52778c4ccabc868330171f09c2cc4c9b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Chapter 12 Marketing Communication and Personal Selling Prepared by Deborah Baker Texas Christian University Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 1
Chapter 12 Marketing Communication and Personal Selling Prepared by Deborah Baker Texas Christian University Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 1
 Chapter 12 Objectives 1. Discuss the role of promotion in the marketing mix. 2. Discuss the elements of the promotional mix. 3. Describe the communication process. 4. Explain the goals and tasks of promotion. (continued) Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 2
Chapter 12 Objectives 1. Discuss the role of promotion in the marketing mix. 2. Discuss the elements of the promotional mix. 3. Describe the communication process. 4. Explain the goals and tasks of promotion. (continued) Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 2
 Chapter 12 Objectives 5. Discuss the AIDA concept and its relationship to the promotional mix. 6. Describe the factors that affect the promotional mix. 7. Describe personal selling. 8. Discuss the key differences between relationship selling and traditional selling. (continued) Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 3
Chapter 12 Objectives 5. Discuss the AIDA concept and its relationship to the promotional mix. 6. Describe the factors that affect the promotional mix. 7. Describe personal selling. 8. Discuss the key differences between relationship selling and traditional selling. (continued) Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 3
 Chapter 12 Objectives 9. List the steps in the selling process. 10. Describe the functions of sales management. Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 4
Chapter 12 Objectives 9. List the steps in the selling process. 10. Describe the functions of sales management. Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 4
 The Role of Promotion is communication by marketers that informs, persuades, and reminds potential buyers of a product in order to influence their opinions or elicit a response Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 5
The Role of Promotion is communication by marketers that informs, persuades, and reminds potential buyers of a product in order to influence their opinions or elicit a response Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 5
 The Role of Promotion People no longer buy shoes to keep their feet warm and dry. They buy them because of the way the shoes make them feel -masculine, feminine, rugged, different, sophisticated, young, glamorous, “in. ” Buying shoes has become an emotional experience. Our business now is selling excitement rather than shoes. --Francis C. Rooney Chairman, H. H. Brown Shoe Co. Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 6
