a9d1d95c3a344d5c098bc08dcb943564.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Chapter 12 and Chapter 13 Products and Services for Consumers Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2005 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
Chapter 12 and Chapter 13 Products and Services for Consumers Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2005 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 Chapter Learning Objectives 1. The importance of offering a product suitable for the intended market 2. The relationship between product acceptance and the market into which it is introduced 3. The importance of quality and how quality is defined
Chapter Learning Objectives 1. The importance of offering a product suitable for the intended market 2. The relationship between product acceptance and the market into which it is introduced 3. The importance of quality and how quality is defined
 Chapter Learning Objectives 4. Country-of-origin effects on product image 5. Physical, mandatory, and cultural requirements for product adaptation 6. The need to view all attributes of a product in order to overcome resistance to acceptance
Chapter Learning Objectives 4. Country-of-origin effects on product image 5. Physical, mandatory, and cultural requirements for product adaptation 6. The need to view all attributes of a product in order to overcome resistance to acceptance
 Global Perspective u Disney’s experiences internationally – Tokyo Disney – Euro Disney – Hong Kong Disney (2006)
Global Perspective u Disney’s experiences internationally – Tokyo Disney – Euro Disney – Hong Kong Disney (2006)
 What Is a Product ? u Product: A bundle of attributes u The Total Product – Tangible attributes: materials, size, weight, design, packaging, performance, comfort – Intangibles: brand image, styling, other benefits (installation, delivery, credit, warranty, after-sale service, return policy)
What Is a Product ? u Product: A bundle of attributes u The Total Product – Tangible attributes: materials, size, weight, design, packaging, performance, comfort – Intangibles: brand image, styling, other benefits (installation, delivery, credit, warranty, after-sale service, return policy)
 Quality Defined in 2 ways: F 1. “Market-perceived” quality – How does the market (consumer) perceive the quality of the product or service F 2. “Performance” quality – What is the overall “performance” of the product or service (firm’s perspective) – Tends to be focused on attributes or features or meeting certain “performance” criteria
Quality Defined in 2 ways: F 1. “Market-perceived” quality – How does the market (consumer) perceive the quality of the product or service F 2. “Performance” quality – What is the overall “performance” of the product or service (firm’s perspective) – Tends to be focused on attributes or features or meeting certain “performance” criteria
 Quality (Cont. ) u Physical or Mandatory Requirements and Adaptation – Many countries require “homologation” F Requires changes to be made to products based on local product and service standards – Mandatory adaptation vs. cultural adaptation F u u Many believe adaptation occurs most often based upon local laws, or policies that are economic, political or environmental – Green Marketing and Product Development Quality is associated with customer satisfaction Customer satisfaction indexes developed are now being used to measure satisfaction across a wide variety of consumer products and services
