dcb307e3f503837935a0f8bf91e7edd2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Chapter 14 Leadership
Chapter 14 Leadership
 Learning Outcomes After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Explain what leadership is. 2. Describe who leaders are and what effective leaders do. 3. Explain Fiedler’s contingency theory. 4. Describe how path-goal theory works. Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -2
Learning Outcomes After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Explain what leadership is. 2. Describe who leaders are and what effective leaders do. 3. Explain Fiedler’s contingency theory. 4. Describe how path-goal theory works. Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -2
 Learning Outcomes After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 5. Explain the normative decision theory. 6. Discuss gender and leadership. 7. Explain how visionary leadership (i. e. , charismatic and transformational leadership) helps leaders achieve strategic leadership. Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -3
Learning Outcomes After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 5. Explain the normative decision theory. 6. Discuss gender and leadership. 7. Explain how visionary leadership (i. e. , charismatic and transformational leadership) helps leaders achieve strategic leadership. Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -3
 Leadership • The process of influencing others to achieve group or organizational goals 4 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -4
Leadership • The process of influencing others to achieve group or organizational goals 4 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -4
 Class Activity: Leadership versus Managership Beyond the Book • What is the difference between leadership and managership? • Discuss as a class. 5 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -5
Class Activity: Leadership versus Managership Beyond the Book • What is the difference between leadership and managership? • Discuss as a class. 5 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -5
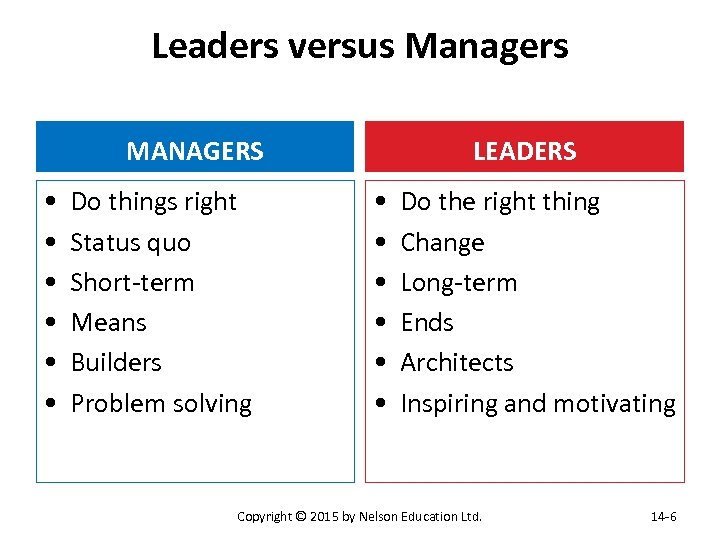 Leaders versus Managers MANAGERS • • • Do things right Status quo Short-term Means Builders Problem solving LEADERS • • • Do the right thing Change Long-term Ends Architects Inspiring and motivating Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -6
Leaders versus Managers MANAGERS • • • Do things right Status quo Short-term Means Builders Problem solving LEADERS • • • Do the right thing Change Long-term Ends Architects Inspiring and motivating Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -6
 Leadership Traits Trait Theory: A leadership theory that holds that effective leaders possess a similar set of traits or characteristics 2. 1 Leadership Traits: • Desire to lead • Drive • Knowledge of the business • Cognitive ability • Emotional stability • Self-confidence • Honesty and integrity Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -7
