eafa7864f6ab9ec9b87ee84b35fa1c6e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Chapter 12: Strategies for Analyzing and Entering Foreign Markets International Business, 4 th Edition Griffin & Pustay 12 -1 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Chapter 12: Strategies for Analyzing and Entering Foreign Markets International Business, 4 th Edition Griffin & Pustay 12 -1 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Chapter Objectives_1 § Discuss how firms analyze foreign markets § Outline the process by which firms choose their mode of entry into a foreign market § Describe forms of exporting and the types of intermediaries available to assist firms in exporting their goods 2 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Chapter Objectives_1 § Discuss how firms analyze foreign markets § Outline the process by which firms choose their mode of entry into a foreign market § Describe forms of exporting and the types of intermediaries available to assist firms in exporting their goods 2 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Chapter Objectives_2 § Identify the basic issues in international licensing and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of licensing § Identify the basic issues in international franchising and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of franchising 3 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Chapter Objectives_2 § Identify the basic issues in international licensing and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of licensing § Identify the basic issues in international franchising and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of franchising 3 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Chapter Objectives_3 § Analyze contract manufacturing, management contracts, and turnkey projects as specialized entry modes for international business § Characterize the greenfield and acquisition forms of FDI 4 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Chapter Objectives_3 § Analyze contract manufacturing, management contracts, and turnkey projects as specialized entry modes for international business § Characterize the greenfield and acquisition forms of FDI 4 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Foreign Market Analysis § Assess alternative markets § Evaluate the respective costs, benefits, and risks of entering each § Select those that hold the most potential for entry or expansion 5 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Foreign Market Analysis § Assess alternative markets § Evaluate the respective costs, benefits, and risks of entering each § Select those that hold the most potential for entry or expansion 5 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Table 12. 1 Factors in Assessing New Market Opportunities § Product-market dimensions § Major productmarket differences § Structural characteristics of the national product market 6 § Competitor analysis § Potential target markets § Relevant trends § Explanation of change § Success factors § Strategic options © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 1 Factors in Assessing New Market Opportunities § Product-market dimensions § Major productmarket differences § Structural characteristics of the national product market 6 § Competitor analysis § Potential target markets § Relevant trends § Explanation of change § Success factors § Strategic options © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Map 12. 