7fc672caf9fd83708a6eb1ca721b0ca2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Chapter 14: Resources

Why are resources being depleted? n Two kinds of natural resources are especially valuable to humans – Minerals – Energy resources n We depend on abundant, low-cost energy and minerals to run our industries, transport ourselves, and keep our homes comfortable n Problem – MDCs want to preserve current standards of living while LDCs are struggling to attain a better standard

Energy Resources n Historically people have relied primarily on power supplied by themselves or by animals – Called animate power n Energy from flowing water and burning biomass fuel supplemented animate power – Biomass = n Wood, plant material, and animal waste n During the Industrial Revolution, MDCs converted to inanimate power – Generated from machines

Energy Resources n n MDCs consume 3 x the amount of energy that LDCs do North Americans are the heaviest per capita consumers of energy n Three substances provide 5/6 ths of the world’s energy – – – n Coal Petroleum Natural gas All three are fossil fuels – Residue of plants and animals that were buried millions of years ago – Use ¼ world’s energy – Have 1/12 world’s population n Two causes for concern – Supply is finite – Distributed unevenly
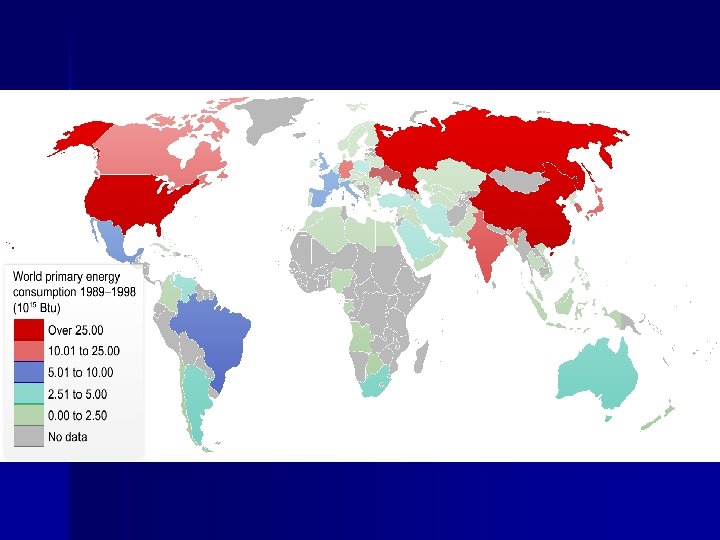

Fossil Fuels n Renewable energy n – Essentially unlimited supply and is not depleted n n Hydroelectric, geothermal, fusion, wind, and solar energy Non-renewable energy – Forms so slowly that it cannot be renewed n Fossil fuels Proven Reserves – Amount of energy remaining in deposits of fossil fuels n Potential Reserves – Energy in deposits that are undiscovered but thought to exist n n n Undiscovered oil fields Enhanced recovery from current fields Unconventional resources – Shale, oil sands
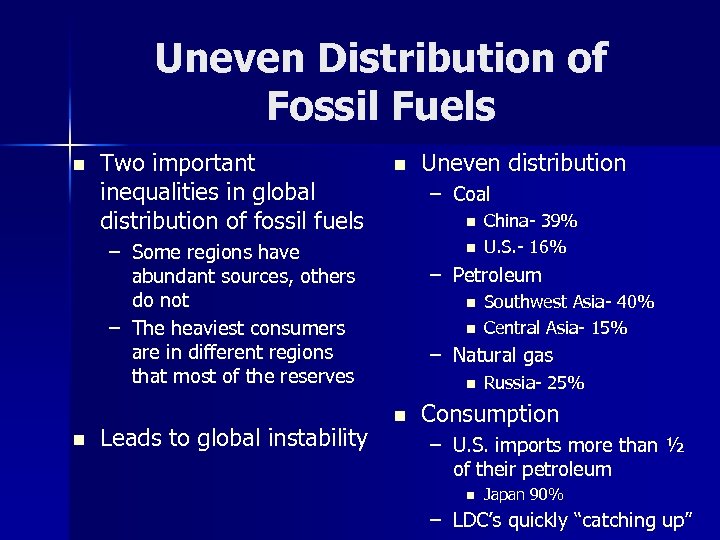
Uneven Distribution of Fossil Fuels n Two important inequalities in global distribution of fossil fuels n – Coal n – Some regions have abundant sources, others do not – The heaviest consumers are in different regions that most of the reserves n Leads to global instability Uneven distribution n China- 39% U. S. - 16% – Petroleum n n Southwest Asia- 40% Central Asia- 15% – Natural gas n n Russia- 25% Consumption – U. S. imports more than ½ of their petroleum n Japan 90% – LDC’s quickly “catching up”