Quality (Cont. ) u Physical or Mandatory Requirements and Adaptation – Many countries require “homologation” F Requires changes to be made to products based on local product and service standards – Mandatory adaptation vs. cultural adaptation F u u Many believe adaptation occurs most often based upon local laws, or policies that are economic, political or environmental – Green Marketing and Product Development Quality is associated with customer satisfaction Customer satisfaction indexes developed are now being used to measure satisfaction across a wide variety of consumer products and services
 ISO 9000 Certification: An International Standard of Quality (Ch 13) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. ISO 9000 s, a series of five international industrial standards (ISO 9000– 9004) originally designed by the International Organization for Standardization in Geneva to meet the need for product quality assurances in purchasing agreements ISO 9000 concerns the registration and certification of a manufacturer’s quality system It is a certification of the existence of a quality control system a company has in place to ensure it can meet published quality standards ISO 9000 standards do not apply to specific products It is a certification of the production process only, and does not guarantee that a manufacturer produces a “quality” product or service. The series describes three quality system models, defines quality concepts, and gives guidelines for using international standards in quality system
ISO 9000 Certification: An International Standard of Quality (Ch 13) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. ISO 9000 s, a series of five international industrial standards (ISO 9000– 9004) originally designed by the International Organization for Standardization in Geneva to meet the need for product quality assurances in purchasing agreements ISO 9000 concerns the registration and certification of a manufacturer’s quality system It is a certification of the existence of a quality control system a company has in place to ensure it can meet published quality standards ISO 9000 standards do not apply to specific products It is a certification of the production process only, and does not guarantee that a manufacturer produces a “quality” product or service. The series describes three quality system models, defines quality concepts, and gives guidelines for using international standards in quality system
 Products and Culture A product is more than a physical item: It is a bundle of satisfactions (or utilities) that the buyer receives 1. 2. 3. Facets of products include its form, taste, color, odor, and texture; how it functions in use; the package; the label; the warranty; manufacturer’s and retailer’s servicing; the confidence or prestige enjoyed by the brand; the manufacturer’s reputation; The adoption of some products by consumers can be affected as much by how the product concept conforms with norms, values, and behavior patterns Thus, many facets of products are influenced by culture, which markets must pay attention to
Products and Culture A product is more than a physical item: It is a bundle of satisfactions (or utilities) that the buyer receives 1. 2. 3. Facets of products include its form, taste, color, odor, and texture; how it functions in use; the package; the label; the warranty; manufacturer’s and retailer’s servicing; the confidence or prestige enjoyed by the brand; the manufacturer’s reputation; The adoption of some products by consumers can be affected as much by how the product concept conforms with norms, values, and behavior patterns Thus, many facets of products are influenced by culture, which markets must pay attention to
 Products and Culture Cultural Influences Innovative Products and Adaptation Three Variables Affecting Diffusion of Innovations ▶ Degree of Perceived Newness ▶ Perceives attributes of Innovation ▶ Communication Methods Characteristics of Innovations Product of Innovation 12 -3 Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
