e1ddf117f0d32b4bb5ccb243623ef2a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Chapter 15 Managing Retailing, Wholesaling, and Market Logistics Power. Point by Karen E. James Louisiana State University - Shreveport © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 0
Chapter 15 Managing Retailing, Wholesaling, and Market Logistics Power. Point by Karen E. James Louisiana State University - Shreveport © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 0
 Objectives § Determine the types of organizations in this sector. § Learn what marketing decisions organizations in this sector make. § Understand the major trends in this sector. © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 1
Objectives § Determine the types of organizations in this sector. § Learn what marketing decisions organizations in this sector make. § Understand the major trends in this sector. © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 1
 Retailing Basics § Retail life cycle § Wheel-of-retailing § Types of retailers § Service levels § Marketing decisions § Retail positioning strategies § Retailing trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Nonstore retailing § Corporate retailing To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 2
Retailing Basics § Retail life cycle § Wheel-of-retailing § Types of retailers § Service levels § Marketing decisions § Retail positioning strategies § Retailing trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Nonstore retailing § Corporate retailing To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 2
 Retailing Major Store Retailer Types § Specialty store § Discount store § Department store § Convenience store § Supermarket § Off-price retailer § Superstore © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 3
Retailing Major Store Retailer Types § Specialty store § Discount store § Department store § Convenience store § Supermarket § Off-price retailer § Superstore © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 3
 Retailing § Retail-store types pass through the retail life cycle. § The wheel-of-retailing describes how new store types emerge. § Retailers can offer one of four levels of service: – Self-service, self-selection, limited service, and full service © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 4
Retailing § Retail-store types pass through the retail life cycle. § The wheel-of-retailing describes how new store types emerge. § Retailers can offer one of four levels of service: – Self-service, self-selection, limited service, and full service © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 4
 Retailing § Four broad retail positioning strategies include: – Bloomingdale’s – Tiffany – Sunglass Hut – Wal-Mart § Non-store retailing has been growing faster than store retailing © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 5
Retailing § Four broad retail positioning strategies include: – Bloomingdale’s – Tiffany – Sunglass Hut – Wal-Mart § Non-store retailing has been growing faster than store retailing © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 5
 Retailing Major Types of Retail Organizations § Corporate chain store § Consumer cooperative § Voluntary chain § Franchise organization § Retailer cooperative § Merchandising conglomerate © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 6
Retailing Major Types of Retail Organizations § Corporate chain store § Consumer cooperative § Voluntary chain § Franchise organization § Retailer cooperative § Merchandising conglomerate © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 6
 Retailing Basics § Types of retailers § Marketing decisions § Retailing trends § Target market § Product assortment and placement § Services mix and store atmosphere § Price § Promotion § Place © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 7
Retailing Basics § Types of retailers § Marketing decisions § Retailing trends § Target market § Product assortment and placement § Services mix and store atmosphere § Price § Promotion § Place © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 7
 Retailing Location Options for Retailers § General business district § Strip mall (shopping strip) § Regional shopping center § Location within a larger store or operation § Community shopping center © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 8
Retailing Location Options for Retailers § General business district § Strip mall (shopping strip) § Regional shopping center § Location within a larger store or operation § Community shopping center © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 8