Control of World Petroleum n n Most intense conflict over energy will be centered on supply of petroleum OPEC – OPEC was angry at North America and Europe for supporting Israel (1970 s) n n Led to embargo Lifted in 1974, but raised prices – Caused severe economic – At 1 st western countries set problems in MDCs oil prices and paid – LDCS hurt even more! southwest Asian countries a small % of oil profits n Changing Supply and – Government policies Demand changed in 1970 s in SW Asian countries – The price of oil settled by 1980 s, 1990 s – Several LDC countries containing petroleum – U. S. reduced its dependency resources created OPEC in on foreign imports 1960

Mineral Resources n Earth has 92 elements BUT 99% of the crust contains just 8 elements n – Metallic n – Oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium n n 8 most common combine with rare ones to create 3, 000 different minerals Each mineral is a potential resource Have properties that are valuable for machinery, vehicles, industry – Non-metallic 90% are building stones Also used for fertilizer Examples – Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Sulfur n n Minerals are either Mineral deposits are not distributed evenly – Australia and China rank has two leading producers

Key Issue #2 - Why Are Resources Being Polluted? n n Pollution occurs when more waste is added than a resource can accommodate Types of pollution: – Air – Water – Land

Air Pollution n Definition: n – Concentration of trace substances at a greater level than occurs in average air n n Earth’s atmosphere (at ground level) is 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 1% Argon Most common human activities that cause pollution – Motor vehicles, industry, and power plants Most common air pollutants – Carbon monoxide, Sulfur dioxide n Air pollution concerns geographers at three levels – Global – Regional – local

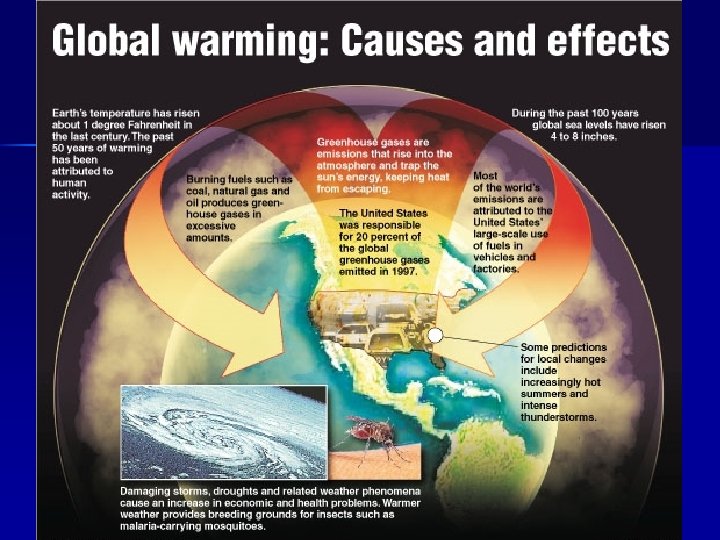
Air Pollution n Global n – Global warming n – At regional scale, air pollution may damage vegetation and water supply through acid deposition Pollution may be causing Earth’s temperature to rise – Greenhouse effect n n Anticipated temp increase on Earth caused by carbon dioxide trapping some of the radiation emitted by the surface Can have devastating consequences, even if only a few degrees – Global-scale ozone damage n Stratosphere contains ozone gases Regional n n n Local – Urban air pollution n – Absorbs dangerous UV rays n Definition: tiny droplets of sulfuric acid and nitric acid form and return to Earth’s surface Leads to acid precipitation n Threatened by pollutants called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) n Carbon monoxide Hydrocarbons particulates

Water Pollution n n American’s consume 5, 300 liters (1, 400 gallons) of water per day Water Pollution Sources – – – n Water-using industries Municipal sewage Agriculture Impact on Aquatic Life – Pollution reduces Oxygen level n Wastewater and Disease – Most MDC’s have passed Clean Water laws – Major impact n Ex. Thames River- London, England – LDCs have less capacity to treat wastewater n n Sewage flows into rivers Leads to high rates of diseases such as Cholera, Typhoid, and Dysentery

Land Pollution n Solid-Waste Disposal – The sanitary landfill is most common strategy for disposal of waste in the United States n n More than ½ of waste disposed this way Number of landfills has declined since 1990 s – Better compaction methods – Recycling and incineration have also increased n Can lead to air pollution n Hazardous Waste – Disposing is difficult n Includes heavy metals , PCB oils, cyanides, solvents, acids, and caustics – Can leach into soil, poisonous n n Must report to EPA Placed in containers and buried

