0a5716dc072118a1135ed63a178a88ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Chapter 13 - Fluids • Pressure variation with height or depth • Pascal’s Principle • Archimedes Principle • Fluid Flow • Bernoulli’s Equation
Chapter 13 - Fluids • Pressure variation with height or depth • Pascal’s Principle • Archimedes Principle • Fluid Flow • Bernoulli’s Equation
 Fluid • Matter that cannot maintain its own shape and therefore flows readily under the influence of forces – Gases – Do not maintain their size (volume) – Liquids – Do maintain their size – “incompressible” • Solids maintain both their size and shape under the influence of forces
Fluid • Matter that cannot maintain its own shape and therefore flows readily under the influence of forces – Gases – Do not maintain their size (volume) – Liquids – Do maintain their size – “incompressible” • Solids maintain both their size and shape under the influence of forces
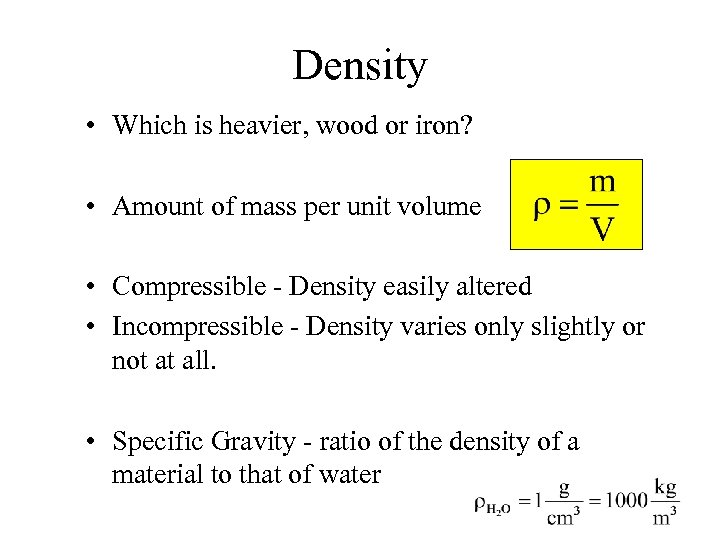 Density • Which is heavier, wood or iron? • Amount of mass per unit volume • Compressible - Density easily altered • Incompressible - Density varies only slightly or not at all. • Specific Gravity - ratio of the density of a material to that of water
