7febf93e42b26b3a1af484a7708f9e0c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

Chapter 13 Foreign Exchange Risk Management

Objectives • To explain why there is concern about FX risk • To illustrate how to manage transaction, economic and translation exposure Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -2

Hedging • Hedging, which is the core risk management operation, is a process whereby a firm can protect itself from unanticipated changes in exchange rates and other sources of risk Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -3

Hedging (cont. ) • The decision to hedge or not to hedge an uncovered or open foreign currency position is basically a speculative decision • It all depends on the expected exchange rate or the movement of the exchange rate between the point in time when the decision is taken and when its effect materialises Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -4

Why is there no need to worry about FX risk? • If international parity conditions hold, FX risk will not arise • If it is possible to forecast exchange rates accurately, FX risk can be controlled • Shareholders are naturally hedged though diversification Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -5

Why worry about FX risk? • International parity conditions do not hold • Forecasting exchange rates is rather difficult • Hedging produces a more stable income stream Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -6

Benefits of hedging • Hedging has a positive effect on the value of the firm • It produces a more stable corporate income stream Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -7

Managing short-term transaction exposure (financial hedging) • • Forward hedging Money market hedging Futures hedging Option hedging Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -8

Financial hedging • By taking an affecting position on a hedging instrument (forward, etc), the profit/loss on the unhedged position is offset by the loss/profit on the hedging instrument Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -9

