8a868231ba67a9add4250c88e8f1402e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Chapter 13 Measuring the Economy’s Performance
Chapter 13 Measuring the Economy’s Performance
 GDP – Gross Domestic Product Definition: total dollar value of all final goods and services produced in a nation in a single year. Must be: Produced within the country’s borders Made available for purchase in this year Expressed in dollar terms In 2009, the US GDP totaled more than $14. 2 trillion.
GDP – Gross Domestic Product Definition: total dollar value of all final goods and services produced in a nation in a single year. Must be: Produced within the country’s borders Made available for purchase in this year Expressed in dollar terms In 2009, the US GDP totaled more than $14. 2 trillion.
 GDP continued… What does final mean? Must avoid double counting Example: you don’t count the memory chips and motherboards if they are installed in computers for sale. You count the computer. If sold separately (not in a comp. ) then it’s also counted Only new items are counted
GDP continued… What does final mean? Must avoid double counting Example: you don’t count the memory chips and motherboards if they are installed in computers for sale. You count the computer. If sold separately (not in a comp. ) then it’s also counted Only new items are counted
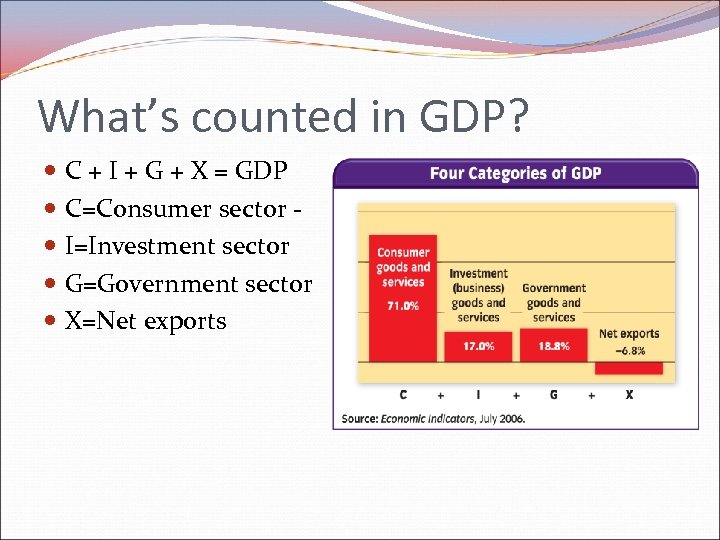 What’s counted in GDP? C + I + G + X = GDP C=Consumer sector I=Investment sector G=Government sector X=Net exports
What’s counted in GDP? C + I + G + X = GDP C=Consumer sector I=Investment sector G=Government sector X=Net exports
 Consumer Sector - Details Durable goods are items such as cars, furniture, and appliances, which are used for several years (9%). Non-durable goods are items such as food, clothing, and disposable products, which are used for only a short time period (21%). Services include rent paid on apartments (or estimated values for owner-occupied housing), airplane tickets, legal and medical advice or treatment, electricity and other utilities. Services are the fastest growing part of consumption spending (41%).
Consumer Sector - Details Durable goods are items such as cars, furniture, and appliances, which are used for several years (9%). Non-durable goods are items such as food, clothing, and disposable products, which are used for only a short time period (21%). Services include rent paid on apartments (or estimated values for owner-occupied housing), airplane tickets, legal and medical advice or treatment, electricity and other utilities. Services are the fastest growing part of consumption spending (41%).
 Investment - Details Non-residential fixed investment is the creation of tools and equipment to use in the production of other goods and services. Examples are the building of factories, the production of new machines, and the manufacturing of computers for business use (10%). Residential investment is the building of a new homes or apartments (5%). Inventory changes consist of changes in the level of stocks of goods necessary for production and finished goods ready to be sold (0%).
Investment - Details Non-residential fixed investment is the creation of tools and equipment to use in the production of other goods and services. Examples are the building of factories, the production of new machines, and the manufacturing of computers for business use (10%). Residential investment is the building of a new homes or apartments (5%). Inventory changes consist of changes in the level of stocks of goods necessary for production and finished goods ready to be sold (0%).
 Government - Details Consists of federal, state, and local government spending on goods and services such as research, roads, defense, schools, and police and fire departments. (19%) Does not include transfer payments such as Social Security, unemployment compensation, and welfare payments, which do not represent production of goods and services. Federal defense spending now accounts for approximately (5%). State and local spending on goods and services accounts for (12%).
