9d302f4ef6284cbc394130db215b611b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Chapter 12 Discovering New Knowledge – Data Mining Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Chapter 12 Discovering New Knowledge – Data Mining Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Chapter Objectives • Introduce the student to the concept of Data Mining. w How it is different from knowledge elicitation from experts w How it is different from extracting existing knowledge from databases. • The objectives of data mining w Explanation of past events (descriptive DM) w Prediction of future events (predictive DM) • (continued) Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Chapter Objectives • Introduce the student to the concept of Data Mining. w How it is different from knowledge elicitation from experts w How it is different from extracting existing knowledge from databases. • The objectives of data mining w Explanation of past events (descriptive DM) w Prediction of future events (predictive DM) • (continued) Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Chapter Objectives (cont. ) • Introduce the student to the different classes of methods available for DM w Symbolic (induction) w Connectionist (neural networks) w Statistical • Introduce the student to the details of some of the methods described in the chapter. Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Chapter Objectives (cont. ) • Introduce the student to the different classes of methods available for DM w Symbolic (induction) w Connectionist (neural networks) w Statistical • Introduce the student to the details of some of the methods described in the chapter. Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Section 12. 1 - Objectives • Introduction of chapter contents Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Section 12. 1 - Objectives • Introduction of chapter contents Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Section 12. 2 - Objectives • Defines the concept of data mining and the reasons for performing DM studies • Defines the objectives of data mining w Descriptive DM w Predictive DM • Introduces the three basic approaches to DM w Symbolic (induction) w Connectionist (neural networks) w Statistical (curve-fitting, others) Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Section 12. 2 - Objectives • Defines the concept of data mining and the reasons for performing DM studies • Defines the objectives of data mining w Descriptive DM w Predictive DM • Introduces the three basic approaches to DM w Symbolic (induction) w Connectionist (neural networks) w Statistical (curve-fitting, others) Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Section 12. 3 - Objectives • Present a detailed description of the symbolic approach to data mining - rule induction • Present the main algorithm for rule induction C 5. 0 and its ancestors, ID 3 and CLS • Present several example applications of rule induction • Present other alternate algorithms for rule induction w CART w CHAID Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Section 12. 3 - Objectives • Present a detailed description of the symbolic approach to data mining - rule induction • Present the main algorithm for rule induction C 5. 0 and its ancestors, ID 3 and CLS • Present several example applications of rule induction • Present other alternate algorithms for rule induction w CART w CHAID Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Section 12. 