ddbe8237a7d453e157afd502bd9ca282.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Chapter 14 Forging the National Economy 1790 - 1860 Sewing Machine Railroad tracks
Chapter 14 Forging the National Economy 1790 - 1860 Sewing Machine Railroad tracks
 Economic Revolution § § 1. Industrial Revolution 2. Why in the North? 3. Early Railroads 4. Expansion of Business § Factory System § Labor Movement: Women § Social Mobility: extremes of wealth § 5. The cotton revolution in the South § 6. Commercial Agriculture
Economic Revolution § § 1. Industrial Revolution 2. Why in the North? 3. Early Railroads 4. Expansion of Business § Factory System § Labor Movement: Women § Social Mobility: extremes of wealth § 5. The cotton revolution in the South § 6. Commercial Agriculture
 The Industrial Revolution § Major changes in agriculture, Mechanical manufacturing and transportation Reaper § Started in Europe and then came to America § in America It was slightly delayed because: § 1. Superior Quality of Imported goods § 2. Lack of adequate, low-cost labor § 3. The greater attraction of shipping, trade, and land speculation than of making improvements on machinery
The Industrial Revolution § Major changes in agriculture, Mechanical manufacturing and transportation Reaper § Started in Europe and then came to America § in America It was slightly delayed because: § 1. Superior Quality of Imported goods § 2. Lack of adequate, low-cost labor § 3. The greater attraction of shipping, trade, and land speculation than of making improvements on machinery
 Why did the North became the Industrialized center of America? Immigrants § 1. Narrow belt of fertile soil made agriculture difficult & manufacturing attractive § 2. Dense population provided labor and accessible markets § 3. Seaports made easy the import of raw materials and the export of the finished products § 4. Rapid rivers provided abundant water power to run machines
Why did the North became the Industrialized center of America? Immigrants § 1. Narrow belt of fertile soil made agriculture difficult & manufacturing attractive § 2. Dense population provided labor and accessible markets § 3. Seaports made easy the import of raw materials and the export of the finished products § 4. Rapid rivers provided abundant water power to run machines
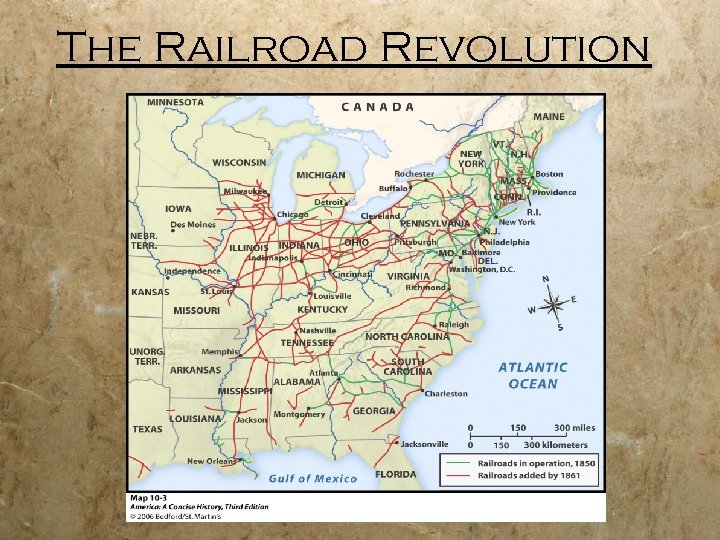
 Early Railroads § Most significant development because it was fast, reliable, Cheaper to built than canals and not frozen over in the winter § Able to go anywhere despite weather and terrain (Mountains) § First R/R appeared in US in 1828 (Jackson) § By 1860, the US had laid 30, 000 miles of R/R track § 3/4 of that 30, 000 miles was in the industrialized north. § The Railroad a. k. a The iron horse
Early Railroads § Most significant development because it was fast, reliable, Cheaper to built than canals and not frozen over in the winter § Able to go anywhere despite weather and terrain (Mountains) § First R/R appeared in US in 1828 (Jackson) § By 1860, the US had laid 30, 000 miles of R/R track § 3/4 of that 30, 000 miles was in the industrialized north. § The Railroad a. k. a The iron horse
 The Railroad Revolution
The Railroad Revolution
 Railroad Opposition Tragic R/R fiery crash § Canal investors hated R/R’s drove them out of Business § “Dangerous public menace flying sparks could set fire to nearby haystacks” § R/R accidents could char (burn and kill passengers)