Products and Culture Cultural Influences Innovative Products and Adaptation Three Variables Affecting Diffusion of Innovations ▶ Degree of Perceived Newness ▶ Perceives attributes of Innovation ▶ Communication Methods Characteristics of Innovations Product of Innovation 12 -3 Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
 Innovative Products and Adaptation u Product Diffusion – 1. Defined: F “process by which innovation spreads” – 2. “Crucial elements” of diffusion of new ideas are (Everett Rogers): F 1) an innovation; 2) which is communicated thru certain channels 3) over time 4) among members of a social system
Innovative Products and Adaptation u Product Diffusion – 1. Defined: F “process by which innovation spreads” – 2. “Crucial elements” of diffusion of new ideas are (Everett Rogers): F 1) an innovation; 2) which is communicated thru certain channels 3) over time 4) among members of a social system
 Degree of Newness Congruent Innovations 12 -4 Continuous Innovation Dynamically Continuous Innovation Discontinuous Innovation Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
Degree of Newness Congruent Innovations 12 -4 Continuous Innovation Dynamically Continuous Innovation Discontinuous Innovation Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
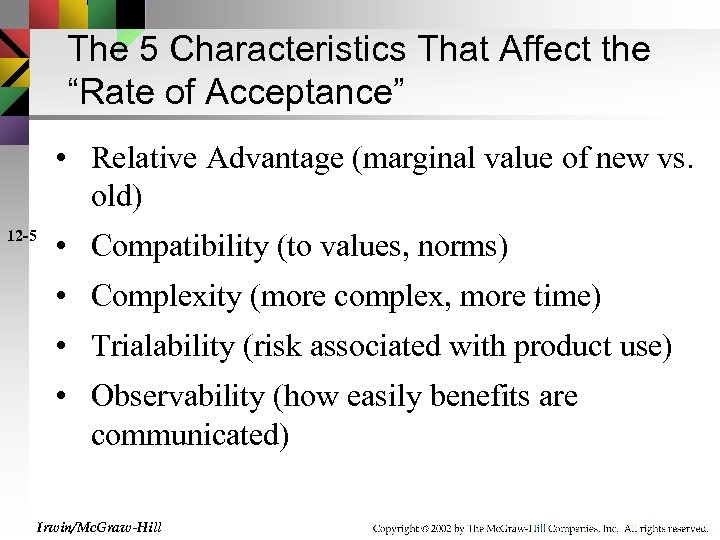 The 5 Characteristics That Affect the “Rate of Acceptance” • Relative Advantage (marginal value of new vs. old) 12 -5 • Compatibility (to values, norms) • Complexity (more complex, more time) • Trialability (risk associated with product use) • Observability (how easily benefits are communicated) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
The 5 Characteristics That Affect the “Rate of Acceptance” • Relative Advantage (marginal value of new vs. old) 12 -5 • Compatibility (to values, norms) • Complexity (more complex, more time) • Trialability (risk associated with product use) • Observability (how easily benefits are communicated) Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
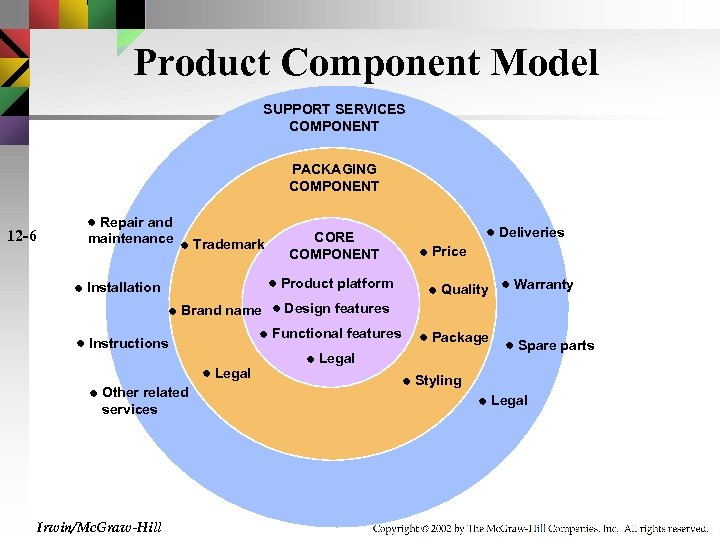 Product Component Model SUPPORT SERVICES COMPONENT PACKAGING COMPONENT Repair and maintenance 12 -6 Brand name Instructions Other related services Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Legal CORE COMPONENT Trademark Installation Product platform Deliveries Price Quality Warranty Design features Functional features Package Legal Spare parts Styling Legal
Product Component Model SUPPORT SERVICES COMPONENT PACKAGING COMPONENT Repair and maintenance 12 -6 Brand name Instructions Other related services Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill Legal CORE COMPONENT Trademark Installation Product platform Deliveries Price Quality Warranty Design features Functional features Package Legal Spare parts Styling Legal
 Product Component Analysis for Adaptation 12 -7 ● Core Component ▶ Physical Product ▶ Design ● Packaging Component ▶ Style ▶ Packaging ▶ Labeling ▶ Trademarks ● Support Services Component ▶ Repair ▶ Maintenance ▶ Instructions ▶ Installation Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill ▶ Features ▶ Brand Name ▶ Quality ▶ Price ▶ Warranties ▶ Deliveries ▶ Spare Parts
Product Component Analysis for Adaptation 12 -7 ● Core Component ▶ Physical Product ▶ Design ● Packaging Component ▶ Style ▶ Packaging ▶ Labeling ▶ Trademarks ● Support Services Component ▶ Repair ▶ Maintenance ▶ Instructions ▶ Installation Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill ▶ Features ▶ Brand Name ▶ Quality ▶ Price ▶ Warranties ▶ Deliveries ▶ Spare Parts