4 - Objectives • Provide a detailed description of the connectionist approach to data mining - neural networks • Present the basic neural network architecture the multi-layer feed forward neural network • Present the main supervised learning algorithm backpropagation • Present the main unsupervised neural network architecture - the Kohonen network Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Section 12. 4 - Objectives • Provide a detailed description of the connectionist approach to data mining - neural networks • Present the basic neural network architecture the multi-layer feed forward neural network • Present the main supervised learning algorithm backpropagation • Present the main unsupervised neural network architecture - the Kohonen network Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Section 12. 5 - Objectives • Provide a detailed description of the most important statistical methods for data mining w w w Curve fitting with least squares method Multi-variate correlation K-Means clustering Market Basket analysis Discriminant analysis Logistic regression Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Section 12. 5 - Objectives • Provide a detailed description of the most important statistical methods for data mining w w w Curve fitting with least squares method Multi-variate correlation K-Means clustering Market Basket analysis Discriminant analysis Logistic regression Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Section 12. 6 - Objectives • Provide useful guidelines for determining what technique to use for specific problems Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Section 12. 6 - Objectives • Provide useful guidelines for determining what technique to use for specific problems Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Section 12. 7 - Objectives • Discuss the importance of errors in data mining studies • Define the types of errors possible in data mining studies Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Section 12. 7 - Objectives • Discuss the importance of errors in data mining studies • Define the types of errors possible in data mining studies Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Section 12. 8 - Objectives • • Summarize the chapter Provide Key terms Provide Review Questions Provide Review Exercises Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Section 12. 8 - Objectives • • Summarize the chapter Provide Key terms Provide Review Questions Provide Review Exercises Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
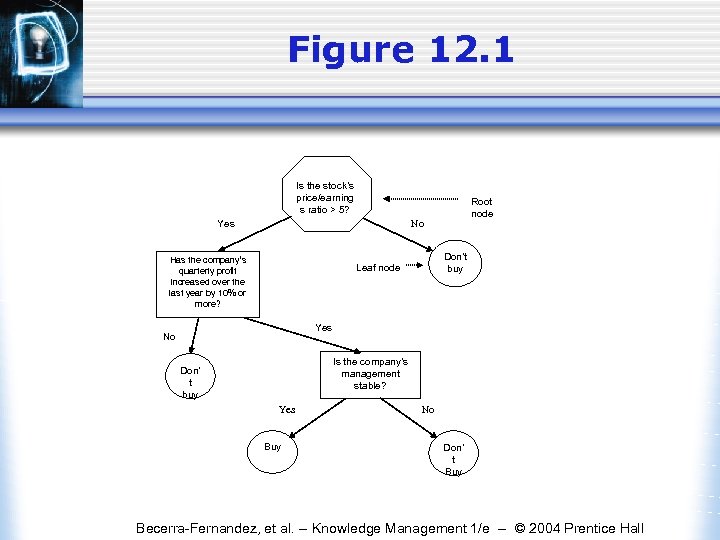 Figure 12. 1 Is the stock’s price/earning s ratio > 5? Yes Root node No Has the company’s quarterly profit increased over the last year by 10% or more? Don’t buy Leaf node Yes No Is the company’s management stable? Don’ t buy Yes Buy No Don’ t Buy Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 1 Is the stock’s price/earning s ratio > 5? Yes Root node No Has the company’s quarterly profit increased over the last year by 10% or more? Don’t buy Leaf node Yes No Is the company’s management stable? Don’ t buy Yes Buy No Don’ t Buy Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
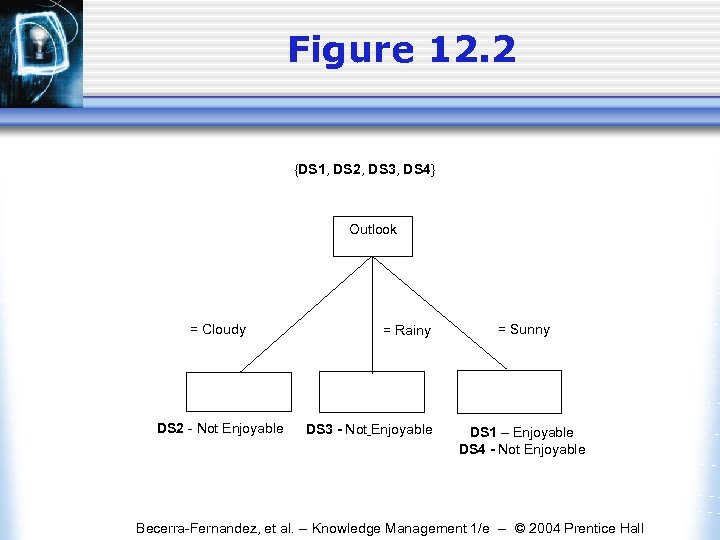 Figure 12. 2 {DS 1, DS 2, DS 3, DS 4} Outlook = Cloudy = Rainy = Sunny Rain DS 2 - Not Enjoyable DS 3 - Not Enjoyable DS 1 – Enjoyable DS 4 - Not Enjoyable Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 2 {DS 1, DS 2, DS 3, DS 4} Outlook = Cloudy = Rainy = Sunny Rain DS 2 - Not Enjoyable DS 3 - Not Enjoyable DS 1 – Enjoyable DS 4 - Not Enjoyable Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