Railroad Opposition Tragic R/R fiery crash § Canal investors hated R/R’s drove them out of Business § “Dangerous public menace flying sparks could set fire to nearby haystacks” § R/R accidents could char (burn and kill passengers)
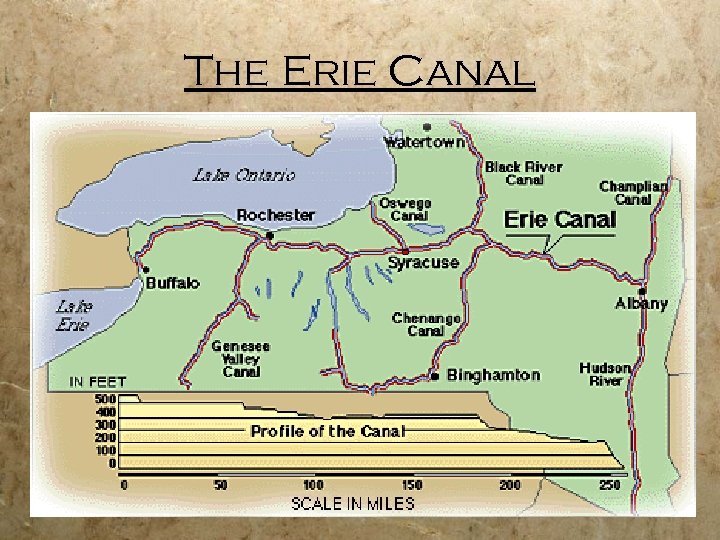
 Early Canals § Clinton’s Big Ditch (Erie Canal) § Headed up by: NY Governor De. Witt Clinton § Connected the Hudson River (NYC) with Buffalo/ the Great Lakes/ The West § Started in : 1817 § Completed in: 1825 § Ran 363 miles across NY (east to West) § Paid for through NY state taxes (not federal aid) § Travel along the canal was 5 MPH by use of Mules pulling the boat down the canal § People as well as freight used the canal § Advantage of the canal: decreased the shipping costs of farmers produce (from $100 to $5)
Early Canals § Clinton’s Big Ditch (Erie Canal) § Headed up by: NY Governor De. Witt Clinton § Connected the Hudson River (NYC) with Buffalo/ the Great Lakes/ The West § Started in : 1817 § Completed in: 1825 § Ran 363 miles across NY (east to West) § Paid for through NY state taxes (not federal aid) § Travel along the canal was 5 MPH by use of Mules pulling the boat down the canal § People as well as freight used the canal § Advantage of the canal: decreased the shipping costs of farmers produce (from $100 to $5)
 The Erie Canal
The Erie Canal
 Expansion of business: Factory System Textile Mill Boarding House § Disadvantages of factory work: § 1. Long hours § 2. Low wages § 3. Meals were small and quick § 4. Unsanitary working conditions § 5. Workers were forbidden by law to form labor unions § 6. Bell system (when to work, when to break) § 7. Lived in boarding house and constant supervision
Expansion of business: Factory System Textile Mill Boarding House § Disadvantages of factory work: § 1. Long hours § 2. Low wages § 3. Meals were small and quick § 4. Unsanitary working conditions § 5. Workers were forbidden by law to form labor unions § 6. Bell system (when to work, when to break) § 7. Lived in boarding house and constant supervision
 Expansion of Business: Factory System § Farm girls were recruited to work in mills (Factories) § Requirements: young and single § Why mill work was attractive: § 1. Earned a wage § 2. Live in the city away from parents § 3. Freedom- independence
Expansion of Business: Factory System § Farm girls were recruited to work in mills (Factories) § Requirements: young and single § Why mill work was attractive: § 1. Earned a wage § 2. Live in the city away from parents § 3. Freedom- independence
 Expansion of business: Labor Movement: Women § When women married they would leave their paying jobs & take up new work (Without Wages) as wives and mothers § “cult of domesticity” glorifying the functions of a homemaker § Workers realized their strongest weapon against unjust working practices was to lay down their tools (Strike) - Commonwealth v. Hunt- legalized strikes
Expansion of business: Labor Movement: Women § When women married they would leave their paying jobs & take up new work (Without Wages) as wives and mothers § “cult of domesticity” glorifying the functions of a homemaker § Workers realized their strongest weapon against unjust working practices was to lay down their tools (Strike) - Commonwealth v. Hunt- legalized strikes
