de3fe3c0a99ec67a7059755ecc360e88.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Chapter 13: Content and Organization This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: *any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; *preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or in part, of any images; *any rental, lease, or lending of the program Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 1
Chapter 13: Content and Organization This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: *any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; *preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or in part, of any images; *any rental, lease, or lending of the program Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 1
 Inventio and Dispositio Cicero. The great Senator and Orator of Ancient Rome Inventio (Content). The speakers attempt “to find out what he should say. ” Dispositio (Organization). The task of arranging ideas and information for a presentation in an orderly sequence. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 2
Inventio and Dispositio Cicero. The great Senator and Orator of Ancient Rome Inventio (Content). The speakers attempt “to find out what he should say. ” Dispositio (Organization). The task of arranging ideas and information for a presentation in an orderly sequence. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 2
 Content and Supporting Material Content The ideas, information, and opinions you include in your message Supporting Material The ideas, opinions, and information that explain and/or advance your presentation’s key points and purpose Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 3
Content and Supporting Material Content The ideas, information, and opinions you include in your message Supporting Material The ideas, opinions, and information that explain and/or advance your presentation’s key points and purpose Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 3
 Types of Supporting Material • • Facts Statistics Testimony Definitions • • Descriptions Analogies Examples Stories Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 4
Types of Supporting Material • • Facts Statistics Testimony Definitions • • Descriptions Analogies Examples Stories Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 4
 Identify the Type of Supporting Material A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. __Deception consists of messages Fact knowingly and intentionally Statistic transmitted to foster false beliefs. Testimony __ Supporting material includes facts, testimony, analogies, and Definition Description stories __ A teacher in my nephew’s school Analogy was suspended for wearing a Tshirt with a peace sign on it. Example Story Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 5
Identify the Type of Supporting Material A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. __Deception consists of messages Fact knowingly and intentionally Statistic transmitted to foster false beliefs. Testimony __ Supporting material includes facts, testimony, analogies, and Definition Description stories __ A teacher in my nephew’s school Analogy was suspended for wearing a Tshirt with a peace sign on it. Example Story Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 5
 Identify the Type of Supporting Material A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Fact Statistic Testimony Definition Analogy Description Example Story __ According to Dr. Alan Hirsch, about 90% of taste is based on smell. __ “America will not bow down to tyrants. ” George W. Bush __ Japan’s Princess Kiko gave birth to a male heir to the Imperial throne. __ He’s king of the hill. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 6
Identify the Type of Supporting Material A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Fact Statistic Testimony Definition Analogy Description Example Story __ According to Dr. Alan Hirsch, about 90% of taste is based on smell. __ “America will not bow down to tyrants. ” George W. Bush __ Japan’s Princess Kiko gave birth to a male heir to the Imperial throne. __ He’s king of the hill. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 6
 Fact or Opinion 1. The whole of human knowledge doubles every five years. 2. The Second Amendment to the Constitution protects your right to own and use a gun. 3. From 1971 to 2004, MBAs went up 426 percent; health degrees went up 743 percent. 4. The word memo comes from the Latin memorandum, meaning “to be remembered. ” 5. A national health care system is the same as socialism. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 7
