dbca42781c782697110ef706e5b6b89e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Chapter 15 Monetary Policy © West Publishing Company 1996

EQUATION OF EXCHANGE MV=P Q l M is the money supply l V is the velocity of money l P is the price level l Q is the real GDP l

INFLATION Inflation refers to an increase in the general price level. l One-shot inflation is a one-time increase in the price level. l Continued inflation is continuous increases in the price level (CPI rises each year) l
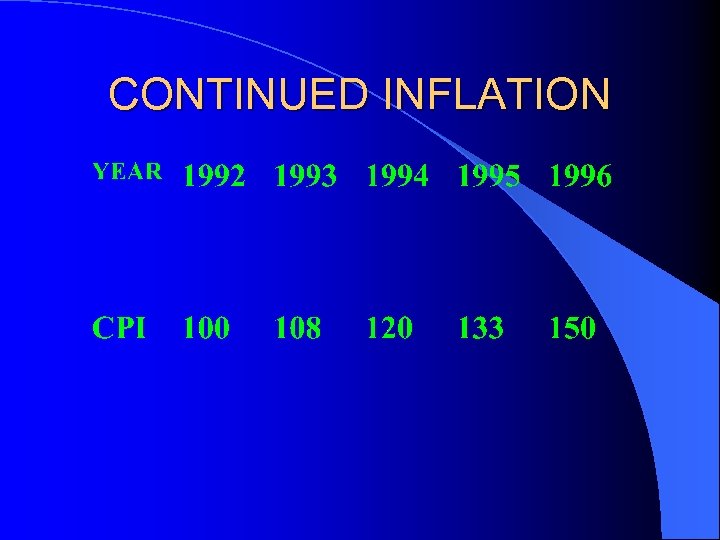
CONTINUED INFLATION

CONTINUED INFLATION Continued inflation results from continued increases in AD. l What causes these continued increases in AD? l Usually continued increases in the Money Supply l

COSTS OF INFLATION Inflation is a “tax” on peoples moneyholdings. l Inflation lowers the real return on your savings. l Inflation redistributes purchasing power from lenders to borrowers. l

COSTS OF INFLATION Inflation can lead to social tension l Inflation creates greater uncertainty l Inflation leads people to divert money away from productive activities. l

INTEREST RATES REAL RATE - the rate of return banks must have to cover costs and provide a return to investors l NOMINAL RATE - real rate plus the expected rate of inflation l

DEMAND FOR MONEY The inverse relationship between the quantity of money balances and the interest rate l the interest rate is the opportunity cost of holding money l

Demand for, and Supply of Money Exhibit 1 Interest Rate Supply of Money i 2 i 1 Demand for Money 0 M 2 M 1 Quantity of Money (a) 0 Quantity of Money (b)
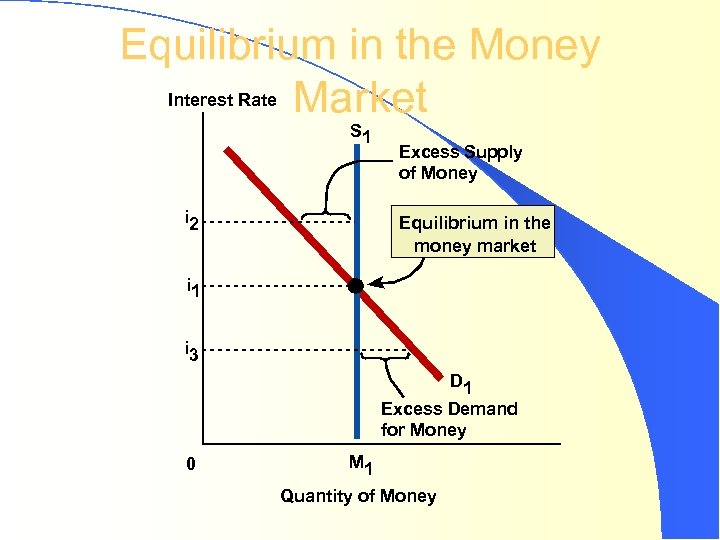
Equilibrium in the Money Interest Rate Market S 1 i 2 Excess Supply of Money Equilibrium in the money market i 1 i 3 D 1 Excess Demand for Money 0 M 1 Quantity of Money

BONDS AND INTEREST RATES bonds have a face value l bonds pay a fixed interest payment each year (coupon pmt) l bond prices are determined by the relationship between current interest rates and the bond’s rate l

BONDS AND INTEREST RATES Bond Prices are inversely related to the current interest rate. l If current interest rates are higher than the bond’s rate then the bond will sell below face value l If interest rates fall, bond prices rise l

APPROPRIATE POLICIES l What are the appropriate monetary policies to close a recessionary gap? – buy bonds – decrease discount rate – decrease reserve requirement

APPROPRIATE POLICIES l What are appropriate monetary policies to close an inflationary gap? – sell bonds – increase the discount rate – increase reserve requirements
dbca42781c782697110ef706e5b6b89e.ppt