Forward hedging • Forward hedging entails locking in the exchange rate at which payables and receivables are converted from the domestic currency into a foreign currency, and vice versa Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -10
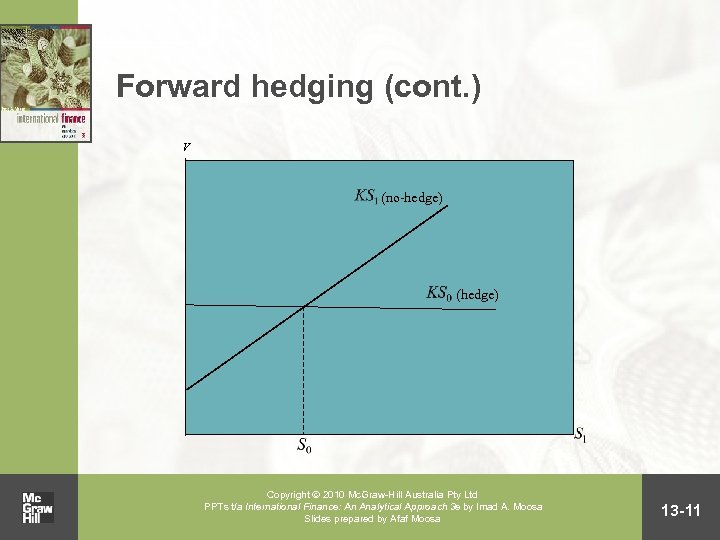
Forward hedging (cont. ) V (no-hedge) (hedge) Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -11
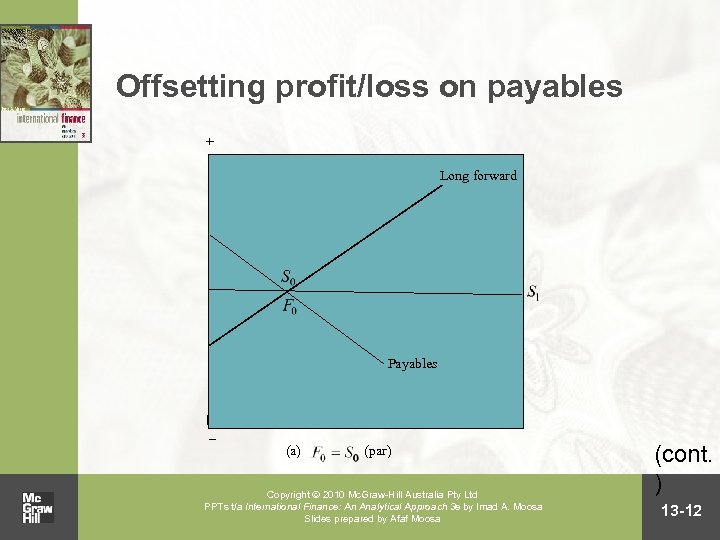
Offsetting profit/loss on payables + Long forward Payables – (a) (par) Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -12
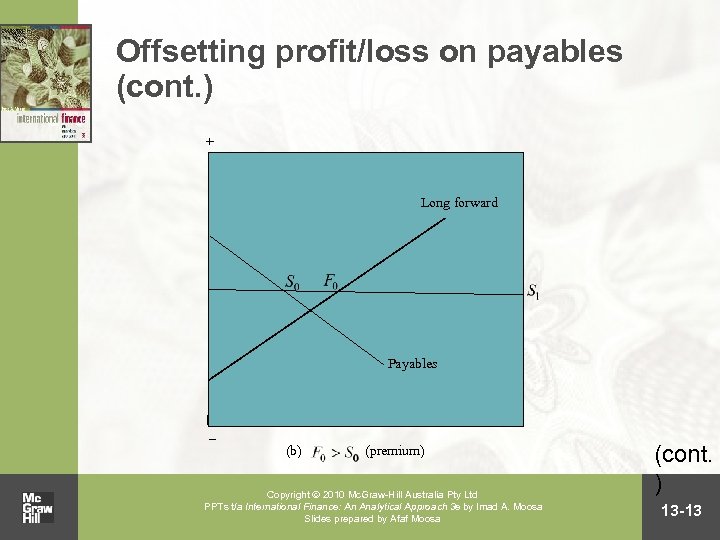
Offsetting profit/loss on payables (cont. ) + Long forward Payables – (b) (premium) Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -13
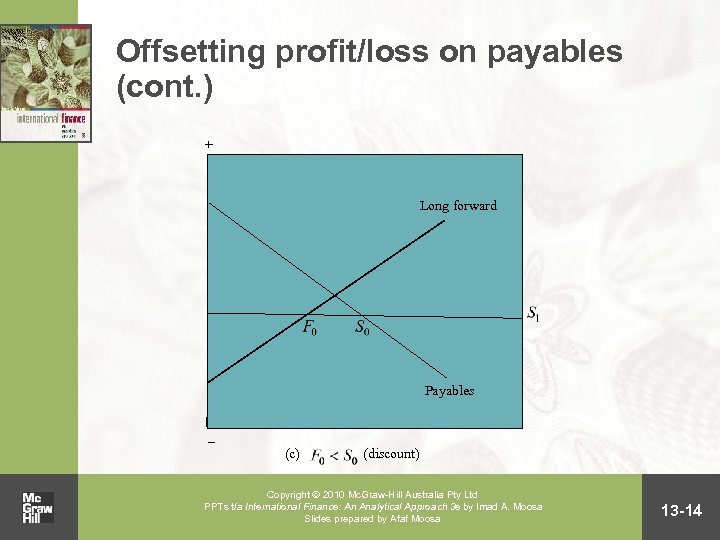
Offsetting profit/loss on payables (cont. ) + Long forward Payables – (c) (discount) Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -14

Introducing the bid-offer spread Hedge No-Hedge Payables Receivables Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -15

Futures hedging • Futures hedging results may differ quantitatively from those of forward hedging • Because of the standardisation of contracts, it may not be possible to hedge the exact amount Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -16

Futures hedging (cont. ) • The due date may not coincide with the settlement date • Marking-to-market introduces some variation Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -17

