a3b4061bbafaa50ff22b8fc0be8e8791.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Chapter 12 Decision Support Systems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 1
Chapter 12 Decision Support Systems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 1
 Learning Objectives • List and explain the steps in decision making • Articulate the difference between structured and unstructured decision making • Describe the typical software components that decision support systems comprise • Describe the typical elements of geographic information systems • Identify business situations in which decisions can be supported by geographic information systems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 2
Learning Objectives • List and explain the steps in decision making • Articulate the difference between structured and unstructured decision making • Describe the typical software components that decision support systems comprise • Describe the typical elements of geographic information systems • Identify business situations in which decisions can be supported by geographic information systems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 2
 Decision Support Aids • Organization’s success depends on quality of managers’ decisions • When decisions involve large amounts of information and processing, computer-based systems can make the process effective and efficient. • Applications now called business analysis tools or business intelligence applications Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 3
Decision Support Aids • Organization’s success depends on quality of managers’ decisions • When decisions involve large amounts of information and processing, computer-based systems can make the process effective and efficient. • Applications now called business analysis tools or business intelligence applications Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 3
 The Decision-Making Process • Three decision-making phases – Intelligence – Design – Choice • Models to analyze data – Maps, mathematical equations of variables Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 4
The Decision-Making Process • Three decision-making phases – Intelligence – Design – Choice • Models to analyze data – Maps, mathematical equations of variables Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 4
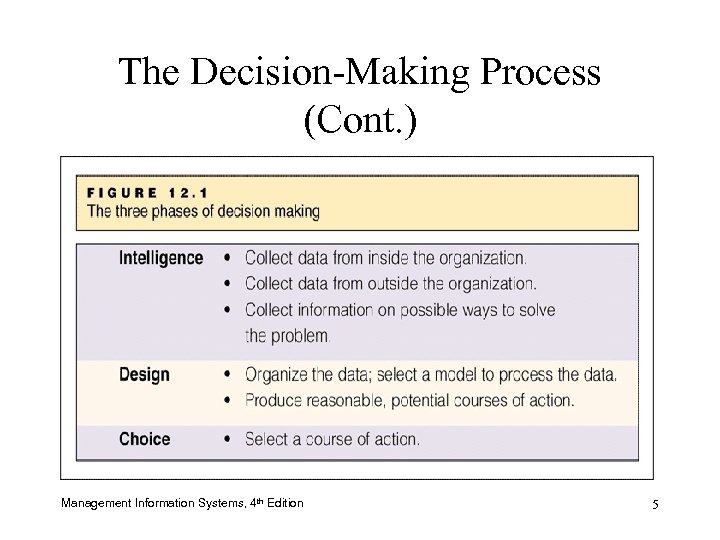 The Decision-Making Process (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 5
The Decision-Making Process (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 5
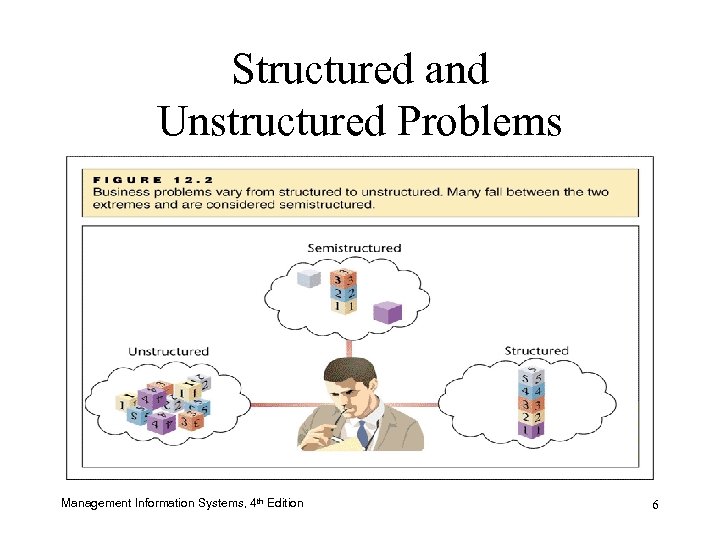 Structured and Unstructured Problems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 6
Structured and Unstructured Problems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 6
 Structured Problems • Proven set of steps for solution – Algorithm – Parameters • Most mathematical and physical problems are structured • Programmable problems: feasible to write a program to solve them Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 7
Structured Problems • Proven set of steps for solution – Algorithm – Parameters • Most mathematical and physical problems are structured • Programmable problems: feasible to write a program to solve them Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 7
