02ab557d17b4f895d6d6b9493a99a6ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Chapter 14: Resources AP Human Geography The Final Chapter!
Chapter 14: Resources AP Human Geography The Final Chapter!
 Why are resources being depleted? • Industrial and Economic Development – Animate power is supplied by humans and animals – Since the Industrial Revolution there has been a tremendous increase in inanimate power which is generated by machines – Three fossil fuels—oil, natural gas and coal, provide 5/6 ths of the world’s energy
Why are resources being depleted? • Industrial and Economic Development – Animate power is supplied by humans and animals – Since the Industrial Revolution there has been a tremendous increase in inanimate power which is generated by machines – Three fossil fuels—oil, natural gas and coal, provide 5/6 ths of the world’s energy
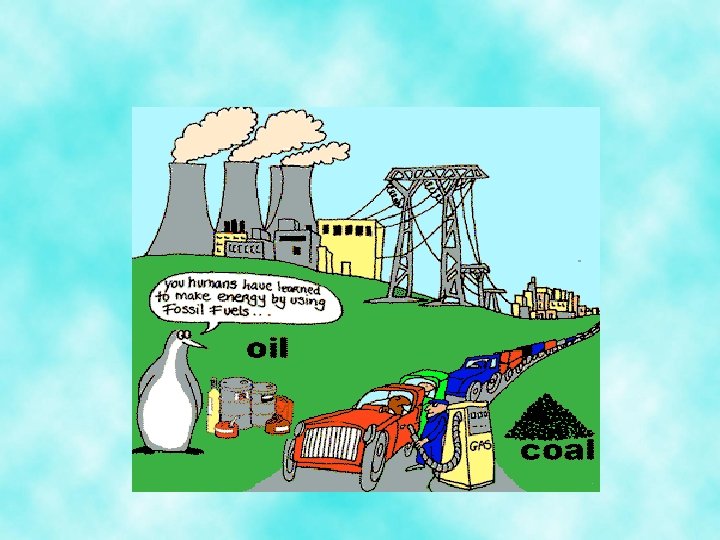

 The changing role of energy and technology • In some LDC’s, biomass fuel—wood, plant material and animal waste—is still the major source of fuel • Fossil fuels are examples of nonrenewable energy – Remaining supplies are proven reserves and potential reserves • The worlds proven reserves of natural gas will last for about 60 years, still less than petroleum reserves and much less than coal reserves
The changing role of energy and technology • In some LDC’s, biomass fuel—wood, plant material and animal waste—is still the major source of fuel • Fossil fuels are examples of nonrenewable energy – Remaining supplies are proven reserves and potential reserves • The worlds proven reserves of natural gas will last for about 60 years, still less than petroleum reserves and much less than coal reserves
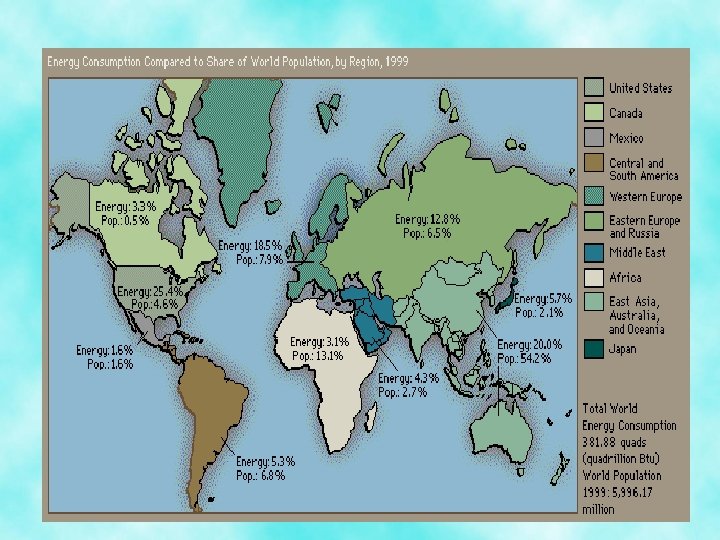
 Distribution of Fossil Fuels • Fossil fuels are unevenly distributed around the globe – China extracts 40% of the world’s total – The US extracts 20% of the world’s total – Australia, India, Russia, and South Africa all have major reserves
Distribution of Fossil Fuels • Fossil fuels are unevenly distributed around the globe – China extracts 40% of the world’s total – The US extracts 20% of the world’s total – Australia, India, Russia, and South Africa all have major reserves
