a8b7be227a65647404eafdcfeca8f045.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Chapter 11 – Section 2 Water Use and Management • Objectives • Identify patterns of global water use • Explain how water is treated so that it can be used for drinking • Identify how water is used in homes, in industry, and in agriculture • Describe how dams and water diversion projects are used to manage freshwater resources • Identify five ways that water can be conserved
Chapter 11 – Section 2 Water Use and Management • Objectives • Identify patterns of global water use • Explain how water is treated so that it can be used for drinking • Identify how water is used in homes, in industry, and in agriculture • Describe how dams and water diversion projects are used to manage freshwater resources • Identify five ways that water can be conserved
 Delaware State Science Standard 8/GLEs • GLE • Identify and measure biological, chemical and physical indicators within a given ecosystem (p. H, dissolved oxygen, macroinvertebrate and other indicator species, salinity). • Evaluate decisions about the use of resources in one country and how these decisions can impact the diversity and stability of ecosystems globally. • Analyze ways in which human activity (i. e. , producing food, transporting materials, generating energy, disposing of waste, obtaining fresh water, or extracting natural resources) can affect ecosystems and the organisms within.
Delaware State Science Standard 8/GLEs • GLE • Identify and measure biological, chemical and physical indicators within a given ecosystem (p. H, dissolved oxygen, macroinvertebrate and other indicator species, salinity). • Evaluate decisions about the use of resources in one country and how these decisions can impact the diversity and stability of ecosystems globally. • Analyze ways in which human activity (i. e. , producing food, transporting materials, generating energy, disposing of waste, obtaining fresh water, or extracting natural resources) can affect ecosystems and the organisms within.
 Bellringer Exercise- Ecolog • Imagine you are camping in a desert. • Think of ways to get water if none ways nearby
Bellringer Exercise- Ecolog • Imagine you are camping in a desert. • Think of ways to get water if none ways nearby
 Earth’s Fresh Water • More people relying on Earth’s fresh water supply everyday – (population growing) • WHO (World Health Organization): More than 1 billion people lack access to a clean, reliable source of fresh water
Earth’s Fresh Water • More people relying on Earth’s fresh water supply everyday – (population growing) • WHO (World Health Organization): More than 1 billion people lack access to a clean, reliable source of fresh water
 Global Water Use • There are three major uses for water globally: – Residential – Industrial – Agricultural Most fresh water used worldwide is to irrigate crops
Global Water Use • There are three major uses for water globally: – Residential – Industrial – Agricultural Most fresh water used worldwide is to irrigate crops
 Water Use- Con’t • The availability of fresh water, population sizes, and economical conditions affect how people use water • Asia – Over 80% of fresh water used for agriculture • Europe – 38% used for agriculture, 44% used for industry
Water Use- Con’t • The availability of fresh water, population sizes, and economical conditions affect how people use water • Asia – Over 80% of fresh water used for agriculture • Europe – 38% used for agriculture, 44% used for industry
 Global Use • Industry accounts for approximately 19% of fresh water use worldwide • Globally, around 8% of all fresh water is used residentially
Global Use • Industry accounts for approximately 19% of fresh water use worldwide • Globally, around 8% of all fresh water is used residentially
 Residential Water Use • Average person in United States uses approximately 80 gallons (300 L) of water per day – ½ for drinking, cooking, washing, and toilet flushing – ½ outside: watering lawns, washing cars, etc. • Average person in India uses approximately 11 gallons (41 L) of water per day