Leadership Traits Trait Theory: A leadership theory that holds that effective leaders possess a similar set of traits or characteristics 2. 1 Leadership Traits: • Desire to lead • Drive • Knowledge of the business • Cognitive ability • Emotional stability • Self-confidence • Honesty and integrity Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -7
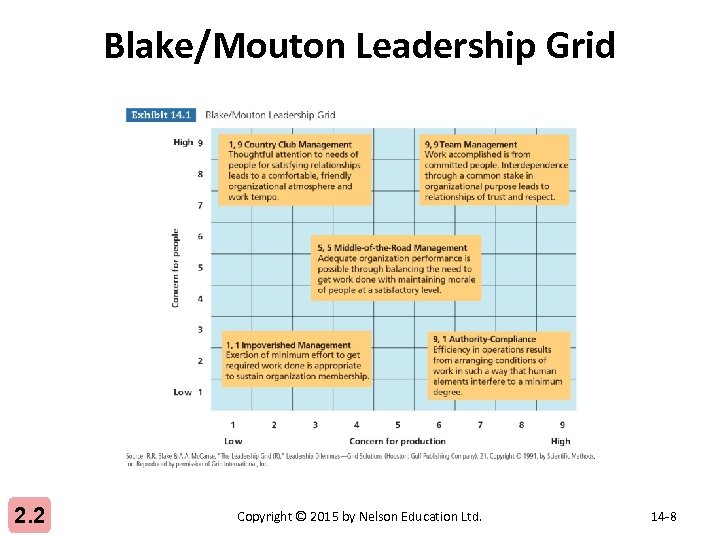 Blake/Mouton Leadership Grid 2. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -8
Blake/Mouton Leadership Grid 2. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -8
 Situational Approaches to Leadership • Fiedler’s Contingency Theory • Path-Goal Theory • Vroom and Yetton’s Normative Decision Model 3 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -9
Situational Approaches to Leadership • Fiedler’s Contingency Theory • Path-Goal Theory • Vroom and Yetton’s Normative Decision Model 3 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -9
 Putting Leaders in the Right Situation 1. Assess leaders in terms of the conduct and performance of the people they are leading. 2. Leaders are generally unable to change their style and that they are more effective when that style fits the situation. 3. The success of a leader depends on the degree to which he or she is able to influence the behaviour of group members. 10 3 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -10
Putting Leaders in the Right Situation 1. Assess leaders in terms of the conduct and performance of the people they are leading. 2. Leaders are generally unable to change their style and that they are more effective when that style fits the situation. 3. The success of a leader depends on the degree to which he or she is able to influence the behaviour of group members. 10 3 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -10
 Fiedler’s Leadership Style: Least Preferred Coworker (LPC) How would you rank your least-preferred coworker? Pleasant Unpleasant Friendly Unfriendly Supportive Hostile Boring Interesting Gloomy Cheerful Insincere Sincere 3. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -11
Fiedler’s Leadership Style: Least Preferred Coworker (LPC) How would you rank your least-preferred coworker? Pleasant Unpleasant Friendly Unfriendly Supportive Hostile Boring Interesting Gloomy Cheerful Insincere Sincere 3. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -11
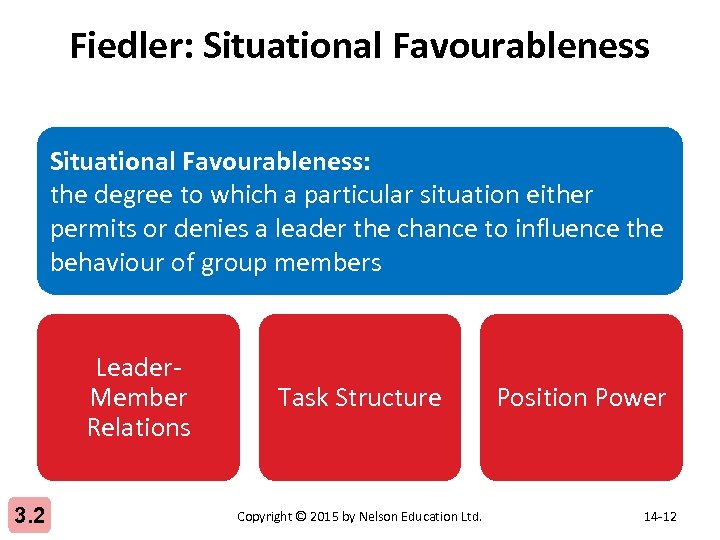 Fiedler: Situational Favourableness: the degree to which a particular situation either permits or denies a leader the chance to influence the behaviour of group members Leader. Member Relations 3. 2 Task Structure Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. Position Power 14 -12