Fact or Opinion 1. The whole of human knowledge doubles every five years. 2. The Second Amendment to the Constitution protects your right to own and use a gun. 3. From 1971 to 2004, MBAs went up 426 percent; health degrees went up 743 percent. 4. The word memo comes from the Latin memorandum, meaning “to be remembered. ” 5. A national health care system is the same as socialism. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 7
 Don’t Take It Out of Context “When context is misplaced, so is the truth. ” Dan Le Batard, columnist, Miami Herald Example: “Martin Luther King, Jr. opposed affirmative action because he believed that merit, not race, should determine the distribution of resources. ” Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 8
Don’t Take It Out of Context “When context is misplaced, so is the truth. ” Dan Le Batard, columnist, Miami Herald Example: “Martin Luther King, Jr. opposed affirmative action because he believed that merit, not race, should determine the distribution of resources. ” Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 8
 Document Your Sources • Cite the sources of your supporting material in writing and orally in your presentation. • Documentation enhances your credibility as a speaker while assuring listeners of the validity of your content. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 9
Document Your Sources • Cite the sources of your supporting material in writing and orally in your presentation. • Documentation enhances your credibility as a speaker while assuring listeners of the validity of your content. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 9
 Tests of Supporting Material • Is the source identified and credible? • Is the source primary or secondary? • Is the source biased? • Is the information recent? • Is the information consistent? • Are the statistics valid? Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 10
Tests of Supporting Material • Is the source identified and credible? • Is the source primary or secondary? • Is the source biased? • Is the information recent? • Is the information consistent? • Are the statistics valid? Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 10
 Quotable Quote Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 11
Quotable Quote Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 11
 Test the Supporting Material • The new health care law gives Obama a Nazi-like “private army” of 6, 000 people. • In March 2010, the Texas Board of Education rightfully dropped President Thomas Jefferson from the world history curriculum because he advocated a “separation between church and state. ” • Around 50, 000 people die each year from alcohol poisoning. By comparison, marijuana is nontoxic and cannot cause death by overdose. NORMAL National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 12
Test the Supporting Material • The new health care law gives Obama a Nazi-like “private army” of 6, 000 people. • In March 2010, the Texas Board of Education rightfully dropped President Thomas Jefferson from the world history curriculum because he advocated a “separation between church and state. ” • Around 50, 000 people die each year from alcohol poisoning. By comparison, marijuana is nontoxic and cannot cause death by overdose. NORMAL National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 12
 Power. Point Quiz What type of supporting material is used in the following example? “Heuristics are shortcut decision-making rules that are correct often enough to be useful. ” A. B. C. D. E. Facts Definitions Statistics Descriptions Analogies Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 13
Power. Point Quiz What type of supporting material is used in the following example? “Heuristics are shortcut decision-making rules that are correct often enough to be useful. ” A. B. C. D. E. Facts Definitions Statistics Descriptions Analogies Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 13
 Wikipedia: Pros and Cons PRO Wikipedia • Provides clear, general information • Provides useful primary references • Information is as accurate as many encyclopedias • ________________ CON Wikipedia • Is written and revised by non-experts • Information may be inaccurate • Students only use Wikipedia rather than primary sources • _________________ Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 14
