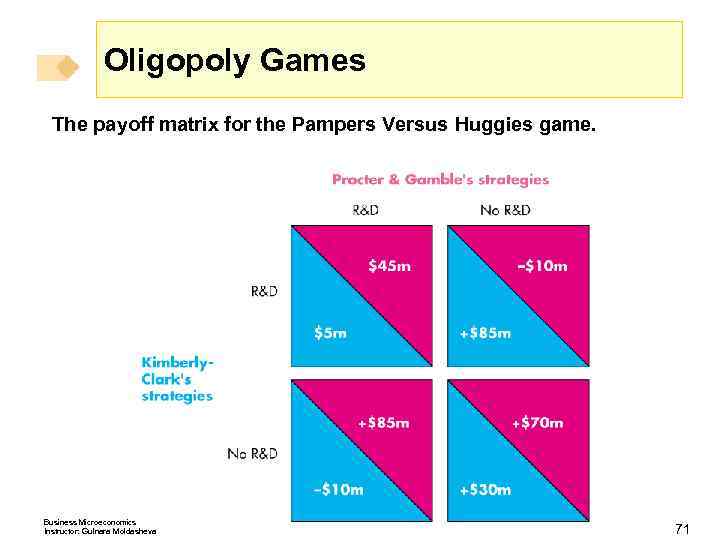
Oligopoly Games The payoff matrix for the Pampers Versus Huggies game. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 71

Oligopoly Games The Disappearing Invisible Hand In all the versions of the prisoners’ dilemma that we’ve examined, the players end up worse off than they would if they were able to cooperate. The pursuit of self-interest does not promote the social interest in these games. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 72

Oligopoly Games A Game of Chicken In the prisoners’ dilemma game, the Nash equilibrium is a dominant strategy equilibrium, by which we mean the best strategy for each player is independent of what the other player does. Not all games have such an equilibrium. One that doesn’t is the game of “chicken. ” Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 73
Payoff Matrix Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 74
KC’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 75
KC’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 76
P&G’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 77
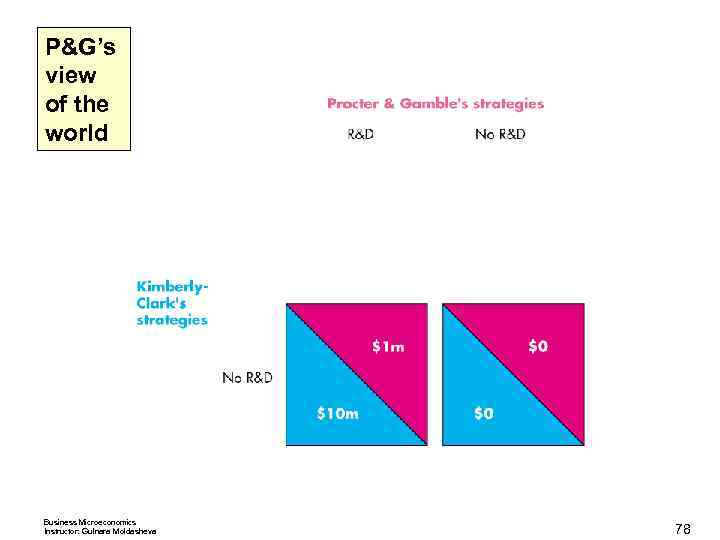
P&G’s view of the world Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 78
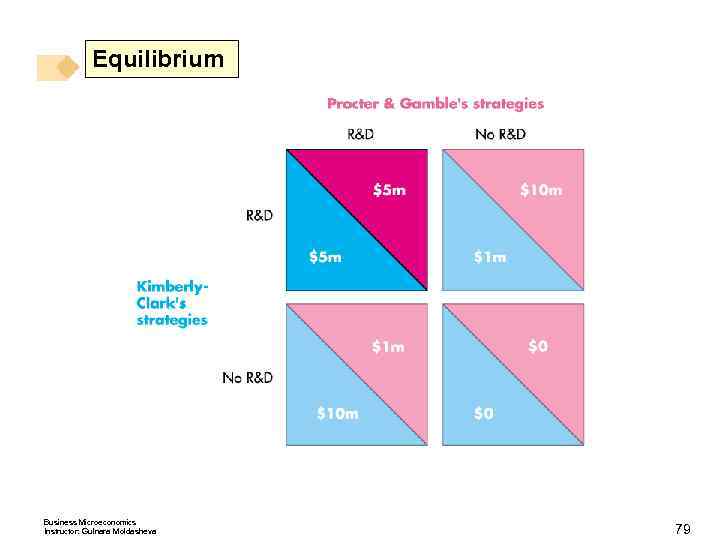
Equilibrium Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 79