Fiedler: Situational Favourableness: the degree to which a particular situation either permits or denies a leader the chance to influence the behaviour of group members Leader. Member Relations 3. 2 Task Structure Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. Position Power 14 -12
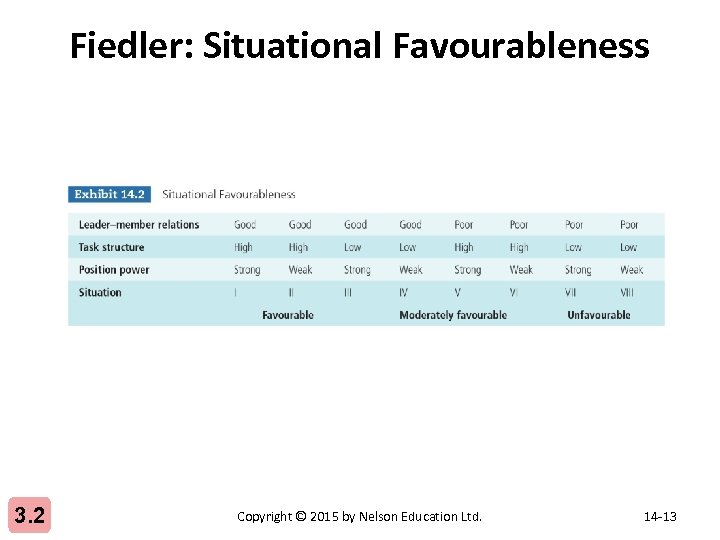 Fiedler: Situational Favourableness 3. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -13
Fiedler: Situational Favourableness 3. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -13
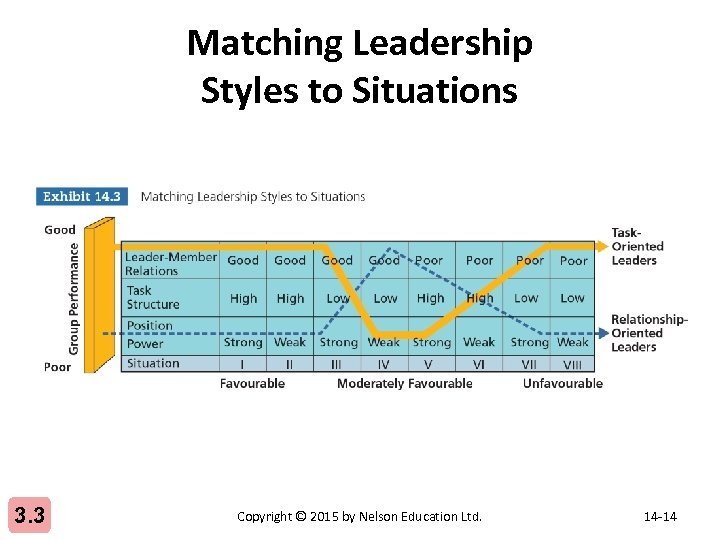 Matching Leadership Styles to Situations 3. 3 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -14
Matching Leadership Styles to Situations 3. 3 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -14
 Adapting Leader Behaviour: Path-Goal Theory: • Leaders can increase subordinate satisfaction and performance by clarifying and clearing the paths to goals and by increasing the number and kinds of rewards available for goal attainment. – Leaders must be a source of immediate or future satisfaction for followers. – Leader must offer uniqueness and value beyond what followers already experience 4 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -15
Adapting Leader Behaviour: Path-Goal Theory: • Leaders can increase subordinate satisfaction and performance by clarifying and clearing the paths to goals and by increasing the number and kinds of rewards available for goal attainment. – Leaders must be a source of immediate or future satisfaction for followers. – Leader must offer uniqueness and value beyond what followers already experience 4 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -15
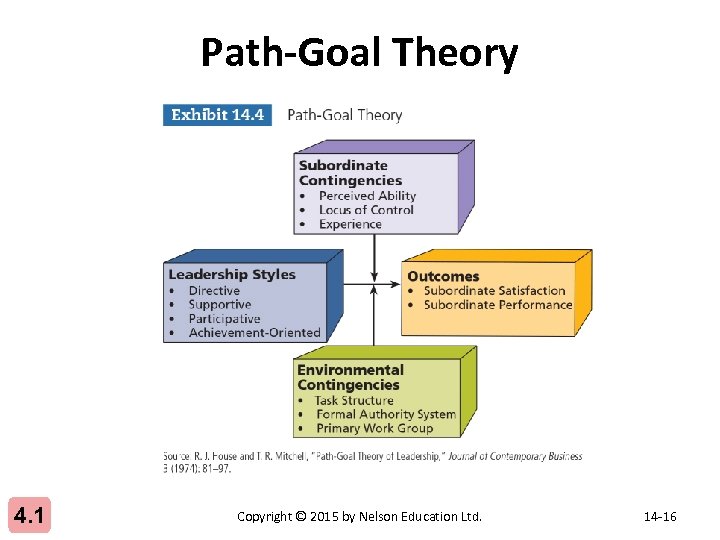 Path-Goal Theory 4. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -16
Path-Goal Theory 4. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -16
 Subordinate and Environmental Contingencies Subordinate Contingencies 1. Perceived ability 2. Experience 3. Locus of control Environmental Contingencies 1. Task structure 2. Formal authority system 3. Primary work groups Source: R. J. House and T. R. Mitchell, “Path-Goal Theory of Leadership, ” Journal of Contemporary Business 3 (1974): 81– 97. 4. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -17
Subordinate and Environmental Contingencies Subordinate Contingencies 1. Perceived ability 2. Experience 3. Locus of control Environmental Contingencies 1. Task structure 2. Formal authority system 3. Primary work groups Source: R. J. House and T. R. Mitchell, “Path-Goal Theory of Leadership, ” Journal of Contemporary Business 3 (1974): 81– 97. 4. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -17
 Path-Goal Theory: When to Use Directive, Supportive, Participative, or Achievement-Oriented Leadership 4. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -18
Path-Goal Theory: When to Use Directive, Supportive, Participative, or Achievement-Oriented Leadership 4. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -18
