8af450fe52b4114bbb7a2b363a3c32d9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Chapter 12 Distribution Channels 12 -

Chapter 12: Distribution Channels LEARNING OBJECTIVES LO 1 Explain the importance of distribution and the interrelationships among distribution channels, supply chain management, and logistics management LO 2 Describe distribution channel design and management decisions and strategies LO 3 Identify how distribution channels add value to businesses and consumers LO 4 Explain how logistics management affects distribution strategy 12 -2

WALMART – INNOVATORS IN DISTRIBUTION! l l LO 1, LO 3 Walmart’s success stems directly from their channel innovations Close co-operation with supplier partners is key Extensive information systems Constantly fine-tuning efficiencies 12 -3

LO 1 THE IMPORTANCE OF DISTRIBUTION • The third P! • Good distribution is critical to marketing success • Royal Canadian Mint released world’s first coloured circulation coin through Tim Hortons (due to huge reach and speed to distribute coins) • Coin to raise breast cancer awareness followed via Shoppers Drug Mart stores 12 -4

LO 1 DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS, SUPPLY CHAINS, & LOGISTICS ARE RELATED l Distribution channel l Supply chain management l Logistics management Similar but different 12 -5
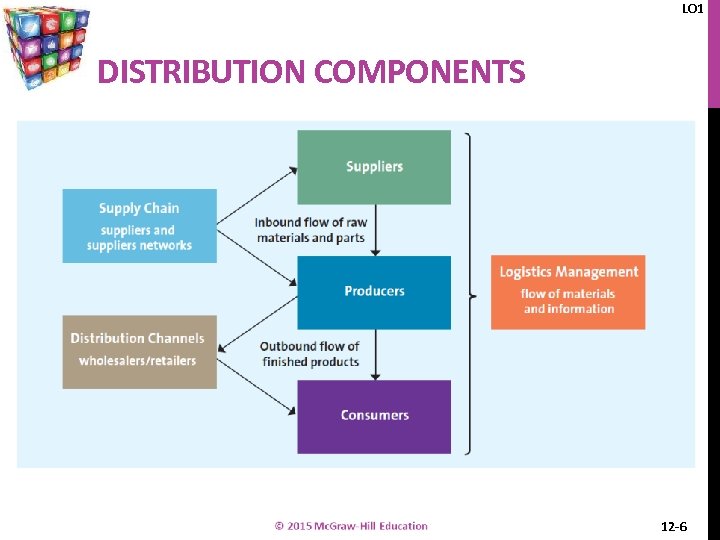
LO 1 DISTRIBUTION COMPONENTS 12 -6
LO 2 DESIGNING DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS Channel Structure • Direct distribution • Indirect distribution • Multichannel distribution or some combination of these forms 12 -7
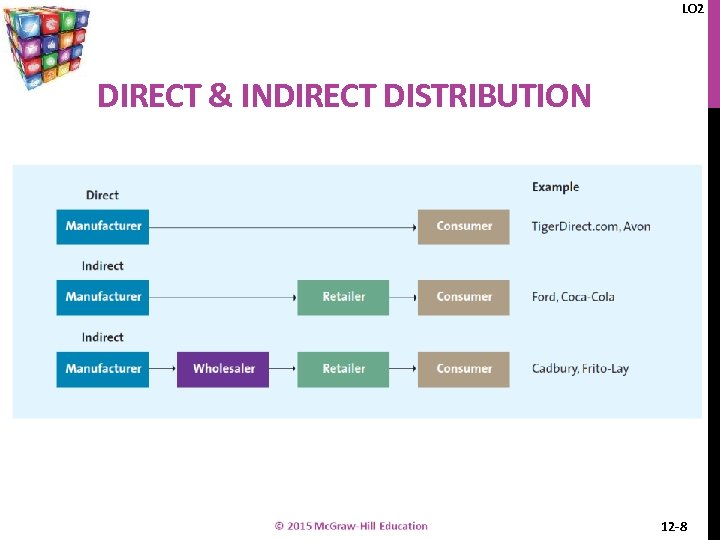
LO 2 DIRECT & INDIRECT DISTRIBUTION 12 -8
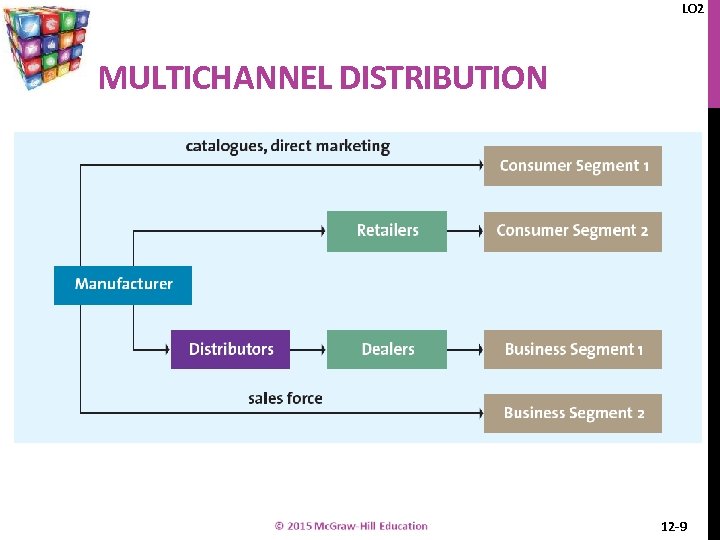
LO 2 MULTICHANNEL DISTRIBUTION 12 -9