 OPEC • Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries – Have 60% of the world’s oil reserves – Russia and US each account for ¼ of the world natural gas production – A few LDC’s in Africa, Asia and Latin America have extensive reserves of one or more fossil fuels, but most have little • MDC’s currently consume about 3/4 ths of the world’s energy. • Developing LDC’s are beginning to consume more
OPEC • Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries – Have 60% of the world’s oil reserves – Russia and US each account for ¼ of the world natural gas production – A few LDC’s in Africa, Asia and Latin America have extensive reserves of one or more fossil fuels, but most have little • MDC’s currently consume about 3/4 ths of the world’s energy. • Developing LDC’s are beginning to consume more
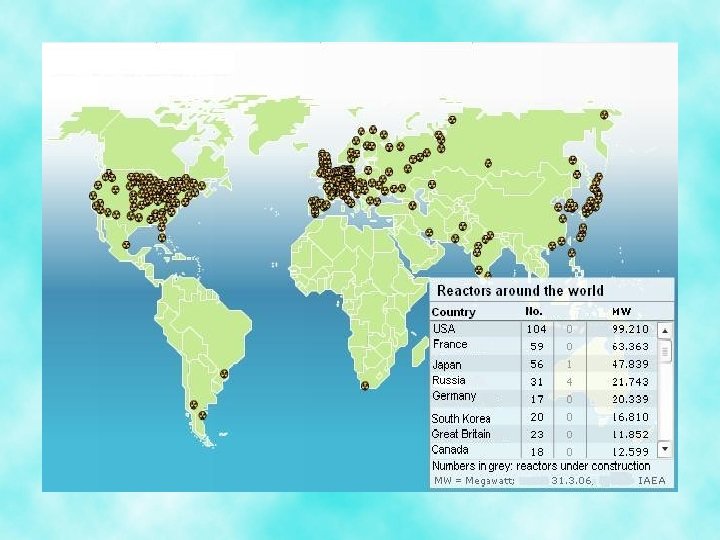
 Nuclear Power • Nuclear power is becoming an increasing energy source – Supplies about 1/6 th of the world’s electricity – The world’s leading generators of nuclear power are: the US, France, and Japan – Problems associated with nuclear power include: potential accidents, radioactive waste, generation of plutonium, a limited uranium supply, geographic distribution and cost.
Nuclear Power • Nuclear power is becoming an increasing energy source – Supplies about 1/6 th of the world’s electricity – The world’s leading generators of nuclear power are: the US, France, and Japan – Problems associated with nuclear power include: potential accidents, radioactive waste, generation of plutonium, a limited uranium supply, geographic distribution and cost.
 Why are resources being depleted? • Air, water, and land remove and disperse waste, but pollution will occur when more waste is added than a resource can accommodate • Air pollution is a concentration of trace substances at a greater level than occurs in the average air • The burning of fossil fuels generate most air pollution
Why are resources being depleted? • Air, water, and land remove and disperse waste, but pollution will occur when more waste is added than a resource can accommodate • Air pollution is a concentration of trace substances at a greater level than occurs in the average air • The burning of fossil fuels generate most air pollution
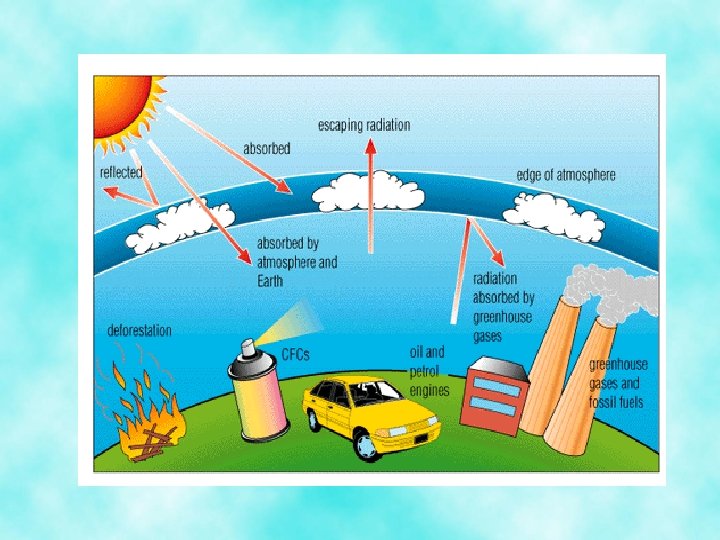