Density • Which is heavier, wood or iron? • Amount of mass per unit volume • Compressible - Density easily altered • Incompressible - Density varies only slightly or not at all. • Specific Gravity - ratio of the density of a material to that of water
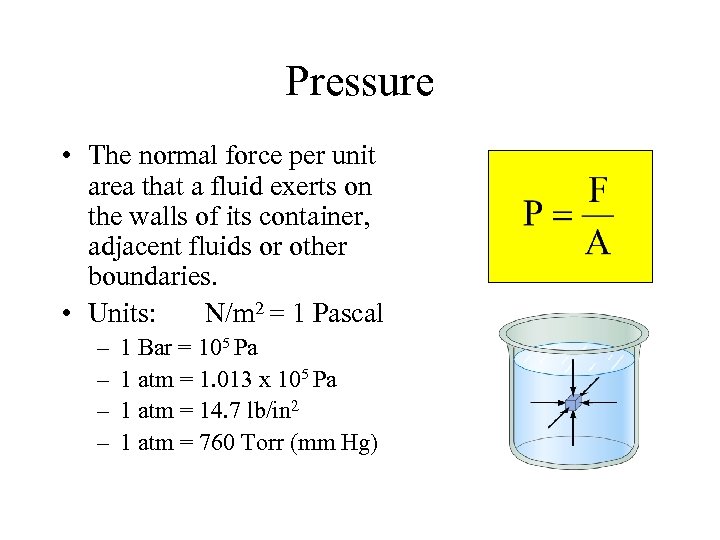 Pressure • The normal force per unit area that a fluid exerts on the walls of its container, adjacent fluids or other boundaries. • Units: N/m 2 = 1 Pascal – – 1 Bar = 105 Pa 1 atm = 1. 013 x 105 Pa 1 atm = 14. 7 lb/in 2 1 atm = 760 Torr (mm Hg)
Pressure • The normal force per unit area that a fluid exerts on the walls of its container, adjacent fluids or other boundaries. • Units: N/m 2 = 1 Pascal – – 1 Bar = 105 Pa 1 atm = 1. 013 x 105 Pa 1 atm = 14. 7 lb/in 2 1 atm = 760 Torr (mm Hg)
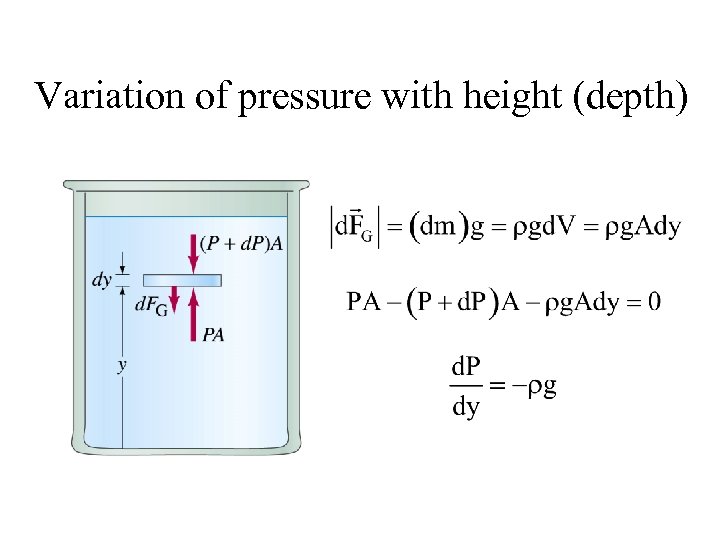 Variation of pressure with height (depth)
Variation of pressure with height (depth)
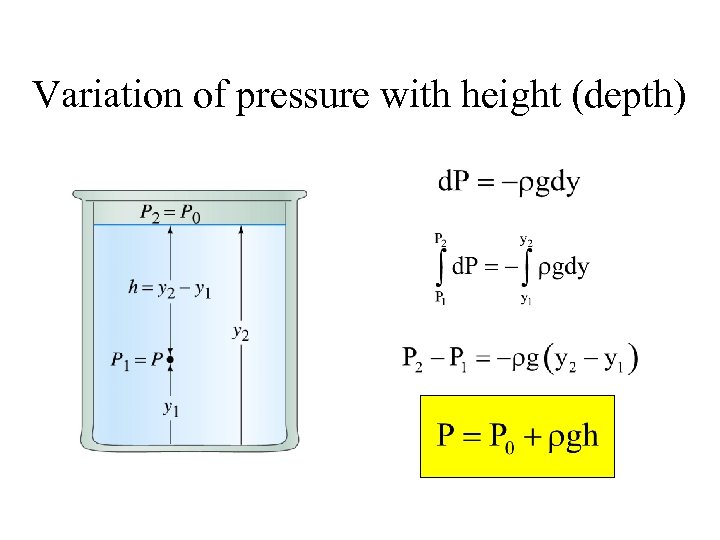 Variation of pressure with height (depth)
Variation of pressure with height (depth)
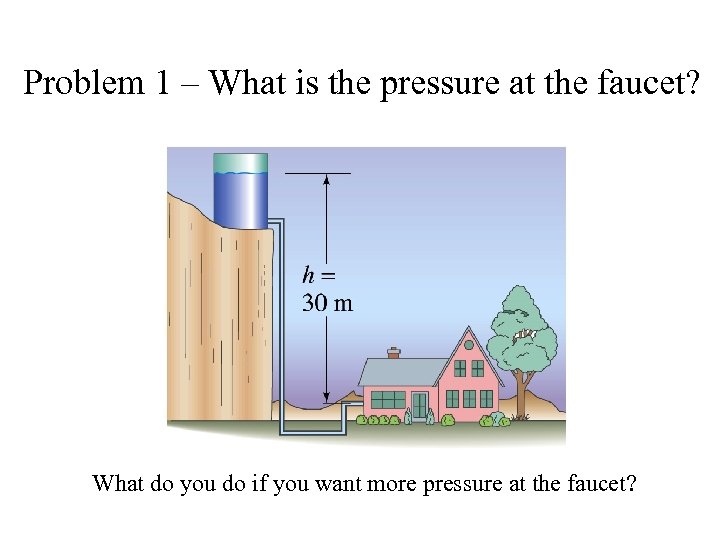 Problem 1 – What is the pressure at the faucet? What do you do if you want more pressure at the faucet?
Problem 1 – What is the pressure at the faucet? What do you do if you want more pressure at the faucet?