LO 2 ETHICAL DILEMMA 12. 1: WHAT DO CUSTOMERS CARE ABOUT? • Labour abuse in Apple producing factories • Apple conducts audits of these facilities, but is it doing enough? • Even if supplier violates the code of conduct, Apple is unlikely to switch due to confidentiality • Slim profit margins to suppliers causes cut-backs • Do customers care more about their new i. Phone or working conditions in China? 12 -10
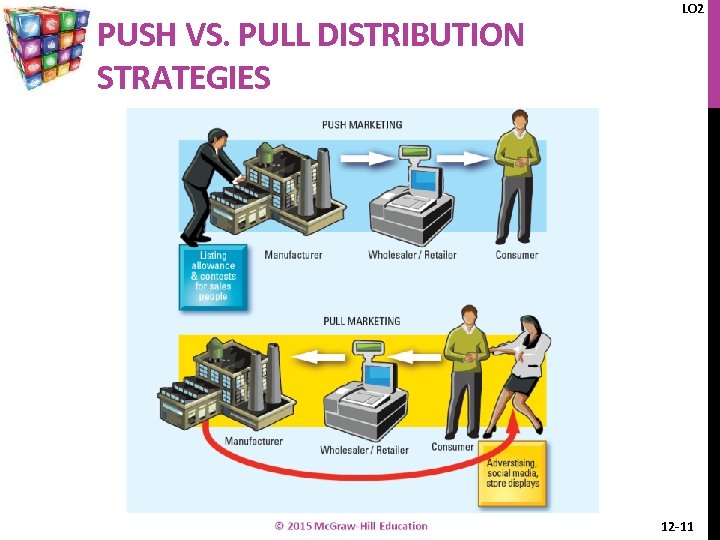
PUSH VS. PULL DISTRIBUTION STRATEGIES LO 2 12 -11