Wikipedia: Pros and Cons PRO Wikipedia • Provides clear, general information • Provides useful primary references • Information is as accurate as many encyclopedias • ________________ CON Wikipedia • Is written and revised by non-experts • Information may be inaccurate • Students only use Wikipedia rather than primary sources • _________________ Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 14
 Myth? Hoax? True? Sources: Web sites and newspapers 1. President Obama’s birth certificate is a forgery. He is not a U. S. Citizen. 2. The face of the Mona Lisa is actually a self-portrait of Leonardo ad Vinci. 3. President Obama canceled National Day of Prayer. 4. The Apollo moon landing is a hoax; it never happened. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 15
Myth? Hoax? True? Sources: Web sites and newspapers 1. President Obama’s birth certificate is a forgery. He is not a U. S. Citizen. 2. The face of the Mona Lisa is actually a self-portrait of Leonardo ad Vinci. 3. President Obama canceled National Day of Prayer. 4. The Apollo moon landing is a hoax; it never happened. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 15
 Quotable Quote “A speech without structure is like a human body without a skeleton. It won’t stand up. Spineless. Like a jellyfish” Michael Kepper, I’d Rather Die than Give a Speech Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 16
Quotable Quote “A speech without structure is like a human body without a skeleton. It won’t stand up. Spineless. Like a jellyfish” Michael Kepper, I’d Rather Die than Give a Speech Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 16
 Determine Your Key Points The most important issues or the main ideas you want your audience to understand remember during and after your presentation Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 17
Determine Your Key Points The most important issues or the main ideas you want your audience to understand remember during and after your presentation Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 17
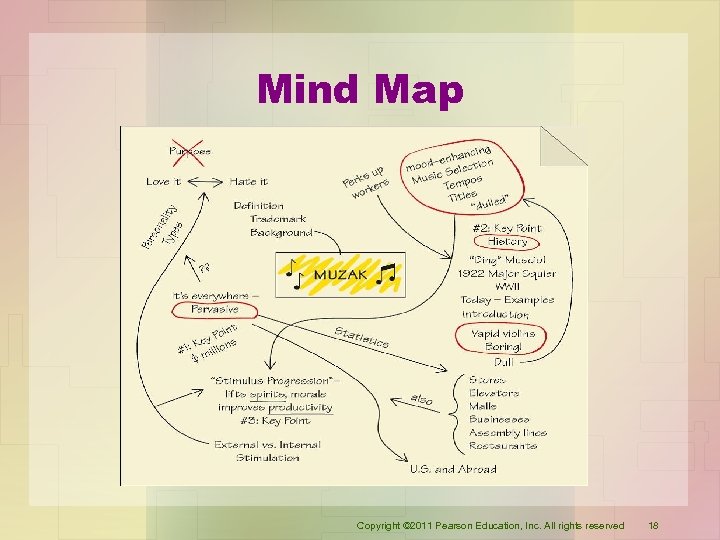 Mind Map Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 18
Mind Map Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 18
 The Speech Framer© • Provides a place for every component of a presentation. • Encourages creativity and experimentation with organizational patterns and formats. • Helps determine the number of key points. • Connects key points to strong, relevant supporting material. • If used as speaking notes, lays out the entire presentation on one page. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 19
The Speech Framer© • Provides a place for every component of a presentation. • Encourages creativity and experimentation with organizational patterns and formats. • Helps determine the number of key points. • Connects key points to strong, relevant supporting material. • If used as speaking notes, lays out the entire presentation on one page. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 19
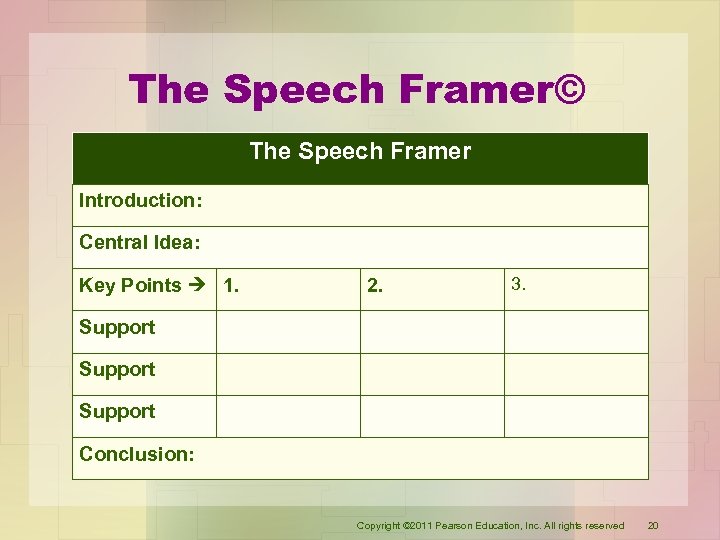 The Speech Framer© The Speech Framer Introduction: Central Idea: Key Points 1. 2. 3. Support Conclusion: Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 20
The Speech Framer© The Speech Framer Introduction: Central Idea: Key Points 1. 2. 3. Support Conclusion: Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 20
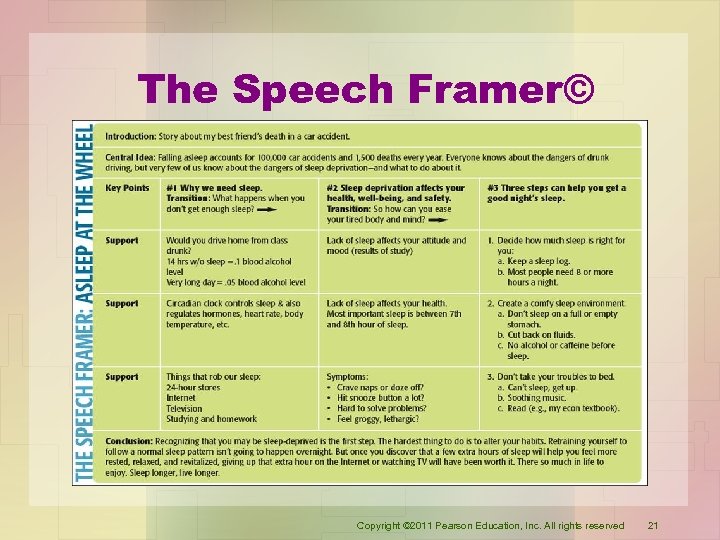 The Speech Framer© Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 21
The Speech Framer© Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 21
 Identify Your Central Idea: A sentence or thesis statement that summarizes the key points that you want your audience to understand remember Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 22
Identify Your Central Idea: A sentence or thesis statement that summarizes the key points that you want your audience to understand remember Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 22
 Topic, Purpose, and Central Idea • Topic • Purpose • Central Idea • Growing tomatoes • To explain how to grow healthy, hearty tomatoes • Growing healthy, hearty tomatoes requires good soil, bright sun, plenty of water, and a watchful eye. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 23
Topic, Purpose, and Central Idea • Topic • Purpose • Central Idea • Growing tomatoes • To explain how to grow healthy, hearty tomatoes • Growing healthy, hearty tomatoes requires good soil, bright sun, plenty of water, and a watchful eye. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 23