 Unstructured Problems • No algorithm to follow to reach optimal solution • Multiple potential solutions • Unstructuredness is closely related to uncertainty Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 8
Unstructured Problems • No algorithm to follow to reach optimal solution • Multiple potential solutions • Unstructuredness is closely related to uncertainty Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 8
 Semistructured Problems • Neither fully structured nor totally unstructured • Managers and Semistructured Problems – Most common type of problem for managers – Task is to choose one alternative that will bring about the best outcome – Often rely on decision support applications to select the best course of action Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 9
Semistructured Problems • Neither fully structured nor totally unstructured • Managers and Semistructured Problems – Most common type of problem for managers – Task is to choose one alternative that will bring about the best outcome – Often rely on decision support applications to select the best course of action Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 9
 Decision Support System (DSS) • Computer-based information systems that help managers select one of many solutions – Automates some of decision-making process – Sophisticated and fast analysis – Used at all management levels Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 10
Decision Support System (DSS) • Computer-based information systems that help managers select one of many solutions – Automates some of decision-making process – Sophisticated and fast analysis – Used at all management levels Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 10
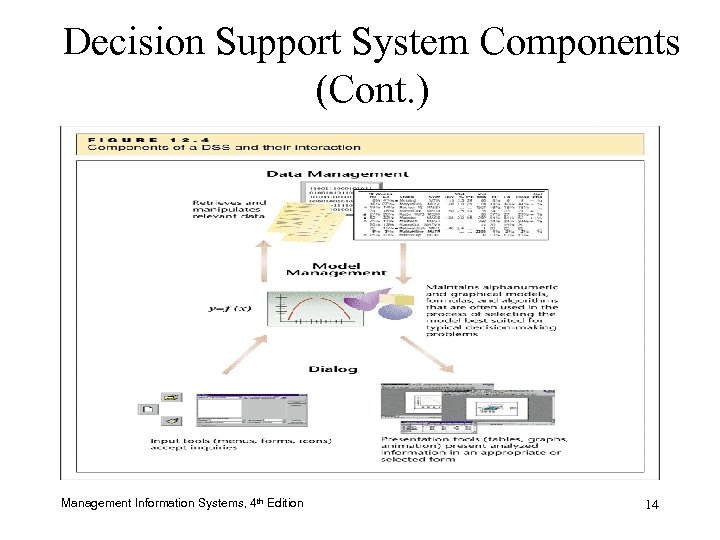
 Decision Support System (DSS) Components • Three Major Components – Data management module – Model management module – Dialog management module Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 11
Decision Support System (DSS) Components • Three Major Components – Data management module – Model management module – Dialog management module Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 11
 Decision Support System (DSS) Components (Cont. ) • Together, DSS modules: – Help enter request conveniently – Search vast amounts of data – Use data in desired models – Present results in readable manner Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 12
Decision Support System (DSS) Components (Cont. ) • Together, DSS modules: – Help enter request conveniently – Search vast amounts of data – Use data in desired models – Present results in readable manner Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 12
 The Data Management Module • Gives user access to databases or data warehouses • Allows decision maker to conduct intelligence phase of decision making Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 13
The Data Management Module • Gives user access to databases or data warehouses • Allows decision maker to conduct intelligence phase of decision making Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 13
 Decision Support System Components (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 14