LO 2 DISTRIBUTION INTENSITY 12 -12

LO 2 Exclusive distribution can benefit manufacturers by assuring them that ________ buy their products. A) a large number of retailers B) the most appropriate customers C) customers with the highest profit margins D) global customers 12 -13
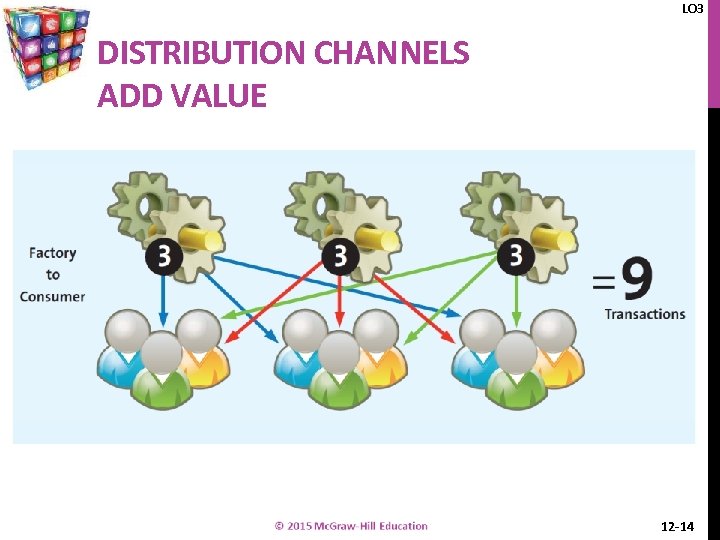
LO 3 DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS ADD VALUE 12 -14
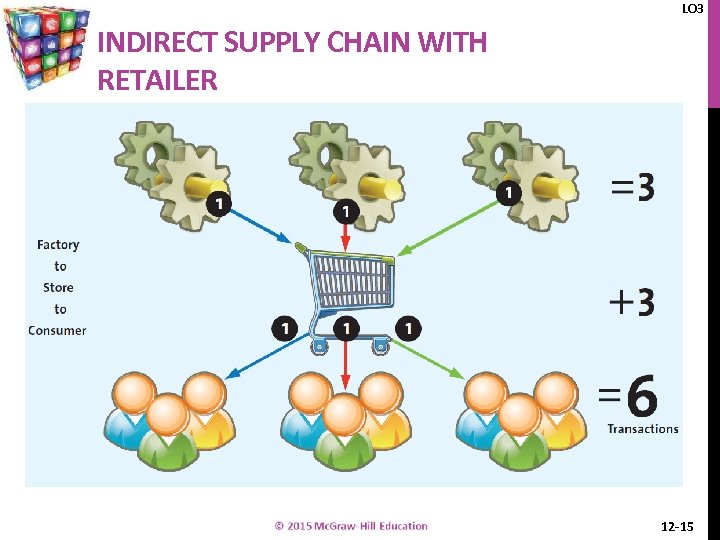
LO 3 INDIRECT SUPPLY CHAIN WITH RETAILER 12 -15
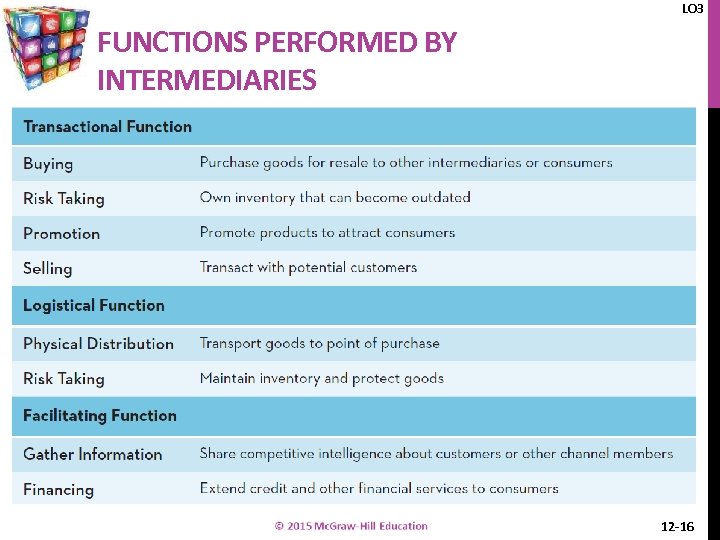
LO 3 FUNCTIONS PERFORMED BY INTERMEDIARIES 12 -16
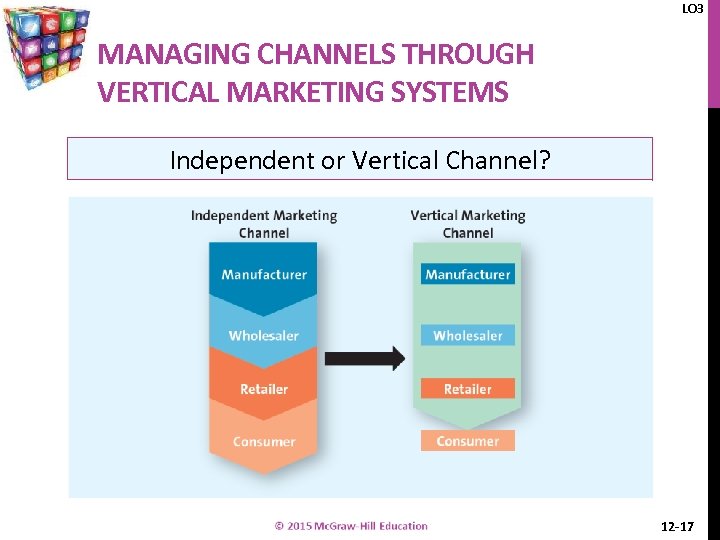
LO 3 MANAGING CHANNELS THROUGH VERTICAL MARKETING SYSTEMS Independent or Vertical Channel? 12 -17
LO 3 TYPES OR PHASES OF VERTICAL MARKETING SYSTEMS Three types or phases of vertical marketing systems: • Administered • Contractual • Franchise • Corporate 12 -18
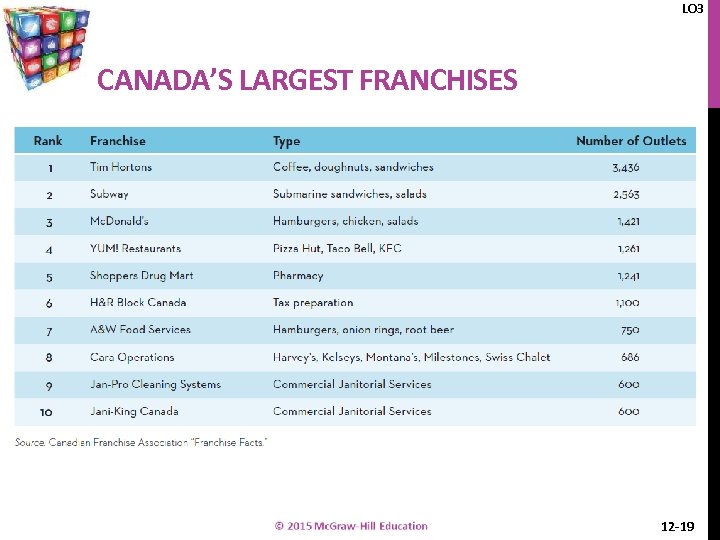
LO 3 CANADA’S LARGEST FRANCHISES 12 -19