Repeated Games and Sequential Games A Repeated Duopoly Game If a game is played repeatedly, it is possible for duopolists to successfully collude and make a monopoly profit. If the players take turns and move sequentially (rather than simultaneously as in the prisoner’s dilemma), many outcomes are possible. In a repeated prisoners’ dilemma duopoly game, additional punishment strategies enable the firms to comply and achieve a cooperative equilibrium, in which the firms make and share the monopoly profit. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 80

Repeated Games and Sequential Games One possible punishment strategy is a tit-for-tat strategy. A tit-for-tat strategy is one in which one player cooperates this period if the other player cooperated in the previous period but cheats in the current period if the other player cheated in the previous period. A more severe punishment strategy is a trigger strategy. A trigger strategy is one in which a player cooperates if the other player cooperates but plays the Nash equilibrium strategy forever thereafter if the other player cheats. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 81
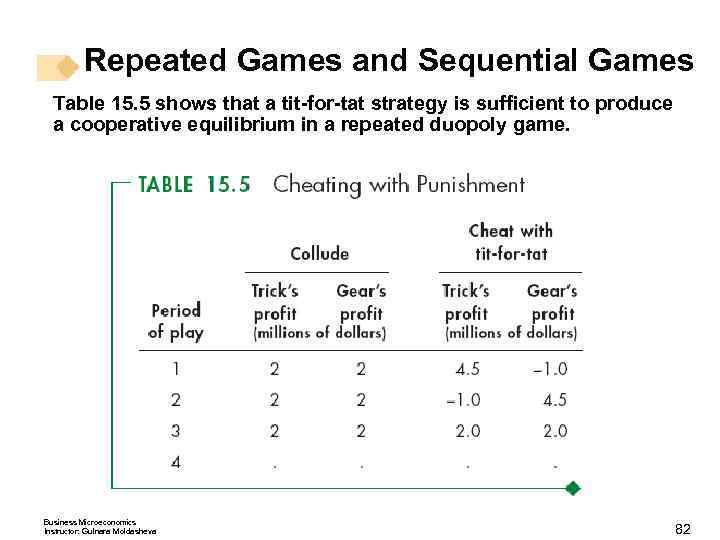
Repeated Games and Sequential Games Table 15. 5 shows that a tit-for-tat strategy is sufficient to produce a cooperative equilibrium in a repeated duopoly game. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 82

Repeated Games and Sequential Games Price wars might result from a tit-for-tat strategy where there is an additional complication—uncertainty about changes in demand. A fall in demand might lower the price and bring forth a round of tit-for-tat punishment. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 84

Repeated Games and Sequential Games A Sequential Entry Game in a Contestable Market In a contestable market—a market in which firms can enter and leave so easily that firms in the market face competition from potential entrants—firms play a sequential entry game. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 85

Repeated Games and Sequential Games Figure 15. 8 shows the game tree for a sequential entry game in a contestable market. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 86
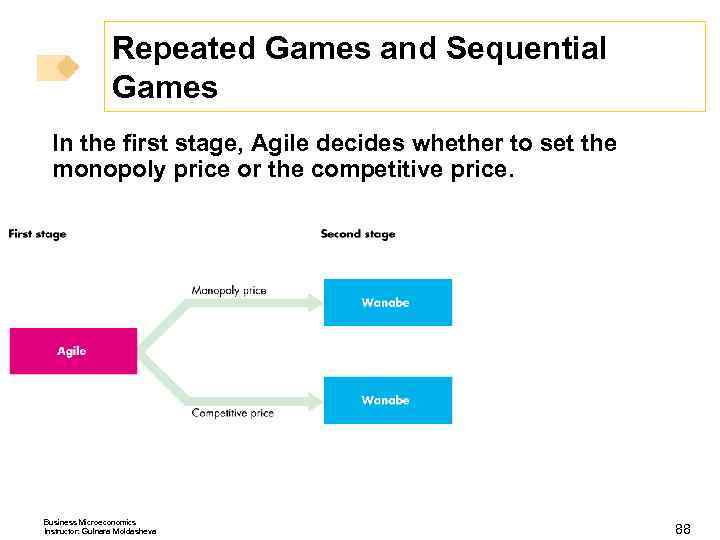
Repeated Games and Sequential Games In the first stage, Agile decides whether to set the monopoly price or the competitive price. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 88
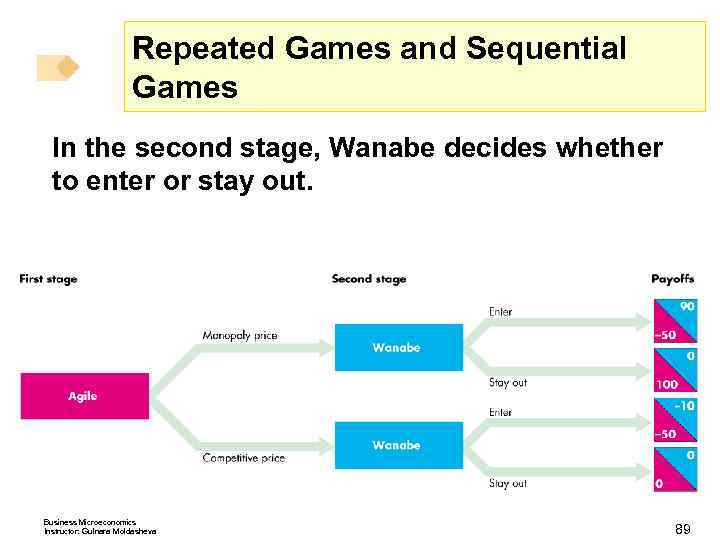
Repeated Games and Sequential Games In the second stage, Wanabe decides whether to enter or stay out. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 89