Decision Support System Components (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 14
 Decision Support System Components • Closely intertwined with other organizational systems – Data warehouses – Data marts – ERP systems • Draw relevant data for decision-making Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 15
Decision Support System Components • Closely intertwined with other organizational systems – Data warehouses – Data marts – ERP systems • Draw relevant data for decision-making Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 15
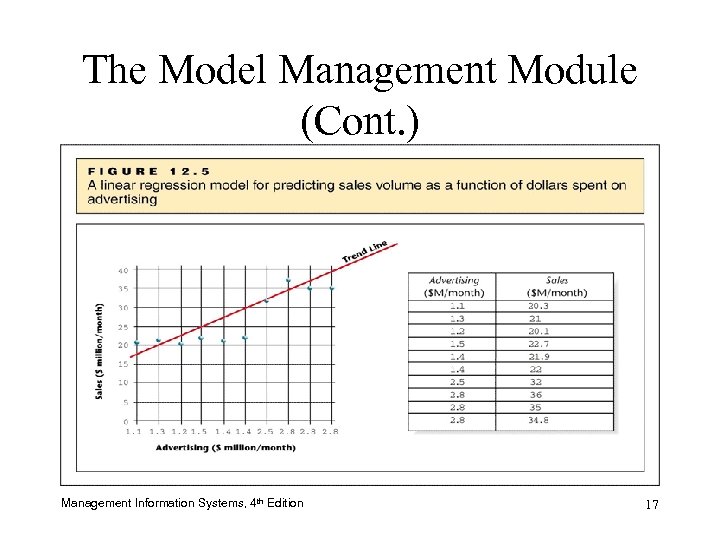
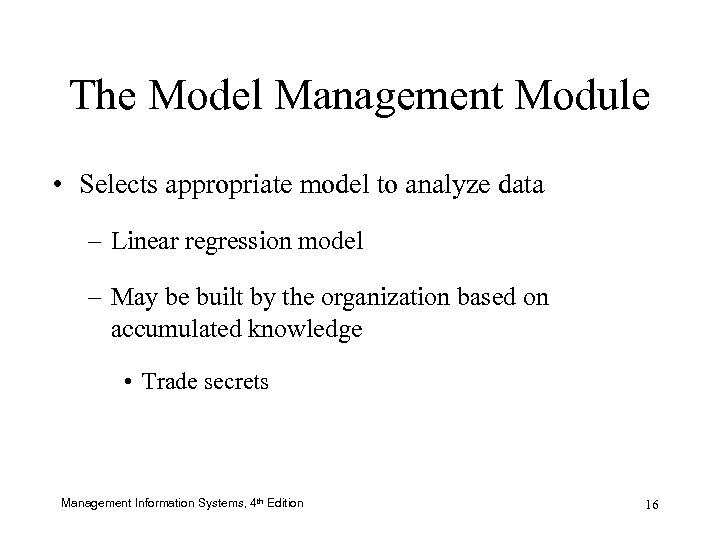 The Model Management Module • Selects appropriate model to analyze data – Linear regression model – May be built by the organization based on accumulated knowledge • Trade secrets Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 16
The Model Management Module • Selects appropriate model to analyze data – Linear regression model – May be built by the organization based on accumulated knowledge • Trade secrets Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 16
 The Model Management Module (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 17
The Model Management Module (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 17
 The Model Management Module (Cont. ) • Creating New Models – Data mining techniques do not rely on predetermined models – No hypothesis on relationships of data required – Software looks for the relationships – Results in a new model or set of relationships Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 18
The Model Management Module (Cont. ) • Creating New Models – Data mining techniques do not rely on predetermined models – No hypothesis on relationships of data required – Software looks for the relationships – Results in a new model or set of relationships Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 18
 The Dialog Module • Interface between user and other modules – Prompts user to select a model – Allows database access and data selection – Lets user enter/change parameters • Displays analysis results • Textual, tabular, and graphical displays Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 19
The Dialog Module • Interface between user and other modules – Prompts user to select a model – Allows database access and data selection – Lets user enter/change parameters • Displays analysis results • Textual, tabular, and graphical displays Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 19
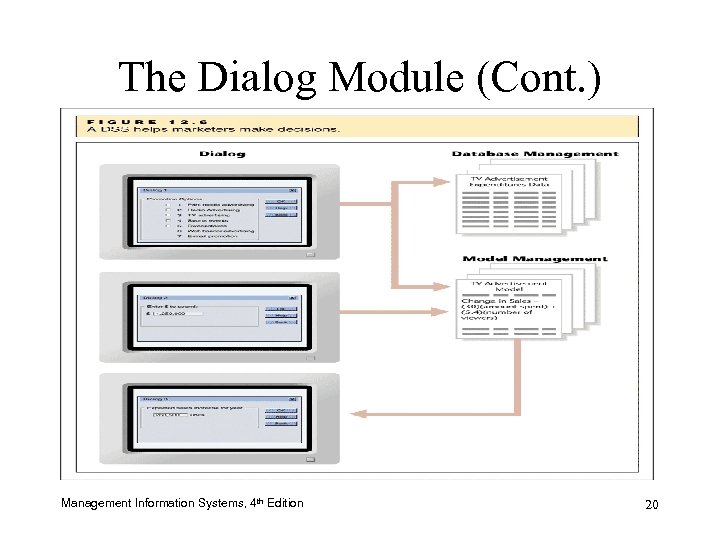 The Dialog Module (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 20
The Dialog Module (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 20
 Types of Decision Support Systems • Personal Decision Support Systems – Individual Knowledge worker uses in daily work – Raw data entered into a program either by user or drawn from other sources – Tax preparation software is an example Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 21
Types of Decision Support Systems • Personal Decision Support Systems – Individual Knowledge worker uses in daily work – Raw data entered into a program either by user or drawn from other sources – Tax preparation software is an example Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 21
