633e03be8f277e24ea699a1ff8bac581.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Chapter 15 Nationalism & Revolution Around the World How did nationalism affect the world in the interwar years?
Chapter 15 Nationalism & Revolution Around the World How did nationalism affect the world in the interwar years?
 Warm-Up: Based on your knowledge of European nationalism, predict how nationalism might affect Latin America. HTTPS: //YOUTU. BE/TSCMMFFV_6 S HTTPS: //YOUTU. BE/4 TXDT 38_HUU
Warm-Up: Based on your knowledge of European nationalism, predict how nationalism might affect Latin America. HTTPS: //YOUTU. BE/TSCMMFFV_6 S HTTPS: //YOUTU. BE/4 TXDT 38_HUU
 Section 1: Struggle for Change in Latin America The Mexican Revolution What were the causes? – Secondary Causes – Sources of discontent • Wealthy landowners benefited • Peasants living in deep poverty • No land or education • Peasants, factory workers (earned meager wages) and middle class liberals (democracy) – resented Porfirio Diaz dictatorship Dictator Porfirio Diaz ruled Mexico for almost 35 years. – Primary Causes: • Francisco Madero – 1910 demands free elections • Diaz resigns in 1911 • Madero becomes president but is murdered in two years • Struggle for power Radical leaders – North – Pancho Villa – fought for personal glory, but won many followers – South Emiliano Zapata – Indian tenant farmer demanded land reform for peasants
Section 1: Struggle for Change in Latin America The Mexican Revolution What were the causes? – Secondary Causes – Sources of discontent • Wealthy landowners benefited • Peasants living in deep poverty • No land or education • Peasants, factory workers (earned meager wages) and middle class liberals (democracy) – resented Porfirio Diaz dictatorship Dictator Porfirio Diaz ruled Mexico for almost 35 years. – Primary Causes: • Francisco Madero – 1910 demands free elections • Diaz resigns in 1911 • Madero becomes president but is murdered in two years • Struggle for power Radical leaders – North – Pancho Villa – fought for personal glory, but won many followers – South Emiliano Zapata – Indian tenant farmer demanded land reform for peasants
 Effects of the Mexican Revolution • What were the effects? – 1. Much bloodshed and death – 2. 1917 – Venustiano Carranza conservative – elected president • Constitution – – Addressed 3 major issues: land, religion and labor » Nationalization – government take over of natural resources » Broke up large estates » Limits foreign ownership of Mexican land » Returns some Indian lands » Gives government control of church land » Sets minimum wage for workers » Protects the right of workers to strike » Gives all men the right to vote » Grants women some new rights
Effects of the Mexican Revolution • What were the effects? – 1. Much bloodshed and death – 2. 1917 – Venustiano Carranza conservative – elected president • Constitution – – Addressed 3 major issues: land, religion and labor » Nationalization – government take over of natural resources » Broke up large estates » Limits foreign ownership of Mexican land » Returns some Indian lands » Gives government control of church land » Sets minimum wage for workers » Protects the right of workers to strike » Gives all men the right to vote » Grants women some new rights
 Effects of the Mexican Revolution • 3. Social Reforms – Schools and libraries were set up – Helped some Indian communities regain lands – Supported labor unions • 4. Economic nationalism – emphasis on domestic control of the economy • Determined to develop own economies and economic dependence. – After WWI trade fell off with Europe – Great depression – no demand for LA goods – price of imports rose • • • Local entrepreneurs set up factories Urged government to raise tariffs Other LA nations follow Mexico’s lead Limited success 5. Cultural Nationalism – Pride in ones own culture – Murals on buildings – Diego Rivera
Effects of the Mexican Revolution • 3. Social Reforms – Schools and libraries were set up – Helped some Indian communities regain lands – Supported labor unions • 4. Economic nationalism – emphasis on domestic control of the economy • Determined to develop own economies and economic dependence. – After WWI trade fell off with Europe – Great depression – no demand for LA goods – price of imports rose • • • Local entrepreneurs set up factories Urged government to raise tariffs Other LA nations follow Mexico’s lead Limited success 5. Cultural Nationalism – Pride in ones own culture – Murals on buildings – Diego Rivera