 The Greenhouse Effect • Air pollution may contribute to the greenhouse effect – This is when carbon dioxide traps some of the radiation emitted by Earth’s surface – The ozone layer of the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs dangerous ultraviolet (UV) rays from the Sun, but is threatened by pollutants called chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s)
The Greenhouse Effect • Air pollution may contribute to the greenhouse effect – This is when carbon dioxide traps some of the radiation emitted by Earth’s surface – The ozone layer of the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs dangerous ultraviolet (UV) rays from the Sun, but is threatened by pollutants called chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s)
 Acid Rain • Pollution in the atmosphere may return to the Earth’s surface as acid precipitation, which damages lakes and agricultural land in regions of heavy industrial development • Urban air pollution consists of: carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and particulates • This is a serious problem in urban areas such as Denver, Salt Lake City and Santiago, Chile, where the mountains help to trap the gases and produce a temperature inversion
Acid Rain • Pollution in the atmosphere may return to the Earth’s surface as acid precipitation, which damages lakes and agricultural land in regions of heavy industrial development • Urban air pollution consists of: carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and particulates • This is a serious problem in urban areas such as Denver, Salt Lake City and Santiago, Chile, where the mountains help to trap the gases and produce a temperature inversion

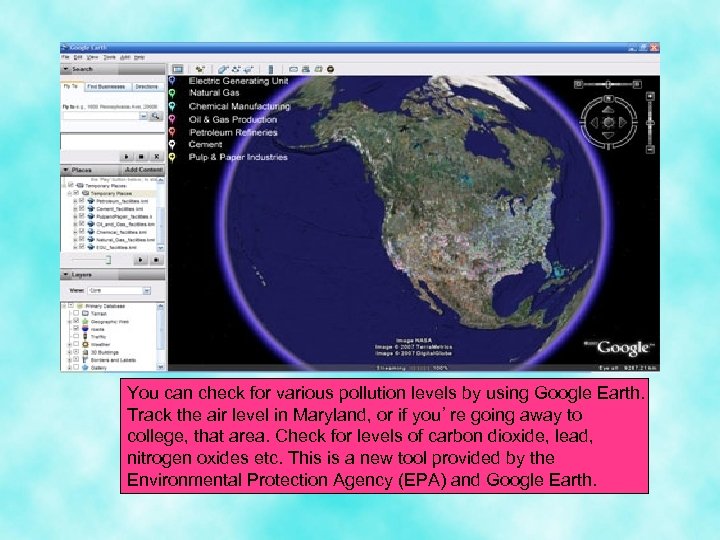 You can check for various pollution levels by using Google Earth. Track the air level in Maryland, or if you’re going away to college, that area. Check for levels of carbon dioxide, lead, nitrogen oxides etc. This is a new tool provided by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Google Earth.
You can check for various pollution levels by using Google Earth. Track the air level in Maryland, or if you’re going away to college, that area. Check for levels of carbon dioxide, lead, nitrogen oxides etc. This is a new tool provided by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Google Earth.
