3e849efda23629057d8b426661ed4a7b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Chapter 11 Retail Organization and Human Resource Management Dr. Pointer’s Notes
Chapter 11 Retail Organization and Human Resource Management Dr. Pointer’s Notes
 Chapter Objectives ¯ To study the procedures involved in setting up a retail organization ¯ To examine the various organizational arrangements utilized in retailing ¯ To consider the special human resource environment of retailing ¯ To describe the principles and practices involved with the human resource management process in retailing 11 -2
Chapter Objectives ¯ To study the procedures involved in setting up a retail organization ¯ To examine the various organizational arrangements utilized in retailing ¯ To consider the special human resource environment of retailing ¯ To describe the principles and practices involved with the human resource management process in retailing 11 -2
 Setting Up a Retail Organization • Through a retail organization, a firm’s structures and assigns tasks, policies, resources, authority, responsibilities in order to efficiently and effectively satisfy the needs of target market, employees, management and shareholders 11 -3
Setting Up a Retail Organization • Through a retail organization, a firm’s structures and assigns tasks, policies, resources, authority, responsibilities in order to efficiently and effectively satisfy the needs of target market, employees, management and shareholders 11 -3
 Figure 11. 1 Planning and Assessing a Retail Organization: Factors to Consider Target market needs • Sufficient personnel to provide appropriate customer service • Knowledgeable and courteous personnel • Well maintained store facilities • Ability address changing needs 11 -4
Figure 11. 1 Planning and Assessing a Retail Organization: Factors to Consider Target market needs • Sufficient personnel to provide appropriate customer service • Knowledgeable and courteous personnel • Well maintained store facilities • Ability address changing needs 11 -4
 Figure 11. 1 Planning and Assessing a Retail Organization: Factors to Consider Employee Needs • Challenging and satisfying positions • Participation in decision making • Clear channel communications • Clear authority-responsibility roles • Fair treatment of employees • Good performance rewards 11 -5
Figure 11. 1 Planning and Assessing a Retail Organization: Factors to Consider Employee Needs • Challenging and satisfying positions • Participation in decision making • Clear channel communications • Clear authority-responsibility roles • Fair treatment of employees • Good performance rewards 11 -5
 Figure 11. 1 Planning and Assessing a Retail Organization: Factors to Consider Management Needs • Ability to obtain and retain good employees • Clear personnel procedures • One worker reporting to only one supervisor • Adequate staff supports in departments • Well integrated organizational plans • Motivated employees • Low absenteeism • System replace employees as needed 11 -6