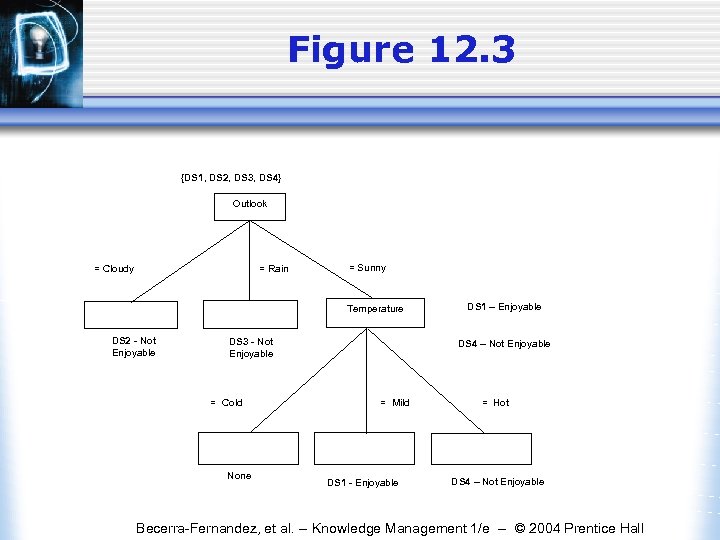 Figure 12. 3 {DS 1, DS 2, DS 3, DS 4} Outlook = Cloudy = Rain DS 2 - Not Enjoyable = Sunny Temperature DS 3 - Not Enjoyable = Cold None DS 1 – Enjoyable DS 4 – Not Enjoyable = Mild DS 1 - Enjoyable = Hot DS 4 – Not Enjoyable Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 3 {DS 1, DS 2, DS 3, DS 4} Outlook = Cloudy = Rain DS 2 - Not Enjoyable = Sunny Temperature DS 3 - Not Enjoyable = Cold None DS 1 – Enjoyable DS 4 – Not Enjoyable = Mild DS 1 - Enjoyable = Hot DS 4 – Not Enjoyable Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
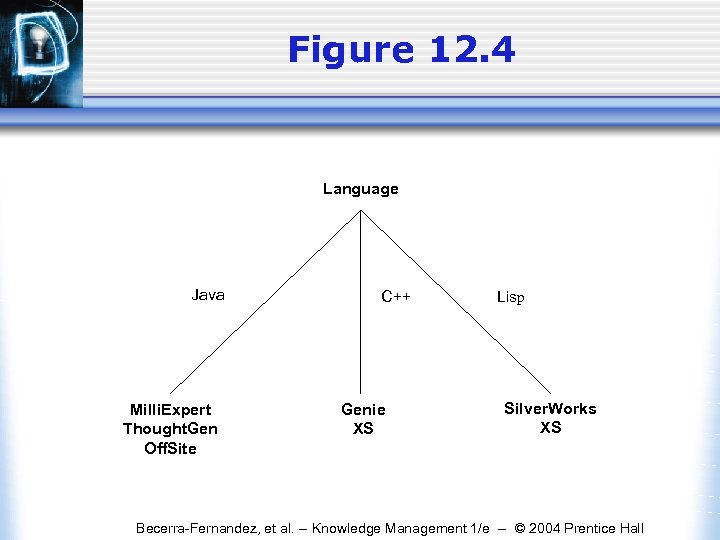 Figure 12. 4 Language Java Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site C++ Genie XS Lisp Silver. Works XS Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 4 Language Java Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site C++ Genie XS Lisp Silver. Works XS Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
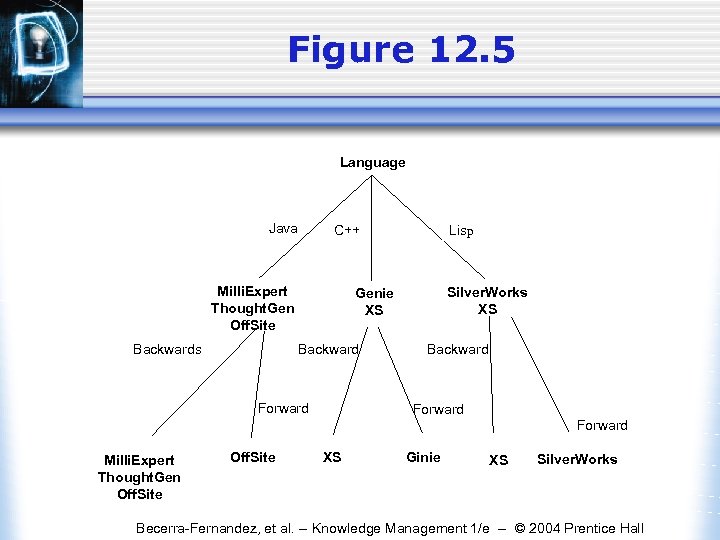 Figure 12. 5 Language Java Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site Silver. Works XS Genie XS Backwards Lisp C++ Forward Backward Forward Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site XS Ginie XS Silver. Works Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 5 Language Java Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site Silver. Works XS Genie XS Backwards Lisp C++ Forward Backward Forward Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site XS Ginie XS Silver. Works Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