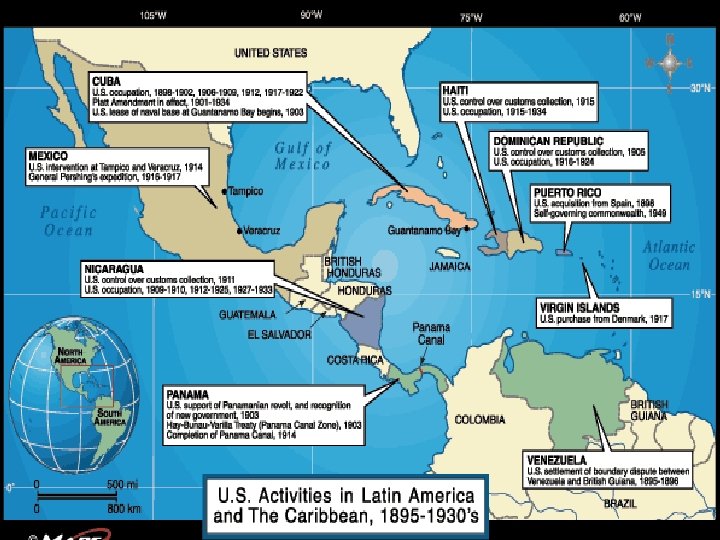
 The Good Neighbor Policy • During the Mexican revolutions the US supported leaders who it thought would protect its investments • In the 1930’s, Franklin Roosevelt abandoned the Roosevelt corollary • Which had been used to justify American intervention • US withdrew troops in Haiti and Nicaragua • Lifted the Platt amendment in Cuba – Pro-American Sentiment
The Good Neighbor Policy • During the Mexican revolutions the US supported leaders who it thought would protect its investments • In the 1930’s, Franklin Roosevelt abandoned the Roosevelt corollary • Which had been used to justify American intervention • US withdrew troops in Haiti and Nicaragua • Lifted the Platt amendment in Cuba – Pro-American Sentiment
 Section 2: Nationalist Movements in Africa and the Middle East • Resentment after World War I – Why? • Colonial Powers sought to strengthen ties and increase exploitation Kenya – ID Cards White settlers forced Africans off the best land Restricted where they could live and travel Africans forced to work on plantations to pay taxes Lost self – sufficiency and dependent on European goods – Land converted to cash crop growers – – – Many western – educated Africans could not hold the best jobs – Excluded from political life
Section 2: Nationalist Movements in Africa and the Middle East • Resentment after World War I – Why? • Colonial Powers sought to strengthen ties and increase exploitation Kenya – ID Cards White settlers forced Africans off the best land Restricted where they could live and travel Africans forced to work on plantations to pay taxes Lost self – sufficiency and dependent on European goods – Land converted to cash crop growers – – – Many western – educated Africans could not hold the best jobs – Excluded from political life
 Resistance • Squatters – settled illegally on white – owned plantations • Formed unions • Some read Lenin’s works and believed that imperialism was the final stage of a corrupt capitalistic society – Socialism had found a new audience
Resistance • Squatters – settled illegally on white – owned plantations • Formed unions • Some read Lenin’s works and believed that imperialism was the final stage of a corrupt capitalistic society – Socialism had found a new audience
 Apartheid in South Africa • Apartheid – Goal – Ensure White economic power – Restricted better paying jobs for whites – Black South Africans had to carry Id badges – Evicted from the best land – The little voting rights that some educated blacks had were taken away • Nationalistic Movements – African churches and newspapers demanded rights – 1912 – Formation of the African National Congress (ANC) – Efforts so far had no effect on the white government of S. Africa
Apartheid in South Africa • Apartheid – Goal – Ensure White economic power – Restricted better paying jobs for whites – Black South Africans had to carry Id badges – Evicted from the best land – The little voting rights that some educated blacks had were taken away • Nationalistic Movements – African churches and newspapers demanded rights – 1912 – Formation of the African National Congress (ANC) – Efforts so far had no effect on the white government of S. Africa
 Pan - Africanism • Pan – Africanism – unity of people of African descent • Pan – African Congress - W. E. B. Dubois – Forge a united front – Met in Paris @ the Peace conference – During the Allied conference – Called nations to sign a charter of rights for Africans. – Western powers ignored demands • Negritude Movement • French Speaking countries in Western Africa and the Caribbean celebrated African’s cultural heritage
Pan - Africanism • Pan – Africanism – unity of people of African descent • Pan – African Congress - W. E. B. Dubois – Forge a united front – Met in Paris @ the Peace conference – During the Allied conference – Called nations to sign a charter of rights for Africans. – Western powers ignored demands • Negritude Movement • French Speaking countries in Western Africa and the Caribbean celebrated African’s cultural heritage
 Egypt WWI – Provided food and workers to help Britain United behind Wafd party Islamic Brotherhood brought Islamic nationalism to Egypt 1922 the British finally agreed to declare Egypt independent • Troops stayed there to guard the Suez Canal and was the real power behind the king • •
