3180629434a817789009d43989478696.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Chapter 12: The Firm’s Market-Entry Strategies EXPORTING ? FRANCHISING? TURNKEY? DIRECT INVESTMENT ? LICENSING ? SUB-CONTRACTING ? Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Chapter 12: The Firm’s Market-Entry Strategies EXPORTING ? FRANCHISING? TURNKEY? DIRECT INVESTMENT ? LICENSING ? SUB-CONTRACTING ? Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 TOPIC PLAN » » » » The firm’s foreign business strategy Exporting Contracting (licensing, leasing etc) Joint ventures Wholly-owned company Advantages and disadvantages of various market entries Strategic FDI plan issues Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
TOPIC PLAN » » » » The firm’s foreign business strategy Exporting Contracting (licensing, leasing etc) Joint ventures Wholly-owned company Advantages and disadvantages of various market entries Strategic FDI plan issues Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Export-import Management l Company business strategies » Domestic strategies – – – » Investment in product development Expand domestic market share Diversify into new industry. Foreign business strategies – – – Exporting International contracting Foreign Direct Investment/Foreign production Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Export-import Management l Company business strategies » Domestic strategies – – – » Investment in product development Expand domestic market share Diversify into new industry. Foreign business strategies – – – Exporting International contracting Foreign Direct Investment/Foreign production Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 The Firm’s Foreign Business Strategy Steps(Figure 12. 1) l 1. The firm’s evaluation » l l l Competitive advantages and disadvantages 2. Selection of a target (geographic) market. 3. Selection of product to make/sell in target market 4. Selection of market-entry mode: » Exporting/Contracting/Foreign Direct Investment l 5. Business plan development and execution. l 6. Monitoring and evaluation of results. Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
The Firm’s Foreign Business Strategy Steps(Figure 12. 1) l 1. The firm’s evaluation » l l l Competitive advantages and disadvantages 2. Selection of a target (geographic) market. 3. Selection of product to make/sell in target market 4. Selection of market-entry mode: » Exporting/Contracting/Foreign Direct Investment l 5. Business plan development and execution. l 6. Monitoring and evaluation of results. Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Exporting World Exports of Goods (US $6, 1862 billion in 2000) have declined in relative importance compared to foreign production (US$ 15, 680 billion in 2000) l Most likely mode for serving a foreign market for a domestic firm starting in international business. l » » The Business Plan (Export marketing plan) Many global companies combine exports and FDI. Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Exporting World Exports of Goods (US $6, 1862 billion in 2000) have declined in relative importance compared to foreign production (US$ 15, 680 billion in 2000) l Most likely mode for serving a foreign market for a domestic firm starting in international business. l » » The Business Plan (Export marketing plan) Many global companies combine exports and FDI. Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 EXPORTS : Advantages Least costly and risky » L/C payment l Specialisation, economies of scale. l Open to any size or kind of firm l Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
EXPORTS : Advantages Least costly and risky » L/C payment l Specialisation, economies of scale. l Open to any size or kind of firm l Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 EXPORTS : Disadvantages Production costs in the home country may be HIGHER l Transport costs may make exporting uneconomical. l Trade barriers in target markets. l Divided loyalties of O/S agents. l Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