 Retailing Basics § Types of retailers § Marketing decisions § Retailing trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § New retail forms § Intertype competition § Growth of giant retailers § Technology § Global expansion § Selling experiences § Competition between store-based and nonstore-based retailing To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 9
Retailing Basics § Types of retailers § Marketing decisions § Retailing trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § New retail forms § Intertype competition § Growth of giant retailers § Technology § Global expansion § Selling experiences § Competition between store-based and nonstore-based retailing To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 9
 Wholesaling § Wholesaling basics § Types of wholesalers § Marketing decisions § Wholesaling trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Wholesaling excludes manufacturers, farmers, and retailers § Wholesalers differ from retailers in three key ways § Wholesalers handle many functions more efficiently than do manufacturers To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 10
Wholesaling § Wholesaling basics § Types of wholesalers § Marketing decisions § Wholesaling trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Wholesaling excludes manufacturers, farmers, and retailers § Wholesalers differ from retailers in three key ways § Wholesalers handle many functions more efficiently than do manufacturers To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 10
 Wholesaling Wholesaler Functions § Selling and promoting § Buying and assortment building § Bulk breaking © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Warehousing § Transportation § Financing § Risk bearing § Market information To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 11
Wholesaling Wholesaler Functions § Selling and promoting § Buying and assortment building § Bulk breaking © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Warehousing § Transportation § Financing § Risk bearing § Market information To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 11
 Wholesaling § Wholesaling basics § Growth and types of wholesalers § Marketing decisions § Wholesaling trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Wholesalers vary in type and function § Wholesaling has been growing due to two key factors: – Many factories are located far from buyers – An increasing need to adapt product quantities, features, or packages to meet buyer needs To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 12
Wholesaling § Wholesaling basics § Growth and types of wholesalers § Marketing decisions § Wholesaling trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Wholesalers vary in type and function § Wholesaling has been growing due to two key factors: – Many factories are located far from buyers – An increasing need to adapt product quantities, features, or packages to meet buyer needs To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 12
 Wholesaling Major Wholesaler Types § Merchant wholesalers § Full-service wholesalers § Limited-service wholesalers § Brokers & agents © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Brokers § Agents § Manufacturers’ and retailers’ branches and offices § Miscellaneous wholesalers To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 13
Wholesaling Major Wholesaler Types § Merchant wholesalers § Full-service wholesalers § Limited-service wholesalers § Brokers & agents © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Brokers § Agents § Manufacturers’ and retailers’ branches and offices § Miscellaneous wholesalers To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 13
 Wholesaling § Wholesaling basics § Target market § Product assortment and placement § Types of wholesalers § Price § Marketing decisions § Place § Promotion § Wholesaling trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 14
Wholesaling § Wholesaling basics § Target market § Product assortment and placement § Types of wholesalers § Price § Marketing decisions § Place § Promotion § Wholesaling trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 14
 Wholesaling § Wholesaling basics § Types of wholesalers § Marketing decisions § Wholesaling trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Direct buying trends initially threatened wholesalers § Wholesalers have adapted by: – Adding value – Reducing costs – Strengthening relationships with manufacturers To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 15