Money market hedging • A money market hedge amounts to taking a money market position to cover expected payables or receivables • By borrowing and lending, a synthetic forward contract is created Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -18
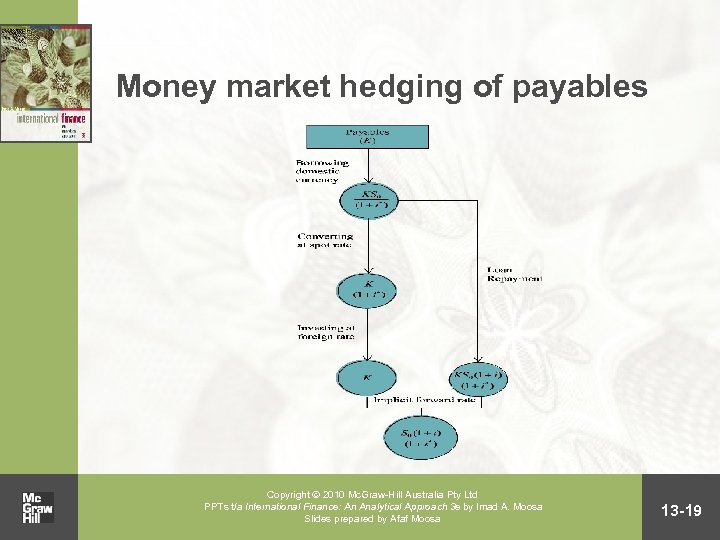
Money market hedging of payables Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -19
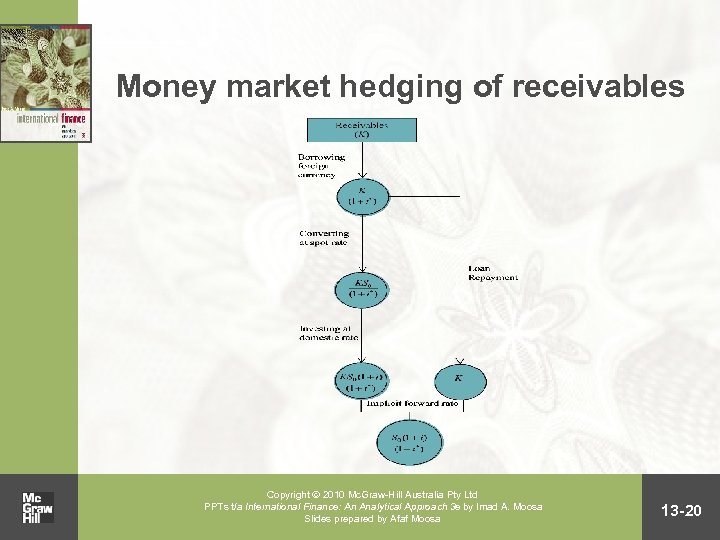
Money market hedging of receivables Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -20

Money market hedging of payables with bid-offer spreads Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -21

Money market hedging as a pricing mechanism • When the banker quotes a forward rate for a future delivery of a particular currency, the banker will be exposed to the risk arising from possible appreciation of the underlying currency Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -22

Money market hedging as a pricing mechanism (cont. ) • The banker can protect himself by hedging the forward position in the money market, so that he receives the amount of the underlying currency to be delivered on the maturity date Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -23

Money market hedging as a pricing mechanism (cont. ) • The minimum forward rate that the banker can quote, therefore, is the cost of money market hedging, which is the forward rate implicit in the synthetic forward contract created by the hedge Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -24
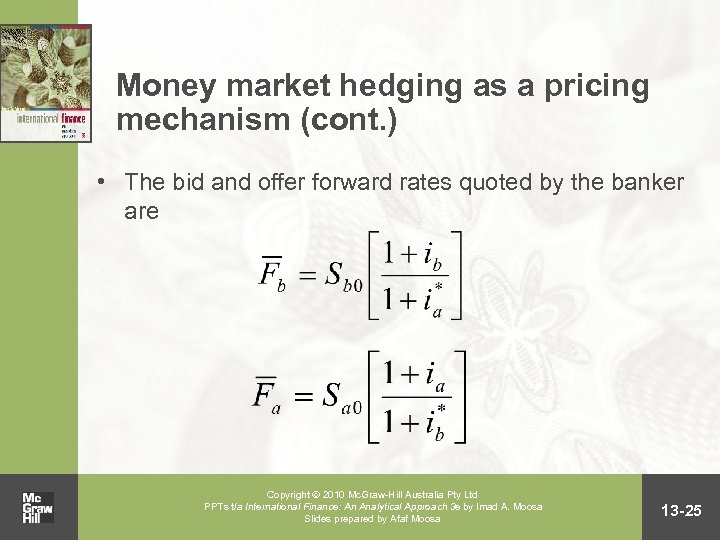
Money market hedging as a pricing mechanism (cont. ) • The bid and offer forward rates quoted by the banker are Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -25