EXPORTS : Disadvantages Production costs in the home country may be HIGHER l Transport costs may make exporting uneconomical. l Trade barriers in target markets. l Divided loyalties of O/S agents. l Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Types of International Exporters l The Casual Exporter » l The Small Scale Exporter » l Domestic firms that do not do international business on a regular basis(< 5% of T/O) 5 -20% of turnover The Experienced/Global Exporter » high ratio of its turnover through involvement in worldwide business deals(Exports +FDI) Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Types of International Exporters l The Casual Exporter » l The Small Scale Exporter » l Domestic firms that do not do international business on a regular basis(< 5% of T/O) 5 -20% of turnover The Experienced/Global Exporter » high ratio of its turnover through involvement in worldwide business deals(Exports +FDI) Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Licensing l Licensor grants rights to intangible property to a Licensee in exchange for a royalty payment. l Time and territorial limits l Advantages: » » Speed of execution. Low risk/investment cost Brand recognition Preliminary cooperation which may be expanded into FDI Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Licensing l Licensor grants rights to intangible property to a Licensee in exchange for a royalty payment. l Time and territorial limits l Advantages: » » Speed of execution. Low risk/investment cost Brand recognition Preliminary cooperation which may be expanded into FDI Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Licensing : Disadvantages Isolation from the market l Lack of managerial control l Limited life. l Risk of technology loss l Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Licensing : Disadvantages Isolation from the market l Lack of managerial control l Limited life. l Risk of technology loss l Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Franchising l l A Franchisor sells limited brand use rights, products and services to a Franchisee in return for a lump sum payment and a share of the Franchisee’s profits. 20% of US franchise systems have foreign operations (Japan, Canada, UK, Australia) -Domino vs. Pizza Haven(200 in 7 years); -Dunkin’Donuts vs. Donut King Low market entry costs and risks. Quality control is difficult due to big number of Franchisees and geographic location. Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Franchising l l A Franchisor sells limited brand use rights, products and services to a Franchisee in return for a lump sum payment and a share of the Franchisee’s profits. 20% of US franchise systems have foreign operations (Japan, Canada, UK, Australia) -Domino vs. Pizza Haven(200 in 7 years); -Dunkin’Donuts vs. Donut King Low market entry costs and risks. Quality control is difficult due to big number of Franchisees and geographic location. Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Subcontracting l l Supply arrangement between a principal and a subcontractor Advantages: » » » l Low investment cost Speed Stable processing cost and quality Control of sales and marketing Can become the basis for later alliance Disadvantages: » Risk of non-delivery or late delivery Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Subcontracting l l Supply arrangement between a principal and a subcontractor Advantages: » » » l Low investment cost Speed Stable processing cost and quality Control of sales and marketing Can become the basis for later alliance Disadvantages: » Risk of non-delivery or late delivery Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 TURNKEY OPERATIONS l Contract for the construction of operating facilities that are transferred for a fee to the owner after commissioning l l Advantages : » high economic returns » less risky than FDI Disadvantages » lack of long-term market presence. » loss of control over technology » the client may turn into a competitor Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