Egypt WWI – Provided food and workers to help Britain United behind Wafd party Islamic Brotherhood brought Islamic nationalism to Egypt 1922 the British finally agreed to declare Egypt independent • Troops stayed there to guard the Suez Canal and was the real power behind the king • •
 Modernization in Turkey & Iran • Mustafa Kemal – Ataturk – “Father of the Turks” – Overthrow western occupation – Declared Turkey a republic – goal was to Modernize Turkey along western lines and create a secular state that separated religion from government.
Modernization in Turkey & Iran • Mustafa Kemal – Ataturk – “Father of the Turks” – Overthrow western occupation – Declared Turkey a republic – goal was to Modernize Turkey along western lines and create a secular state that separated religion from government.
 Ataturk & Turkish Modernization • Westernization – Secularization – Replaced Islamic Law with new law code based on European models – Forced people to wear western clothing – Replaced Arabic with western script – Closed religious schools and opened state run schools – Women – no longer had to veil their faces • Allowed to vote • Polygamy outlawed • Freedom to work outside the home – Industry expanded • Hired westerners to advise on how to make Turkey economically independent
Ataturk & Turkish Modernization • Westernization – Secularization – Replaced Islamic Law with new law code based on European models – Forced people to wear western clothing – Replaced Arabic with western script – Closed religious schools and opened state run schools – Women – no longer had to veil their faces • Allowed to vote • Polygamy outlawed • Freedom to work outside the home – Industry expanded • Hired westerners to advise on how to make Turkey economically independent
 Iran • Reza Khan – a navy officer overthrew Shah – Pahlavi Dynasty • Rushed to modernize Iran – Won better terms from Britain company that controlled oil – Strengthened army – Transportation System – W. Alphabet – Western Clothing – Encouraged women to take part in public life – Muslim religious leaders condemned efforts
Iran • Reza Khan – a navy officer overthrew Shah – Pahlavi Dynasty • Rushed to modernize Iran – Won better terms from Britain company that controlled oil – Strengthened army – Transportation System – W. Alphabet – Western Clothing – Encouraged women to take part in public life – Muslim religious leaders condemned efforts
 Arab Nationalism & The Mandates • Pan-Arabism – built on shared Arab heritage • Recalled the golden age of Arab history – sought to free Arabs from foreign domination • At Peace conference Ottoman minorities promised independence – not administered
Arab Nationalism & The Mandates • Pan-Arabism – built on shared Arab heritage • Recalled the golden age of Arab history – sought to free Arabs from foreign domination • At Peace conference Ottoman minorities promised independence – not administered
 Palestine & The Balfour Note • Zionist movement – During WWI – vague promises from Britain • Promised Arabs own kingdoms in former Ottoman lands • Balfour Declaration 1917 – to win support of European Jews – Supported the idea of setting up a national home for the Jewish people without doing anything that may unjustly impact civil and religious rights of the existing non-Jewish communities – 1930’s – Rise of anti-Semitism in Europe – Seek safety in Palestine – Some Jews bought land from Arab landowners and then forced Arab tenant off the land – Jewish factory owners refused to hire Arabs
Palestine & The Balfour Note • Zionist movement – During WWI – vague promises from Britain • Promised Arabs own kingdoms in former Ottoman lands • Balfour Declaration 1917 – to win support of European Jews – Supported the idea of setting up a national home for the Jewish people without doing anything that may unjustly impact civil and religious rights of the existing non-Jewish communities – 1930’s – Rise of anti-Semitism in Europe – Seek safety in Palestine – Some Jews bought land from Arab landowners and then forced Arab tenant off the land – Jewish factory owners refused to hire Arabs
 Section 3: India Seeks Self Rule • • • Amritsar Massacre: Causes: – British General Dyer had outlawed public meetings – Peaceful crown gathers and British open fire and kill over 350 and wound over a thousand – Britain promised Indians greater self government after the war, but they never fulfilled that promise Effects: – Indian feelings in the INC changed from pushing for self rule to full independence from Britain