Wholesaling § Wholesaling basics § Types of wholesalers § Marketing decisions § Wholesaling trends © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Direct buying trends initially threatened wholesalers § Wholesalers have adapted by: – Adding value – Reducing costs – Strengthening relationships with manufacturers To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 15
 Market Logistics § Interrelated Aspects Associated with Market Logistics: – Physical distribution – Supply chain management (SCM) – Value network – Demand chain planning – Market logistics – Integrated logistics systems (ILS) © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 16
Market Logistics § Interrelated Aspects Associated with Market Logistics: – Physical distribution – Supply chain management (SCM) – Value network – Demand chain planning – Market logistics – Integrated logistics systems (ILS) © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 16
 Market Logistics Key Elements § Market-logistics objectives § Market-logistics decisions § Market logistics lessons © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Logistics involve tradeoffs between costs and customer service § Maximizing profits, not sales, is key § A total system basis should be considered § Designing a system that will minimize the cost of achieving objectives should be the outcome To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 17
Market Logistics Key Elements § Market-logistics objectives § Market-logistics decisions § Market logistics lessons © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Logistics involve tradeoffs between costs and customer service § Maximizing profits, not sales, is key § A total system basis should be considered § Designing a system that will minimize the cost of achieving objectives should be the outcome To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 17
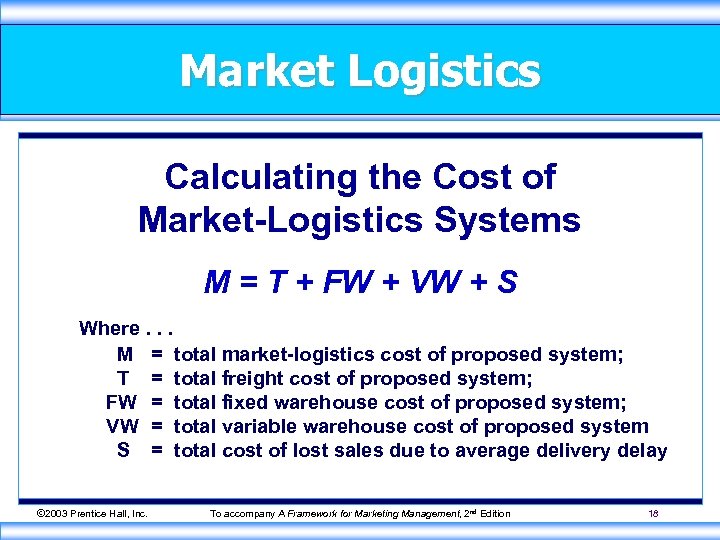 Market Logistics Calculating the Cost of Market-Logistics Systems M = T + FW + VW + S Where. . . M = total market-logistics cost of proposed system; T = total freight cost of proposed system; FW = total fixed warehouse cost of proposed system; VW = total variable warehouse cost of proposed system S = total cost of lost sales due to average delivery delay © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 18
Market Logistics Calculating the Cost of Market-Logistics Systems M = T + FW + VW + S Where. . . M = total market-logistics cost of proposed system; T = total freight cost of proposed system; FW = total fixed warehouse cost of proposed system; VW = total variable warehouse cost of proposed system S = total cost of lost sales due to average delivery delay © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 18
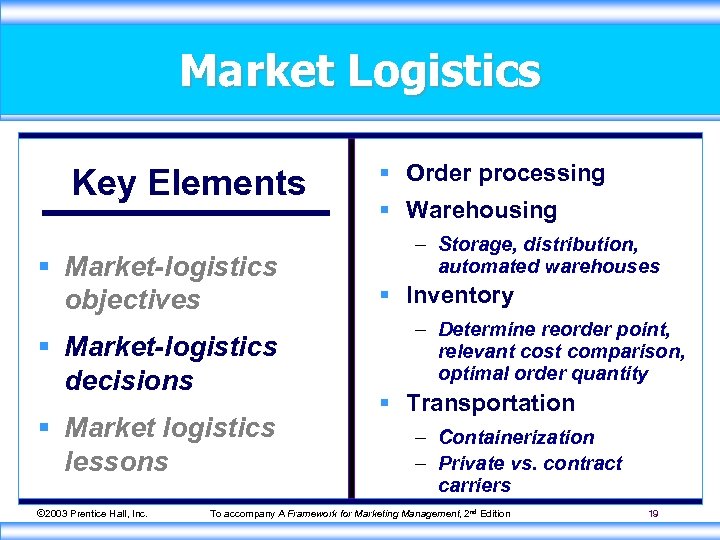 Market Logistics Key Elements § Market-logistics objectives § Market-logistics decisions § Market logistics lessons © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Order processing § Warehousing – Storage, distribution, automated warehouses § Inventory – Determine reorder point, relevant cost comparison, optimal order quantity § Transportation – Containerization – Private vs. contract carriers To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 19
Market Logistics Key Elements § Market-logistics objectives § Market-logistics decisions § Market logistics lessons © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § Order processing § Warehousing – Storage, distribution, automated warehouses § Inventory – Determine reorder point, relevant cost comparison, optimal order quantity § Transportation – Containerization – Private vs. contract carriers To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 19
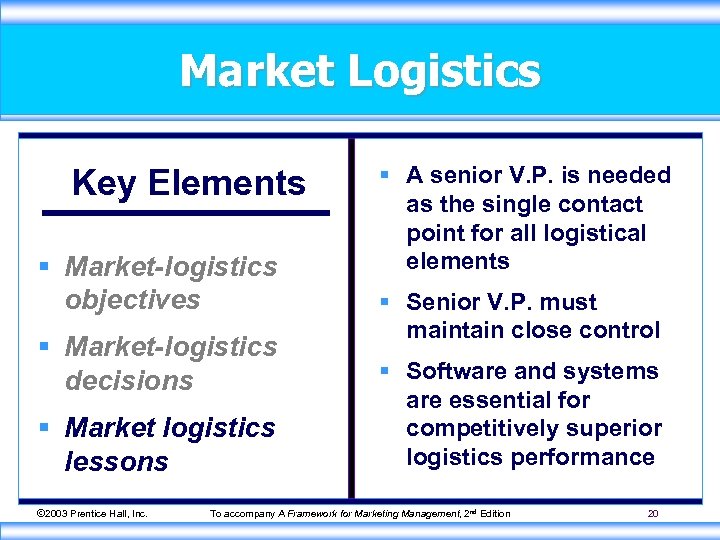 Market Logistics Key Elements § Market-logistics objectives § Market-logistics decisions § Market logistics lessons © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § A senior V. P. is needed as the single contact point for all logistical elements § Senior V. P. must maintain close control § Software and systems are essential for competitively superior logistics performance To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 20
Market Logistics Key Elements § Market-logistics objectives § Market-logistics decisions § Market logistics lessons © 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. § A senior V. P. is needed as the single contact point for all logistical elements § Senior V. P. must maintain close control § Software and systems are essential for competitively superior logistics performance To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2 nd Edition 20