 Types of Decision Support Systems (Cont. ) • Group Decision Support Systems – Promote brainstorming and group decision making – Located in conference room or on networked computers – Weigh votes to overcome impasses Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 22
Types of Decision Support Systems (Cont. ) • Group Decision Support Systems – Promote brainstorming and group decision making – Located in conference room or on networked computers – Weigh votes to overcome impasses Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 22
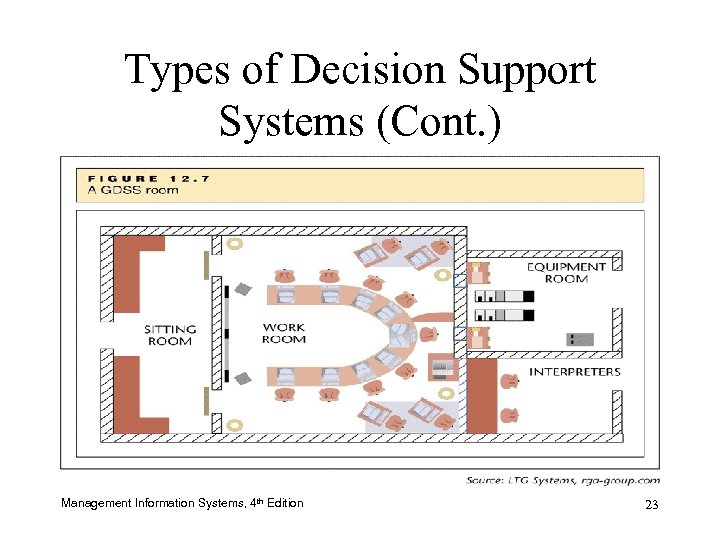 Types of Decision Support Systems (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 23
Types of Decision Support Systems (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 23
 Sensitivity Analysis • Tests degree to which result is affected by change in parameters • What-if analysis • Can change multiple parameters at once Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 24
Sensitivity Analysis • Tests degree to which result is affected by change in parameters • What-if analysis • Can change multiple parameters at once Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 24
 Executive Information Systems • Alleviate information overload for executives • Select most relevant data for analysis – Drilling down • Consolidate and summarize data • Display data graphically Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 25
Executive Information Systems • Alleviate information overload for executives • Select most relevant data for analysis – Drilling down • Consolidate and summarize data • Display data graphically Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 25
 Effective EIS features • An easy-to-use and easy-to-learn graphical user interface • On-request “drill-down” capability • On-demand financial and other ratios, and other indicators • Easy-to-use but sophisticated tools to allow navigation in databases and data warehouses Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 26
Effective EIS features • An easy-to-use and easy-to-learn graphical user interface • On-request “drill-down” capability • On-demand financial and other ratios, and other indicators • Easy-to-use but sophisticated tools to allow navigation in databases and data warehouses Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 26
 Effective EIS Features (Cont. ) • Statistical analysis tools • The ability to respond to ad hoc queries and sensitivity analyses • Access to external data pools • The ability to solve diverse business problems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 27
Effective EIS Features (Cont. ) • Statistical analysis tools • The ability to respond to ad hoc queries and sensitivity analyses • Access to external data pools • The ability to solve diverse business problems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 27
 Developing Decision Support Systems • When Should a DSS Be Built? – What is the type problem and how structured is it? – Are the required data available in databases and data warehouses? – How often do managers encounter the problem? – Who will use the system? – Can the prospective users spare adequate time for the development process? Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 28