TURNKEY OPERATIONS l Contract for the construction of operating facilities that are transferred for a fee to the owner after commissioning l l Advantages : » high economic returns » less risky than FDI Disadvantages » lack of long-term market presence. » loss of control over technology » the client may turn into a competitor Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 JOINT VENTURES A legal entity jointly owned by two or more legally distinct organisations which share in the J. V. ’s decision-making activities. l Various options l » » » 2 companies from the same country Foreign/Local 2 or > companies setting a j. v. in a third country Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
JOINT VENTURES A legal entity jointly owned by two or more legally distinct organisations which share in the J. V. ’s decision-making activities. l Various options l » » » 2 companies from the same country Foreign/Local 2 or > companies setting a j. v. in a third country Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 JOINT VENTURES(cont. ) l Advantages : » » l Partner’s local knowledge Cost/risk sharing Host government legislation Low risk of nationalisation. Disadvantages : » » » Technology control risk. Less control over subsidiaries. Management control conflicts Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
JOINT VENTURES(cont. ) l Advantages : » » l Partner’s local knowledge Cost/risk sharing Host government legislation Low risk of nationalisation. Disadvantages : » » » Technology control risk. Less control over subsidiaries. Management control conflicts Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Wholly Owned subsidiaries l l l A firm owns 100 percent of the stock. Trend in the motor-car sector(e. g. India, China) Advantages : » » » l complete management control. Optimum security for technology. “Internalisation” economies. Disadvantages : » » High costs and risks Long lead time to first sale(especially for" Greenfield”) Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Wholly Owned subsidiaries l l l A firm owns 100 percent of the stock. Trend in the motor-car sector(e. g. India, China) Advantages : » » » l complete management control. Optimum security for technology. “Internalisation” economies. Disadvantages : » » High costs and risks Long lead time to first sale(especially for" Greenfield”) Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
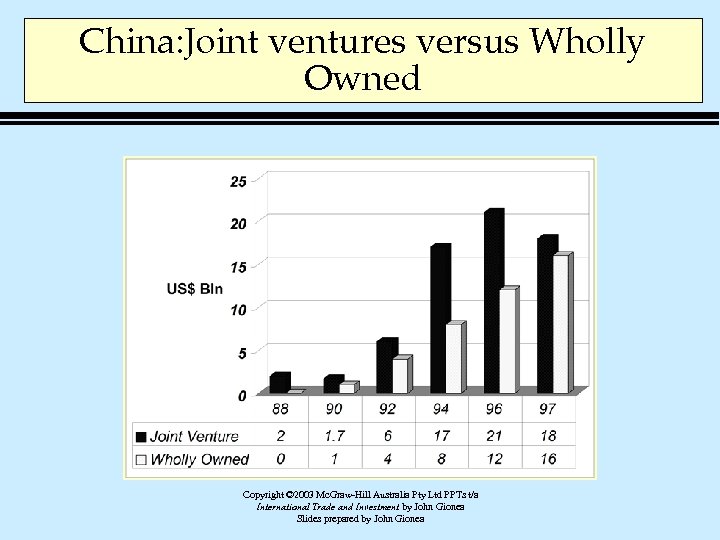 China: Joint ventures versus Wholly Owned Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
China: Joint ventures versus Wholly Owned Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Strategic FDI Plan Issues l Investment location evaluation » See Matrix on next slide l Strategic organisation » International group » Business/product units » Functional units » Global matrix Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Strategic FDI Plan Issues l Investment location evaluation » See Matrix on next slide l Strategic organisation » International group » Business/product units » Functional units » Global matrix Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
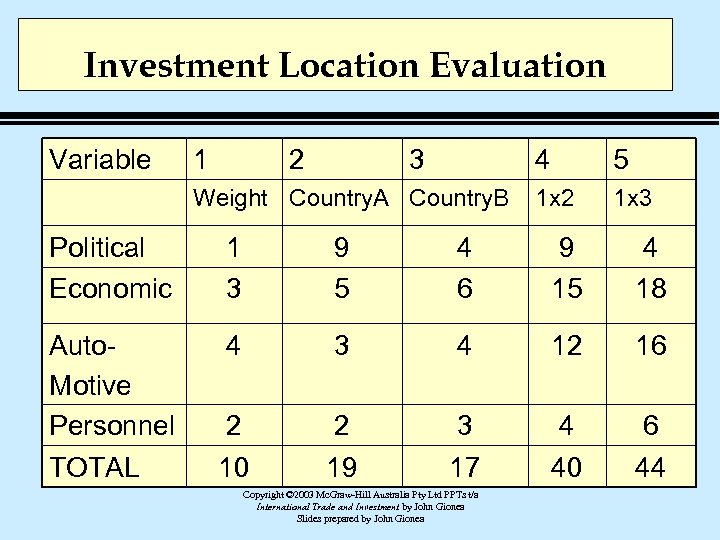 Investment Location Evaluation Variable 1 2 3 4 Weight Country. A Country. B 5 1 x 2 1 x 3 Political Economic 1 3 9 5 4 6 9 15 4 18 Auto. Motive Personnel TOTAL 4 3 4 12 16 2 10 2 19 3 17 4 40 6 44 Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Investment Location Evaluation Variable 1 2 3 4 Weight Country. A Country. B 5 1 x 2 1 x 3 Political Economic 1 3 9 5 4 6 9 15 4 18 Auto. Motive Personnel TOTAL 4 3 4 12 16 2 10 2 19 3 17 4 40 6 44 Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
 Strategic FDI Plan Issues l Financial Management and Control » Investment decisions » Financing decisions » Global money management l Global Sourcing Strategy » Outsourcing l Global Human Resource Strategies Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea
Strategic FDI Plan Issues l Financial Management and Control » Investment decisions » Financing decisions » Global money management l Global Sourcing Strategy » Outsourcing l Global Human Resource Strategies Copyright © 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Trade and Investment by John Gionea Slides prepared by John Gionea