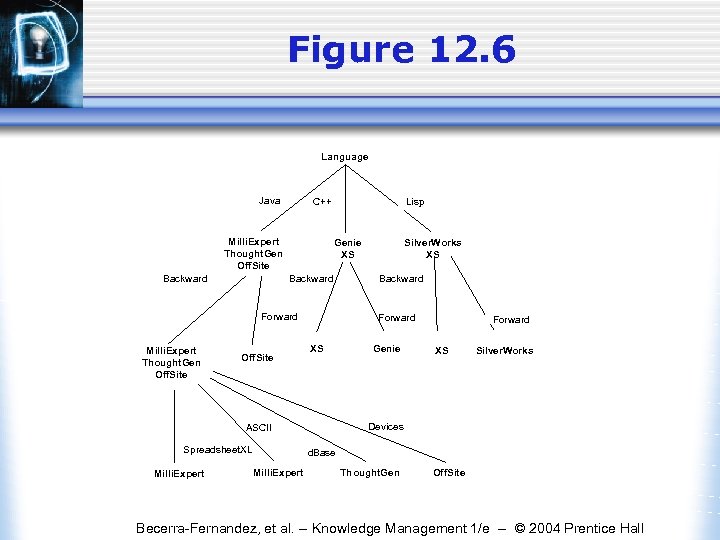 Figure 12. 6 Language Java Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site Backward Lisp C++ Backward Forward Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site Spreadsheet. XL Backward Forward XS Genie Forward XS Silver. Works Devices ASCII Milli. Expert Silver. Works XS Genie XS d. Base Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 6 Language Java Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site Backward Lisp C++ Backward Forward Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site Spreadsheet. XL Backward Forward XS Genie Forward XS Silver. Works Devices ASCII Milli. Expert Silver. Works XS Genie XS d. Base Milli. Expert Thought. Gen Off. Site Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
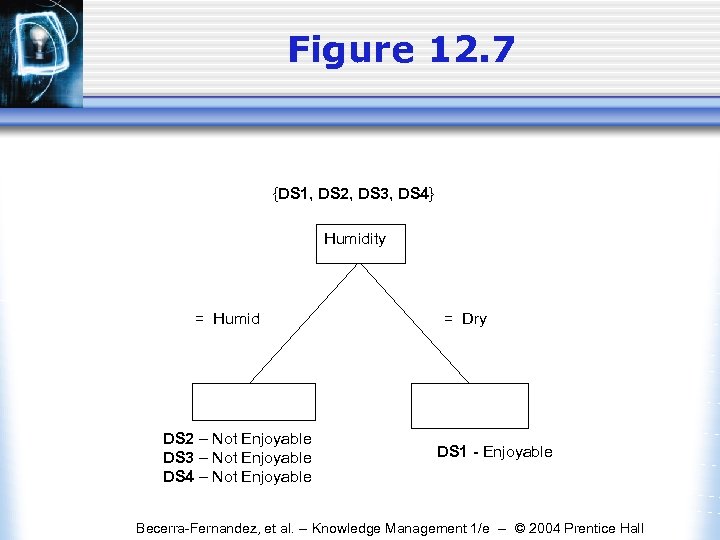 Figure 12. 7 {DS 1, DS 2, DS 3, DS 4} Humidity = Humid DS 2 – Not Enjoyable DS 3 – Not Enjoyable DS 4 – Not Enjoyable = Dry DS 1 - Enjoyable Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 7 {DS 1, DS 2, DS 3, DS 4} Humidity = Humid DS 2 – Not Enjoyable DS 3 – Not Enjoyable DS 4 – Not Enjoyable = Dry DS 1 - Enjoyable Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
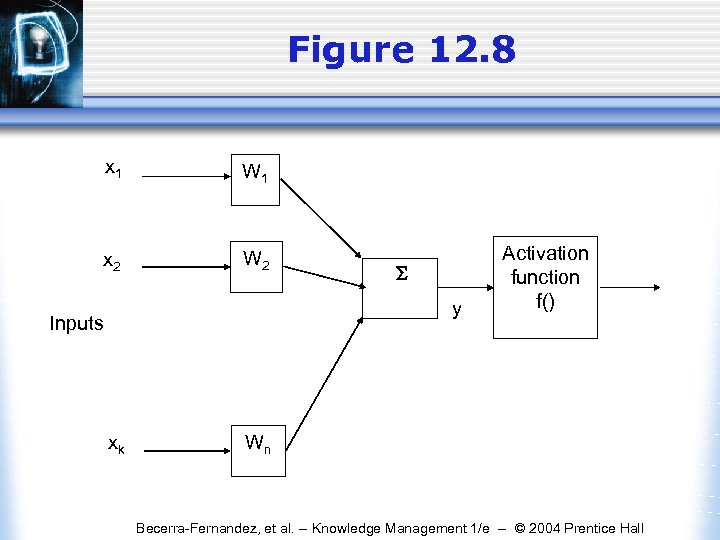 Figure 12. 8 x 1 W 1 x 2 W 2 y Inputs xk Activation function f() Wn Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 8 x 1 W 1 x 2 W 2 y Inputs xk Activation function f() Wn Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
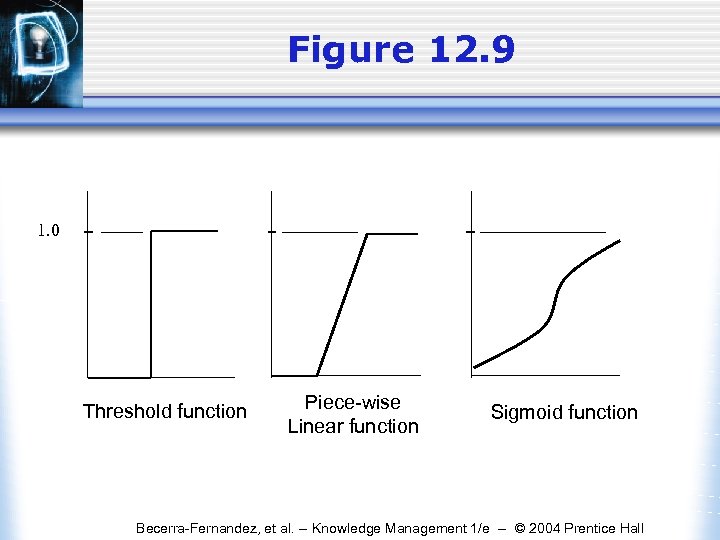 Figure 12. 9 1. 0 Threshold function Piece-wise Linear function Sigmoid function Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 9 1. 0 Threshold function Piece-wise Linear function Sigmoid function Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
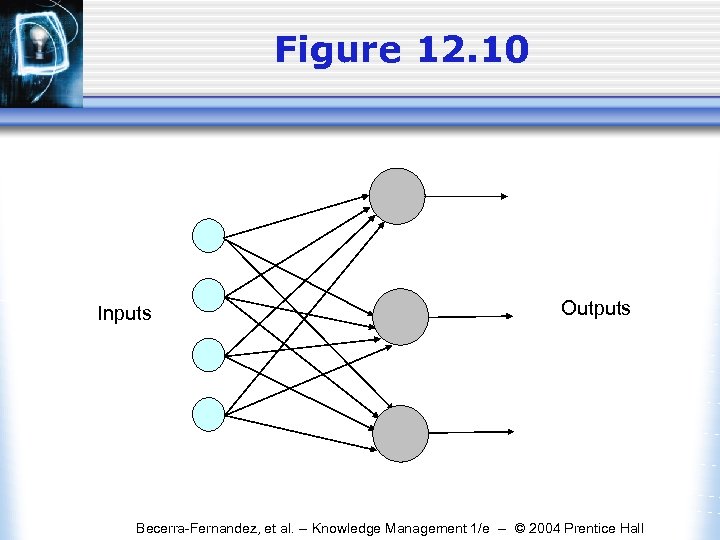 Figure 12. 10 Inputs Outputs Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 10 Inputs Outputs Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