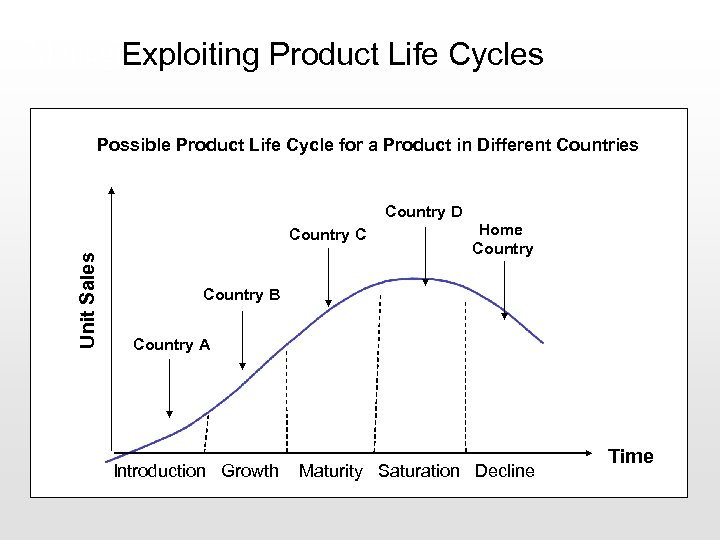 Managing a Global Product. Line Cycles Exploiting Product Life Possible Product Life Cycle for a Product in Different Countries Country D Unit Sales Country C Home Country B Country A Introduction Growth Maturity Saturation Decline Time
Managing a Global Product. Line Cycles Exploiting Product Life Possible Product Life Cycle for a Product in Different Countries Country D Unit Sales Country C Home Country B Country A Introduction Growth Maturity Saturation Decline Time
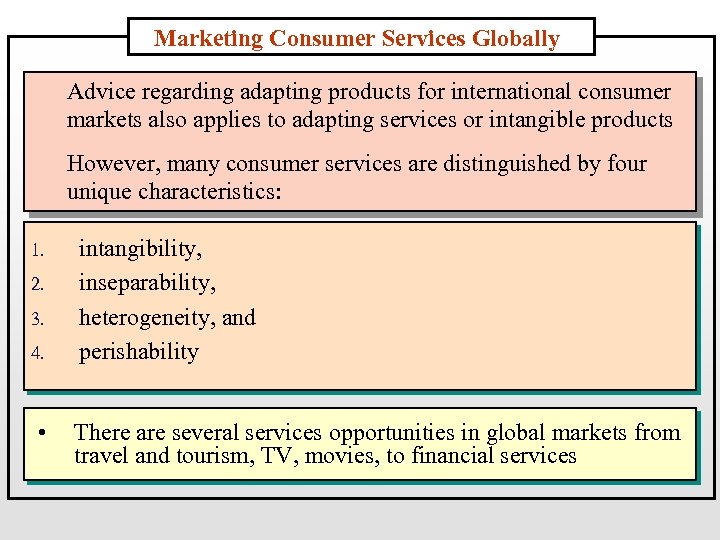 Marketing Consumer Services Globally Advice regarding adapting products for international consumer markets also applies to adapting services or intangible products However, many consumer services are distinguished by four unique characteristics: 1. 2. 3. 4. • intangibility, inseparability, heterogeneity, and perishability There are several services opportunities in global markets from travel and tourism, TV, movies, to financial services
Marketing Consumer Services Globally Advice regarding adapting products for international consumer markets also applies to adapting services or intangible products However, many consumer services are distinguished by four unique characteristics: 1. 2. 3. 4. • intangibility, inseparability, heterogeneity, and perishability There are several services opportunities in global markets from travel and tourism, TV, movies, to financial services
 Top Consumer Services Exports Service Opportunities in Global Markets 1. Tourism 12 -9 5. Telecommunications 2. Transportation 6. Entertainment 3. Financial Services 7. Information 4. Education 8. Health Care Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
Top Consumer Services Exports Service Opportunities in Global Markets 1. Tourism 12 -9 5. Telecommunications 2. Transportation 6. Entertainment 3. Financial Services 7. Information 4. Education 8. Health Care Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
 Four Barriers That Face Consumer Services Marketers 12 -10 1. Protectionism 2. Restrictions on trans-border data flows • Transferring personal data on consumers over borders (income, spending preferences) conflict with rights to privacy. 3. Protection of intellectual property 4. Cultural Barriers and Adaptation • Foreign companies policies or “ways of conducting business” may be conflicting with host country values Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
Four Barriers That Face Consumer Services Marketers 12 -10 1. Protectionism 2. Restrictions on trans-border data flows • Transferring personal data on consumers over borders (income, spending preferences) conflict with rights to privacy. 3. Protection of intellectual property 4. Cultural Barriers and Adaptation • Foreign companies policies or “ways of conducting business” may be conflicting with host country values Irwin/Mc. Graw-Hill
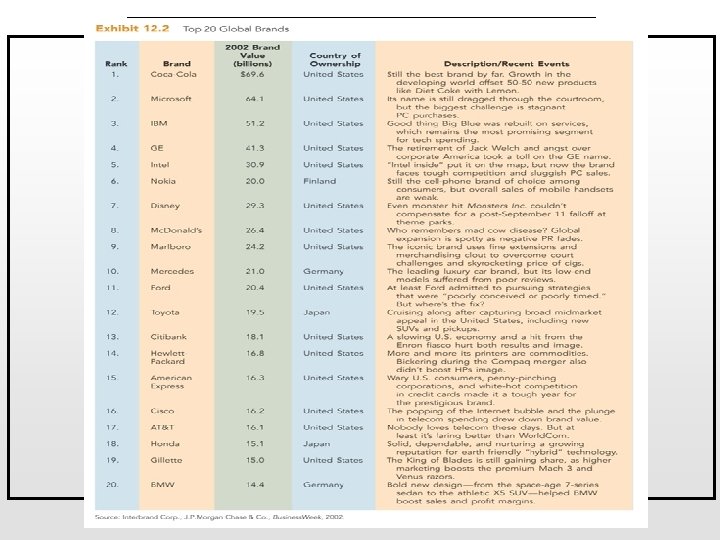
 Brands in International Markets A global brand is defined as the worldwide use of a name, term, sign, symbol (visual and/or auditory), design, or combination thereof intended to identify goods or services of one seller and to differentiate them from those of competitors A successful brand is the most valuable resource of a company Brand image is at the very core of business identity and strategy 1. 2. Global brands such as Kodak, Sony, Coca-Cola, Mc. Donald’s, Toyota, and Marlboro play an important role in that process Perceived brand “globalness” leads to increases in sales
Brands in International Markets A global brand is defined as the worldwide use of a name, term, sign, symbol (visual and/or auditory), design, or combination thereof intended to identify goods or services of one seller and to differentiate them from those of competitors A successful brand is the most valuable resource of a company Brand image is at the very core of business identity and strategy 1. 2. Global brands such as Kodak, Sony, Coca-Cola, Mc. Donald’s, Toyota, and Marlboro play an important role in that process Perceived brand “globalness” leads to increases in sales