 Absolute vs. Gauge Pressure • Gauge Pressure That read on a gauge which compares it to atmospheric pressure • Absolute Pressure Sum of the gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure
Absolute vs. Gauge Pressure • Gauge Pressure That read on a gauge which compares it to atmospheric pressure • Absolute Pressure Sum of the gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure
 Problem 2 • What is the pressure at a depth of 1300 feet (approximately 400 m) • rw = 1000 kg/m 3
Problem 2 • What is the pressure at a depth of 1300 feet (approximately 400 m) • rw = 1000 kg/m 3
 Problem 3 • What is the height of a mercury column if the pressure at the bottom is 101. 325 k. Pa and the pressure at the top is zero? • r. Hg = 13. 595 x 103 kg/m 3 h
Problem 3 • What is the height of a mercury column if the pressure at the bottom is 101. 325 k. Pa and the pressure at the top is zero? • r. Hg = 13. 595 x 103 kg/m 3 h
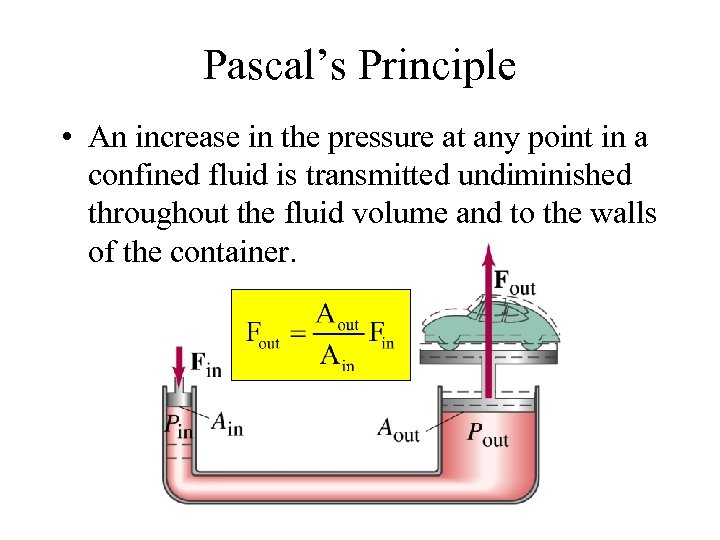 Pascal’s Principle • An increase in the pressure at any point in a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid volume and to the walls of the container.
Pascal’s Principle • An increase in the pressure at any point in a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid volume and to the walls of the container.
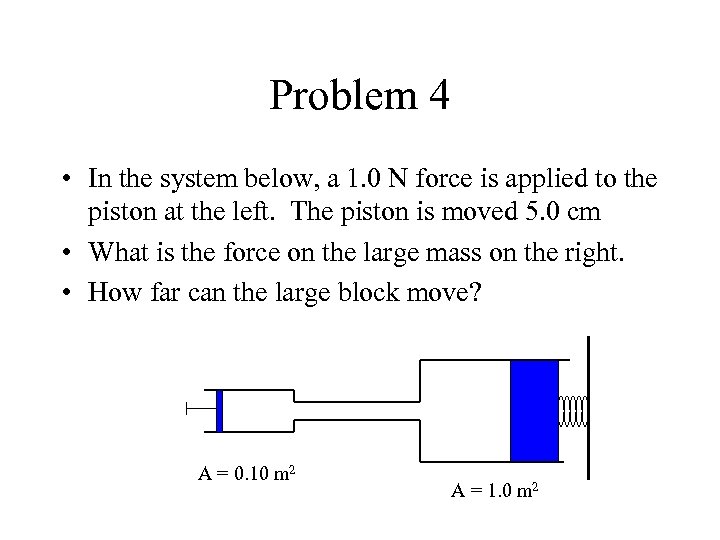 Problem 4 • In the system below, a 1. 0 N force is applied to the piston at the left. The piston is moved 5. 0 cm • What is the force on the large mass on the right. • How far can the large block move? A = 0. 10 m 2 A = 1. 0 m 2