Option hedging • The outcome of option hedging is not known with certainty, since it depends on whether or not the option is exercised Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -26

Hedging with a call option Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -27

Hedging with a put option Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -28

Contingent exposure • A contingent exposure arises only if a certain outcome materialises, such as winning a contract Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -29
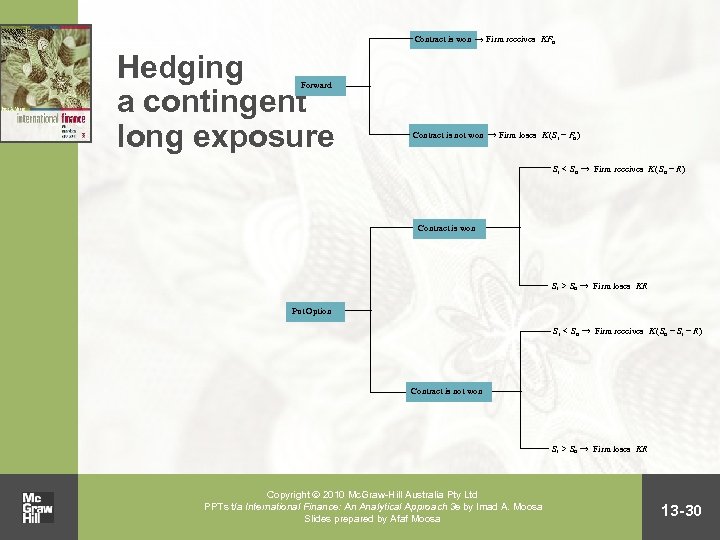
Contract is won ® Firm receives KF 0 Hedging a contingent long exposure Forward Contract is not won ® Firm loses K ( S 1 - F 0 ) S 1 < S 0 ® Firm receives K ( S 0 - R ) Contract is won S 1 > S 0 ® Firm loses KR Put Option S 1 < S 0 ® Firm receives K ( S 0 - S 1 - R ) Contract is not won S 1 > S 0 ® Firm loses KR Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -30

Managing long-term transaction exposure • • Long-term forward contracts Currency swaps Parallel loans Leading and lagging Cross hedging Currency diversification Exposure netting Price variation and currency of invoicing Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa (cont. ) 13 -31

Managing long-term transaction exposure (cont. ) • Price variation and currency of invoicing • Risk sharing arrangement • Currency collars Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -32

Long-term forward contracts • Commercial banks do provide forward contracts in major currencies with long maturities (for example, five or ten years) • Because of the risk involved, banks only offer these contracts to the most creditworthy customers Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -33

Currency swaps • Two parties exchanging cash flows denominated in two different currencies Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -34

Parallel loans • Parallel loans are the origin of currency swaps. They can be used to exchange cash flows Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -35

Leading and lagging • If the foreign currency is expected to appreciate, foreign currency dues are paid sooner rather than later: this is called leading • If, on the other hand, the foreign currency is expected to depreciate, payables are met later rather than sooner: this is called lagging Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -36

Cross hedging • Hedging a position on one currency with a position on another currency • Correlation between the exchange rates against the base currency is important Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -37

Currency diversification • Depending on correlation of the exchange rates against the base currency, currency diversification reduces risk Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -38

Exposure netting • A natural hedge would arise when the firm has payables and receivables in the same currency, in which case only net exposure should be covered Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -39

Price variation and currency of invoicing • The foreign currency price of a product can be adjusted by varying its domestic currency price • Exposure to FX risk can be eliminated completely by using the domestic currency as the currency of invoicing Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -40