Residential Water Use • Average person in United States uses approximately 80 gallons (300 L) of water per day – ½ for drinking, cooking, washing, and toilet flushing – ½ outside: watering lawns, washing cars, etc. • Average person in India uses approximately 11 gallons (41 L) of water per day
 Daily Water Use – U. S. • • Lawn watering/Pools – 95 L – (25 gal) Toilet flushing 90 L – (24 gal) Bathing 70 L – (18. 6 gal) Brushing teeth 10 L - (2. 7 gal) Cleaning-(in/outside) 20 L – (5. 4 gal) Cooking/drinking 10 L- (2. 7 gal) Other 5 L – (1. 4 gal)
Daily Water Use – U. S. • • Lawn watering/Pools – 95 L – (25 gal) Toilet flushing 90 L – (24 gal) Bathing 70 L – (18. 6 gal) Brushing teeth 10 L - (2. 7 gal) Cleaning-(in/outside) 20 L – (5. 4 gal) Cooking/drinking 10 L- (2. 7 gal) Other 5 L – (1. 4 gal)
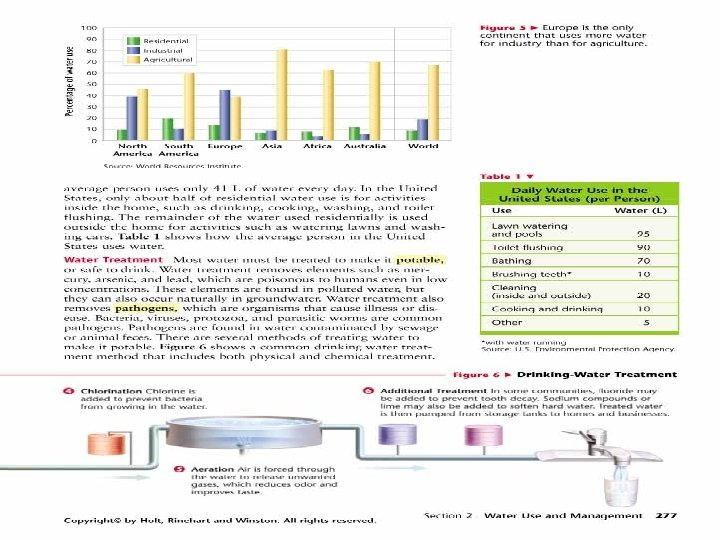
 Graphing Exercise • Draw a bar graph of the information on page 277 (297 -new book) • Then, draw a pie graph showing the relative percentages of each type of water use
Graphing Exercise • Draw a bar graph of the information on page 277 (297 -new book) • Then, draw a pie graph showing the relative percentages of each type of water use
 Daily Use- Products • 400 gal. of water needed to produce one cotton shirt • 49 gal. needed to produce one glass of milk • It takes more than 2000 gal. of water to produce a single serving of steak • Can you describe how and why it takes so much water to produce these products?
Daily Use- Products • 400 gal. of water needed to produce one cotton shirt • 49 gal. needed to produce one glass of milk • It takes more than 2000 gal. of water to produce a single serving of steak • Can you describe how and why it takes so much water to produce these products?
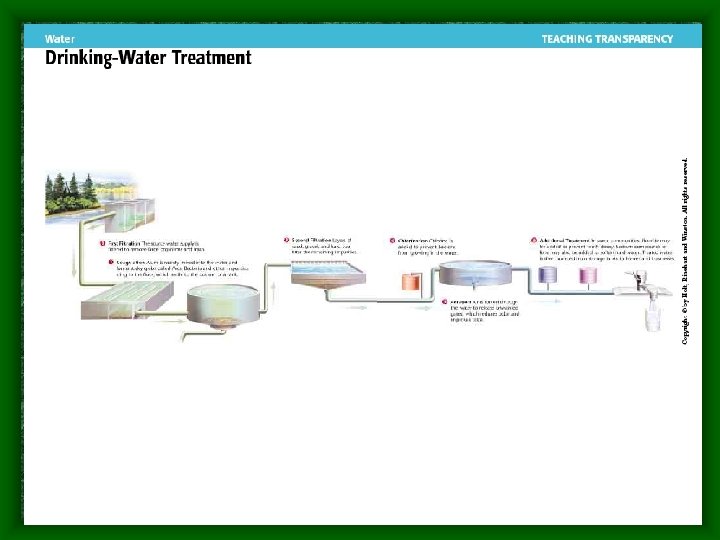
 Water Treatment • Potable: means safe to drink • Water is treated to remove elements like: mercury, arsenic, and lead • These elements can appear in polluted water or occur naturally • Pathogens: organisms that cause illness or disease: bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and parasitic worms (usually found in sewage or animal feces)
Water Treatment • Potable: means safe to drink • Water is treated to remove elements like: mercury, arsenic, and lead • These elements can appear in polluted water or occur naturally • Pathogens: organisms that cause illness or disease: bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and parasitic worms (usually found in sewage or animal feces)
 Industrial Water Use • Accounts for 19% of water use worldwide • Water used to: manufacture goods, dispose of waste, and to generate power • Nearly 1000 L (267 gal) of water is needed to produce 1 kg (2. 2 lb) • Almost 500, 000 L (133, 500 gal) of water needed to manufacture a car • Most industrial use is for cooling power plants
Industrial Water Use • Accounts for 19% of water use worldwide • Water used to: manufacture goods, dispose of waste, and to generate power • Nearly 1000 L (267 gal) of water is needed to produce 1 kg (2. 2 lb) • Almost 500, 000 L (133, 500 gal) of water needed to manufacture a car • Most industrial use is for cooling power plants
 Computer Industry • Computer chips go through an elaborate cleaning process that involves a large volume of water and 500 to 1000 different chemicals, including arsenic • The production process generates toxic wastes, contaminating groundwater and soil • The process consumes vast amounts of electricity and water, millions of gallons per day • Silicon Valley, CA has 24 “Super-Fund” sites created by high-tech industry
Computer Industry • Computer chips go through an elaborate cleaning process that involves a large volume of water and 500 to 1000 different chemicals, including arsenic • The production process generates toxic wastes, contaminating groundwater and soil • The process consumes vast amounts of electricity and water, millions of gallons per day • Silicon Valley, CA has 24 “Super-Fund” sites created by high-tech industry