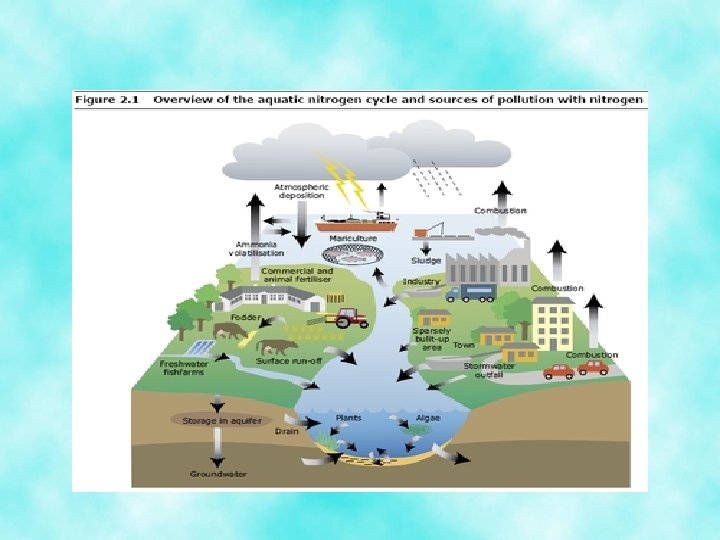
 Water Pollution • Most water pollution is generated by water -using industries, municipal sewage, and agriculture • Polluted water can harm aquatic plants and animals • It can also cause waterborne diseases such as: cholera, typhoid and dysentery, especially in LDC’s that suffer from poor sanitation and untreated water
Water Pollution • Most water pollution is generated by water -using industries, municipal sewage, and agriculture • Polluted water can harm aquatic plants and animals • It can also cause waterborne diseases such as: cholera, typhoid and dysentery, especially in LDC’s that suffer from poor sanitation and untreated water
 Land Pollution • Paper products constitute the larges percentage of solid waste in the US • Most of this waste is disposed in sanitary landfills • The number of landfills in the US has declined by 3/4 th since 1990 • There are now a smaller number of regional landfills • Incineration reduces the bulk of trash by about ¾, but burning leads to toxins in the air.
Land Pollution • Paper products constitute the larges percentage of solid waste in the US • Most of this waste is disposed in sanitary landfills • The number of landfills in the US has declined by 3/4 th since 1990 • There are now a smaller number of regional landfills • Incineration reduces the bulk of trash by about ¾, but burning leads to toxins in the air.
 Disposal of Hazardous Waste • The disposal of hazardous waste is especially difficult • Hazardous waste sites such as Love Canal near Niagara Falls, NY have leaked and caused health problems
Disposal of Hazardous Waste • The disposal of hazardous waste is especially difficult • Hazardous waste sites such as Love Canal near Niagara Falls, NY have leaked and caused health problems

 Renewable Resources • The leading renewable resources are biomass and hydroelectric power • Geothermal and wind power are also becoming important • Wood and plants are important forms of biomass that are renewable resources if they are carefully harvested
Renewable Resources • The leading renewable resources are biomass and hydroelectric power • Geothermal and wind power are also becoming important • Wood and plants are important forms of biomass that are renewable resources if they are carefully harvested
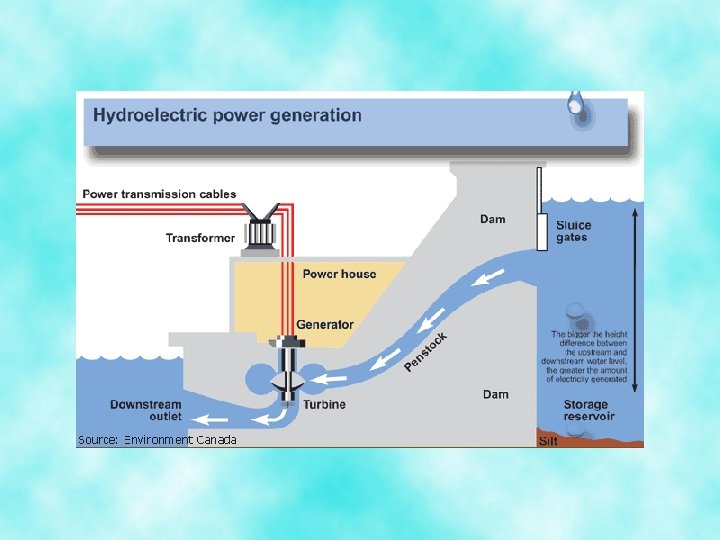
 Hydroelectric Power • This is the second most important source of energy after coal, supplying about 1/4 teh of the world’s demand • The biggest drawback with hydroelectric power is that is often generated by the building of dams that can cause serious environmental damage
Hydroelectric Power • This is the second most important source of energy after coal, supplying about 1/4 teh of the world’s demand • The biggest drawback with hydroelectric power is that is often generated by the building of dams that can cause serious environmental damage