 Expansion of business: Social Mobility § Greatest extremes of economic inequality in cities § Unskilled labor (usually immigrants were drifters moving from one place to the next to find work) § American Dream part of the PULL for immigrants coming to America § “Rags to riches” § John Jacob Astor fur trader and land speculator. America’s 1 st millionaire
Expansion of business: Social Mobility § Greatest extremes of economic inequality in cities § Unskilled labor (usually immigrants were drifters moving from one place to the next to find work) § American Dream part of the PULL for immigrants coming to America § “Rags to riches” § John Jacob Astor fur trader and land speculator. America’s 1 st millionaire
 The Cotton revolution in the South § Rapid expansion of cotton production with the invention of Eli Whitney’s Cotton Gin § Whitney born in MA, graduated from Yale, traveled to GA to be a private Tutor § While in GA, Whitney learned about the South’s poverty and their desire for someone to invent a workable device to separate the seeds & from the cotton fiber § Because Whitney was a genius he built the cotton gin in just 10 days § Gin is short for engine § The gin could quickly cut the seeds from fibers of cotton- it was 50 times more effective than the handpicking process
The Cotton revolution in the South § Rapid expansion of cotton production with the invention of Eli Whitney’s Cotton Gin § Whitney born in MA, graduated from Yale, traveled to GA to be a private Tutor § While in GA, Whitney learned about the South’s poverty and their desire for someone to invent a workable device to separate the seeds & from the cotton fiber § Because Whitney was a genius he built the cotton gin in just 10 days § Gin is short for engine § The gin could quickly cut the seeds from fibers of cotton- it was 50 times more effective than the handpicking process
 The Cotton Revolution in the South Slave labor Musket § The Yankee (Northern) Eli Whitney, by inventing the cotton gin, increased the need for slave labor in the south § At the same time, Whitney’s principle of interchangeable parts helped factories to flourish in the North (muskets)- the trigger from 1 musket might not fit in another musket
The Cotton Revolution in the South Slave labor Musket § The Yankee (Northern) Eli Whitney, by inventing the cotton gin, increased the need for slave labor in the south § At the same time, Whitney’s principle of interchangeable parts helped factories to flourish in the North (muskets)- the trigger from 1 musket might not fit in another musket
 Commercial Agriculture § The production of crops for sale, crops intended for widespread distribution and any nonfood crops such as cotton and tobacco. § Each region in America was specializing in something § NE- livestock & grain § Midwest- corn, wheat, hogs and cattle meat packing centers § South- growing and selling cotton mostly to Britain and then to the North
Commercial Agriculture § The production of crops for sale, crops intended for widespread distribution and any nonfood crops such as cotton and tobacco. § Each region in America was specializing in something § NE- livestock & grain § Midwest- corn, wheat, hogs and cattle meat packing centers § South- growing and selling cotton mostly to Britain and then to the North