 Agricultural Water Use • Nearly 300 l (80 gal) of water needed to produce one ear of corn • Agriculture accounts for 67% of water use in world today • Approximately 80% of water used in agriculture evaporates and never reaches plant roots
Agricultural Water Use • Nearly 300 l (80 gal) of water needed to produce one ear of corn • Agriculture accounts for 67% of water use in world today • Approximately 80% of water used in agriculture evaporates and never reaches plant roots
 Irrigation • Definition: a method of providing plants with a water sources other than direct precipitation • Different methods: water-filled ditches (cotton), high-pressure overhead sprinklers (most common) • ½ of water from over head sprinklers evaporates (very inefficient)
Irrigation • Definition: a method of providing plants with a water sources other than direct precipitation • Different methods: water-filled ditches (cotton), high-pressure overhead sprinklers (most common) • ½ of water from over head sprinklers evaporates (very inefficient)
 Water Management Projects • 2000 years ago Romans built aqueducts to carry water from mountains to dry areas of France and Spain • Modern water managements projects include dams and water diversion canals • Project goals include: bringing water in to make a dry area habitable, creating a reservoir for recreation or drinking water or generating electric power
Water Management Projects • 2000 years ago Romans built aqueducts to carry water from mountains to dry areas of France and Spain • Modern water managements projects include dams and water diversion canals • Project goals include: bringing water in to make a dry area habitable, creating a reservoir for recreation or drinking water or generating electric power
 Water Diversion Projects • To supply dry regions with water, all or part of a river can be diverted into canals that carry water great distances • Ex: The Owens River in CA is diverted to supply water to Los Angeles • The Colorado River is diverted top supply several western states. So much of the Colorado River is diverted fro irrigation and drinking water in states like Arizona, Utah, and California, that it dries up before it reaches the Gulf of California
Water Diversion Projects • To supply dry regions with water, all or part of a river can be diverted into canals that carry water great distances • Ex: The Owens River in CA is diverted to supply water to Los Angeles • The Colorado River is diverted top supply several western states. So much of the Colorado River is diverted fro irrigation and drinking water in states like Arizona, Utah, and California, that it dries up before it reaches the Gulf of California
 Dams and Reservoirs • Dam: A structure built across a river to control the river’s flow • Reservoir: an artificial lake formed behind a dam used for flood control, drinking water, irrigation, recreation, and industry • Dams are also used to generate electricity • About 20% of world’s electricity is supplied by hydroelectric dams
Dams and Reservoirs • Dam: A structure built across a river to control the river’s flow • Reservoir: an artificial lake formed behind a dam used for flood control, drinking water, irrigation, recreation, and industry • Dams are also used to generate electricity • About 20% of world’s electricity is supplied by hydroelectric dams
 Dam Problems • When land behind dams are flooded, many people are displaced • It is estimated that 50 million people worldwide have been displaced by dam projects • Many eco-systems have also been destroyed by dam projects
Dam Problems • When land behind dams are flooded, many people are displaced • It is estimated that 50 million people worldwide have been displaced by dam projects • Many eco-systems have also been destroyed by dam projects