Figure 11. 1 Planning and Assessing a Retail Organization: Factors to Consider Management Needs • Ability to obtain and retain good employees • Clear personnel procedures • One worker reporting to only one supervisor • Adequate staff supports in departments • Well integrated organizational plans • Motivated employees • Low absenteeism • System replace employees as needed 11 -6
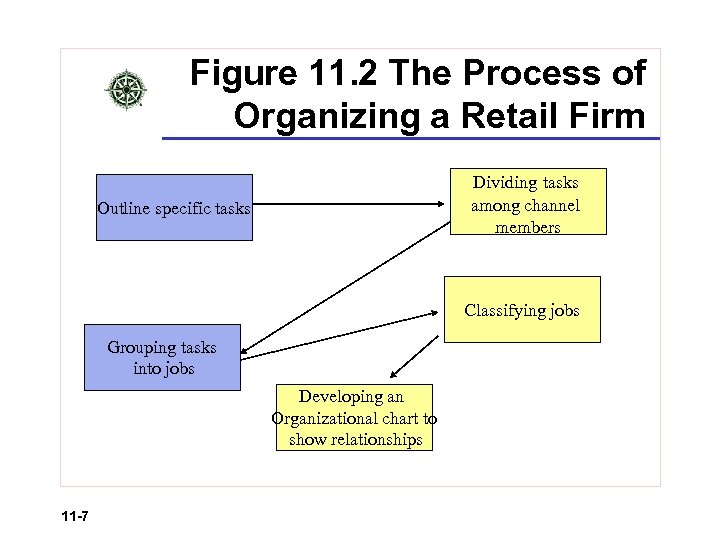 Figure 11. 2 The Process of Organizing a Retail Firm Dividing tasks among channel members Outline specific tasks Classifying jobs Grouping tasks into jobs Developing an Organizational chart to show relationships 11 -7
Figure 11. 2 The Process of Organizing a Retail Firm Dividing tasks among channel members Outline specific tasks Classifying jobs Grouping tasks into jobs Developing an Organizational chart to show relationships 11 -7
 Specifying Tasks 1. Buying/shipping merchandise 2. Receiving and checking in goods 3. Setting prices/marking merchandise 4. Inventory storage and control 5. Facilities maintenance 6. Personnel management 7. Billing customers/credit operations 8. Customer service operations- delivery, gift wrapping, , 9. Sales forecasting and budgeting 11 -8
Specifying Tasks 1. Buying/shipping merchandise 2. Receiving and checking in goods 3. Setting prices/marking merchandise 4. Inventory storage and control 5. Facilities maintenance 6. Personnel management 7. Billing customers/credit operations 8. Customer service operations- delivery, gift wrapping, , 9. Sales forecasting and budgeting 11 -8
 Figure 11. 3 Division of Tasks in a Distribution Channel • Retailer- can perform all or some tasks from buying to coordination • Manufacturer or wholesaler – few of functions such as shipping and marking, inventory storage, displays and research • Specialists – particular tasks: market research, ad agency, credit, computer services 11 -9
Figure 11. 3 Division of Tasks in a Distribution Channel • Retailer- can perform all or some tasks from buying to coordination • Manufacturer or wholesaler – few of functions such as shipping and marking, inventory storage, displays and research • Specialists – particular tasks: market research, ad agency, credit, computer services 11 -9
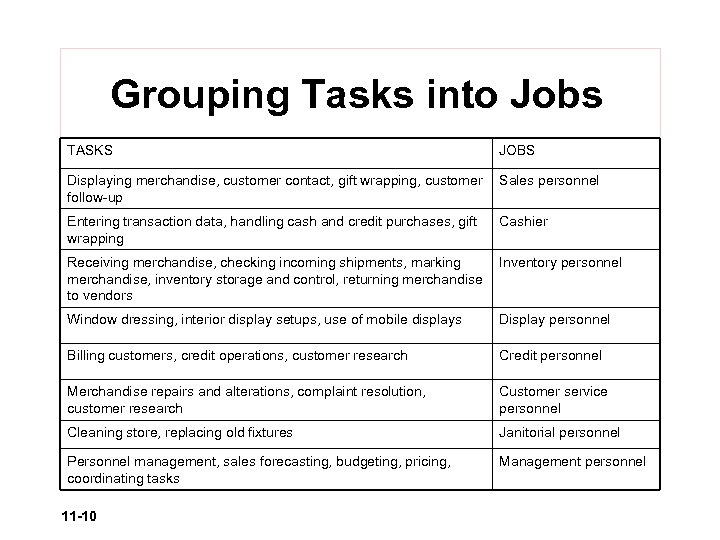 Grouping Tasks into Jobs TASKS JOBS Displaying merchandise, customer contact, gift wrapping, customer follow-up Sales personnel Entering transaction data, handling cash and credit purchases, gift wrapping Cashier Receiving merchandise, checking incoming shipments, marking merchandise, inventory storage and control, returning merchandise to vendors Inventory personnel Window dressing, interior display setups, use of mobile displays Display personnel Billing customers, credit operations, customer research Credit personnel Merchandise repairs and alterations, complaint resolution, customer research Customer service personnel Cleaning store, replacing old fixtures Janitorial personnel Personnel management, sales forecasting, budgeting, pricing, coordinating tasks Management personnel 11 -10