The Role of Promotion People no longer buy shoes to keep their feet warm and dry. They buy them because of the way the shoes make them feel -masculine, feminine, rugged, different, sophisticated, young, glamorous, “in. ” Buying shoes has become an emotional experience. Our business now is selling excitement rather than shoes. --Francis C. Rooney Chairman, H. H. Brown Shoe Co. Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 6
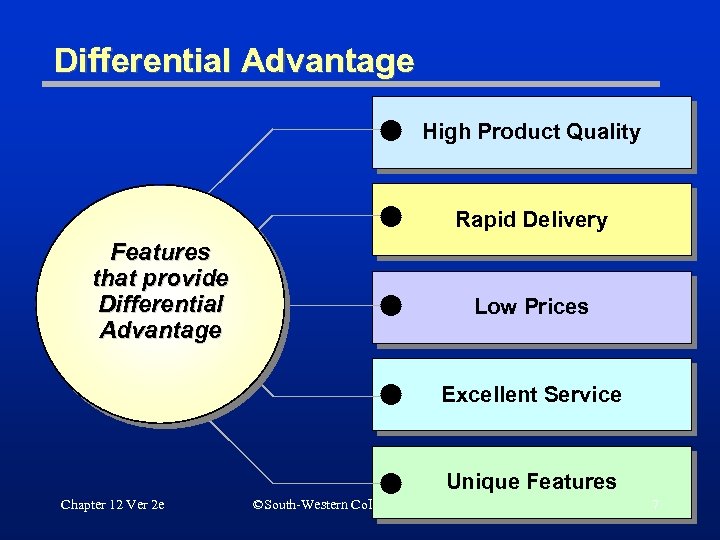 Differential Advantage High Product Quality Rapid Delivery Features that provide Differential Advantage Low Prices Excellent Service Unique Features Chapter 12 Ver 2 e ©South-Western College Publishing 7
Differential Advantage High Product Quality Rapid Delivery Features that provide Differential Advantage Low Prices Excellent Service Unique Features Chapter 12 Ver 2 e ©South-Western College Publishing 7
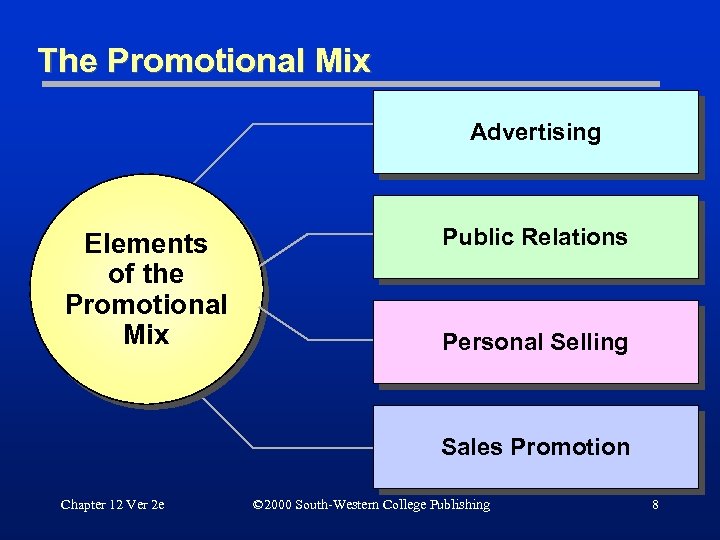 The Promotional Mix Advertising Elements of the Promotional Mix Public Relations Personal Selling Sales Promotion Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 8
The Promotional Mix Advertising Elements of the Promotional Mix Public Relations Personal Selling Sales Promotion Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 8
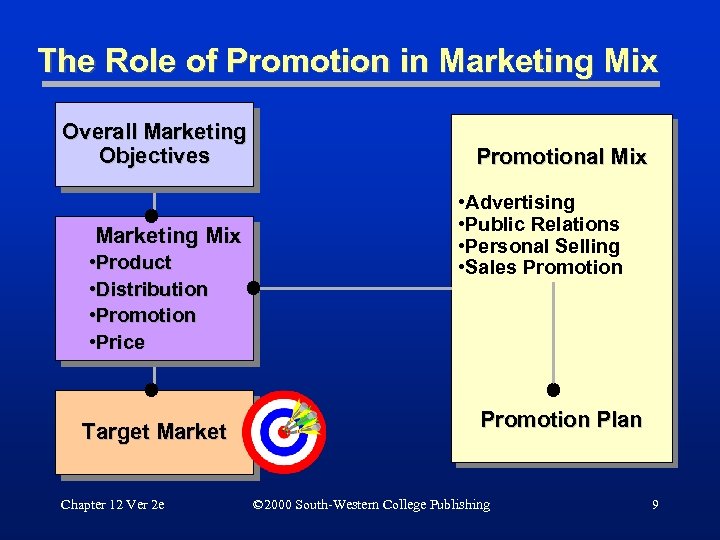 The Role of Promotion in Marketing Mix Overall Marketing Objectives Marketing Mix • Product • Distribution • Promotion • Price Target Market Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Promotional Mix • Advertising • Public Relations • Personal Selling • Sales Promotion Plan © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 9
The Role of Promotion in Marketing Mix Overall Marketing Objectives Marketing Mix • Product • Distribution • Promotion • Price Target Market Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Promotional Mix • Advertising • Public Relations • Personal Selling • Sales Promotion Plan © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 9
 Personal Selling Traditional Selling Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Relationship Selling © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 10
Personal Selling Traditional Selling Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Relationship Selling © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 10
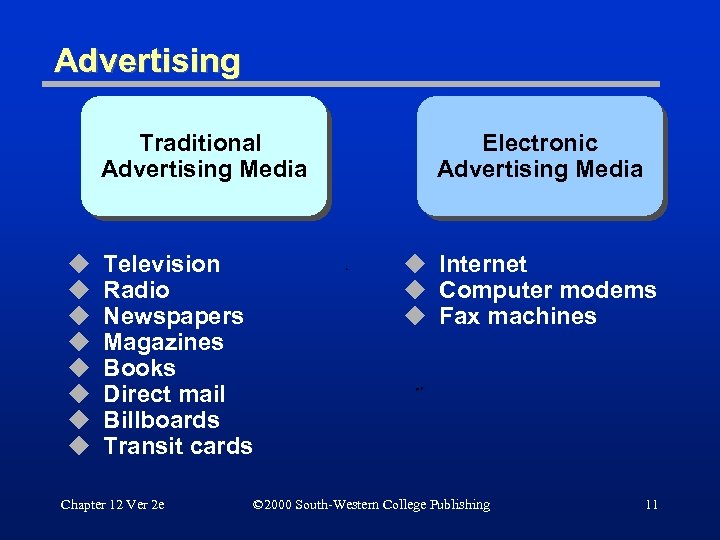 Advertising Traditional Advertising Media u u u u Television Radio Newspapers Magazines Books Direct mail Billboards Transit cards Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Electronic Advertising Media u Internet u Computer modems u Fax machines © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 11
Advertising Traditional Advertising Media u u u u Television Radio Newspapers Magazines Books Direct mail Billboards Transit cards Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Electronic Advertising Media u Internet u Computer modems u Fax machines © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 11
 Sales Promotion Free Samples Contests Premiums Trade Shows Types of Sales Promotion Sweepstakes Coupons Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 12
Sales Promotion Free Samples Contests Premiums Trade Shows Types of Sales Promotion Sweepstakes Coupons Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 12