Developing Decision Support Systems • When Should a DSS Be Built? – What is the type problem and how structured is it? – Are the required data available in databases and data warehouses? – How often do managers encounter the problem? – Who will use the system? – Can the prospective users spare adequate time for the development process? Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 28
 The Electronic Spreadsheet: A DSS Tool • Provide two facilities for building DSS – Preprogrammed functions – Ability to use IF-THEN statements • Most widely used tool – Inexperienced users can use to develop DSSs Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 29
The Electronic Spreadsheet: A DSS Tool • Provide two facilities for building DSS – Preprogrammed functions – Ability to use IF-THEN statements • Most widely used tool – Inexperienced users can use to develop DSSs Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 29
 Geographic Information Systems • Decision aid for map-related decisions • Typical GIS contains: – database of quantitative and qualitative data – database of maps – program to display information on maps Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 30
Geographic Information Systems • Decision aid for map-related decisions • Typical GIS contains: – database of quantitative and qualitative data – database of maps – program to display information on maps Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 30
 Ethical and Societal Issues Decisions by Machines • Automated decisions can affect individuals – Mortgage companies, credit card companies, employers, banks, etc. • European Protection – “Automated Individual Decisions” Directive Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 31
Ethical and Societal Issues Decisions by Machines • Automated decisions can affect individuals – Mortgage companies, credit card companies, employers, banks, etc. • European Protection – “Automated Individual Decisions” Directive Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 31
 Ethical and Societal Issues Decisions by Machines • Who Needs Protection – Determining creditworthiness • Efficient • Effective • Hidden Injustice – Mistakes on records – Decisions final Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 32
Ethical and Societal Issues Decisions by Machines • Who Needs Protection – Determining creditworthiness • Efficient • Effective • Hidden Injustice – Mistakes on records – Decisions final Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 32
 Summary • Decisions are made in three steps: intelligence, design, and choice • Structured and unstructured are two types of decision-making techniques and are based on the type of problem to be solved • Decision support systems have typical components • Geographic information systems use certain elements Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 33
Summary • Decisions are made in three steps: intelligence, design, and choice • Structured and unstructured are two types of decision-making techniques and are based on the type of problem to be solved • Decision support systems have typical components • Geographic information systems use certain elements Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 33