 Insert Photo of two cars
Insert Photo of two cars
 Branding Strategies – 1. Global Brands F Uniform worldwide – 2. National Brands F Country specific – 3. Private Brands – Note: Country-of-origin effect can create positive or negative impact on consumers’ perceptions
Branding Strategies – 1. Global Brands F Uniform worldwide – 2. National Brands F Country specific – 3. Private Brands – Note: Country-of-origin effect can create positive or negative impact on consumers’ perceptions
 Country-of-Origin Effect and Global Brands u u u Brands are used as external cues to taste, design, performance, quality, value, and prestige Many factors affect brand image, but one factor of great concern is the country-of-origin effect on the market’s perception of the product Country-of-origin effect (COE) can be defined as any influence that the country of manufacture, assembly, or design has on a consumer’s positive or negative perception of a product When the customer becomes aware of the country of origin, there is the possibility that the place of manufacture will affect product or brand image The country, the type of product, and the image of the company and its brands all influence whether the country of origin will engender a positive or negative reaction
Country-of-Origin Effect and Global Brands u u u Brands are used as external cues to taste, design, performance, quality, value, and prestige Many factors affect brand image, but one factor of great concern is the country-of-origin effect on the market’s perception of the product Country-of-origin effect (COE) can be defined as any influence that the country of manufacture, assembly, or design has on a consumer’s positive or negative perception of a product When the customer becomes aware of the country of origin, there is the possibility that the place of manufacture will affect product or brand image The country, the type of product, and the image of the company and its brands all influence whether the country of origin will engender a positive or negative reaction
 Global Warranty and Service Policies u Product Warranties u Global Product Service
Global Warranty and Service Policies u Product Warranties u Global Product Service
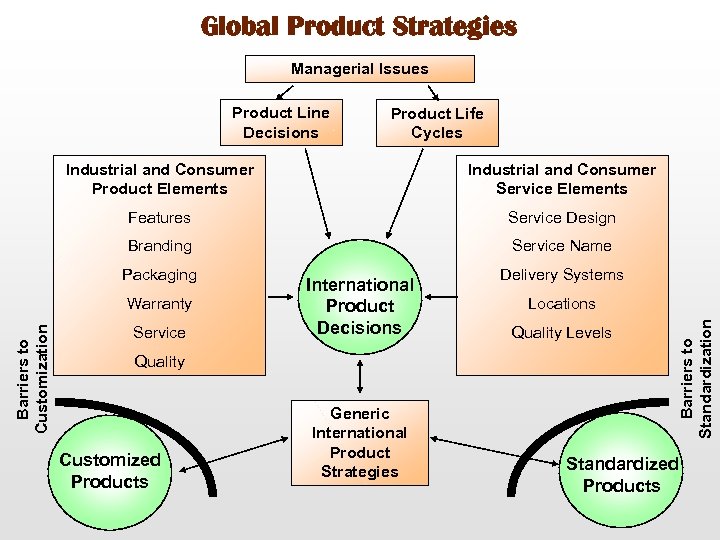 Global Product Strategies Managerial Issues Product Line Decisions Product Life Cycles Industrial and Consumer Product Elements Industrial and Consumer Service Elements Features Service Design Branding Service Name Barriers to Customization Warranty Service International Product Decisions Quality Customized Products Generic International Product Strategies Delivery Systems Locations Quality Levels Barriers to Standardization Packaging Standardized Products
Global Product Strategies Managerial Issues Product Line Decisions Product Life Cycles Industrial and Consumer Product Elements Industrial and Consumer Service Elements Features Service Design Branding Service Name Barriers to Customization Warranty Service International Product Decisions Quality Customized Products Generic International Product Strategies Delivery Systems Locations Quality Levels Barriers to Standardization Packaging Standardized Products
 The View from Toyota u. Our global strategy used to center on “world cars, ” which we would modify slightly to accommodate demand in different markets. Today our focus is shifting to models that we develop and manufacture especially for selected regional markets.