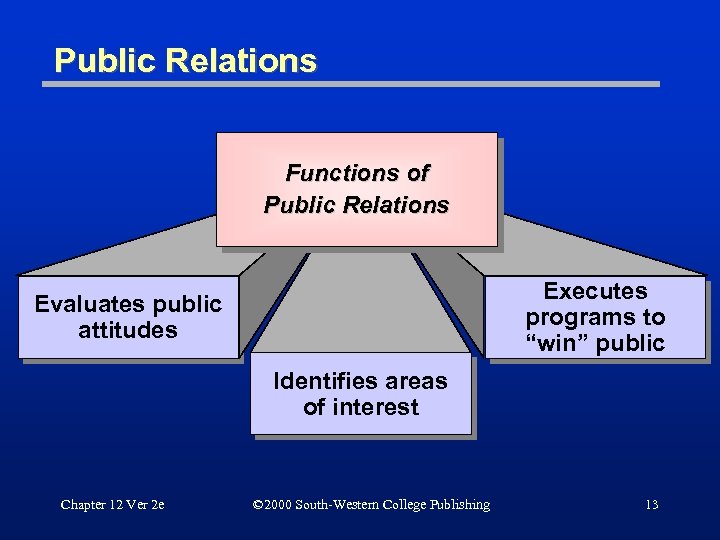 Public Relations Functions of Public Relations Executes programs to “win” public Evaluates public attitudes Identifies areas of interest Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 13
Public Relations Functions of Public Relations Executes programs to “win” public Evaluates public attitudes Identifies areas of interest Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 13
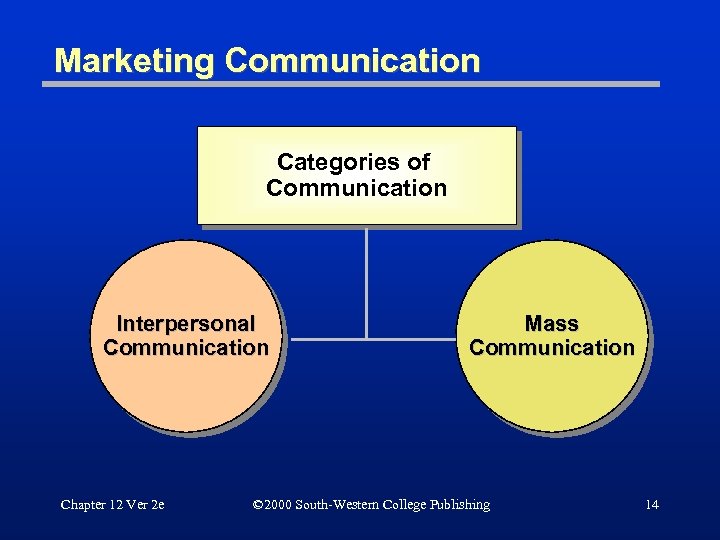 Marketing Communication Categories of Communication Interpersonal Communication Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Mass Communication © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 14
Marketing Communication Categories of Communication Interpersonal Communication Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Mass Communication © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 14
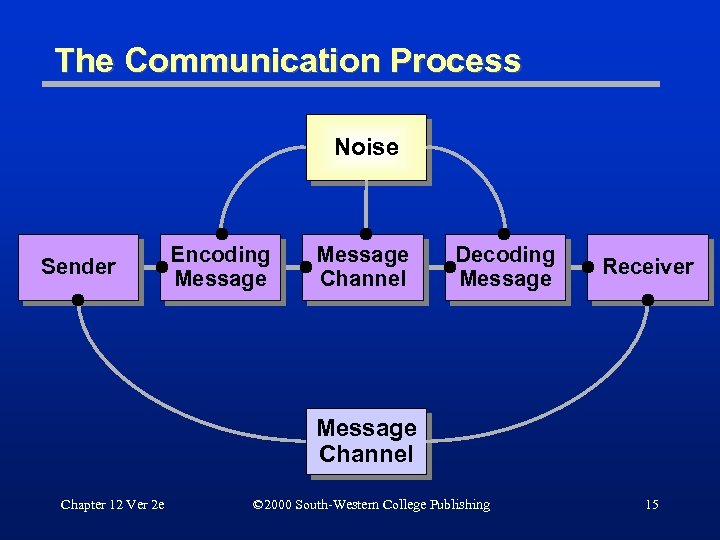 The Communication Process Noise Sender Encoding Message Channel Decoding Message Receiver Message Channel Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 15
The Communication Process Noise Sender Encoding Message Channel Decoding Message Receiver Message Channel Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 15
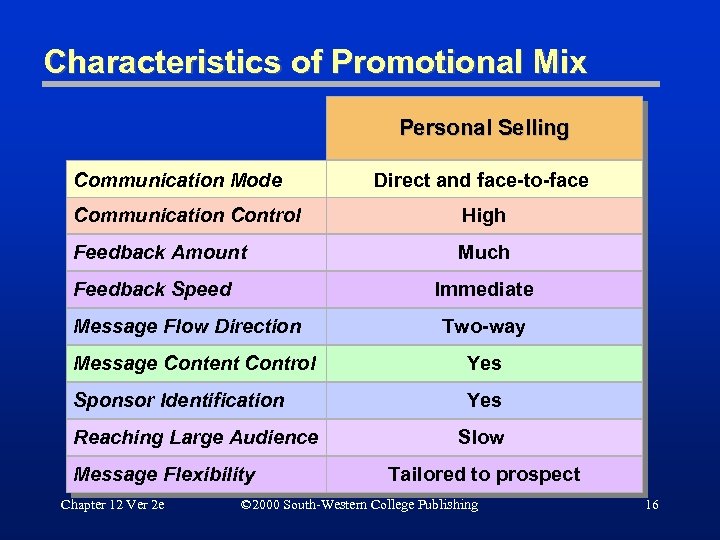 Characteristics of Promotional Mix Personal Selling Communication Mode Direct and face-to-face Communication Control High Feedback Amount Much Feedback Speed Immediate Message Flow Direction Two-way Message Content Control Yes Sponsor Identification Yes Reaching Large Audience Message Flexibility Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Slow Tailored to prospect © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 16
Characteristics of Promotional Mix Personal Selling Communication Mode Direct and face-to-face Communication Control High Feedback Amount Much Feedback Speed Immediate Message Flow Direction Two-way Message Content Control Yes Sponsor Identification Yes Reaching Large Audience Message Flexibility Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Slow Tailored to prospect © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 16
 Characteristics of Promotional Mix Advertising Communication Mode Indirect and non-personal Communication Control Low Feedback Amount Little Feedback Speed Delayed Message Flow Direction One-way Message Content Control Yes Sponsor Identification Yes Reaching Large Audience Fast Message Flexibility Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Same message to all audiences © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 17
Characteristics of Promotional Mix Advertising Communication Mode Indirect and non-personal Communication Control Low Feedback Amount Little Feedback Speed Delayed Message Flow Direction One-way Message Content Control Yes Sponsor Identification Yes Reaching Large Audience Fast Message Flexibility Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Same message to all audiences © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 17