 Dam Problems- Con’t • As rivers enter reservoirs, they slow down and deposit some of it’s sediment. This fertile sediment builds up behind the dam instead of enriching farmland farther downstream • If a dam bursts, many people can lose their lives • No other dams are being built in the US, only in developing countries such as Brazil, India, and China
Dam Problems- Con’t • As rivers enter reservoirs, they slow down and deposit some of it’s sediment. This fertile sediment builds up behind the dam instead of enriching farmland farther downstream • If a dam bursts, many people can lose their lives • No other dams are being built in the US, only in developing countries such as Brazil, India, and China
 Dam Salmon Deaths • A series of hydroelectric dams on the Columbia River, in the Pacific N. W. , has severely reduced the salmon population. As salmon migrate they must pass through the turbines of each dam. • Only 15% of salmon die passing through each dam • However, because each salmon must pass through eight dams on the river, there is a large cumulative loss. • How many fish would survive out of an initial population of 1000?
Dam Salmon Deaths • A series of hydroelectric dams on the Columbia River, in the Pacific N. W. , has severely reduced the salmon population. As salmon migrate they must pass through the turbines of each dam. • Only 15% of salmon die passing through each dam • However, because each salmon must pass through eight dams on the river, there is a large cumulative loss. • How many fish would survive out of an initial population of 1000?
 Salmon Death Solution • • • 1 st dam = 1000 fish x. 15 = 150, 1000 -150 = 850 2 nd dam = 850 fish x. 15 = 127. 5, 850 – 127. 5 = 722. 5 3 rd dam = 722. 5 x. 15 = 108. 4, 722. 5 -108. 4=614 4 th dam = 614 x. 15 = 92, 614 – 92 = 522 5 th dam = 522 x. 15 = 78, 522 – 78 = 444 6 th dam = 444 x. 15 = 67, 444 – 67 = 378 7 th dam = 378 x. 15 = 57, 378 – 57 = 321 8 th dam = 321 x. 15 = 48, 321 – 48 = 273 salmon out of 1000 would survive!!
Salmon Death Solution • • • 1 st dam = 1000 fish x. 15 = 150, 1000 -150 = 850 2 nd dam = 850 fish x. 15 = 127. 5, 850 – 127. 5 = 722. 5 3 rd dam = 722. 5 x. 15 = 108. 4, 722. 5 -108. 4=614 4 th dam = 614 x. 15 = 92, 614 – 92 = 522 5 th dam = 522 x. 15 = 78, 522 – 78 = 444 6 th dam = 444 x. 15 = 67, 444 – 67 = 378 7 th dam = 378 x. 15 = 57, 378 – 57 = 321 8 th dam = 321 x. 15 = 48, 321 – 48 = 273 salmon out of 1000 would survive!!
 Water Conservation • As water sources become depleted, water becomes more expensive • Why? : wells must be dug deeper, water must be piped greater distances, and polluted water must be cleaned up before it can be used • Water conservation is one way of helping situation
Water Conservation • As water sources become depleted, water becomes more expensive • Why? : wells must be dug deeper, water must be piped greater distances, and polluted water must be cleaned up before it can be used • Water conservation is one way of helping situation
 Water Conservation Methods • In Agriculture: Most water loss comes from evaporation, seepage, and runoff • Some solutions: – Drip irrigation systems: deliver small amounts of water directly to plant roots by using perforated tubing. Controlled and coordinated by computers and satellite data
Water Conservation Methods • In Agriculture: Most water loss comes from evaporation, seepage, and runoff • Some solutions: – Drip irrigation systems: deliver small amounts of water directly to plant roots by using perforated tubing. Controlled and coordinated by computers and satellite data
 Israeli Agriculture • From 1950 to 1980, Israel reduced the amount of water loss in agriculture from 83% to 5% by switching from overhead sprinklers to water saving methods like drip irrigation • If a small farm uses 10, 000 L of water a day for overhead sprinklers, how much water would be saved in one year by using a drip irrigation system that consumes 75% less water?