Grouping Tasks into Jobs TASKS JOBS Displaying merchandise, customer contact, gift wrapping, customer follow-up Sales personnel Entering transaction data, handling cash and credit purchases, gift wrapping Cashier Receiving merchandise, checking incoming shipments, marking merchandise, inventory storage and control, returning merchandise to vendors Inventory personnel Window dressing, interior display setups, use of mobile displays Display personnel Billing customers, credit operations, customer research Credit personnel Merchandise repairs and alterations, complaint resolution, customer research Customer service personnel Cleaning store, replacing old fixtures Janitorial personnel Personnel management, sales forecasting, budgeting, pricing, coordinating tasks Management personnel 11 -10
 Figure 11. 4 A Job Description for a Store Manager • Job Title: Store manager • Position Reports To: Senior Vice-President • Positions reporting to store manager: all personnel in store • Objectives: to properly staff and operate store • Duties: sales forecasting, budgeting, personnel hiring, merchandise display and etc. • Committees: Attendance at monthly meetings with V-President • Weekly meetings with department managers 11 -11
Figure 11. 4 A Job Description for a Store Manager • Job Title: Store manager • Position Reports To: Senior Vice-President • Positions reporting to store manager: all personnel in store • Objectives: to properly staff and operate store • Duties: sales forecasting, budgeting, personnel hiring, merchandise display and etc. • Committees: Attendance at monthly meetings with V-President • Weekly meetings with department managers 11 -11
 Classifying Jobs ¯ Functional- divides jobs by task ¯ Product diversification divides jobs on a goods or service basis ¯ Geographic- is useful for chains operating in different areas. ¯ Combination – large organizations find it easier to use a combination 11 -12
Classifying Jobs ¯ Functional- divides jobs by task ¯ Product diversification divides jobs on a goods or service basis ¯ Geographic- is useful for chains operating in different areas. ¯ Combination – large organizations find it easier to use a combination 11 -12
 Develop an Organization Chart • It is important to build a good organization which will help build the business • Hierarchy of Authority- outlines the job interactions within a company by describing the reporting relationships among employees • Flat organization – many workers reporting to one manager • Tall organization – has several management levels 11 -13
Develop an Organization Chart • It is important to build a good organization which will help build the business • Hierarchy of Authority- outlines the job interactions within a company by describing the reporting relationships among employees • Flat organization – many workers reporting to one manager • Tall organization – has several management levels 11 -13
 Table 11. 1 Principles for Organizing a Retail Firm 1. Show interest in employees 2. Monitor employee turnover, lateness, and absenteeism 3. Trace line of authority from top to bottom 4. Limit span of control 5. Empower employees 6. Delegate authority while maintaining responsibility 7. Acknowledge need for coordination and communication 8. Recognize the power of informal relationships 11 -14