 Characteristics of Promotional Mix Sales Promotion Communication Mode Communication Control Usually Indirect and non-personal Moderate to low Little to moderate Feedback Amount Feedback Speed Varies Message Flow Direction Mostly one-way Message Content Control Yes Sponsor Identification Yes Reaching Large Audience Fast Message Flexibility Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Same message to varied target © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 18
Characteristics of Promotional Mix Sales Promotion Communication Mode Communication Control Usually Indirect and non-personal Moderate to low Little to moderate Feedback Amount Feedback Speed Varies Message Flow Direction Mostly one-way Message Content Control Yes Sponsor Identification Yes Reaching Large Audience Fast Message Flexibility Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Same message to varied target © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 18
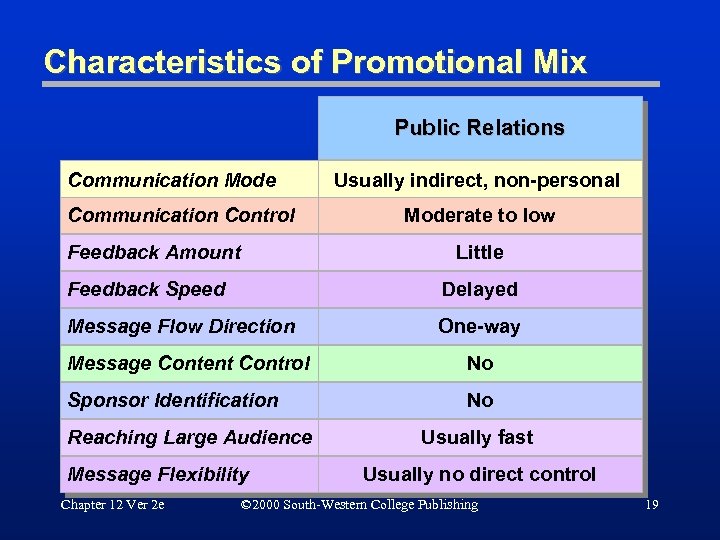 Characteristics of Promotional Mix Public Relations Communication Mode Communication Control Usually indirect, non-personal Moderate to low Little Feedback Amount Feedback Speed Delayed Message Flow Direction One-way Message Content Control No Sponsor Identification No Reaching Large Audience Message Flexibility Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Usually fast Usually no direct control © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 19
Characteristics of Promotional Mix Public Relations Communication Mode Communication Control Usually indirect, non-personal Moderate to low Little Feedback Amount Feedback Speed Delayed Message Flow Direction One-way Message Content Control No Sponsor Identification No Reaching Large Audience Message Flexibility Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Usually fast Usually no direct control © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 19
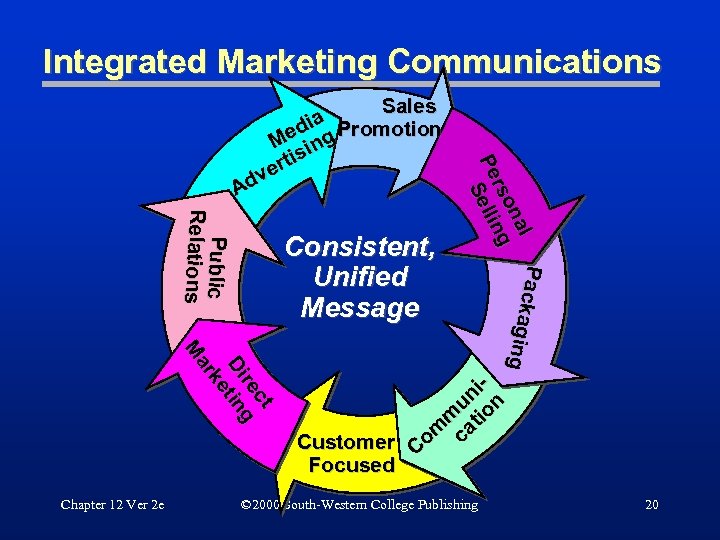 Integrated Marketing Communications Public Relations Consistent, Unified Message ct ct re g Dii tiin D tn ke ke ar ar M M Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Pa ckagin ll Packaging g na na rso g Pe elllliin Pe S e n S Sales a Promotion i ed g M in rtis e dv A ni n u o m ti om ca Customer C Focused © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 20
Integrated Marketing Communications Public Relations Consistent, Unified Message ct ct re g Dii tiin D tn ke ke ar ar M M Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Pa ckagin ll Packaging g na na rso g Pe elllliin Pe S e n S Sales a Promotion i ed g M in rtis e dv A ni n u o m ti om ca Customer C Focused © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 20
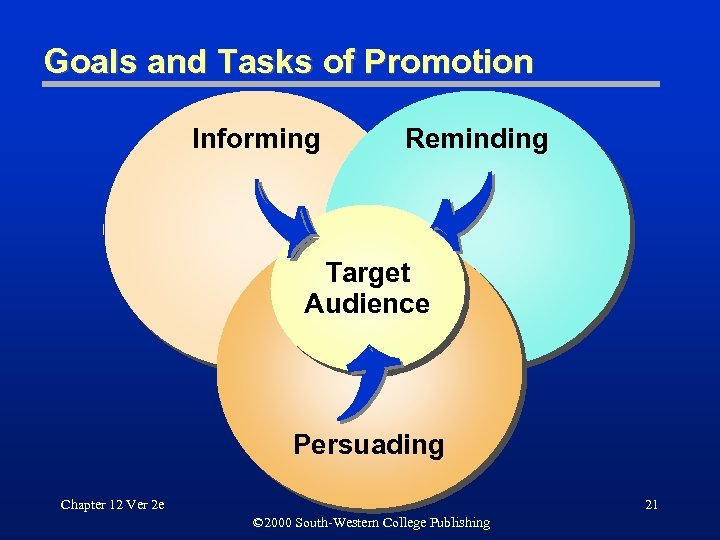 Goals and Tasks of Promotion Informing Reminding Target Audience Persuading Chapter 12 Ver 2 e 21 © 2000 South-Western College Publishing
Goals and Tasks of Promotion Informing Reminding Target Audience Persuading Chapter 12 Ver 2 e 21 © 2000 South-Western College Publishing