 Normative Theory, Decision Styles, and Levels of Employee Participation 5 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -19
Normative Theory, Decision Styles, and Levels of Employee Participation 5 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -19
 Normative Decision Theory: Decision Styles • Autocratic (AI or AII) – Leaders make the decisions. • Consultative (CI or CII) – Leaders share the problems – Then they make the decisions themselves. • Group (GII) – Leaders share the problems. – Then they have the group make decisions. 5. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -20
Normative Decision Theory: Decision Styles • Autocratic (AI or AII) – Leaders make the decisions. • Consultative (CI or CII) – Leaders share the problems – Then they make the decisions themselves. • Group (GII) – Leaders share the problems. – Then they have the group make decisions. 5. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -20
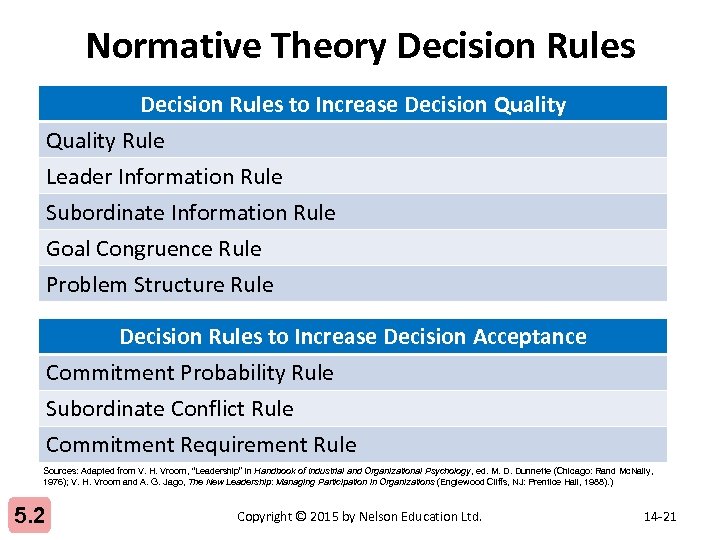 Normative Theory Decision Rules to Increase Decision Quality Rule Leader Information Rule Subordinate Information Rule Goal Congruence Rule Problem Structure Rule Decision Rules to Increase Decision Acceptance Commitment Probability Rule Subordinate Conflict Rule Commitment Requirement Rule Sources: Adapted from V. H. Vroom, “Leadership” in Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, ed. M. D. Dunnette (Chicago: Rand Mc. Nally, 1976); V. H. Vroom and A. G. Jago, The New Leadership: Managing Participation in Organizations (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1988). ) 5. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -21
Normative Theory Decision Rules to Increase Decision Quality Rule Leader Information Rule Subordinate Information Rule Goal Congruence Rule Problem Structure Rule Decision Rules to Increase Decision Acceptance Commitment Probability Rule Subordinate Conflict Rule Commitment Requirement Rule Sources: Adapted from V. H. Vroom, “Leadership” in Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, ed. M. D. Dunnette (Chicago: Rand Mc. Nally, 1976); V. H. Vroom and A. G. Jago, The New Leadership: Managing Participation in Organizations (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1988). ) 5. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -21
 Normative Decision Theory Tree for Determining the Level of Participation in Decision Making 5. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -22
Normative Decision Theory Tree for Determining the Level of Participation in Decision Making 5. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -22
 Gender and Leadership • Several studies reflect how stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination contribute to women’s underrepresentation in elite leadership roles. • Traits do play an important, albeit limited, role in leadership effectiveness between genders. 6 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -23