Section 3: India Seeks Self Rule • • • Amritsar Massacre: Causes: – British General Dyer had outlawed public meetings – Peaceful crown gathers and British open fire and kill over 350 and wound over a thousand – Britain promised Indians greater self government after the war, but they never fulfilled that promise Effects: – Indian feelings in the INC changed from pushing for self rule to full independence from Britain
 Mohandas Gandhi • • Joined a law firm in S. Africa – faced racial prejudice. Fought laws with non-violent resistance – Satyagraha “Soul Force” (his nonviolent passive resistance) – Ahisma – ancient doctrine of non-violence and respect for life – Rejected Caste system inequalities and embraced western thought such as democracy and nationalism as well as Christian thought – Refused to obey unjust laws – civil disobedience – Organized boycotts of British goods – especially textiles and encouraged people to wear home spun cotton clothing (called a dhoti) – Symbol is the spinning wheel
Mohandas Gandhi • • Joined a law firm in S. Africa – faced racial prejudice. Fought laws with non-violent resistance – Satyagraha “Soul Force” (his nonviolent passive resistance) – Ahisma – ancient doctrine of non-violence and respect for life – Rejected Caste system inequalities and embraced western thought such as democracy and nationalism as well as Christian thought – Refused to obey unjust laws – civil disobedience – Organized boycotts of British goods – especially textiles and encouraged people to wear home spun cotton clothing (called a dhoti) – Symbol is the spinning wheel
 The Salt March • Causes: – British Salt Monopoly – could only buy British Salt – Indians were forbidden to touch the salt on the coast • Events – March 12 – March to the sea gathered followers as they marched – April 6 – Gandhi touched the salt on the coast and was jailed
The Salt March • Causes: – British Salt Monopoly – could only buy British Salt – Indians were forbidden to touch the salt on the coast • Events – March 12 – March to the sea gathered followers as they marched – April 6 – Gandhi touched the salt on the coast and was jailed
 The Salt March • Effects: – Followers sold salt on the streets – Countries began writing stories about the brutality administered to the Indians by the British • How do you think Indians were viewed in newspapers around the world? – Non-violence persevered and Britain began to hand over power to the Indians
The Salt March • Effects: – Followers sold salt on the streets – Countries began writing stories about the brutality administered to the Indians by the British • How do you think Indians were viewed in newspapers around the world? – Non-violence persevered and Britain began to hand over power to the Indians
 Muslim vs. Hindu • • • Tensions between the two groups – Muslim League – Muhammad Ali Jinnah • Supported a separate Muslim state Tensions lead to Britain partitioning the subcontinent – Pakistan for the Muslims and India for the Hindus – Britain worked to keep the population divided, why? – Sikh and Hindu mobs slaughtered Muslims going into Pakistan, Muslims massacred Hindus Gandhi used satyagraha to try and restore peace – Famous hunger strike – He was killed by a Hindu extremists in 1948 https: //youtu. be/ibag. ACLb-6 s
Muslim vs. Hindu • • • Tensions between the two groups – Muslim League – Muhammad Ali Jinnah • Supported a separate Muslim state Tensions lead to Britain partitioning the subcontinent – Pakistan for the Muslims and India for the Hindus – Britain worked to keep the population divided, why? – Sikh and Hindu mobs slaughtered Muslims going into Pakistan, Muslims massacred Hindus Gandhi used satyagraha to try and restore peace – Famous hunger strike – He was killed by a Hindu extremists in 1948 https: //youtu. be/ibag. ACLb-6 s
 Section 4: Upheavels in China • • The Chinese Republic – 1911 Qing dynasty collapsed – Sun Yixian hoped to rebuild China based on the Three Principles of the People - nationalism, democracy, and economic security for everyone. Internal Problems – 1912 Sun Yixian steps down in favor of a powerful General Yuan Shikai • Hoped Yuan would restore order and set up a strong central government – He tried to set up a dynasty with him as emperor – military did not support him – Foreign Imperialism • During this time of chaos, foreign powers increased influence over Chinese affairs • Ports dominated by foreign merchants, missionaries and soldiers • Japan – 1915 – During World War I – Japan presented Yuan Shikai with 21 demands – goal was to make China a Japanese protectorate – Japan finally given German possessions – When he died in 1916 the country was plunged into civil war