LO 3 All of the following are forms of vertical marketing systems EXCEPT: A) Corporate B) Franchise C) Contractual D) Administered 12 -20
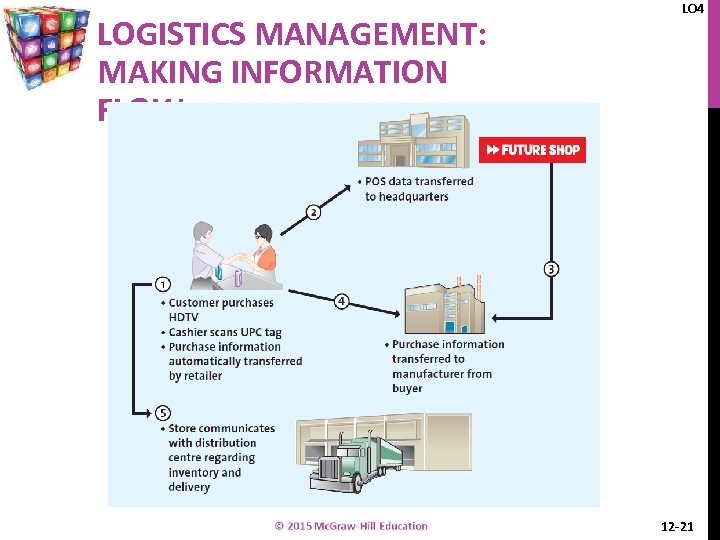
LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT: MAKING INFORMATION FLOW LO 4 12 -21