Government - Details Consists of federal, state, and local government spending on goods and services such as research, roads, defense, schools, and police and fire departments. (19%) Does not include transfer payments such as Social Security, unemployment compensation, and welfare payments, which do not represent production of goods and services. Federal defense spending now accounts for approximately (5%). State and local spending on goods and services accounts for (12%).
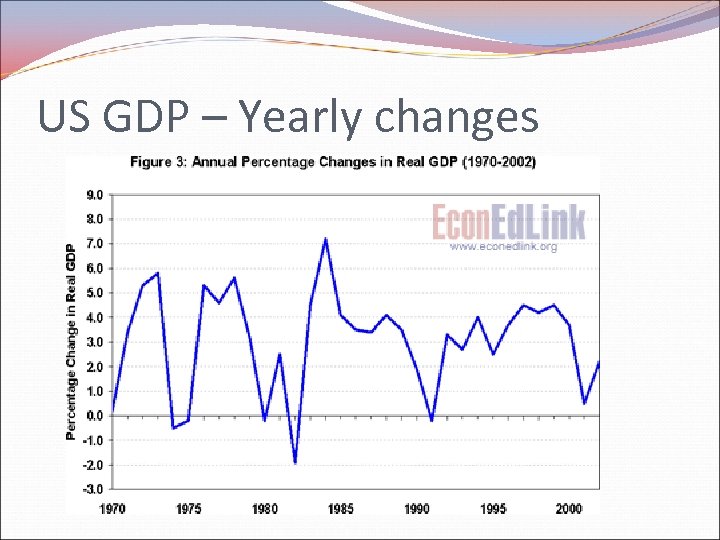 US GDP – Yearly changes
US GDP – Yearly changes
 Measurements of Income National Income Personal Income Disposable Personal Income
Measurements of Income National Income Personal Income Disposable Personal Income
 Elements of National Income
Elements of National Income
 Disposable Personal Income people have left after taxes are paid Important because it actually measures the amount of money people have to spend and save
Disposable Personal Income people have left after taxes are paid Important because it actually measures the amount of money people have to spend and save
 Inflation Definition: prolonged rise in the general price level of final goods and services Purchasing power of the dollar decreases In other words, a dollar can not buy the same amount as it did before the inflation occurred.
Inflation Definition: prolonged rise in the general price level of final goods and services Purchasing power of the dollar decreases In other words, a dollar can not buy the same amount as it did before the inflation occurred.
 Learn economic indicators & business cycle Get out yesterday’s notes too
Learn economic indicators & business cycle Get out yesterday’s notes too
 Measure of Inflation… Consumer Price Index – statistical measure of the average of prices of a specified set of goods and services purchased by typical consumers in city areas.
Measure of Inflation… Consumer Price Index – statistical measure of the average of prices of a specified set of goods and services purchased by typical consumers in city areas.
 Bell Ringer #7
Bell Ringer #7
 Deflation Prolonged decline in the general price level of goods and services. Rarely happens during modern times
Deflation Prolonged decline in the general price level of goods and services. Rarely happens during modern times
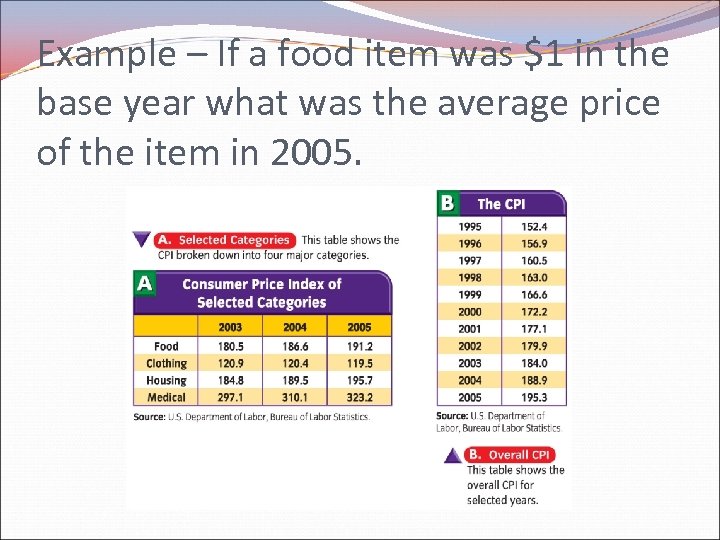 Example – If a food item was $1 in the base year what was the average price of the item in 2005.
Example – If a food item was $1 in the base year what was the average price of the item in 2005.
 Producer Price Index (PPI) Measures the changes in prices that producers charge for their goods and services PPI usually increases before CPI since most of time the increased cost is passed to consumers from the producer.