Section 4: Upheavels in China • • The Chinese Republic – 1911 Qing dynasty collapsed – Sun Yixian hoped to rebuild China based on the Three Principles of the People - nationalism, democracy, and economic security for everyone. Internal Problems – 1912 Sun Yixian steps down in favor of a powerful General Yuan Shikai • Hoped Yuan would restore order and set up a strong central government – He tried to set up a dynasty with him as emperor – military did not support him – Foreign Imperialism • During this time of chaos, foreign powers increased influence over Chinese affairs • Ports dominated by foreign merchants, missionaries and soldiers • Japan – 1915 – During World War I – Japan presented Yuan Shikai with 21 demands – goal was to make China a Japanese protectorate – Japan finally given German possessions – When he died in 1916 the country was plunged into civil war
 May Fourth Movement • • 1919 – Goal was to Strengthen China Student protests against imperialism erupted on Beijing and later spread in China Students organized boycotts of Japanese goods. – What do you think their goal was? – How is China going to fight off European influence and imperialism? • Look to West to modernize – looked to democracy and nationalism to solve China’s problems Women campaigned to end arranged marriages, foot binding and the seclusion of women in the home
May Fourth Movement • • 1919 – Goal was to Strengthen China Student protests against imperialism erupted on Beijing and later spread in China Students organized boycotts of Japanese goods. – What do you think their goal was? – How is China going to fight off European influence and imperialism? • Look to West to modernize – looked to democracy and nationalism to solve China’s problems Women campaigned to end arranged marriages, foot binding and the seclusion of women in the home
 Marxism in China • Marxism – Why would Marxism appeal to the Chinese? – USSR more than willing to train Chinese to become vanguard or elite, leaders of the communist revolution. – Russian revolution model of how a strong wellorganized party could transform a nation – 1920 s – Chinese communist party formed
Marxism in China • Marxism – Why would Marxism appeal to the Chinese? – USSR more than willing to train Chinese to become vanguard or elite, leaders of the communist revolution. – Russian revolution model of how a strong wellorganized party could transform a nation – 1920 s – Chinese communist party formed
 The Guomindang • • Sun Yixian – Guomindang (Nationalists) – Gov’t in S. China – Wanted to defeat the warlords and reunited China – Western powers ignored please for help in building a democratic China Sun Yixian dies in 1925 – Jiang Jieshi (Chang Kai-Shek) takes over as head of the Guomindang – 1926 succeeds in marching into N. China - Guomingdang – support of the landlords and business leaders – Communists winning converts of the small proletariat – 1927 – Guomingdang slaughtered Communist party members and workers who supported them – Result of this massacre was a civil war that lasted 22 years
The Guomindang • • Sun Yixian – Guomindang (Nationalists) – Gov’t in S. China – Wanted to defeat the warlords and reunited China – Western powers ignored please for help in building a democratic China Sun Yixian dies in 1925 – Jiang Jieshi (Chang Kai-Shek) takes over as head of the Guomindang – 1926 succeeds in marching into N. China - Guomingdang – support of the landlords and business leaders – Communists winning converts of the small proletariat – 1927 – Guomingdang slaughtered Communist party members and workers who supported them – Result of this massacre was a civil war that lasted 22 years
 Mao Zedong • Mao believed that communists should seek support not among the small urban working class but among the large peasant masses. Why? • Mao and the communists organized peasants in S. E. China – giving them land, schooling and healthcare • Jiang Jieshi wanted to destroy “Red Bandits” – Extermination campaign
Mao Zedong • Mao believed that communists should seek support not among the small urban working class but among the large peasant masses. Why? • Mao and the communists organized peasants in S. E. China – giving them land, schooling and healthcare • Jiang Jieshi wanted to destroy “Red Bandits” – Extermination campaign