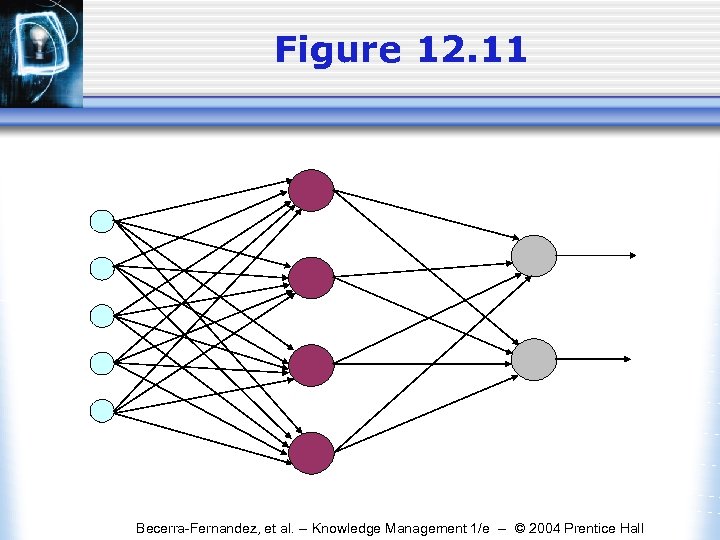 Figure 12. 11 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 11 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
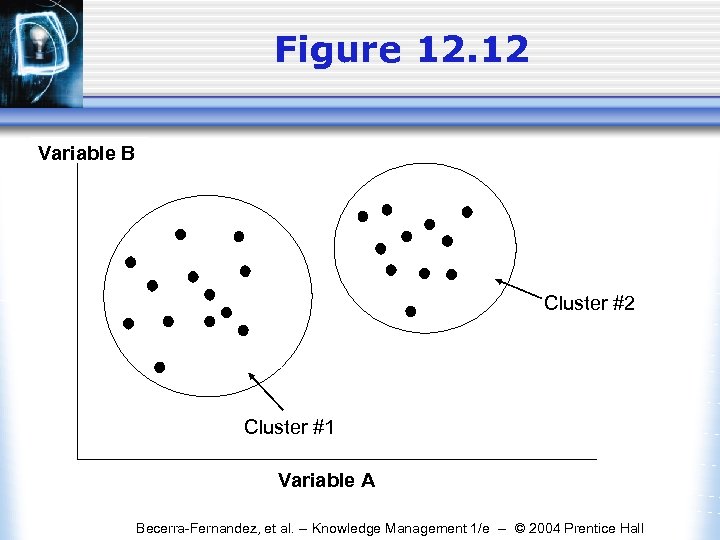 Figure 12. 12 Variable B Cluster #2 Cluster #1 Variable A Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 12 Variable B Cluster #2 Cluster #1 Variable A Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
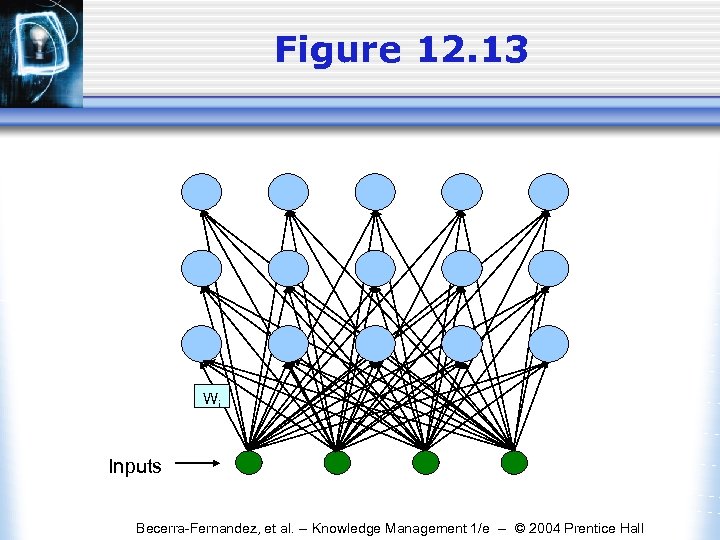 Figure 12. 13 Wi Inputs Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 13 Wi Inputs Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
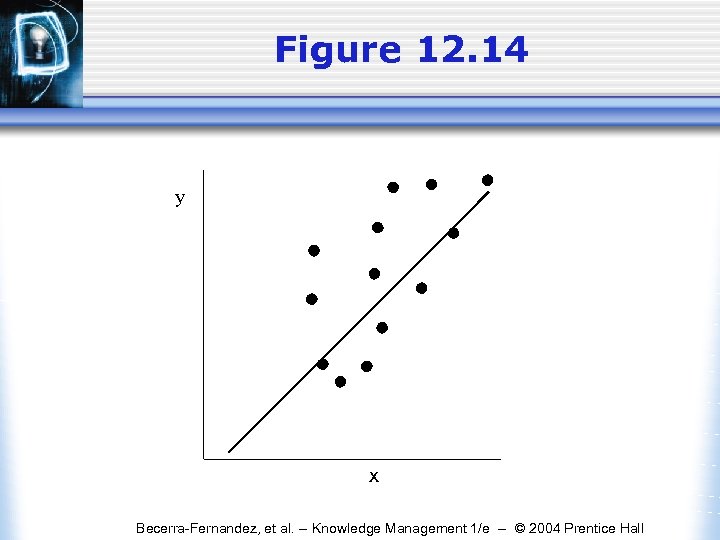 Figure 12. 14 y x Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 14 y x Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
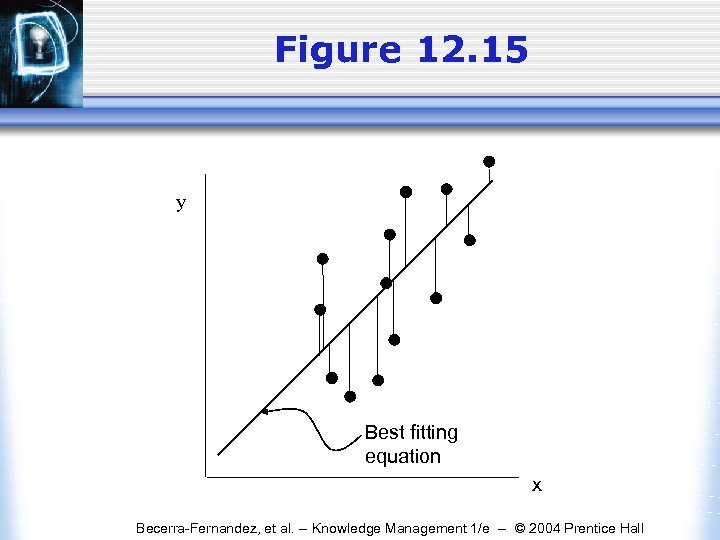 Figure 12. 15 y x Best fitting equation x Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Figure 12. 15 y x Best fitting equation x Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
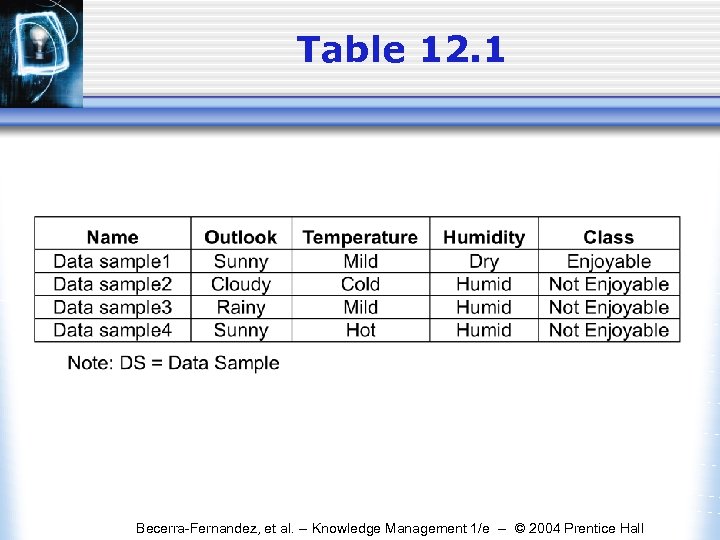 Table 12. 1 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 1 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
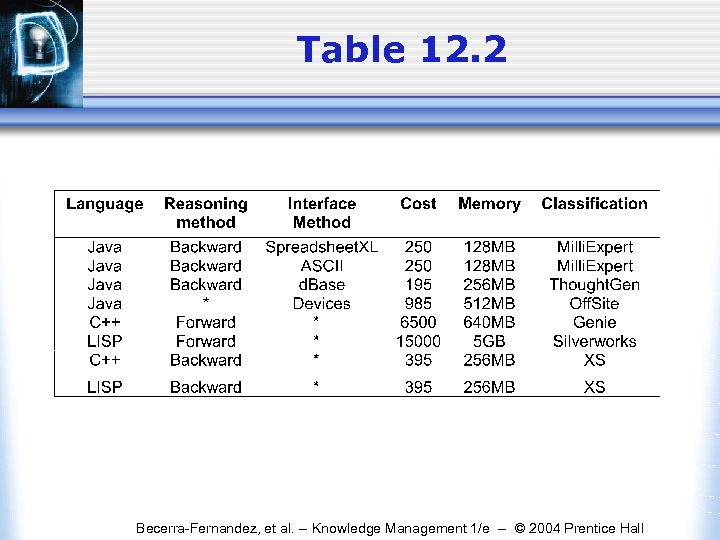 Table 12. 2 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 2 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
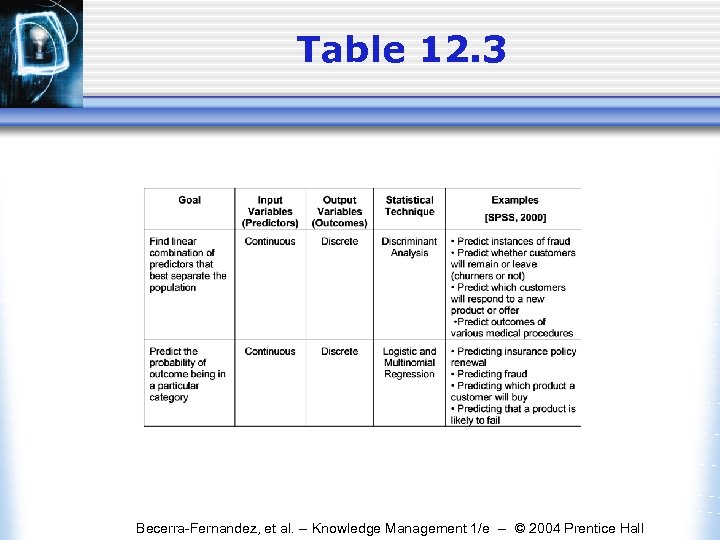 Table 12. 3 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 3 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
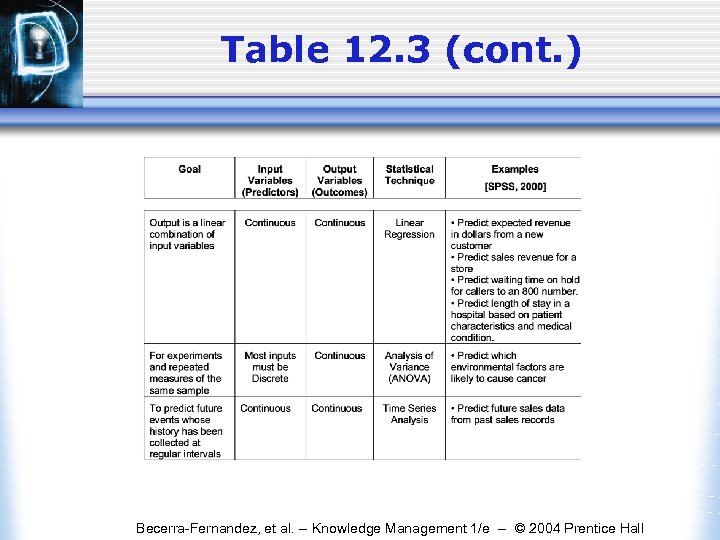 Table 12. 3 (cont. ) Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 3 (cont. ) Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
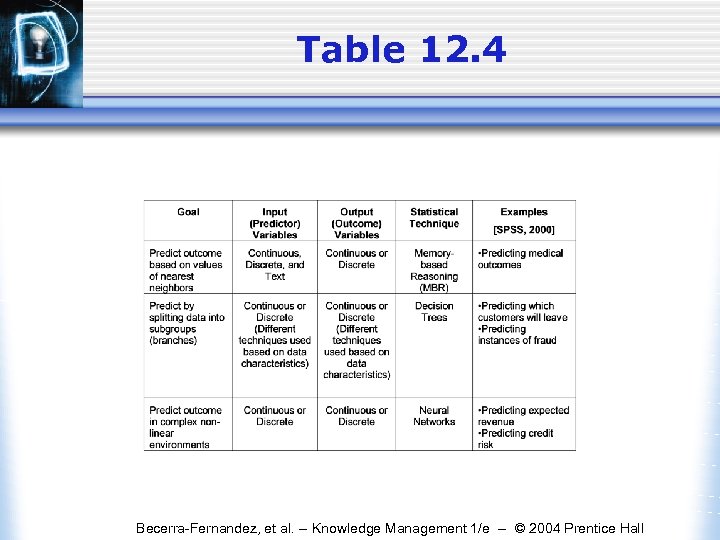 Table 12. 4 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 4 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