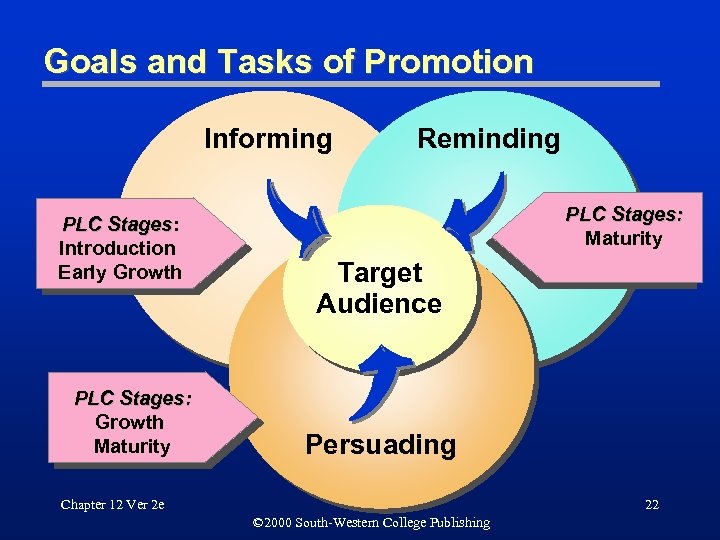 Goals and Tasks of Promotion Informing PLC Stages: Stages Introduction Early Growth PLC Stages: Growth Maturity Reminding PLC Stages: Maturity Target Audience Persuading Chapter 12 Ver 2 e 22 © 2000 South-Western College Publishing
Goals and Tasks of Promotion Informing PLC Stages: Stages Introduction Early Growth PLC Stages: Growth Maturity Reminding PLC Stages: Maturity Target Audience Persuading Chapter 12 Ver 2 e 22 © 2000 South-Western College Publishing
 Goals and Tasks of Promotion Informative Objective • • Increase awareness Explain how product works Suggest new uses Build company image Persuasion Objective • • Encourage brand switching Change customers’ perception of product attributes Influence buying decision Persuade customers to call Reminder Objective • • • Remind customers that product may be needed Remind customers where to buy product Maintain customer awareness Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 23
Goals and Tasks of Promotion Informative Objective • • Increase awareness Explain how product works Suggest new uses Build company image Persuasion Objective • • Encourage brand switching Change customers’ perception of product attributes Influence buying decision Persuade customers to call Reminder Objective • • • Remind customers that product may be needed Remind customers where to buy product Maintain customer awareness Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 23
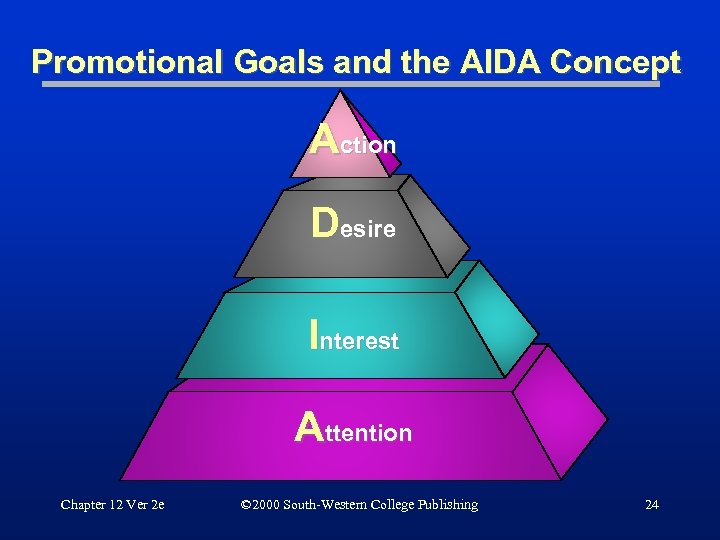 Promotional Goals and the AIDA Concept Action Desire Interest Attention Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 24
Promotional Goals and the AIDA Concept Action Desire Interest Attention Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 24
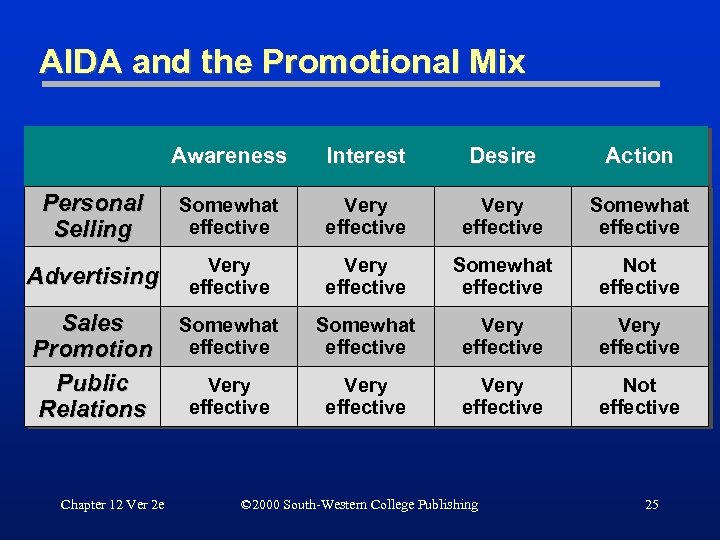 AIDA and the Promotional Mix Awareness Interest Desire Action Personal Selling Somewhat effective Very effective Somewhat effective Advertising Very effective Somewhat effective Not effective Sales Promotion Public Relations Somewhat effective Very effective Very effective Not effective Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 25
AIDA and the Promotional Mix Awareness Interest Desire Action Personal Selling Somewhat effective Very effective Somewhat effective Advertising Very effective Somewhat effective Not effective Sales Promotion Public Relations Somewhat effective Very effective Very effective Not effective Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 25
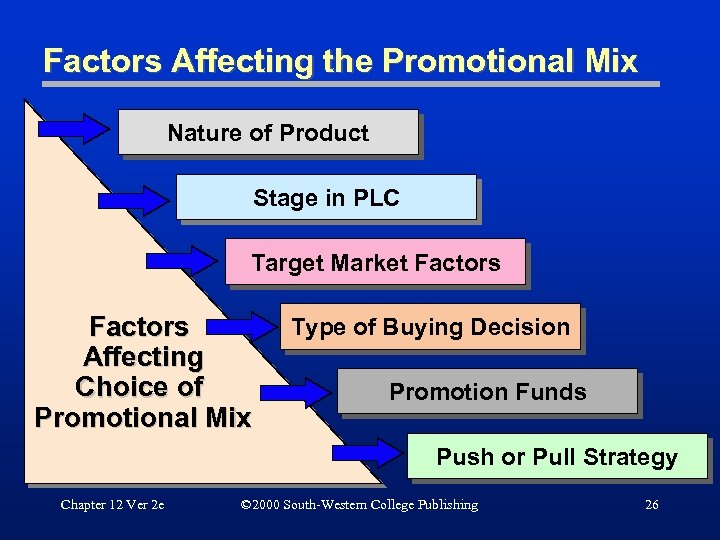 Factors Affecting the Promotional Mix Nature of Product Stage in PLC Target Market Factors Affecting Choice of Promotional Mix Type of Buying Decision Promotion Funds Push or Pull Strategy Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 26
Factors Affecting the Promotional Mix Nature of Product Stage in PLC Target Market Factors Affecting Choice of Promotional Mix Type of Buying Decision Promotion Funds Push or Pull Strategy Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 26