1 A Tale of Two Chinas 7 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Map 12. 1 A Tale of Two Chinas 7 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Dole Food Company’s international operations are subject to a variety of costs, benefits, and risks. 8 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Dole Food Company’s international operations are subject to a variety of costs, benefits, and risks. 8 © 2004 Prentice Hall
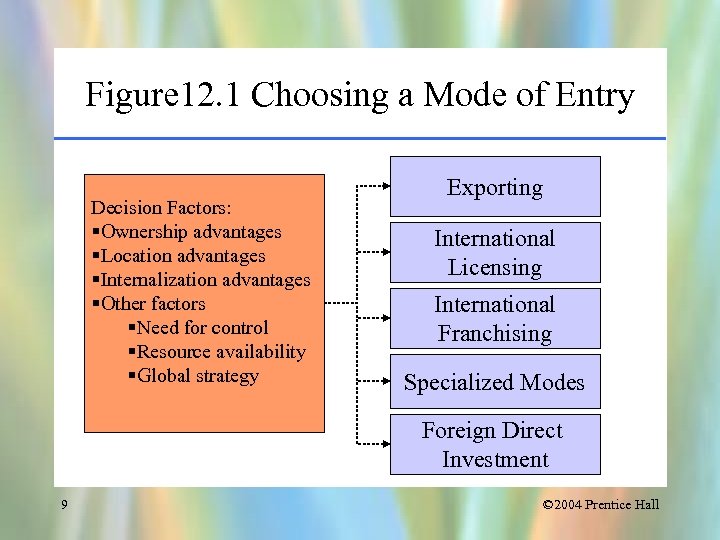 Figure 12. 1 Choosing a Mode of Entry Decision Factors: §Ownership advantages §Location advantages §Internalization advantages §Other factors §Need for control §Resource availability §Global strategy Exporting International Licensing International Franchising Specialized Modes Foreign Direct Investment 9 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 1 Choosing a Mode of Entry Decision Factors: §Ownership advantages §Location advantages §Internalization advantages §Other factors §Need for control §Resource availability §Global strategy Exporting International Licensing International Franchising Specialized Modes Foreign Direct Investment 9 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Map 12. 2 Turkey 10 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Map 12. 2 Turkey 10 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Exporting Advantages § Relatively low financial exposure § Permit gradual market entry § Acquire knowledge about local market § Avoid restrictions on foreign investment 11 Disadvantages § Vulnerability to tariffs and NTBs § Logistical complexities § Potential conflicts with distributors © 2004 Prentice Hall
Exporting Advantages § Relatively low financial exposure § Permit gradual market entry § Acquire knowledge about local market § Avoid restrictions on foreign investment 11 Disadvantages § Vulnerability to tariffs and NTBs § Logistical complexities § Potential conflicts with distributors © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Motivations for Exporting § Proactive motivations: pull a firm into foreign markets as a result of opportunities available there 12 § Reactive motivations: push a firm into foreign markets because opportunities are decreasing in the domestic market © 2004 Prentice Hall
Motivations for Exporting § Proactive motivations: pull a firm into foreign markets as a result of opportunities available there 12 § Reactive motivations: push a firm into foreign markets because opportunities are decreasing in the domestic market © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Forms of Exporting § Indirect exporting § Direct exporting § Intracorporate transfers 13 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Forms of Exporting § Indirect exporting § Direct exporting § Intracorporate transfers 13 © 2004 Prentice Hall
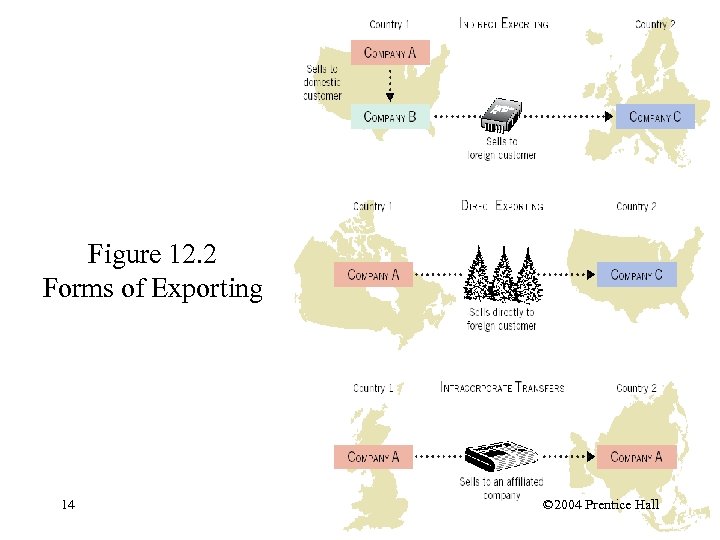 Figure 12. 2 Forms of Exporting 14 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 2 Forms of Exporting 14 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Export Intermediaries § Export Management Company § Webb-Pomerene Association § International Trading Company § Other intermediaries 15 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Export Intermediaries § Export Management Company § Webb-Pomerene Association § International Trading Company § Other intermediaries 15 © 2004 Prentice Hall