Table 11. 1 Principles for Organizing a Retail Firm 1. Show interest in employees 2. Monitor employee turnover, lateness, and absenteeism 3. Trace line of authority from top to bottom 4. Limit span of control 5. Empower employees 6. Delegate authority while maintaining responsibility 7. Acknowledge need for coordination and communication 8. Recognize the power of informal relationships 11 -14
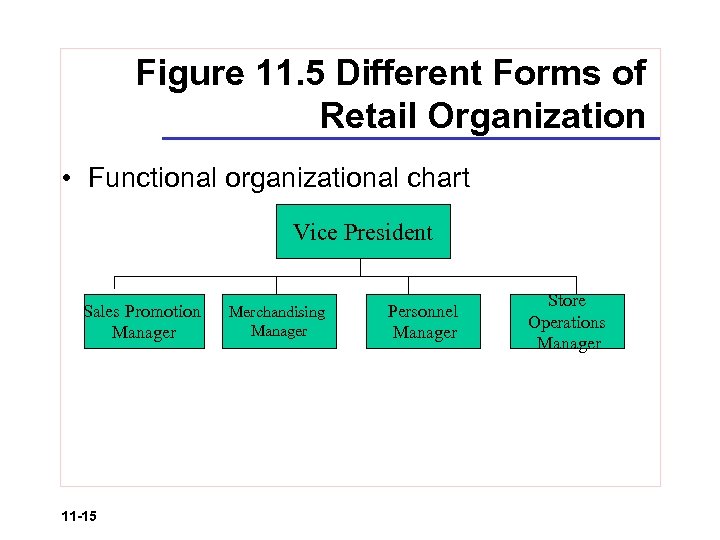 Figure 11. 5 Different Forms of Retail Organization • Functional organizational chart Vice President Sales Promotion Manager 11 -15 Merchandising Manager Personnel Manager Store Operations Manager
Figure 11. 5 Different Forms of Retail Organization • Functional organizational chart Vice President Sales Promotion Manager 11 -15 Merchandising Manager Personnel Manager Store Operations Manager
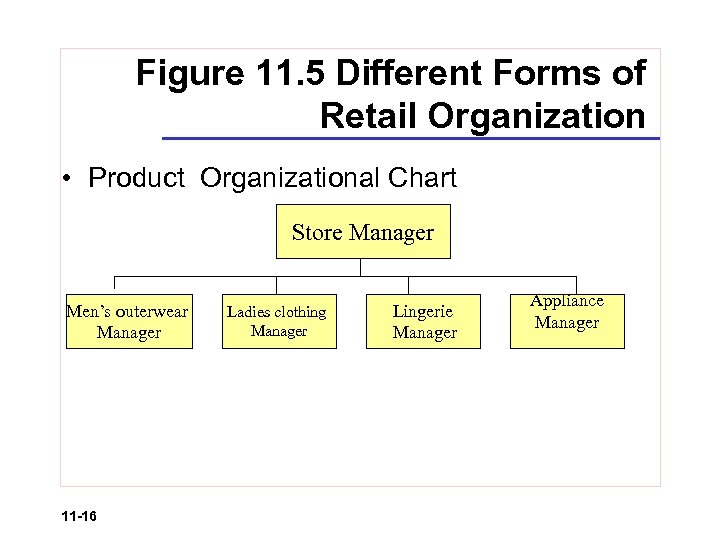 Figure 11. 5 Different Forms of Retail Organization • Product Organizational Chart Store Manager Men’s outerwear Manager 11 -16 Ladies clothing Manager Lingerie Manager Appliance Manager
Figure 11. 5 Different Forms of Retail Organization • Product Organizational Chart Store Manager Men’s outerwear Manager 11 -16 Ladies clothing Manager Lingerie Manager Appliance Manager
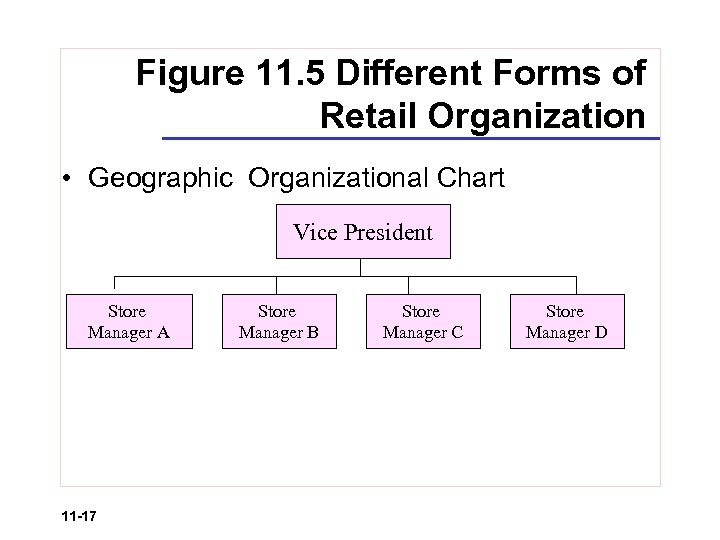 Figure 11. 5 Different Forms of Retail Organization • Geographic Organizational Chart Vice President Store Manager A 11 -17 Store Manager B Store Manager C Store Manager D
Figure 11. 5 Different Forms of Retail Organization • Geographic Organizational Chart Vice President Store Manager A 11 -17 Store Manager B Store Manager C Store Manager D
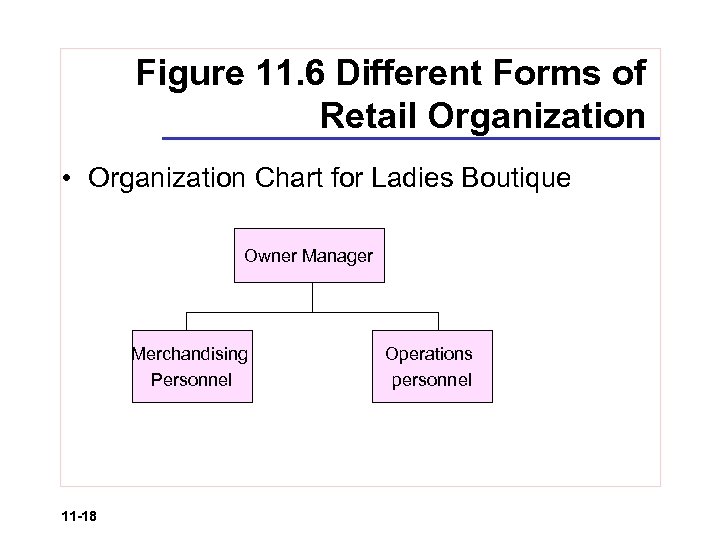 Figure 11. 6 Different Forms of Retail Organization • Organization Chart for Ladies Boutique Owner Manager Merchandising Personnel 11 -18 Operations personnel
Figure 11. 6 Different Forms of Retail Organization • Organization Chart for Ladies Boutique Owner Manager Merchandising Personnel 11 -18 Operations personnel
 Organizational Arrangements Used by Diversified Retailers ¯ A diversified retailer is a multiline firm operating under central ownership. Usually involved in different types of retail operations ¯Toys “R” Us, Inc. – Toys “R” Us – Kids “R” Us – Babies “R” Us – Imaginarium – Toys “R” Us. com 11 -19
Organizational Arrangements Used by Diversified Retailers ¯ A diversified retailer is a multiline firm operating under central ownership. Usually involved in different types of retail operations ¯Toys “R” Us, Inc. – Toys “R” Us – Kids “R” Us – Babies “R” Us – Imaginarium – Toys “R” Us. com 11 -19
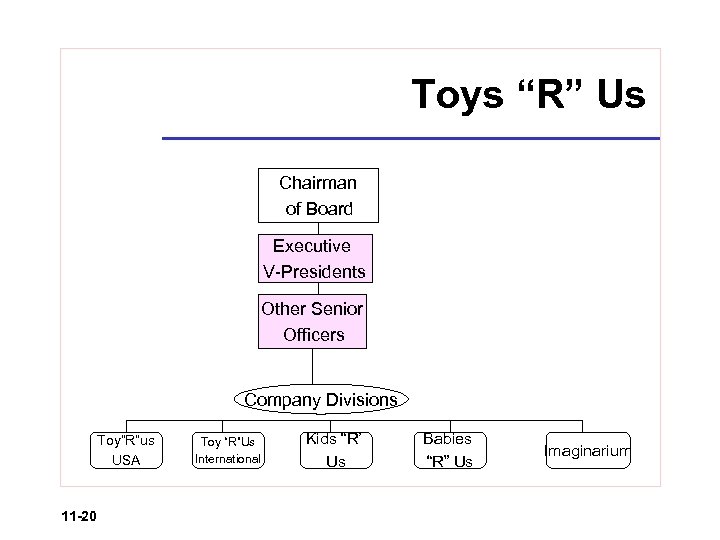 Toys “R” Us Chairman of Board Executive V-Presidents Other Senior Officers Company Divisions Toy”R”us USA 11 -20 Toy “R”Us International Kids “R’ Us Babies “R” Us Imaginarium