Gender and Leadership • Several studies reflect how stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination contribute to women’s underrepresentation in elite leadership roles. • Traits do play an important, albeit limited, role in leadership effectiveness between genders. 6 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -23
 Strategic Leadership The ability to: • anticipate • envision • maintain flexibility • think strategically • work with others • initiate changes • create a positive future Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -24
Strategic Leadership The ability to: • anticipate • envision • maintain flexibility • think strategically • work with others • initiate changes • create a positive future Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -24
 Visionary Leadership • Creates a positive image of the future that motivates organizational members and provides direction for future planning and goal setting 7 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -25
Visionary Leadership • Creates a positive image of the future that motivates organizational members and provides direction for future planning and goal setting 7 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -25
 Visionary Leadership Charismatic Leadership Transformational Leadership 7. 1 7. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -26
Visionary Leadership Charismatic Leadership Transformational Leadership 7. 1 7. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -26
 Charismatic Leadership • • 7. 1 Creates an exceptionally strong relationship Articulates a clear vision Models values consistent with that vision Communicates high-performance expectations Strong, confident, dynamic personalities Establishes trust and loyalty from followers Concern is with ego-driven charismatic leaders who take advantage of fanatical followers Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -27
Charismatic Leadership • • 7. 1 Creates an exceptionally strong relationship Articulates a clear vision Models values consistent with that vision Communicates high-performance expectations Strong, confident, dynamic personalities Establishes trust and loyalty from followers Concern is with ego-driven charismatic leaders who take advantage of fanatical followers Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -27
 Charismatic Leadership Unethical Charismatic Ethical Charismatic Leadership 7. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -28
Charismatic Leadership Unethical Charismatic Ethical Charismatic Leadership 7. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -28
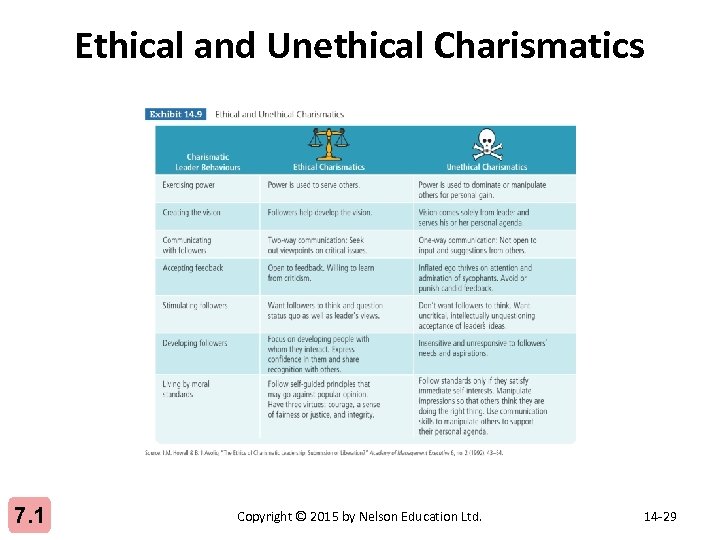 Ethical and Unethical Charismatics 7. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -29