Repeated Games and Sequential Games In the equilibrium of this entry game, Agile sets a competitive price and makes zero economic profit to keep Wanabe out. A less costly strategy is limit pricing, which sets the price at the highest level that is consistent with keeping the potential entrant out. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 90

Antitrust Law Antitrust law provides an alternative way in which the government may influence the marketplace. The Antitrust Laws The first antitrust law, the Sherman Act, was passed in 1890. It outlawed any “combination, trust, or conspiracy that restricts interstate trade, ” and prohibited the “attempt to monopolize. ” Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 91

Antitrust Law Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 92

Antitrust Law A wave of merger activities at the beginning of the twentieth century produced a stronger antitrust law, the Clayton Act, and created the Federal Trade Commission. The Clayton Act was passed in 1914. The Clayton Act made illegal specific business practices such as price discrimination, interlocking directorships, and acquisition of a competitor’s shares if the practices “substantially lessen competition or create monopoly. ” Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 93

Antitrust Law Table 15. 7 (next slide) summarizes the Clayton Act and its amendments, the Robinson. Patman Act passed in 1936 and the Cellar. Kefauver Act passed in 1950. The Federal Trade Commission, formed in 1914, looks for cases of “unfair methods of competition and unfair or deceptive business practices. ” Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 94

Antitrust Law Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 95

Antitrust Law Price Fixing Always Illegal Price fixing is always a violation of the antitrust law. If the Justice Department can prove the existence of price fixing, there is no defense. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 96

Antitrust Law Three Antitrust Policy Debates But some practices are more controversial and generate debate. Three of them are < Resale price maintenance < Tying arrangements < Predatory pricing Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 97

Antitrust Law Resale Price Maintenance Most manufacturers sell their product to the final consumer through a wholesale and retail distribution chain. Resale price maintenance occurs when a manufacturer agrees with a distributor on the price at which the product will be resold. Resale price maintenance is inefficient if it promotes monopoly pricing. But resale price maintenance can be efficient if it provides retailers with an incentive to provide an efficient level of retail service in selling a product. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 98

Antitrust Law Tying Arrangements A tying arrangement is an agreement to sell one product only if the buyer agrees to buy another different product as well. Some people argue that by tying, a firm can make a larger profit. Where buyers have a differing willingness to pay for the separate items, a firm can price discriminate and take a larger amount of the consumer surplus by tying. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 99

Antitrust Law Predatory Pricing Predatory pricing is setting a low price to drive competitors out of business with the intention of then setting the monopoly price. Economists are skeptical that predatory pricing actually occurs. A high, certain, and immediate loss is a poor exchange for a temporary, uncertain, and future gain. No case of predatory pricing has been definitively found. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva 100

Antitrust Law Merger Rules The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) uses guidelines to determine which mergers to examine and possibly block. The Herfindahl-Hirschman index (HHI) is one of those guidelines (explained in Chapter 9). § If the original HHI is between 1, 000 and 1, 800, any merger that raises the HHI by 100 or more is challenged. § If the original HHI is greater than 1, 800, any merger that the HHI by more than 50 is challenged. Business Microeconomics Instructor: Gulnara Moldasheva raises 101
Sess 11 Oligipoly and Antitrust regulation.ppt