Problem 4 • In the system below, a 1. 0 N force is applied to the piston at the left. The piston is moved 5. 0 cm • What is the force on the large mass on the right. • How far can the large block move? A = 0. 10 m 2 A = 1. 0 m 2
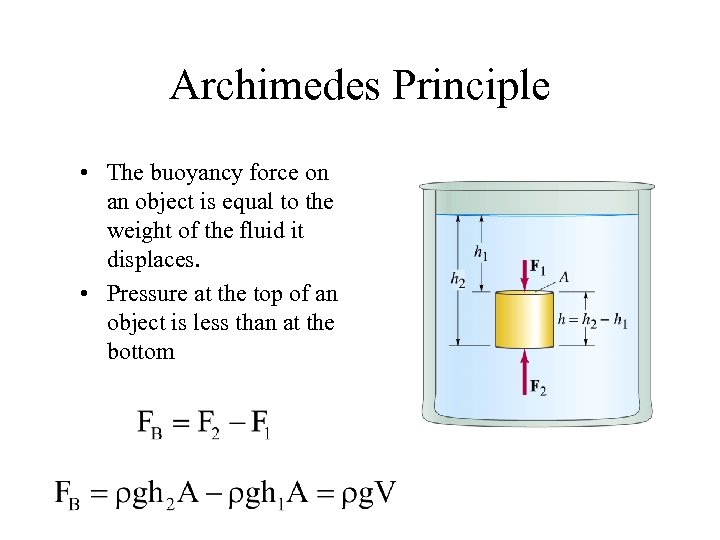 Archimedes Principle • The buoyancy force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces. • Pressure at the top of an object is less than at the bottom
Archimedes Principle • The buoyancy force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces. • Pressure at the top of an object is less than at the bottom
 Problem 5 • What volume of water must be displaced for a 6900 Ton submarine to hover?
Problem 5 • What volume of water must be displaced for a 6900 Ton submarine to hover?
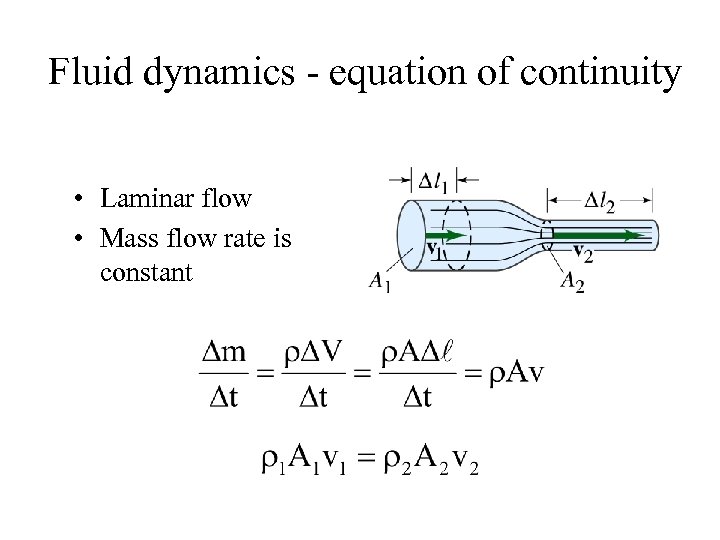 Fluid dynamics - equation of continuity • Laminar flow • Mass flow rate is constant
Fluid dynamics - equation of continuity • Laminar flow • Mass flow rate is constant
 Problem 4 • Water leaves the nozzle of a firehose at 50 m/s. What is the velocity of water in the hose. • Hose inner diameter = 10 cm • Nozzle inner diameter = 3 cm • Using the rocket equation, how much thrust does a fireman feel from this exiting fluid?
Problem 4 • Water leaves the nozzle of a firehose at 50 m/s. What is the velocity of water in the hose. • Hose inner diameter = 10 cm • Nozzle inner diameter = 3 cm • Using the rocket equation, how much thrust does a fireman feel from this exiting fluid?
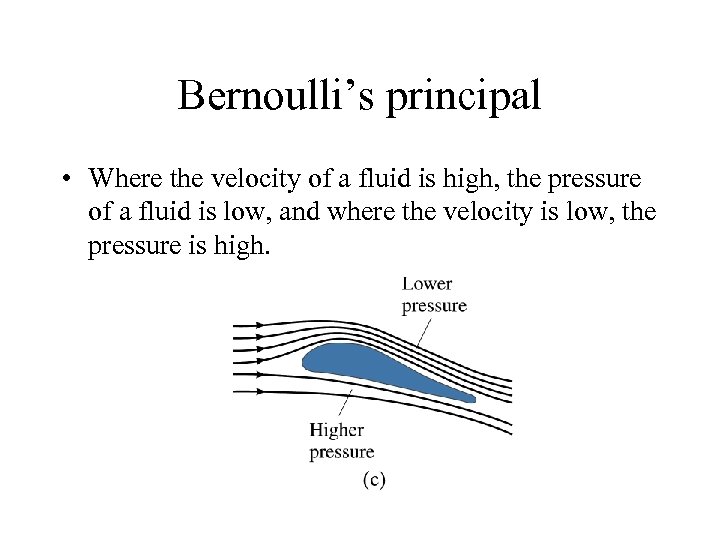 Bernoulli’s principal • Where the velocity of a fluid is high, the pressure of a fluid is low, and where the velocity is low, the pressure is high.