Israeli Agriculture • From 1950 to 1980, Israel reduced the amount of water loss in agriculture from 83% to 5% by switching from overhead sprinklers to water saving methods like drip irrigation • If a small farm uses 10, 000 L of water a day for overhead sprinklers, how much water would be saved in one year by using a drip irrigation system that consumes 75% less water?
 Israeli Ag. Solution • 10, 000 L /day x 365 days = 3, 650, 000 L/year • 3, 650, 000 L x 0. 75 = 2, 737, 500 L saved per year
Israeli Ag. Solution • 10, 000 L /day x 365 days = 3, 650, 000 L/year • 3, 650, 000 L x 0. 75 = 2, 737, 500 L saved per year
 Methods Con’t • In Industry: Most widely used method is recycling of cooling water and wastewater • Instead of discharging used water into nearby rivers, businesses often recycle • Ex. : The production of 1 kg of paper now consumes less than 30% of the water it required 50 years ago
Methods Con’t • In Industry: Most widely used method is recycling of cooling water and wastewater • Instead of discharging used water into nearby rivers, businesses often recycle • Ex. : The production of 1 kg of paper now consumes less than 30% of the water it required 50 years ago
 Methods Con’t • At Home: People can conserve water by changing a few everyday habits and using only the water they need. • Ex. : Take shorter showers, avoid taking baths, unless water levels are low • Install a low flow shower head • Install low flow aerators in your faucets
Methods Con’t • At Home: People can conserve water by changing a few everyday habits and using only the water they need. • Ex. : Take shorter showers, avoid taking baths, unless water levels are low • Install a low flow shower head • Install low flow aerators in your faucets
 Home Methods Con’t • Purchase a modern, low flow toilet, install a water saving device in your toilet, or simply place a water filled bottle inside your toilet tank to reduce water use per flush • Don’t let water run when brushing teeth • Fill up sink basin rather than letting water run
Home Methods Con’t • Purchase a modern, low flow toilet, install a water saving device in your toilet, or simply place a water filled bottle inside your toilet tank to reduce water use per flush • Don’t let water run when brushing teeth • Fill up sink basin rather than letting water run
 Home Method’s Con’t • Wash only full loads in your dishwasher and washing machine • Water your lawn s sparingly and in the evening to reduce evaporation • Xeriscaping: designing a landscape that requires minimal water use • Can one person make a difference? When multiplied by millions, absolutely!
Home Method’s Con’t • Wash only full loads in your dishwasher and washing machine • Water your lawn s sparingly and in the evening to reduce evaporation • Xeriscaping: designing a landscape that requires minimal water use • Can one person make a difference? When multiplied by millions, absolutely!
 Future Solutions • Desalination: Process of removing salt from salt water. • Countries in drier parts of world, like the Mid-East, have built desalination plants • Most de-sal plants heat salt water and collect the fresh water that evaporates • This process consumes a lot of energy and is too expensive for most countries
Future Solutions • Desalination: Process of removing salt from salt water. • Countries in drier parts of world, like the Mid-East, have built desalination plants • Most de-sal plants heat salt water and collect the fresh water that evaporates • This process consumes a lot of energy and is too expensive for most countries
 Future Solutions Con’t • Transporting Water: Water transported form other regions to drier regions • Large bags of water is transported to some Greek islands • U. S. is considering transporting bags of water from Alaska, where almost ½ of all US fresh water is located, to California • Towing icebergs to arid regions is being considered, but an efficient method must be developed
Future Solutions Con’t • Transporting Water: Water transported form other regions to drier regions • Large bags of water is transported to some Greek islands • U. S. is considering transporting bags of water from Alaska, where almost ½ of all US fresh water is located, to California • Towing icebergs to arid regions is being considered, but an efficient method must be developed