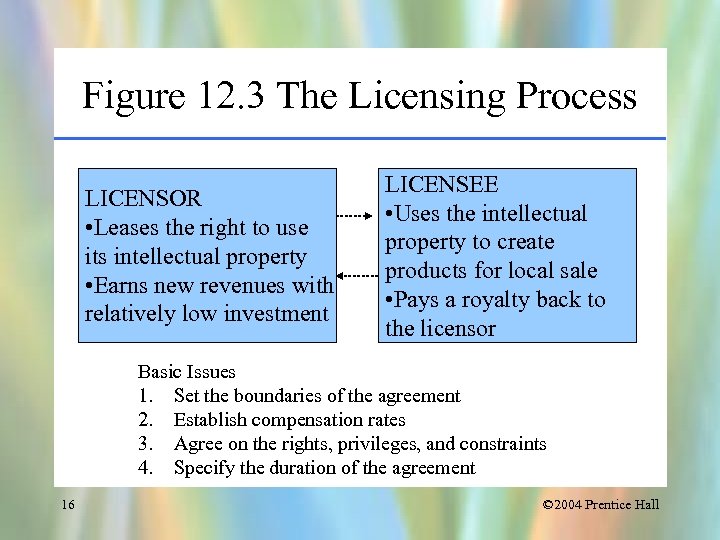 Figure 12. 3 The Licensing Process LICENSOR • Leases the right to use its intellectual property • Earns new revenues with relatively low investment LICENSEE • Uses the intellectual property to create products for local sale • Pays a royalty back to the licensor Basic Issues 1. Set the boundaries of the agreement 2. Establish compensation rates 3. Agree on the rights, privileges, and constraints 4. Specify the duration of the agreement 16 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 3 The Licensing Process LICENSOR • Leases the right to use its intellectual property • Earns new revenues with relatively low investment LICENSEE • Uses the intellectual property to create products for local sale • Pays a royalty back to the licensor Basic Issues 1. Set the boundaries of the agreement 2. Establish compensation rates 3. Agree on the rights, privileges, and constraints 4. Specify the duration of the agreement 16 © 2004 Prentice Hall
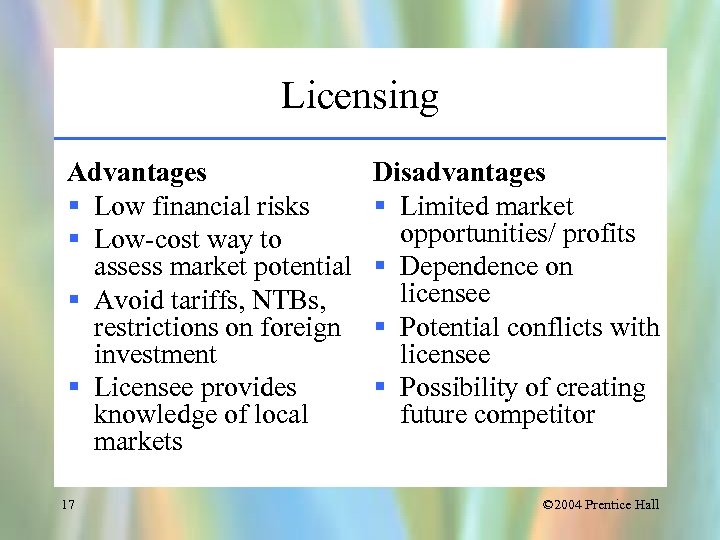 Licensing Advantages § Low financial risks § Low-cost way to assess market potential § Avoid tariffs, NTBs, restrictions on foreign investment § Licensee provides knowledge of local markets 17 Disadvantages § Limited market opportunities/ profits § Dependence on licensee § Potential conflicts with licensee § Possibility of creating future competitor © 2004 Prentice Hall
Licensing Advantages § Low financial risks § Low-cost way to assess market potential § Avoid tariffs, NTBs, restrictions on foreign investment § Licensee provides knowledge of local markets 17 Disadvantages § Limited market opportunities/ profits § Dependence on licensee § Potential conflicts with licensee § Possibility of creating future competitor © 2004 Prentice Hall
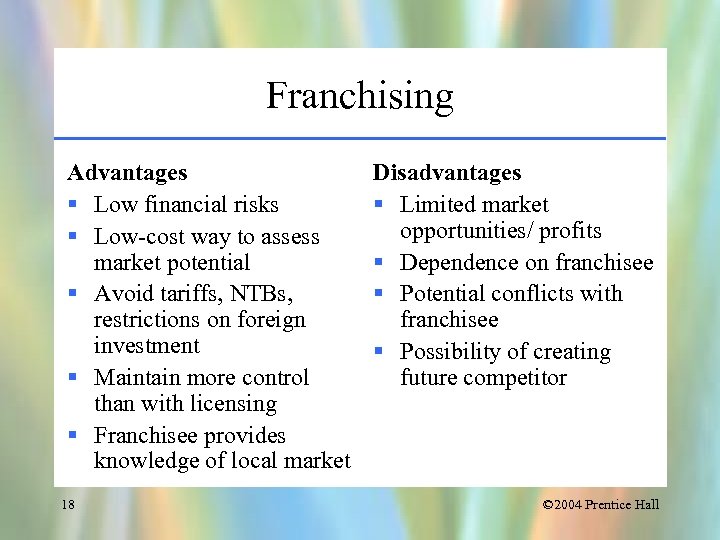 Franchising Advantages § Low financial risks § Low-cost way to assess market potential § Avoid tariffs, NTBs, restrictions on foreign investment § Maintain more control than with licensing § Franchisee provides knowledge of local market 18 Disadvantages § Limited market opportunities/ profits § Dependence on franchisee § Potential conflicts with franchisee § Possibility of creating future competitor © 2004 Prentice Hall
Franchising Advantages § Low financial risks § Low-cost way to assess market potential § Avoid tariffs, NTBs, restrictions on foreign investment § Maintain more control than with licensing § Franchisee provides knowledge of local market 18 Disadvantages § Limited market opportunities/ profits § Dependence on franchisee § Potential conflicts with franchisee § Possibility of creating future competitor © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Specialized Entry Modes § Contract Manufacturing § Management Contract § Turnkey Project 19 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Specialized Entry Modes § Contract Manufacturing § Management Contract § Turnkey Project 19 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Contract Manufacturing Advantages § Low financial risks § Minimize resources devoted to manufacturing § Focus firm’s resources on other elements of the value chain 20 Disadvantages § Reduced control (may affect quality, delivery schedules, etc. ) § Reduce learning potential § Potential public relations problems © 2004 Prentice Hall