Toys “R” Us Chairman of Board Executive V-Presidents Other Senior Officers Company Divisions Toy”R”us USA 11 -20 Toy “R”Us International Kids “R’ Us Babies “R” Us Imaginarium
 Human Resource Management In Retailing • Human resource management involving, recruiting, selecting, training, compensating and supervising personnel in a manner consistent with the retail organization’s structure and strategy mix. • 23 million people are employed in retailing 11 -21
Human Resource Management In Retailing • Human resource management involving, recruiting, selecting, training, compensating and supervising personnel in a manner consistent with the retail organization’s structure and strategy mix. • 23 million people are employed in retailing 11 -21
 Human Resource Management in Retailing ¯ Recruiting- need procedures to efficiently generate sufficient applicants ¯ Selecting- diverse work force ¯ Training- must be short because most workers are inexperience and temporary ¯ Compensating- must be perceived as being fair ¯ Supervising-must closely monitor workers because many are part-time and unmotivated 11 -22
Human Resource Management in Retailing ¯ Recruiting- need procedures to efficiently generate sufficient applicants ¯ Selecting- diverse work force ¯ Training- must be short because most workers are inexperience and temporary ¯ Compensating- must be perceived as being fair ¯ Supervising-must closely monitor workers because many are part-time and unmotivated 11 -22
 Table 11. 2 True Cost of Employee Turnover 1. Recruiting and hiring new employees 2. Training costs – including management time 3. Full pay and benefits during training, before full productivity is reached 4. Costs of mistakes made by new, inexperienced employees 5. Loss of customers loyal to departing employees 6. Lost or damaged relationships with suppliers 7. Employee morale and customer perceptions of that morale 11 -23
Table 11. 2 True Cost of Employee Turnover 1. Recruiting and hiring new employees 2. Training costs – including management time 3. Full pay and benefits during training, before full productivity is reached 4. Costs of mistakes made by new, inexperienced employees 5. Loss of customers loyal to departing employees 6. Lost or damaged relationships with suppliers 7. Employee morale and customer perceptions of that morale 11 -23
 Women in Retailing ¯ Women have more career opportunities in retailing as demonstrated in our text ¯ Issues to address with regard to female workers – Meaningful training programs – Advancement opportunities – Flex time –the ability of employees to adapt their hours – Job sharing among two or more employees who each work less than full time – Child care ¯ Retailing empires – Mary Kay – Avon 11 -24
Women in Retailing ¯ Women have more career opportunities in retailing as demonstrated in our text ¯ Issues to address with regard to female workers – Meaningful training programs – Advancement opportunities – Flex time –the ability of employees to adapt their hours – Job sharing among two or more employees who each work less than full time – Child care ¯ Retailing empires – Mary Kay – Avon 11 -24