 Topic, Purpose, and Central Idea • The cost of college • _________________ • Central Idea • _________________ • Topic • Purpose Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 24
Topic, Purpose, and Central Idea • The cost of college • _________________ • Central Idea • _________________ • Topic • Purpose Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 24
 Organizational Patterns • • Topical Time Space Problem-Solution Causes and Effects Stories and Examples Comparison-Contrast Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 25
Organizational Patterns • • Topical Time Space Problem-Solution Causes and Effects Stories and Examples Comparison-Contrast Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 25
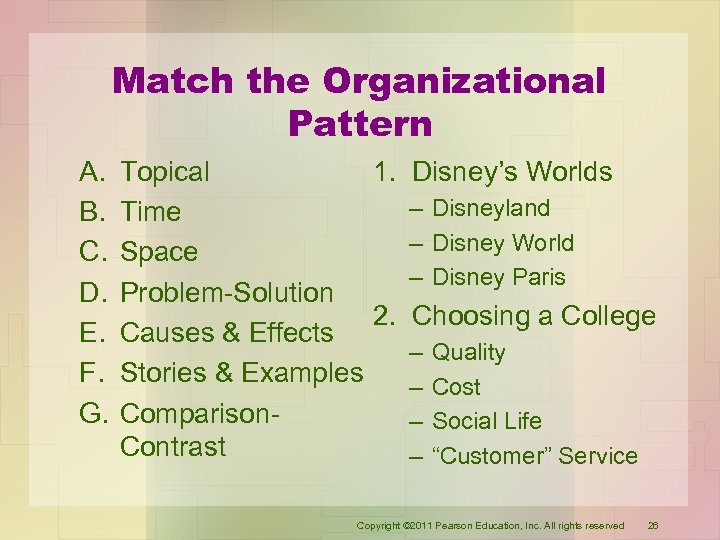 Match the Organizational Pattern A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Topical 1. Disney’s Worlds – Disneyland Time – Disney World Space – Disney Paris Problem-Solution 2. Choosing a College Causes & Effects – Quality Stories & Examples – Cost Comparison– Social Life Contrast – “Customer” Service Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 26
Match the Organizational Pattern A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Topical 1. Disney’s Worlds – Disneyland Time – Disney World Space – Disney Paris Problem-Solution 2. Choosing a College Causes & Effects – Quality Stories & Examples – Cost Comparison– Social Life Contrast – “Customer” Service Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 26
 Provide Examples for a Presentation on Sleep • Topical • • Four reasons to get 7 to 8 hours of sleep • _________ Time • _________ Space • _________ Problem-Solution • _________ Causes and Effects Stories and Examples • _________ Comparison-Contrast • _________ Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 27
Provide Examples for a Presentation on Sleep • Topical • • Four reasons to get 7 to 8 hours of sleep • _________ Time • _________ Space • _________ Problem-Solution • _________ Causes and Effects Stories and Examples • _________ Comparison-Contrast • _________ Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 27
 Outline Your Presentation • Preliminary Outline: Puts the major pieces of a presentation in order • Comprehensive Outline: Provides an all-inclusive framework that follows established outlining rules • Speaking Outline: A short outline that includes little more than a list of key points and reminders of supporting material Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 28
Outline Your Presentation • Preliminary Outline: Puts the major pieces of a presentation in order • Comprehensive Outline: Provides an all-inclusive framework that follows established outlining rules • Speaking Outline: A short outline that includes little more than a list of key points and reminders of supporting material Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 28
 Preliminary Outline I. Introduction A. Purpose/Topic B. Central Idea & Preview of Key Points II. Body of the Presentation A. Key Point #1 B. Key Point #2 C. Key Point #3 III. Conclusion See p. 274 for an example of a Comprehensive Outline Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 29
Preliminary Outline I. Introduction A. Purpose/Topic B. Central Idea & Preview of Key Points II. Body of the Presentation A. Key Point #1 B. Key Point #2 C. Key Point #3 III. Conclusion See p. 274 for an example of a Comprehensive Outline Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 29
 Ordering Your Key Points • Strength and Familiarity. Put your strongest key points first and last; your weakest or least familiar in the middle. • Logistics. Put your strongest key points first if you may need to cut your talk short as you speak. • Audience Needs. If listeners need current information, provide it first. If the issue is controversial, provide background material explaining your justification first. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 30
Ordering Your Key Points • Strength and Familiarity. Put your strongest key points first and last; your weakest or least familiar in the middle. • Logistics. Put your strongest key points first if you may need to cut your talk short as you speak. • Audience Needs. If listeners need current information, provide it first. If the issue is controversial, provide background material explaining your justification first. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 30