LO 4 VOLVO LOGISTICS CORPORATION – AN EXAMPLE 12 -22
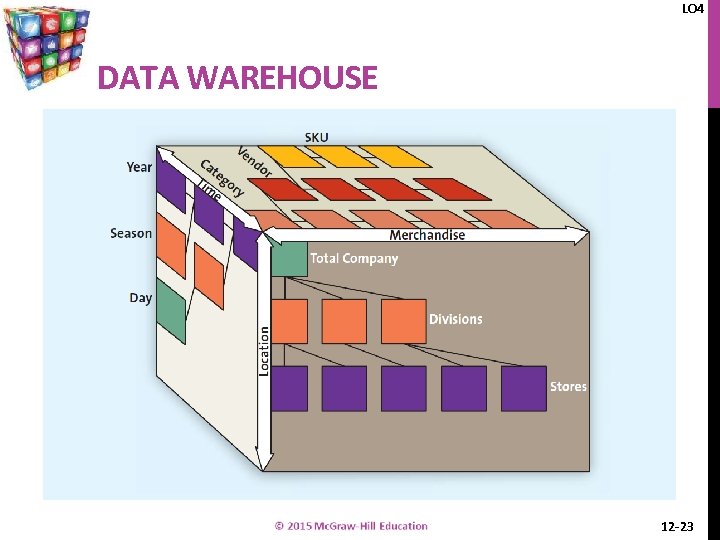
LO 4 DATA WAREHOUSE 12 -23
LO 4 ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE l l l Computer-to-computer exchange of business documents from retailer to vendor and back Advanced shipping notice Reduces cycle time Communication is improved Easy data analysis 12 -24
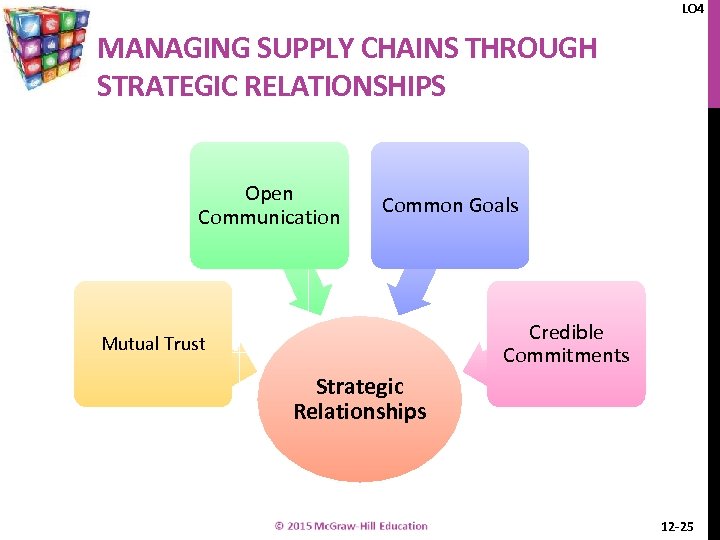
LO 4 MANAGING SUPPLY CHAINS THROUGH STRATEGIC RELATIONSHIPS Open Communication Common Goals Credible Commitments Mutual Trust Strategic Relationships 12 -25

LO 4 Why is it crucial for marketers to understand the information flows through the supply chain? A) This ensures the timely delivery of goods. B) This ensures that customers find the goods they desire in the store ready for purchase. C) This ensures that the manufacture is aware of potential stock outs and other issues at the retail level. D) All of these choices are correct. 12 -26

LO 4 LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT: MAKING MERCHANDISE FLOW • Inbound transportation • Receiving and checking • Storing and cross-docking • Getting merchandise floorready • Shipping merchandise to stores • Just-in-time systems (JIT) 12 -27
LO 4 INBOUND TRANSPORTATION • In-bound transportation involves the co-ordination of deliveries • Dispatcher: a person who is responsible to co-ordinate all the deliveries • If deliveries are missed or are not on time, costs will increase 12 -28
LO 4 RECEIVING AND CHECKING Receiving Arrival receipt Checking Undamaged Radio Frequency Distribution (RFID) Tags Container computer chips Ordered = received 12 -29
LO 4 STORING AND CROSS-DOCKING Types of distribution centres: • • • Traditional Cross-docking Combination 12 -30

LO 4 GETTING MERCHANDISE FLOOR READY & SHIPPING TO STORES Floor-ready merchandise • • • Ready to be placed on the selling floor Create price & ID labels Suppliers sometimes ship floor-ready Shipping to stores • • A complex process for multistore chains Sophisticated computer systems are used 12 -31

LO 4 INVENTORY MANAGEMENT THROUGH JUST-IN-TIME SYSTEMS Just-in-time (JIT) Quick response (QR) 12 -32
LO 4 BENEFITS OF JIT SYSTEMS Reduced lead time Increased product availability and lower inventory investment 12 -33
LO 4 CASE-IN-POINT: GUINNESS Challenge 99% of the product left the UK on time but only 59% arrived on time. Answer Partner with SAP using their See Why software began to identify issues in container shipments to U. S. and track demand delivery. Results Set up a Supplier Management Inventory system in the U. S. Allowing Guinness to maintain stock and predict demand for the U. S. market. Better able to schedule shipping and contain costs. 12 -34
8af450fe52b4114bbb7a2b363a3c32d9.ppt