 Marxism in China • • The Long March – 1934 Mao and 100, 000 followers fled the Guomingdang – Faced daily attacks – Symbol of communist heroism – Soldiers had to follow three main rules: • Obey orders, “do not take anything from the people and turn in everything you capture • In additions, treat peasants politely, pay for goods they wanted and avoid damaging crops In the end communists set up base in remote area of N. China
Marxism in China • • The Long March – 1934 Mao and 100, 000 followers fled the Guomingdang – Faced daily attacks – Symbol of communist heroism – Soldiers had to follow three main rules: • Obey orders, “do not take anything from the people and turn in everything you capture • In additions, treat peasants politely, pay for goods they wanted and avoid damaging crops In the end communists set up base in remote area of N. China
 Japanese Invasion • Japanese invasion – 1931 – Japan invades Manchuria in N. E. China – Jiang’s own generals didn’t understand why they would continue to fight other Chinese (communists) when they should be working together to fight the Japanese – Forced to Combine efforts – 1937 Japan strikes again – overran eastern china • Set up Puppet government in Nanjing – former nationalists capital • Brutality into the city- “Rape of Nanjing” • Japanese killed hundreds of thousands of soldiers and civilians – and they brutalized still more. https: //youtu. be/kl. Ajaujd. E 6 M
Japanese Invasion • Japanese invasion – 1931 – Japan invades Manchuria in N. E. China – Jiang’s own generals didn’t understand why they would continue to fight other Chinese (communists) when they should be working together to fight the Japanese – Forced to Combine efforts – 1937 Japan strikes again – overran eastern china • Set up Puppet government in Nanjing – former nationalists capital • Brutality into the city- “Rape of Nanjing” • Japanese killed hundreds of thousands of soldiers and civilians – and they brutalized still more. https: //youtu. be/kl. Ajaujd. E 6 M
 https: //youtu. be/Wd 0 a. W-4 m. V 68
https: //youtu. be/Wd 0 a. W-4 m. V 68
 The Chinese Nationalist Party (Kuomintang or KMT) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) had originally cooperated in seeking to wrest control of China from landlords and foreign forces. In April 1927, they split and began a decades-long civil war, interrupted only in part by Japan's invasion. With Japan's surrender and the failure of the American mediation effort, the two sides resumed their struggle in late 1945. This segment of Assignment: China examines efforts by journalists to report on this final four years of the war and its impact on Chinese society. It features archival photos and interviews as well as interviews with some of those who brought news of this battle for the world's largest country to Americans via newspapers and magazines, news reels, and radio. https: //youtu. be/Jfhjq 8 o. BBCQ
The Chinese Nationalist Party (Kuomintang or KMT) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) had originally cooperated in seeking to wrest control of China from landlords and foreign forces. In April 1927, they split and began a decades-long civil war, interrupted only in part by Japan's invasion. With Japan's surrender and the failure of the American mediation effort, the two sides resumed their struggle in late 1945. This segment of Assignment: China examines efforts by journalists to report on this final four years of the war and its impact on Chinese society. It features archival photos and interviews as well as interviews with some of those who brought news of this battle for the world's largest country to Americans via newspapers and magazines, news reels, and radio. https: //youtu. be/Jfhjq 8 o. BBCQ