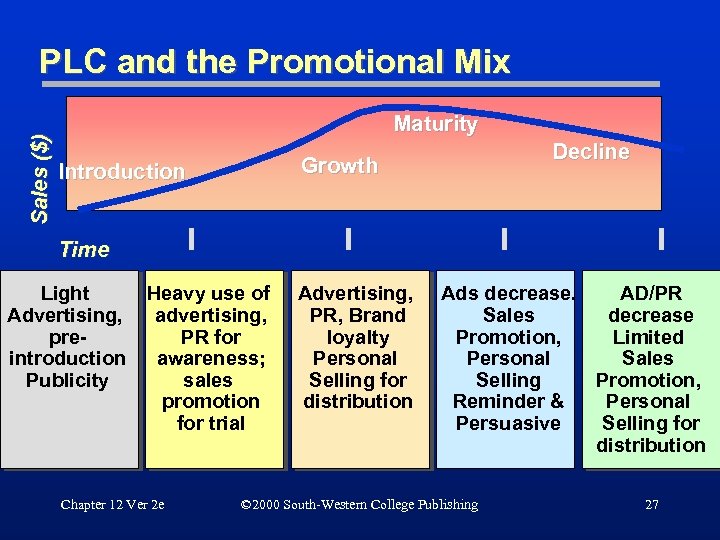 Sales ($) PLC and the Promotional Mix Maturity Decline Growth Introduction Time Light Advertising, preintroduction Publicity Heavy use of advertising, PR for awareness; sales promotion for trial Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Advertising, PR, Brand loyalty Personal Selling for distribution Ads decrease. AD/PR Sales decrease Promotion, Limited Personal Sales Selling Promotion, Reminder & Personal Persuasive Selling for distribution © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 27
Sales ($) PLC and the Promotional Mix Maturity Decline Growth Introduction Time Light Advertising, preintroduction Publicity Heavy use of advertising, PR for awareness; sales promotion for trial Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Advertising, PR, Brand loyalty Personal Selling for distribution Ads decrease. AD/PR Sales decrease Promotion, Limited Personal Sales Selling Promotion, Reminder & Personal Persuasive Selling for distribution © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 27
 Target Market Characteristics Widely-scattered markets Highly-informed buyers Brand-loyal repeat purchasers Advertising Sales Promotion Less Personal Selling Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 28
Target Market Characteristics Widely-scattered markets Highly-informed buyers Brand-loyal repeat purchasers Advertising Sales Promotion Less Personal Selling Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 28
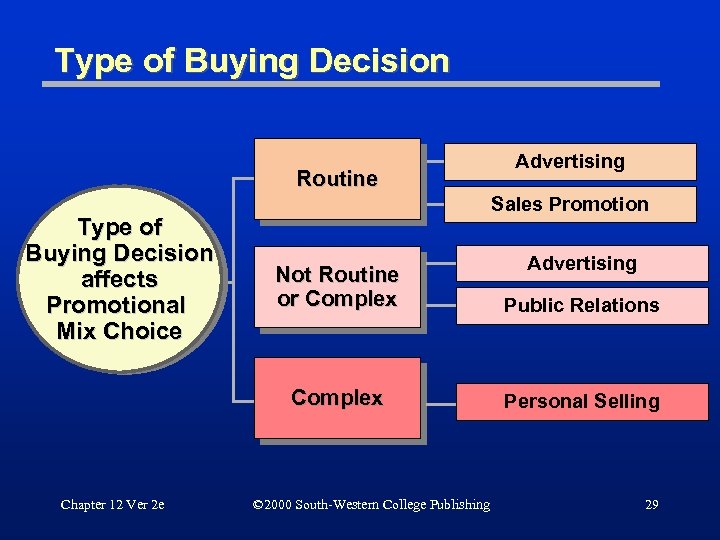 Type of Buying Decision Routine Type of Buying Decision affects Promotional Mix Choice Advertising Sales Promotion Advertising Public Relations Complex Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Not Routine or Complex Personal Selling © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 29
Type of Buying Decision Routine Type of Buying Decision affects Promotional Mix Choice Advertising Sales Promotion Advertising Public Relations Complex Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Not Routine or Complex Personal Selling © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 29
 Available Funds u Trade-offs with funds available u Number of people in target market u Quality of communication needed u Relative costs of promotional elements Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 30
Available Funds u Trade-offs with funds available u Number of people in target market u Quality of communication needed u Relative costs of promotional elements Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 30
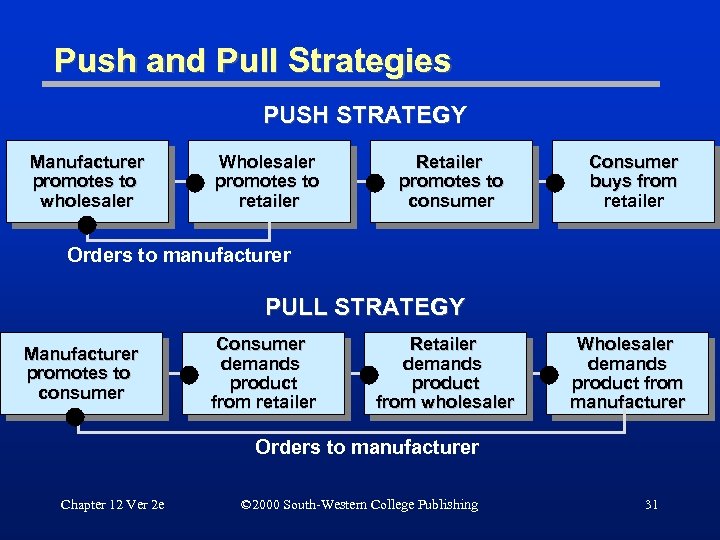 Push and Pull Strategies PUSH STRATEGY Manufacturer promotes to wholesaler Wholesaler promotes to retailer Retailer promotes to consumer Consumer buys from retailer Orders to manufacturer PULL STRATEGY Manufacturer promotes to consumer Consumer demands product from retailer Retailer demands product from wholesaler Wholesaler demands product from manufacturer Orders to manufacturer Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 31