Producer Price Index (PPI) Measures the changes in prices that producers charge for their goods and services PPI usually increases before CPI since most of time the increased cost is passed to consumers from the producer.
 GDP Price Deflator Economists use this to remove the effects of inflation so the overall economy of one year can be compared to the overall economy of another year. When the price deflator is applied to GDP the new figure is referred to real GDP.
GDP Price Deflator Economists use this to remove the effects of inflation so the overall economy of one year can be compared to the overall economy of another year. When the price deflator is applied to GDP the new figure is referred to real GDP.
 Nominal & Real GDP Nominal GDP – Also called current GDP Real GDP – has been adjusted for inflation using the GDP deflator.
Nominal & Real GDP Nominal GDP – Also called current GDP Real GDP – has been adjusted for inflation using the GDP deflator.
 Aggregate Supply & Demand Aggregate Demand – is the quantity of goods demanded by an entire economy Aggregate Supply – is the quantity of goods supplied by an entire economy
Aggregate Supply & Demand Aggregate Demand – is the quantity of goods demanded by an entire economy Aggregate Supply – is the quantity of goods supplied by an entire economy
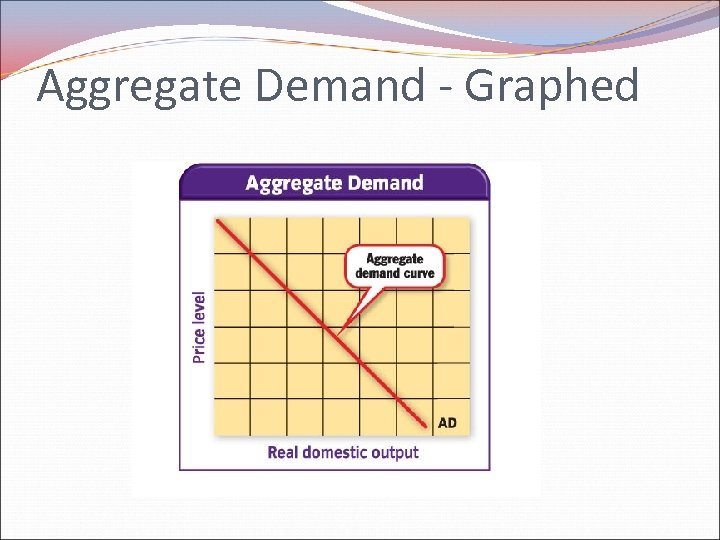 Aggregate Demand - Graphed
Aggregate Demand - Graphed
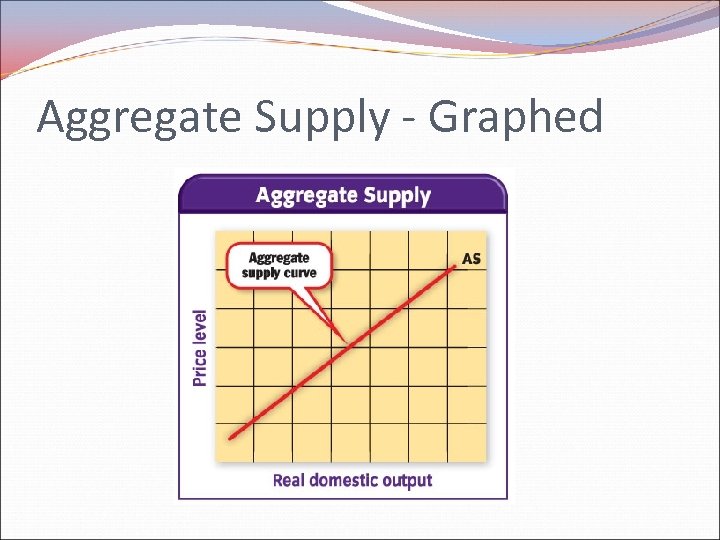 Aggregate Supply - Graphed
Aggregate Supply - Graphed
 Business Cycle – Changes in the level of total output measured by real GDP Parts Peak/boom – level of economic activity is at it highest Contraction – occurs when economic activity is slowing down Trough – Point where downward spiral of economy levels off Expansion/recovery – occurs when economic activity slowly rises Recession – point in which the real GDP declines for at least 6 months Depression - major slowdown in economic activity
Business Cycle – Changes in the level of total output measured by real GDP Parts Peak/boom – level of economic activity is at it highest Contraction – occurs when economic activity is slowing down Trough – Point where downward spiral of economy levels off Expansion/recovery – occurs when economic activity slowly rises Recession – point in which the real GDP declines for at least 6 months Depression - major slowdown in economic activity