 The Battle of China This motion picture film explores Japanese aggression. In Reel 1, Japanese planes bomb Shanghai; citizens flee. Describes Chinese development of the compass, printing, astronomy, gunpowder, and porcelain. The reel shows views of the Gobi Desert, sampans, and types of architecture and statuary. Japanese artillery fires and cavalry advances. The reel also describes Japanese plans for world conquest; contrasts Japanese unity with Chinese disunity. Footage also shows Emperor Hirohito. Reel 2 shows Sun Yat-sen and uprisings against the Manchu dynasty. Students go abroad. Hospitals, highways, schools, and factories are constructed. Children play at school. Emperor Hirohito reviews Japanese troops; tanks roll down a street. The reel shows a Japanese munitions factory, a Japanese fleet at sea, troops marching, the Army occupying Manchuria, views of the League of Nations as the action is condemned, the Great Wall of China, the puppet premier Pu-Yi, Japanese attacking Chinese at Marco Polo Bridge in 1937, and Chiang Kai-shek. Reel 3 shows street and harbor scenes in Shanghai, the bombing and naval bombardment of the city, street fighting, and the city's capture by Japanese units. Japanese troops advance toward Nanking. The gunboat Panay is bombed in the Yangtze. The reel also shows fighting in and around Nanking. In Reel 4, the battle continues. Footage describes Japanese atrocities during the rape of Nanking and shows dead and injured civilians. Chinese demonstrate against Japan. Chiang Kai-shek speaks. Hordes of Chinese emigrate to the West carrying their belongings with them. Reel 5 shows the establishment of the new Chinese capitol at Chungking. Air raid shelters are dug; the city is bombed. The reel shows an underground factory, fires being fought, recruits for the Chinese Army, the "Flying Tigers" taking off, and Japanese units occupying the Chinese coast. In Reel 6, coolies repair and expand the Burma Road by hand; trucks move over it. Dikes on the Yellow River are blown up to stem a Japanese offensive on Chengchow. Guerrillas ambush a Japanese patrol. Japanese planes attack Pearl Harbor. Footage shows the Japanese high command. In Reel 7, Japanese units advance against Changsha, their supply lines are cut forcing their withdrawal, and the Chinese infantry advances. Footage shows Generals Douglas Mac. Arthur and Joseph Stilwell. Madame Chiang Kai-shek addresses the U. S. Congress. The Ledo Road is constructed; transport planes fly over "the Hump. " The "Flying Tigers" bomb Japanese airfields in China. https: //youtu. be/TIkrg. Omsb. VY
The Battle of China This motion picture film explores Japanese aggression. In Reel 1, Japanese planes bomb Shanghai; citizens flee. Describes Chinese development of the compass, printing, astronomy, gunpowder, and porcelain. The reel shows views of the Gobi Desert, sampans, and types of architecture and statuary. Japanese artillery fires and cavalry advances. The reel also describes Japanese plans for world conquest; contrasts Japanese unity with Chinese disunity. Footage also shows Emperor Hirohito. Reel 2 shows Sun Yat-sen and uprisings against the Manchu dynasty. Students go abroad. Hospitals, highways, schools, and factories are constructed. Children play at school. Emperor Hirohito reviews Japanese troops; tanks roll down a street. The reel shows a Japanese munitions factory, a Japanese fleet at sea, troops marching, the Army occupying Manchuria, views of the League of Nations as the action is condemned, the Great Wall of China, the puppet premier Pu-Yi, Japanese attacking Chinese at Marco Polo Bridge in 1937, and Chiang Kai-shek. Reel 3 shows street and harbor scenes in Shanghai, the bombing and naval bombardment of the city, street fighting, and the city's capture by Japanese units. Japanese troops advance toward Nanking. The gunboat Panay is bombed in the Yangtze. The reel also shows fighting in and around Nanking. In Reel 4, the battle continues. Footage describes Japanese atrocities during the rape of Nanking and shows dead and injured civilians. Chinese demonstrate against Japan. Chiang Kai-shek speaks. Hordes of Chinese emigrate to the West carrying their belongings with them. Reel 5 shows the establishment of the new Chinese capitol at Chungking. Air raid shelters are dug; the city is bombed. The reel shows an underground factory, fires being fought, recruits for the Chinese Army, the "Flying Tigers" taking off, and Japanese units occupying the Chinese coast. In Reel 6, coolies repair and expand the Burma Road by hand; trucks move over it. Dikes on the Yellow River are blown up to stem a Japanese offensive on Chengchow. Guerrillas ambush a Japanese patrol. Japanese planes attack Pearl Harbor. Footage shows the Japanese high command. In Reel 7, Japanese units advance against Changsha, their supply lines are cut forcing their withdrawal, and the Chinese infantry advances. Footage shows Generals Douglas Mac. Arthur and Joseph Stilwell. Madame Chiang Kai-shek addresses the U. S. Congress. The Ledo Road is constructed; transport planes fly over "the Hump. " The "Flying Tigers" bomb Japanese airfields in China. https: //youtu. be/TIkrg. Omsb. VY