Contract Manufacturing Advantages § Low financial risks § Minimize resources devoted to manufacturing § Focus firm’s resources on other elements of the value chain 20 Disadvantages § Reduced control (may affect quality, delivery schedules, etc. ) § Reduce learning potential § Potential public relations problems © 2004 Prentice Hall
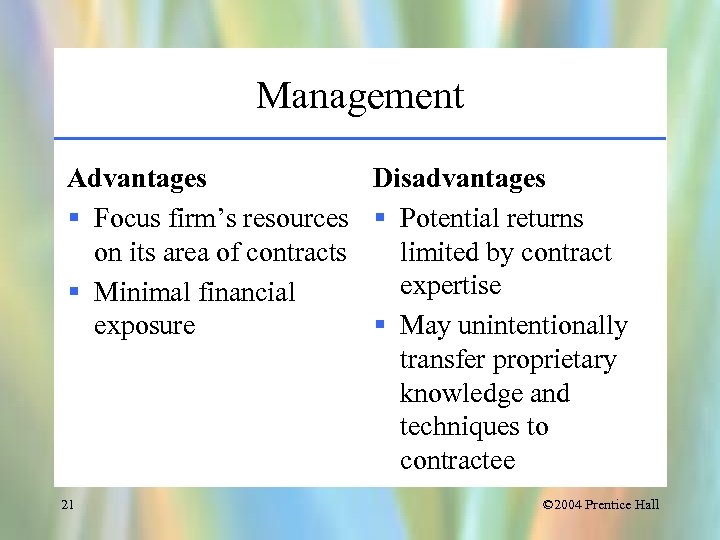 Management Advantages Disadvantages § Focus firm’s resources § Potential returns on its area of contracts limited by contract expertise § Minimal financial exposure § May unintentionally transfer proprietary knowledge and techniques to contractee 21 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Management Advantages Disadvantages § Focus firm’s resources § Potential returns on its area of contracts limited by contract expertise § Minimal financial exposure § May unintentionally transfer proprietary knowledge and techniques to contractee 21 © 2004 Prentice Hall
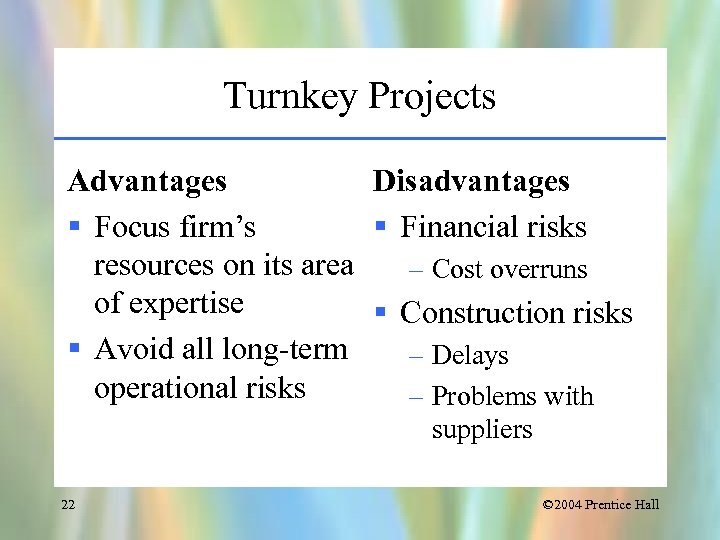 Turnkey Projects Advantages Disadvantages § Focus firm’s § Financial risks resources on its area – Cost overruns of expertise § Construction risks § Avoid all long-term – Delays operational risks – Problems with suppliers 22 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Turnkey Projects Advantages Disadvantages § Focus firm’s § Financial risks resources on its area – Cost overruns of expertise § Construction risks § Avoid all long-term – Delays operational risks – Problems with suppliers 22 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Foreign Direct Investment § Building new facilities (the greenfield strategy) § Buying existing assets in a foreign country (acquisition strategy) § Participating in a joint venture 23 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Foreign Direct Investment § Building new facilities (the greenfield strategy) § Buying existing assets in a foreign country (acquisition strategy) § Participating in a joint venture 23 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Volkswagon was the first auto manufacturer to open a plant in Mexico 24 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Volkswagon was the first auto manufacturer to open a plant in Mexico 24 © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Foreign Direct Investment Advantages § High profit potential § Maintain control over operations § Acquire knowledge of local market § Avoid tariffs and NTBs 25 Disadvantages § High financial and managerial investments § Higher exposure to political risk § Vulnerability to restrictions on foreign investment § Greater managerial complexity © 2004 Prentice Hall
Foreign Direct Investment Advantages § High profit potential § Maintain control over operations § Acquire knowledge of local market § Avoid tariffs and NTBs 25 Disadvantages § High financial and managerial investments § Higher exposure to political risk § Vulnerability to restrictions on foreign investment § Greater managerial complexity © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Greenfield Strategy § Best site § Modern facilities § Economic development incentives § Clean slate 26 © 2004 Prentice Hall
Greenfield Strategy § Best site § Modern facilities § Economic development incentives § Clean slate 26 © 2004 Prentice Hall