 Minorities in Retailing ¯ Again minorities have done well in retailing ¯ Issues to address with regard to female workers – Clear policy statements from top management as to the value of employee diversity – Active recruitment programs to stimulate minority applications – Meaningful training programs – Advancement opportunities – Zero tolerance for insensitive workplace behavior ¯ See Diversity. Inc. com 11 -25
Minorities in Retailing ¯ Again minorities have done well in retailing ¯ Issues to address with regard to female workers – Clear policy statements from top management as to the value of employee diversity – Active recruitment programs to stimulate minority applications – Meaningful training programs – Advancement opportunities – Zero tolerance for insensitive workplace behavior ¯ See Diversity. Inc. com 11 -25
 Diversity ¯ Two premises: ¯That employees be hired and promoted in a fair and open way, without regard to gender, ethnic background, and other related factors ¯That in a diverse society, the workplace should be representative of such diversity 11 -26
Diversity ¯ Two premises: ¯That employees be hired and promoted in a fair and open way, without regard to gender, ethnic background, and other related factors ¯That in a diverse society, the workplace should be representative of such diversity 11 -26
 Human resource management process in Retailing Human resource management process consist of 5 interrelated personnel activities • Recruitment- sources of employees? • Selecting Retail Personnel- matching traits of new employees with job requirements. job analysis – information on job functions and requirements and job description contains, position title, relationship, and specific roles and tasks application blank and weighted application blanktests are done and references are usually needed 11 -27
Human resource management process in Retailing Human resource management process consist of 5 interrelated personnel activities • Recruitment- sources of employees? • Selecting Retail Personnel- matching traits of new employees with job requirements. job analysis – information on job functions and requirements and job description contains, position title, relationship, and specific roles and tasks application blank and weighted application blanktests are done and references are usually needed 11 -27
 Human resource management process in Retailing Human resource management process consist of 5 interrelated personnel activities *Training- teach new and existing personnel how to perform their jobs or improve themselves Training should be viewed as an ongoing activity • Compensation –direct monetary payments( salary, commissions, and bonuses • Supervision- is manner of providing a job environment that encourages employee accomplishments Job motivation – develop the drive within people to attain work related goals. 11 -28