 Connectives • Internal Previews: Tells audience what you will cover • Internal Summaries: Reminds audience what you have covered • Transitions: Brief phrases to help move from one key point or idea to another • Signposts: Phrases that remind listeners where you are in a presentation Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 31
Connectives • Internal Previews: Tells audience what you will cover • Internal Summaries: Reminds audience what you have covered • Transitions: Brief phrases to help move from one key point or idea to another • Signposts: Phrases that remind listeners where you are in a presentation Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 31
 Goals of the Introduction • Focus audience attention and interest. • Connect to your audience. • Put you in your presentation. • Set the emotional tone. • Preview the message. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 32
Goals of the Introduction • Focus audience attention and interest. • Connect to your audience. • Put you in your presentation. • Set the emotional tone. • Preview the message. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 32
 Primacy and Recency Effects Primacy Effect. We recall information in a sequence we hear first. Recency Effect. We recall information in a sequence we hear last. Hermann Ebbinghuas, German psychologist Audiences tend to remember the introduction and conclusion of presentations. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 33
Primacy and Recency Effects Primacy Effect. We recall information in a sequence we hear first. Recency Effect. We recall information in a sequence we hear last. Hermann Ebbinghuas, German psychologist Audiences tend to remember the introduction and conclusion of presentations. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 33
 Power. Point Quiz In effective introductions, the power of the first impression, also described as the _______ Effect, is critical for gaining and maintaining audience attention. A. Recency B. Primacy C. Secondary D. Impression E. Hyperbole Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 34
Power. Point Quiz In effective introductions, the power of the first impression, also described as the _______ Effect, is critical for gaining and maintaining audience attention. A. Recency B. Primacy C. Secondary D. Impression E. Hyperbole Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 34
 Introductory Strategies • • Use a Statistic or Example Quote Someone Tell a Story Use a Metaphor Ask a Question Refer to the Place or Occasion Refer to a Well-Known Incident Address Audience Needs Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 35
Introductory Strategies • • Use a Statistic or Example Quote Someone Tell a Story Use a Metaphor Ask a Question Refer to the Place or Occasion Refer to a Well-Known Incident Address Audience Needs Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 35
 Match the Method of Introduction A. Use a Statistic or Example B. Quote Someone C. Tell a Story D. Refer to the Place or Occasion E. Refer to a Well. Known Incident Aisha Parveen doesn’t matter. She’s simply one more impoverished young girl from the countryside, and if her brothel owner goes ahead and kills her, almost no one will care. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 36
Match the Method of Introduction A. Use a Statistic or Example B. Quote Someone C. Tell a Story D. Refer to the Place or Occasion E. Refer to a Well. Known Incident Aisha Parveen doesn’t matter. She’s simply one more impoverished young girl from the countryside, and if her brothel owner goes ahead and kills her, almost no one will care. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 36
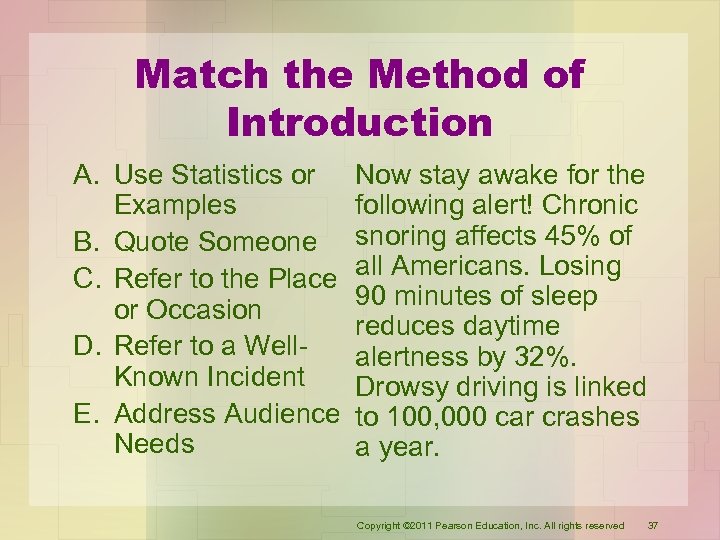 Match the Method of Introduction A. Use Statistics or Examples B. Quote Someone C. Refer to the Place or Occasion D. Refer to a Well. Known Incident E. Address Audience Needs Now stay awake for the following alert! Chronic snoring affects 45% of all Americans. Losing 90 minutes of sleep reduces daytime alertness by 32%. Drowsy driving is linked to 100, 000 car crashes a year. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 37
Match the Method of Introduction A. Use Statistics or Examples B. Quote Someone C. Refer to the Place or Occasion D. Refer to a Well. Known Incident E. Address Audience Needs Now stay awake for the following alert! Chronic snoring affects 45% of all Americans. Losing 90 minutes of sleep reduces daytime alertness by 32%. Drowsy driving is linked to 100, 000 car crashes a year. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 37
 Tips for Introductions Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 38