Ethical and Unethical Charismatics 7. 1 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -29
 Transformational Leadership • Generates awareness and acceptance of mission • Employees see beyond own needs and self-interests • Followers accomplish more than intended or thought possible • Encourage followers to make sacrifices for the organization • Followers prosper when organization prospers • Do the right thing • Maintain high standards for ethical and personal conduct 7. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -30
Transformational Leadership • Generates awareness and acceptance of mission • Employees see beyond own needs and self-interests • Followers accomplish more than intended or thought possible • Encourage followers to make sacrifices for the organization • Followers prosper when organization prospers • Do the right thing • Maintain high standards for ethical and personal conduct 7. 2 Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -30
 Charismatic Leadership Inspirational Motivation Transformational Leadership Intellectual Stimulation 7. 2 Individualized Consideration Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -31
Charismatic Leadership Inspirational Motivation Transformational Leadership Intellectual Stimulation 7. 2 Individualized Consideration Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -31
 How to Reduce the Risks Associated with Unethical Charismatics 1. Have a clearly written code of conduct that is fairly and consistently enforced for all managers. 2. Recruit, select, and promote managers with high ethical standards. 3. Train leaders to value, seek, and use diverse points of view. 4. Train leaders and subordinates regarding ethical leader behaviours so that abuses can be recognized and corrected. 5. Reward people who exhibit ethical behaviours, especially ethical leader behaviours. Sources: J. M. Burns, Leadership (New York: Harper and Row, 1978); B. M. Bass, “From Transactional to Transformational Leadership: Learning to Share the Vision, ” Organizational Dynamics 18 (1990): 19– 36. ) Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -32
How to Reduce the Risks Associated with Unethical Charismatics 1. Have a clearly written code of conduct that is fairly and consistently enforced for all managers. 2. Recruit, select, and promote managers with high ethical standards. 3. Train leaders to value, seek, and use diverse points of view. 4. Train leaders and subordinates regarding ethical leader behaviours so that abuses can be recognized and corrected. 5. Reward people who exhibit ethical behaviours, especially ethical leader behaviours. Sources: J. M. Burns, Leadership (New York: Harper and Row, 1978); B. M. Bass, “From Transactional to Transformational Leadership: Learning to Share the Vision, ” Organizational Dynamics 18 (1990): 19– 36. ) Copyright © 2015 by Nelson Education Ltd. 14 -32