Bernoulli’s principal • Where the velocity of a fluid is high, the pressure of a fluid is low, and where the velocity is low, the pressure is high.
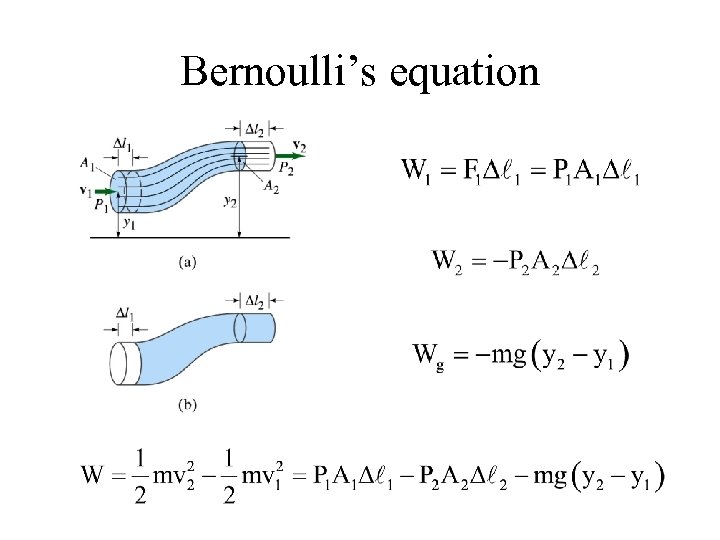 Bernoulli’s equation
Bernoulli’s equation
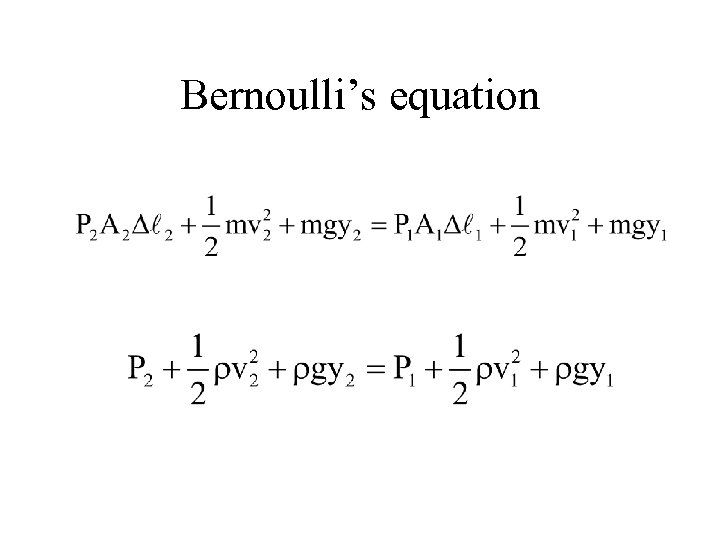 Bernoulli’s equation
Bernoulli’s equation
 Problem 5 • Find the pressure in the fire hose with exhaust velocity = 50 m/s
Problem 5 • Find the pressure in the fire hose with exhaust velocity = 50 m/s
 Problem 6 • What is the velocity of the fluid leaving the pipe at point 2. • A small pipe directs the water upward. What is the height of the plume? 1 h 2
Problem 6 • What is the velocity of the fluid leaving the pipe at point 2. • A small pipe directs the water upward. What is the height of the plume? 1 h 2
 Problem 7 (#47) • What gauge pressure is necessary in a fire main if a firehose is to spray water to a height of 15 m?
Problem 7 (#47) • What gauge pressure is necessary in a fire main if a firehose is to spray water to a height of 15 m?
 Problem 8 (#50) • If the wind blows at 25 m/s over your house, what is the net force on the roof if its area is 240 m 2?
Problem 8 (#50) • If the wind blows at 25 m/s over your house, what is the net force on the roof if its area is 240 m 2?