Renewing Resources n Nuclear Energy – Not renewable but seen as alternative – Advantage n Small amount of material releases large amount of energy – Supplies 1/6 th world’s energy n Mostly in MDCs – Problems n n n Accidents Radioactive waste Material for nucs Limited uranium supply Cost/ distribution n Nuclear Fusion – Some nuclear power issues could be addressed by fusion – Definition: n Fusing of hydrogen atoms to helium – Can only occur at high temps

Leading Renewable Energy Sources n Biomass n – More than ½ of renewable energy n n – Historical source of power – Benefits Wood is a renewable resource Crops such as corn, sugarcane, and soybeans can be used for energy n n – Limited use n n – Use of moving water to create energy n Has been used throughout history – 2 nd most popular source of electricity – Can be environmental disaster n China – Three Gorges Dam Less change to environment Greater potential for increased use – Problems Energy to grow crops = to output Forest reduced Serves other purposes already such a food, clothing, shelter Hydroelectric Power Wind Power n n Noisy Lethal to birds Visual blight Geothermal Energy – Energy from hot water or steam – Prominent in volcanic areas – Lots of research currently underway


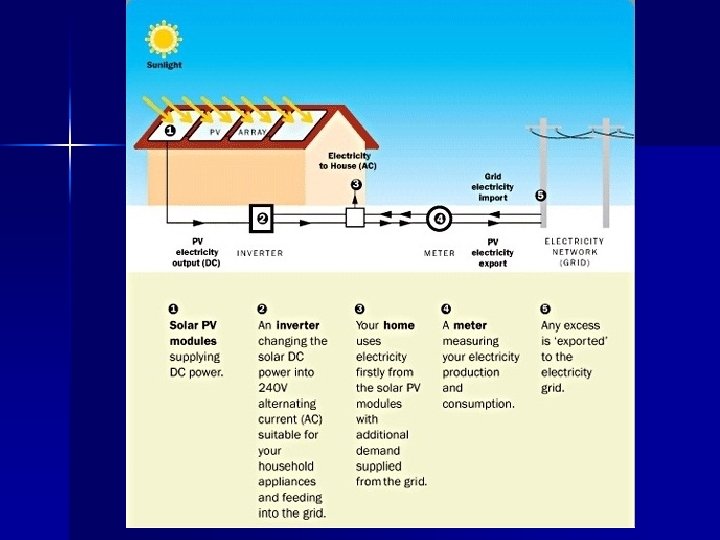
Solar Energy n The ultimate renewable source is solar energy n – Collect solar energy and convert it either to heat energy or to electricity – Currently supply 1% of electricity to U. S. n Active solar energy Potential is limitless n – Solar panels – Sun’s estimated life = 5 billion years n Sun’s energy is free, can’t be owned, bought, or sold – Does not damage the environment or cause pollution Example: n Passive solar energy – Capture of solar energy without any devices n Example: – South-facing windows – greenhouses
Renewable Energy in Motor Vehicles n n Most serious challenge to reducing dependence on nonrenewable energy is the motor vehicle Batteries – Battery-powered, electric cars popular in 1900 s – Shortcomings n n n Limited range Costs more to operate Recharging can take several hours Led to creation of hybrids Biofuels – Ethanol can be produced from biomass (corn in U. S. , sugarcane in Brazil) – Takes a lot of energy, is source of food n Hydrogen fuel cells – Convert hydrogen and oxygen into water, producing electricity and heat in the process n Can be used to power motors or electrical devices – Obtaining hydrogen a problem n Have to separate it – Hydrogen fuel used to lift shuttles into orbit, power shuttle’s electrical systems – For motor vehicle use would require a new distribution system


Recycling n Definition: – The separation, collection, processing, marketing, and reuse of the unwanted material n Increased in U. S. from 1970 from 7% to 33% in 2007 n Main items recycled – Paper, plastic, glass, aluminum

Sustainable Development n Definition: – Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs n Conservation – definition: n Sustainable use and management of natural resources such as wildlife, water, air, and Earth’s resources to meet human’s needs n Preservation – Definition: n n Maintenance of resources in their present condition Sustainability – Difficult to balance environment with concern for economic growth – Example: China n Has 16 of 20 most polluted cities in the world

7fc672caf9fd83708a6eb1ca721b0ca2.ppt