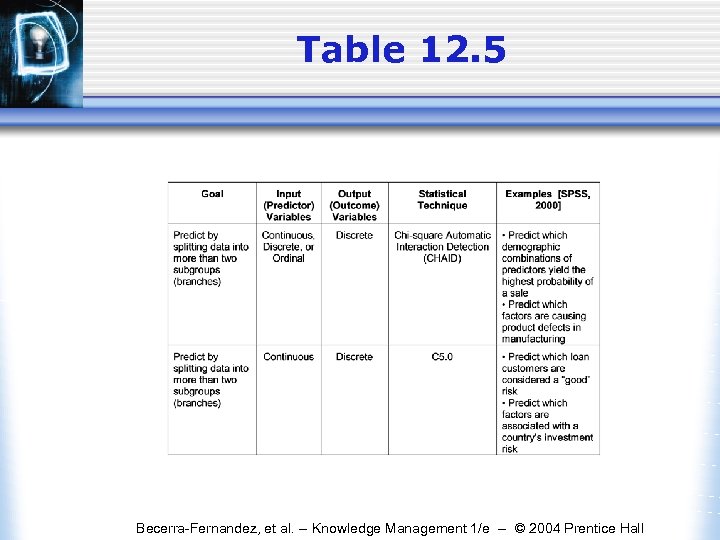 Table 12. 5 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 5 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
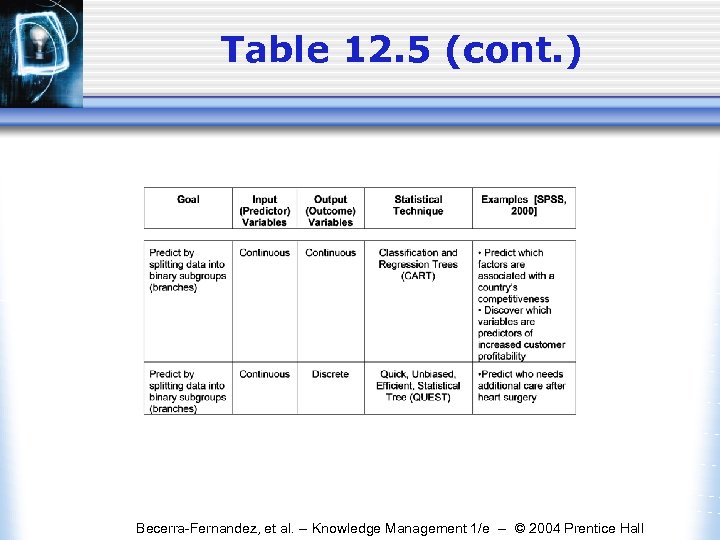 Table 12. 5 (cont. ) Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 5 (cont. ) Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
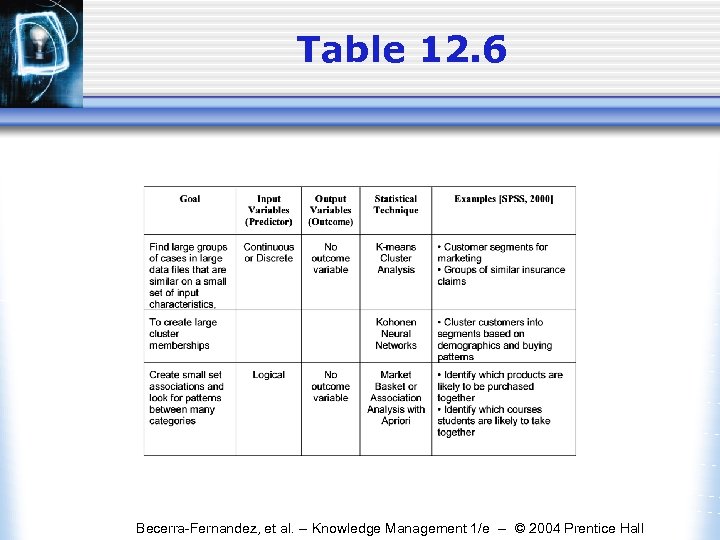 Table 12. 6 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 6 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
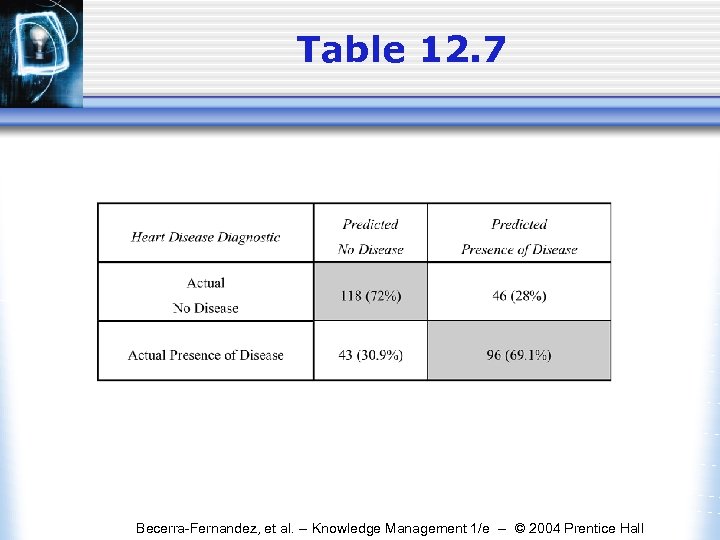 Table 12. 7 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Table 12. 7 Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Conclusions • The student should be able to use: w The C 5. 0 algorithm to capture rules from examples. w Basic feedforward neural networks with supervised learning. w Unsupervised learning, clustering techniques and the Kohonen networks. w Curve-fitting algorithms. w Statistical methods for clustering. w Other statistical techniques. Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Conclusions • The student should be able to use: w The C 5. 0 algorithm to capture rules from examples. w Basic feedforward neural networks with supervised learning. w Unsupervised learning, clustering techniques and the Kohonen networks. w Curve-fitting algorithms. w Statistical methods for clustering. w Other statistical techniques. Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
 Chapter 12 Discovering New Knowledge – Data Mining Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall
Chapter 12 Discovering New Knowledge – Data Mining Becerra-Fernandez, et al. -- Knowledge Management 1/e -- © 2004 Prentice Hall