Human resource management process in Retailing Human resource management process consist of 5 interrelated personnel activities *Training- teach new and existing personnel how to perform their jobs or improve themselves Training should be viewed as an ongoing activity • Compensation –direct monetary payments( salary, commissions, and bonuses • Supervision- is manner of providing a job environment that encourages employee accomplishments Job motivation – develop the drive within people to attain work related goals. 11 -28
 Labor Law Considerations 1. Retailers must not 1. Hire underage workers 2. Pay workers “off the books” 3. Require workers to engage in illegal acts 4. Discriminate in hiring or promoting workers 5. Violate worker safety regulations 6. Disobey the Americans with Disabilities Act 7. Deal with suppliers that disobey labor laws 11 -29
Labor Law Considerations 1. Retailers must not 1. Hire underage workers 2. Pay workers “off the books” 3. Require workers to engage in illegal acts 4. Discriminate in hiring or promoting workers 5. Violate worker safety regulations 6. Disobey the Americans with Disabilities Act 7. Deal with suppliers that disobey labor laws 11 -29
 Figure 11. 11 A Checklist of Selected Training Decisions • When should training occur • How long should training be • What programs for new and existing employees • Where should training take place • Should audiovisuals be used • Use of computerized training • How the effectiveness of training be measured 11 -30
Figure 11. 11 A Checklist of Selected Training Decisions • When should training occur • How long should training be • What programs for new and existing employees • Where should training take place • Should audiovisuals be used • Use of computerized training • How the effectiveness of training be measured 11 -30
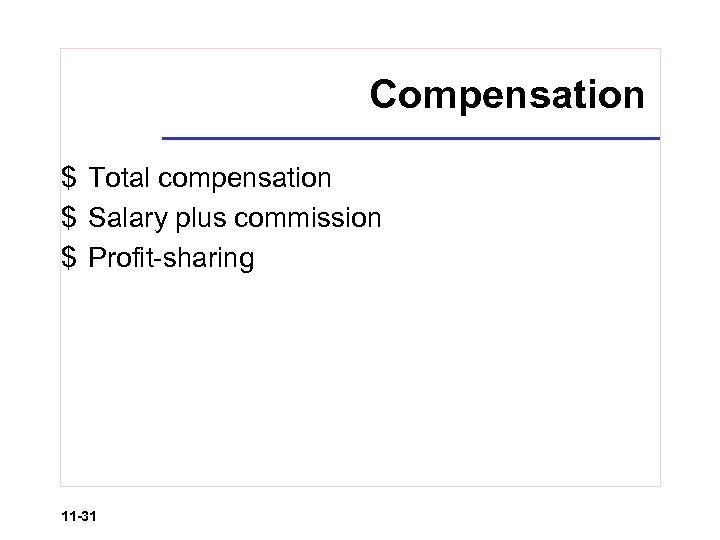 Compensation $ Total compensation $ Salary plus commission $ Profit-sharing 11 -31
Compensation $ Total compensation $ Salary plus commission $ Profit-sharing 11 -31
 Employee Behavior and Motivation ¯ Several attitudes may affect employee behavior ¯Sense of accomplishment ¯Liking of work ¯Attitude toward physical work conditions ¯Attitude toward supervisors ¯Confidence in company ¯Knowledge of business strategy ¯Recognition of employee role in achieving corporate objectives 11 -32
Employee Behavior and Motivation ¯ Several attitudes may affect employee behavior ¯Sense of accomplishment ¯Liking of work ¯Attitude toward physical work conditions ¯Attitude toward supervisors ¯Confidence in company ¯Knowledge of business strategy ¯Recognition of employee role in achieving corporate objectives 11 -32
 Style of Supervising Retail Employees v Management assumes employees must be closely supervised and controlled; only economic inducements motivate employees v Management assumes employees can be self-managers and assigned authority; motivation is intrinsic v Management applies self-management approach 11 -33
Style of Supervising Retail Employees v Management assumes employees must be closely supervised and controlled; only economic inducements motivate employees v Management assumes employees can be self-managers and assigned authority; motivation is intrinsic v Management applies self-management approach 11 -33