Push and Pull Strategies PUSH STRATEGY Manufacturer promotes to wholesaler Wholesaler promotes to retailer Retailer promotes to consumer Consumer buys from retailer Orders to manufacturer PULL STRATEGY Manufacturer promotes to consumer Consumer demands product from retailer Retailer demands product from wholesaler Wholesaler demands product from manufacturer Orders to manufacturer Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 31
 Advantages of Personal Selling u Provides a detailed explanation or demonstration of product u Message can be varied to fit the needs of each prospective customer u Can be directed to specific qualified prospects u Costs can be controlled by adjusting sales force size u Most effective in obtaining sales and gaining satisfied customers Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 32
Advantages of Personal Selling u Provides a detailed explanation or demonstration of product u Message can be varied to fit the needs of each prospective customer u Can be directed to specific qualified prospects u Costs can be controlled by adjusting sales force size u Most effective in obtaining sales and gaining satisfied customers Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 32
 Personal Selling is more important if. . . Advertising & sales promotion are more important if. . . Product has a high value Product has a low value Product is custom made Product is standardized Product is technically complex Product is simple to understand There are few customers There are many customers Customers are concentrated Customers are geographically dispersed Chapter 12 Ver 2 e ©South-Western College Publishing 33
Personal Selling is more important if. . . Advertising & sales promotion are more important if. . . Product has a high value Product has a low value Product is custom made Product is standardized Product is technically complex Product is simple to understand There are few customers There are many customers Customers are concentrated Customers are geographically dispersed Chapter 12 Ver 2 e ©South-Western College Publishing 33
 Relationship Selling Traditional Personal Selling Relationship Selling Sell products Sell advice, assistance, counsel Focus on closing sales Focus on customer’s bottom line Limited sales planning Sales planning is top priority Discuss product Build problem-solving environment Assess “Product-specific” needs Conduct discovery in scope of operations “Lone wolf” approach Team approach Pricing/product focus Profit impact and strategic benefit focus Short-term sales follow-up Long-term sales follow-up Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 34
Relationship Selling Traditional Personal Selling Relationship Selling Sell products Sell advice, assistance, counsel Focus on closing sales Focus on customer’s bottom line Limited sales planning Sales planning is top priority Discuss product Build problem-solving environment Assess “Product-specific” needs Conduct discovery in scope of operations “Lone wolf” approach Team approach Pricing/product focus Profit impact and strategic benefit focus Short-term sales follow-up Long-term sales follow-up Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 34