 Section 5: Empire of the Rising Sun • 1920’s – Japan moving toward greater democracy – Emperor Hirohito 1929 -1989 – Political parties grew stronger / elected members of the Diet exerted their power – 1925 – Adult men won the right to vote – Women’s suffrage 1947 https: //youtu. be/tvu. CE-b. LCQA (20 Minutes)
Section 5: Empire of the Rising Sun • 1920’s – Japan moving toward greater democracy – Emperor Hirohito 1929 -1989 – Political parties grew stronger / elected members of the Diet exerted their power – 1925 – Adult men won the right to vote – Women’s suffrage 1947 https: //youtu. be/tvu. CE-b. LCQA (20 Minutes)
 Empire of the Rising Sun • Economic growth – During WWI – Japanese economy grew – trade with allies – Zaibatsu influenced politics 1920’s – Pushed for policies to favor international trade and their own interests – Japan signed agreement with the US and Britain to limit the size of its navy – in the spirit of world peace
Empire of the Rising Sun • Economic growth – During WWI – Japanese economy grew – trade with allies – Zaibatsu influenced politics 1920’s – Pushed for policies to favor international trade and their own interests – Japan signed agreement with the US and Britain to limit the size of its navy – in the spirit of world peace
 Empire of the Rising Sun • Serious problems – Economy grew slowly after WWI – DISCONTENT • Rural peasants enjoyed none of the prosperity of city – dwellers • Factory workers – low wages – Attracted to socialism – Younger generation in cities adopted western fashions and rejected family authority – During the 1920’s Conservatives (military officers) blasted government corruption, including payoffs by powerful zaibatsu • Condemned western influences for undermining basic Japanese values of obedience and respect for authority
Empire of the Rising Sun • Serious problems – Economy grew slowly after WWI – DISCONTENT • Rural peasants enjoyed none of the prosperity of city – dwellers • Factory workers – low wages – Attracted to socialism – Younger generation in cities adopted western fashions and rejected family authority – During the 1920’s Conservatives (military officers) blasted government corruption, including payoffs by powerful zaibatsu • Condemned western influences for undermining basic Japanese values of obedience and respect for authority
 Empire of the Rising Sun • • Economic disaster – Military and Ultranationalists condemned politicians for agreeing to western demands to stop overseas expansions – Outraged by Racial policies in the US – Took great pride in their achievements and history and resented the treatment by the Americans – Nationalists wanted to expand – Raw materials and land for population Militarists in power – Military leaders plotted to overthrow the government – Briefly occupied Tokyo – Civilian government survived but by 1937 forced to accept military domination – Cracked down on socialists and most democratic freedoms – Revived ancient culture and built a cult around the emperor who was believed to descended from the Sun goddess
Empire of the Rising Sun • • Economic disaster – Military and Ultranationalists condemned politicians for agreeing to western demands to stop overseas expansions – Outraged by Racial policies in the US – Took great pride in their achievements and history and resented the treatment by the Americans – Nationalists wanted to expand – Raw materials and land for population Militarists in power – Military leaders plotted to overthrow the government – Briefly occupied Tokyo – Civilian government survived but by 1937 forced to accept military domination – Cracked down on socialists and most democratic freedoms – Revived ancient culture and built a cult around the emperor who was believed to descended from the Sun goddess
 Empire of the Rising Sun • Renewed Expansion – 1939 - WWII spread to Asia – Manchurian Incident 1931 • Set up explosives on Japanese owned Railroad tracks • Claimed China did it • Japanese took over • Set up a puppet government Manzhouguo – League of Nations condemned activity
Empire of the Rising Sun • Renewed Expansion – 1939 - WWII spread to Asia – Manchurian Incident 1931 • Set up explosives on Japanese owned Railroad tracks • Claimed China did it • Japanese took over • Set up a puppet government Manzhouguo – League of Nations condemned activity