Tips for Introductions Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 38
 Goals of the Conclusion Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 39
Goals of the Conclusion Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 39
 Strategies for Concluding • • • Summarize Quote Someone Tell a Story Use Poetic Language Call for Action Refer to the Beginning Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 40
Strategies for Concluding • • • Summarize Quote Someone Tell a Story Use Poetic Language Call for Action Refer to the Beginning Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 40
 Match the Method of Concluding A. B. C. D. E. Summarize. . . we will be able to join hands and sing in the Quote Someone words of the old Negro Tell a Story spiritual, “Free at last! Free Call for Action at last! Thank God Refer to the almighty, we’re free at Beginning last!” Conclusion of the Rev. Martin Luther King, Jr. ’s, I Have a Dream speech Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 41
Match the Method of Concluding A. B. C. D. E. Summarize. . . we will be able to join hands and sing in the Quote Someone words of the old Negro Tell a Story spiritual, “Free at last! Free Call for Action at last! Thank God Refer to the almighty, we’re free at Beginning last!” Conclusion of the Rev. Martin Luther King, Jr. ’s, I Have a Dream speech Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 41
 Match the Method of Concluding A. Summarize B. Quote Someone C. Tell a Story D. Use Poetic Language E. Refer to the Beginning Capital punishment does not deter crime. But, it does kill the poor, innocent, and disenfranchised. And it will never bring back the innocent dead. It is time to abandon revenge and honor life. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 42
Match the Method of Concluding A. Summarize B. Quote Someone C. Tell a Story D. Use Poetic Language E. Refer to the Beginning Capital punishment does not deter crime. But, it does kill the poor, innocent, and disenfranchised. And it will never bring back the innocent dead. It is time to abandon revenge and honor life. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 42
 Power. Point Quiz Concluding a presentation with the same technique you used in the introduction is called the A. B. C. D. E. bookmarks method. bookends method. cataloging method. reverse-introduction method. reverse-conclusion method. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 43
Power. Point Quiz Concluding a presentation with the same technique you used in the introduction is called the A. B. C. D. E. bookmarks method. bookends method. cataloging method. reverse-introduction method. reverse-conclusion method. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 43
 Tips for Conclusions Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 44
Tips for Conclusions Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 44
 Communication Assessment Can You Match the Organizational Pattern? Match each brief outline with the appropriate organizational pattern (topical, time, space, problem-solving, causes and effects, stories and examples, comparison-contrast. 1. The three stages of pregnancy: first trimester, second trimester, third trimester. 2. Four basic techniques for playing volleyball: setting, bumping, spiking, serving. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 45
Communication Assessment Can You Match the Organizational Pattern? Match each brief outline with the appropriate organizational pattern (topical, time, space, problem-solving, causes and effects, stories and examples, comparison-contrast. 1. The three stages of pregnancy: first trimester, second trimester, third trimester. 2. Four basic techniques for playing volleyball: setting, bumping, spiking, serving. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 45
 TEST Your Knowledge Which organizational pattern works best for explaining the migratory patterns of hummingbirds? A. Time arrangement B. Topical arrangement C. Space arrangement D. Causes and effects arrangement E. Comparison-contrast arrangement See p. 257 for more review questions. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 46
TEST Your Knowledge Which organizational pattern works best for explaining the migratory patterns of hummingbirds? A. Time arrangement B. Topical arrangement C. Space arrangement D. Causes and effects arrangement E. Comparison-contrast arrangement See p. 257 for more review questions. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 46