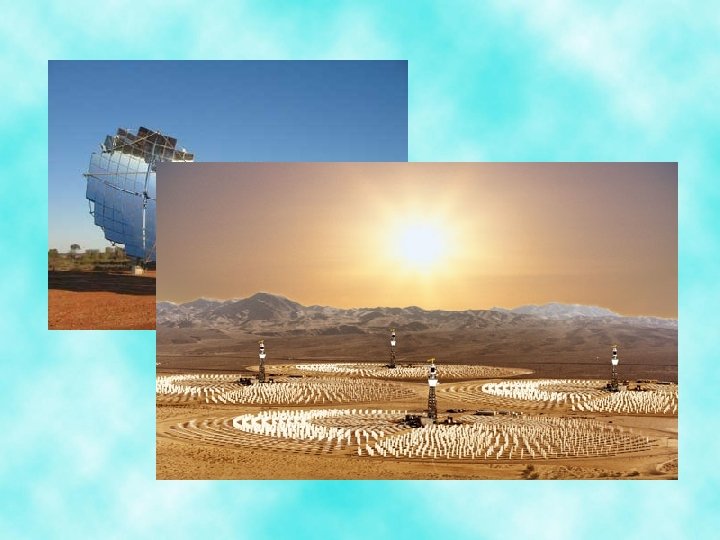
 Solar Energy • Solar energy is free and ubiquitous, and thus potentially the most important renewable resource • It can be harnessed either through passive or active means • Passive solar energy systems capture solar energy without any special devices • Active solar energy systems collect solar energy and convert it to heat or electricity
Solar Energy • Solar energy is free and ubiquitous, and thus potentially the most important renewable resource • It can be harnessed either through passive or active means • Passive solar energy systems capture solar energy without any special devices • Active solar energy systems collect solar energy and convert it to heat or electricity

 Recycling • Is the separation, collection, processing, and reuse of unwanted material • Recycling has increased in the US from 7% of all solid waste in 1970, to about 32% in 2005 • Recycled products are picked up, processed, and manufactured into marketable products
Recycling • Is the separation, collection, processing, and reuse of unwanted material • Recycling has increased in the US from 7% of all solid waste in 1970, to about 32% in 2005 • Recycled products are picked up, processed, and manufactured into marketable products
 Why Can Resources be Conserved? • According to the United Nations; Sustainable development is “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. ” • Preservation: the maintenance of resources in their present condition • Conservation: sustainable use and management of natural resources
Why Can Resources be Conserved? • According to the United Nations; Sustainable development is “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. ” • Preservation: the maintenance of resources in their present condition • Conservation: sustainable use and management of natural resources
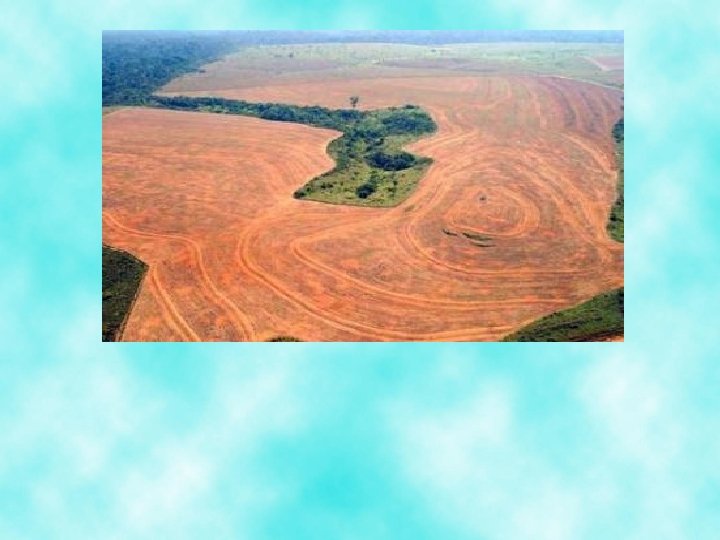
 Biodiversity v. Closely related to sustainable diversity is biodiversity, which refers to the variety of plant and animal species across Earth’s surface v. When biodiversity is protected, sustainable development is promoted v. More than ½ of the Earth’s species are located in tropical rainforests v. The main cause of high rates of species extinction is rapid deforestation
Biodiversity v. Closely related to sustainable diversity is biodiversity, which refers to the variety of plant and animal species across Earth’s surface v. When biodiversity is protected, sustainable development is promoted v. More than ½ of the Earth’s species are located in tropical rainforests v. The main cause of high rates of species extinction is rapid deforestation

 The Future? ? ?