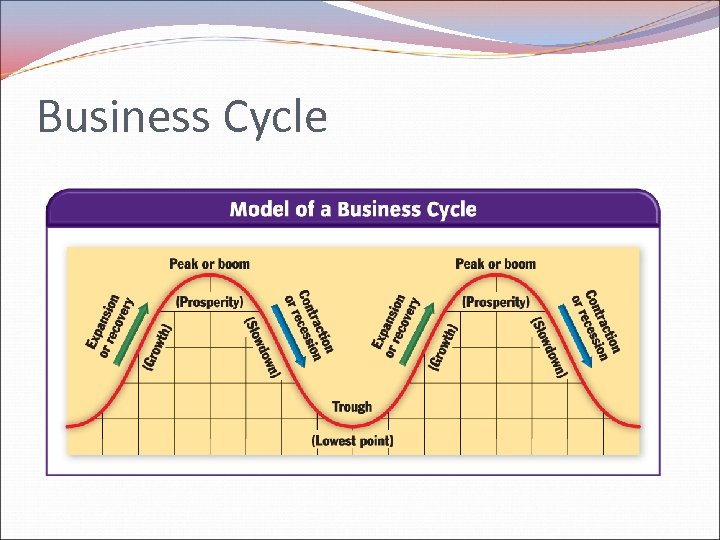 Business Cycle
Business Cycle
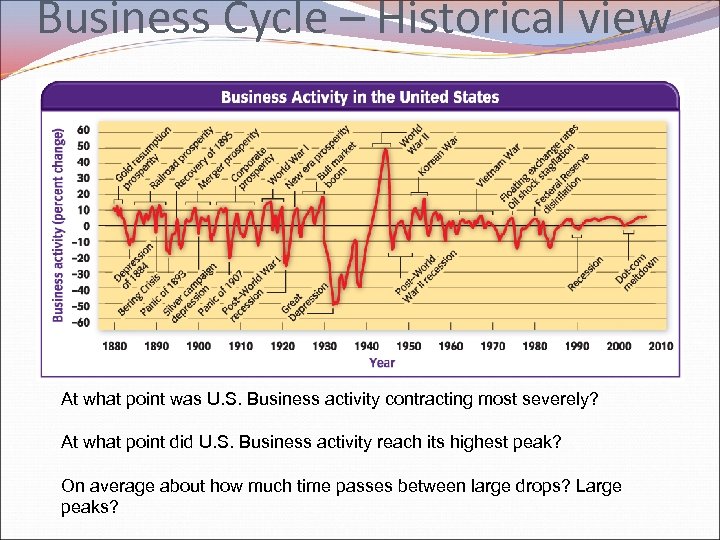 Business Cycle – Historical view At what point was U. S. Business activity contracting most severely? At what point did U. S. Business activity reach its highest peak? On average about how much time passes between large drops? Large peaks?
Business Cycle – Historical view At what point was U. S. Business activity contracting most severely? At what point did U. S. Business activity reach its highest peak? On average about how much time passes between large drops? Large peaks?
 Unemployment Rate Definition – The percentage of the population that is without jobs but actively seeking employment When high is a a sign of a poor economy. Maintaining a low unemployment rate is a major goal in stabilizing the economy. FULL Employment – occurs when the unemployment rate is around 4 – 6%.
Unemployment Rate Definition – The percentage of the population that is without jobs but actively seeking employment When high is a a sign of a poor economy. Maintaining a low unemployment rate is a major goal in stabilizing the economy. FULL Employment – occurs when the unemployment rate is around 4 – 6%.
 4 types of Unemployment Cyclical – unemployment caused by fluctuations in the business cycle Example: People all over the country are losing their jobs in many types of industries Structural – Caused by changes in the economic system Example: replaced by machines, new industries & technologies
4 types of Unemployment Cyclical – unemployment caused by fluctuations in the business cycle Example: People all over the country are losing their jobs in many types of industries Structural – Caused by changes in the economic system Example: replaced by machines, new industries & technologies
 4 types con’t Seasonal – caused by changes in weather or seasons Example: Life guards, farm workers and snow removal Frictional – temporary unemployment; between jobs caused by layoffs, firings, search for new job or retraining Example: Always exists due to people changing jobs, moving and relocating.
4 types con’t Seasonal – caused by changes in weather or seasons Example: Life guards, farm workers and snow removal Frictional – temporary unemployment; between jobs caused by layoffs, firings, search for new job or retraining Example: Always exists due to people changing jobs, moving and relocating.