The View from Toyota u. Our global strategy used to center on “world cars, ” which we would modify slightly to accommodate demand in different markets. Today our focus is shifting to models that we develop and manufacture especially for selected regional markets.
 The View from Honda “We are the most international of the Japanese companies. At the moment we are the most diversified, and we will be more diversified in the future. Still, I think it would be very hard to build a one-type world car. In the end, I don’t think it would be very efficient. ” ---Nobuhiko Kawamoto President and CEO, Honda Motor Company
The View from Honda “We are the most international of the Japanese companies. At the moment we are the most diversified, and we will be more diversified in the future. Still, I think it would be very hard to build a one-type world car. In the end, I don’t think it would be very efficient. ” ---Nobuhiko Kawamoto President and CEO, Honda Motor Company

 Ch 13 --Trade Shows: A Crucial Part of Business-to-Business Marketing u u u Trade shows serve as the most important vehicles for selling products, reaching prospective customers, contacting and evaluating potential agents and distributors, and marketing in most countries Trade shows serve a much more important role in other countries where most prospects are found European trade shows attract high-level decision makers who are there to buy products Trade shows provide the facilities for a manufacturer to exhibit and demonstrate products to potential users and to view competitors’ products Trade shows create an opportunity to create sales and establish relationships with agents, distributors, franchisees, and suppliers that can lead to morepermanent distribution channels in foreign markets
Ch 13 --Trade Shows: A Crucial Part of Business-to-Business Marketing u u u Trade shows serve as the most important vehicles for selling products, reaching prospective customers, contacting and evaluating potential agents and distributors, and marketing in most countries Trade shows serve a much more important role in other countries where most prospects are found European trade shows attract high-level decision makers who are there to buy products Trade shows provide the facilities for a manufacturer to exhibit and demonstrate products to potential users and to view competitors’ products Trade shows create an opportunity to create sales and establish relationships with agents, distributors, franchisees, and suppliers that can lead to morepermanent distribution channels in foreign markets

 Relationship Marketing in Business-to-Business Contexts u u u Building long-term relationships with customers is a viable strategy for business-to-business marketing The objective of relationship marketing is to make the relationship an important attribute of the transaction, thus differentiating oneself from competitor It shifts the focus away from price to service and long-term benefits The reward is loyal customers that translate into substantial long -term profits Focusing on long-term relationship building will be especially important in most international markets where culture dictates stronger ties between people and companies
Relationship Marketing in Business-to-Business Contexts u u u Building long-term relationships with customers is a viable strategy for business-to-business marketing The objective of relationship marketing is to make the relationship an important attribute of the transaction, thus differentiating oneself from competitor It shifts the focus away from price to service and long-term benefits The reward is loyal customers that translate into substantial long -term profits Focusing on long-term relationship building will be especially important in most international markets where culture dictates stronger ties between people and companies