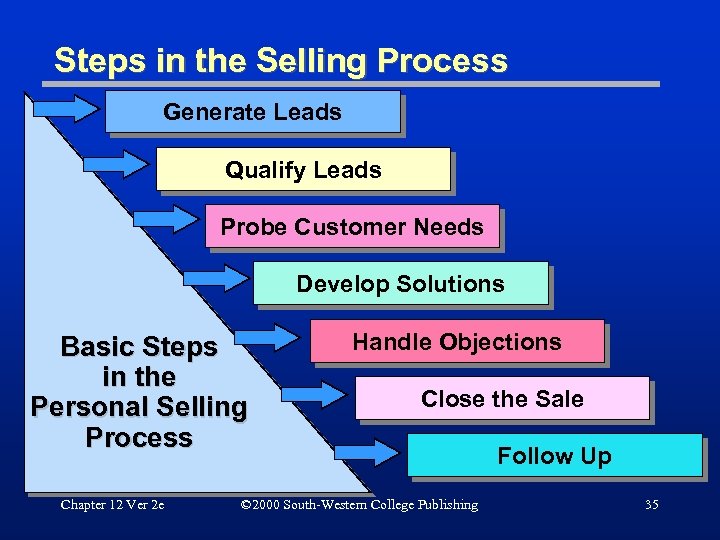 Steps in the Selling Process Generate Leads Qualify Leads Probe Customer Needs Develop Solutions Basic Steps in the Personal Selling Process Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Handle Objections Close the Sale © 2000 South-Western College Publishing Follow Up 35
Steps in the Selling Process Generate Leads Qualify Leads Probe Customer Needs Develop Solutions Basic Steps in the Personal Selling Process Chapter 12 Ver 2 e Handle Objections Close the Sale © 2000 South-Western College Publishing Follow Up 35
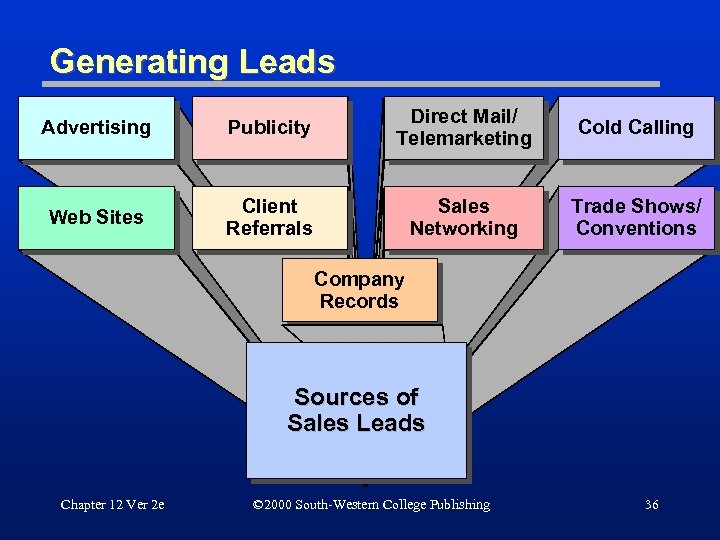 Generating Leads Advertising Publicity Direct Mail/ Telemarketing Cold Calling Web Sites Client Referrals Sales Networking Trade Shows/ Conventions Company Records Sources of Sales Leads Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 36
Generating Leads Advertising Publicity Direct Mail/ Telemarketing Cold Calling Web Sites Client Referrals Sales Networking Trade Shows/ Conventions Company Records Sources of Sales Leads Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 36
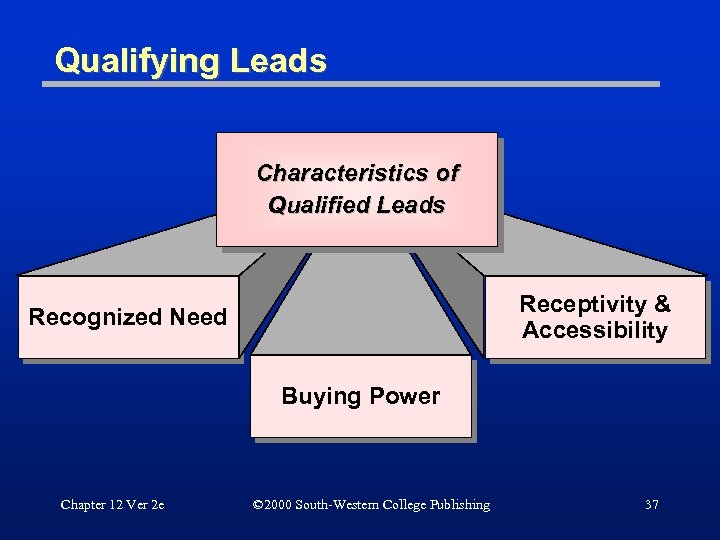 Qualifying Leads Characteristics of Qualified Leads Receptivity & Accessibility Recognized Need Buying Power Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 37
Qualifying Leads Characteristics of Qualified Leads Receptivity & Accessibility Recognized Need Buying Power Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 37
 Probing Needs Product or service Salesperson must know everything about. . . Customers and their needs Competition Industry Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 38
Probing Needs Product or service Salesperson must know everything about. . . Customers and their needs Competition Industry Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 38
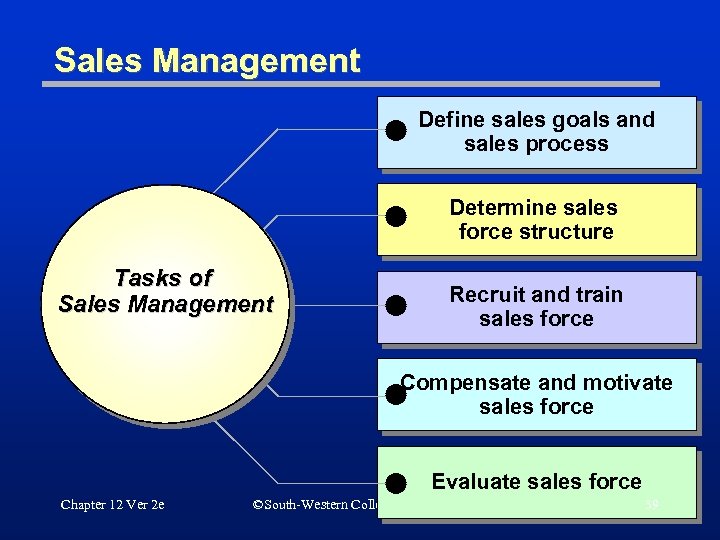 Sales Management Define sales goals and sales process Determine sales force structure Tasks of Sales Management Recruit and train sales force Compensate and motivate sales force Evaluate sales force Chapter 12 Ver 2 e ©South-Western College Publishing 39
Sales Management Define sales goals and sales process Determine sales force structure Tasks of Sales Management Recruit and train sales force Compensate and motivate sales force Evaluate sales force Chapter 12 Ver 2 e ©South-Western College Publishing 39
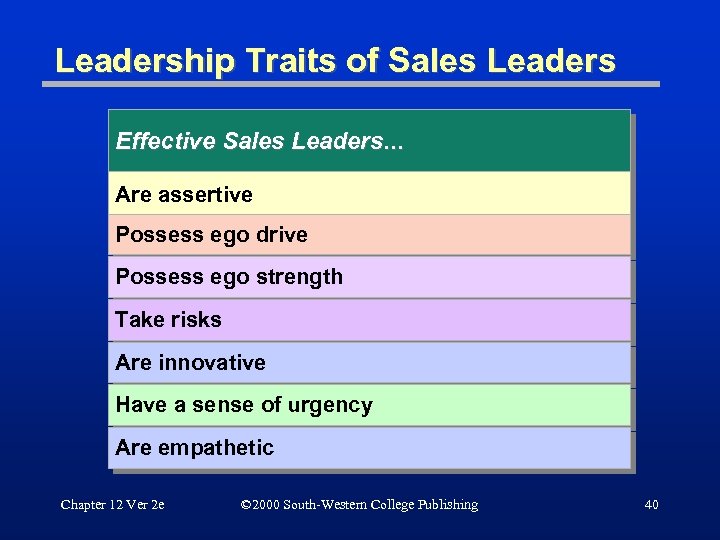 Leadership Traits of Sales Leaders Effective Sales Leaders. . . Are assertive Possess ego drive Possess ego strength Take risks Are innovative Have a sense of urgency Are empathetic Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 40
Leadership Traits of Sales Leaders Effective Sales Leaders. . . Are assertive Possess ego drive Possess ego strength Take risks Are innovative Have a sense of urgency Are empathetic Chapter 12 Ver 2 e © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 40