The Future? ? ?
 The End (Sort of)
The End (Sort of)
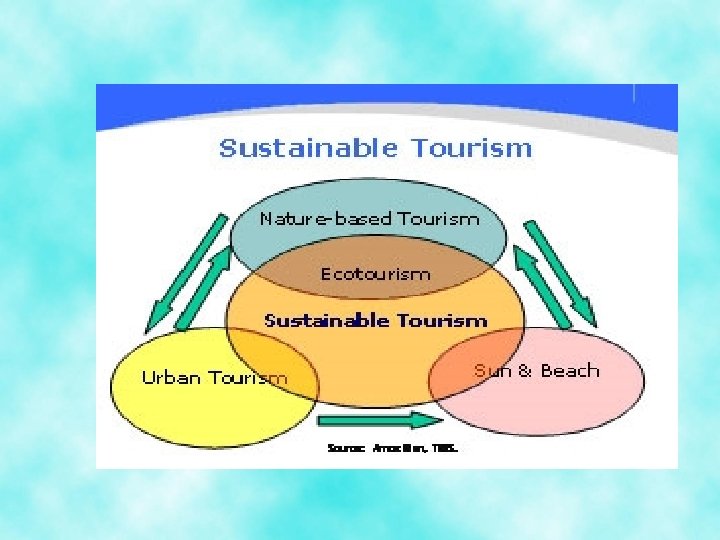
 Sustainable Tourism • minimizes negative economic, environmental, and social impacts • generates greater economic benefits for local people and enhances the well-being of host communities, improves working conditions and access to the industry • involves local people in decisions that affect their lives and life chances • makes positive contributions to the conservation of natural and cultural heritage, to the maintenance of the world’s diversity
Sustainable Tourism • minimizes negative economic, environmental, and social impacts • generates greater economic benefits for local people and enhances the well-being of host communities, improves working conditions and access to the industry • involves local people in decisions that affect their lives and life chances • makes positive contributions to the conservation of natural and cultural heritage, to the maintenance of the world’s diversity

 Sustainable Tourism • Sustainable tourism is attempting to make as low an impact on the environment and local culture as possible, while helping to generate future employment for local people. • The aim of sustainable tourism is to ensure that development brings a positive experience for local people, tourism companies and the tourists themselves
Sustainable Tourism • Sustainable tourism is attempting to make as low an impact on the environment and local culture as possible, while helping to generate future employment for local people. • The aim of sustainable tourism is to ensure that development brings a positive experience for local people, tourism companies and the tourists themselves
 Examples • See two video clips • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=JFbb. K bdqo. Jg • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=s. Sh. PD p. Dop 8 Q • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Meynz Qz 4 SXk • What Is NOT a good example of sustainable tourism? • Caribbean Cruises! They bring all of their
Examples • See two video clips • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=JFbb. K bdqo. Jg • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=s. Sh. PD p. Dop 8 Q • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Meynz Qz 4 SXk • What Is NOT a good example of sustainable tourism? • Caribbean Cruises! They bring all of their
 What Is NOT a good example of sustainable tourism? • Caribbean Cruises! They bring all of their food with them, and most companies they contract with in ports are run by ex-pats or other foreign companies (many are run by British citizens) – In order to be sustainable they should buy food from wherever they pull into port, and use only local people for tours
What Is NOT a good example of sustainable tourism? • Caribbean Cruises! They bring all of their food with them, and most companies they contract with in ports are run by ex-pats or other foreign companies (many are run by British citizens) – In order to be sustainable they should buy food from wherever they pull into port, and use only local people for tours
 Your Task • In groups of NO MORE than 4 people: you and your group are the owners of a tour company based in the local area (your choice: DC, Baltimore or Annapolis). Create a tourist package that defines AND FOLLOWS sustainable tourism. Create a print advertisement. Be prepared to sell your to your classmates.
Your Task • In groups of NO MORE than 4 people: you and your group are the owners of a tour company based in the local area (your choice: DC, Baltimore or Annapolis). Create a tourist package that defines AND FOLLOWS sustainable tourism. Create a print advertisement. Be prepared to sell your to your classmates.