Risk sharing and currency collars • Risk-sharing arrangements and currency collars involve the use of various values of the exchange rate to convert cash flows Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -41
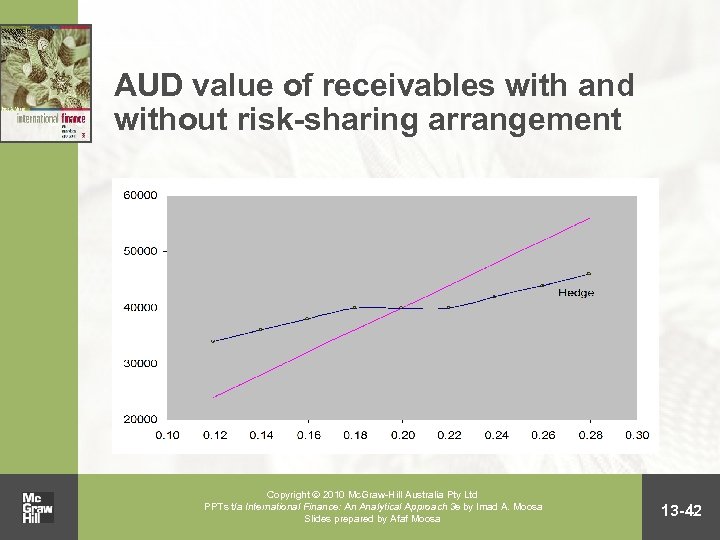
AUD value of receivables with and without risk-sharing arrangement Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -42
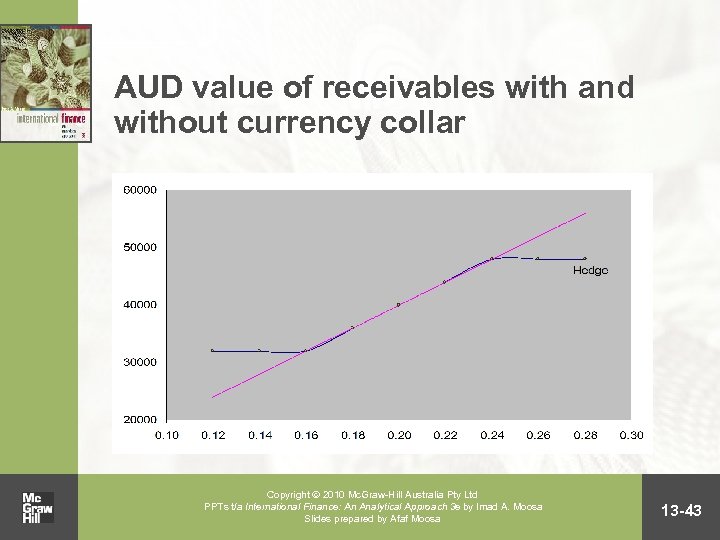
AUD value of receivables with and without currency collar Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -43

Economic exposure • Economic exposure arises because revenues and costs vary with changes in the real exchange rate Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -44

The effects of real appreciation • Assuming elastic demand, real appreciation of the foreign currency leads to: 4 an increase in domestic sales revenue 4 an increase in foreign sales revenue 4 an increase in the costs of imported raw materials and foreign borrowing Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -45

The effects of real depreciation • Assuming elastic demand, real depreciation of the foreign currency leads to: 4 a decrease in domestic sales revenue 4 a decrease in foreign sales revenue 4 a decrease in the costs of imported raw materials and foreign borrowing Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -46

Hedging economic exposure • Reducing economic exposure requires: 4 changing sales in new or existing foreign markets 4 changing dependence on foreign supply of raw materials 4 establishing or eliminating production facilities abroad 4 changing the level of foreign debt Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -47

Why worry about translation exposure? • Translation exposure does not affect the economic value of the firm • Different translation methods affect reported earnings per share and other financial indicators Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -48

Hedging translation exposure • Fund adjustment • Forward contracts • Exposure netting and balance sheet hedging Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -49

Fund adjustment • Fund adjustment involves altering the amounts and/or currencies of the planned cash flows of the firm or its subsidiaries to reduce exposure to the currency of the subsidiary (the local currency) Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -50

Forward contracts • If the base currency of a foreign subsidiary is expected to depreciate against the parent firm’s base currency, then translation exposure exists Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -51

Exposure netting and balance sheet hedging • Exposure netting can be used by multinational firms with offsetting positions in more than one foreign currency • A balance sheet hedge eliminates the mismatch between assets and liabilities in the same currency Copyright 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Finance: An Analytical Approach 3 e by Imad A. Moosa Slides prepared by Afaf Moosa 13 -52
7febf93e42b26b3a1af484a7708f9e0c.ppt