883c7ddce054f7b68a03a549f4e87ffa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Chapter 11 – Part I Total Quality Management COB 300 Busing
Chapter 11 – Part I Total Quality Management COB 300 Busing
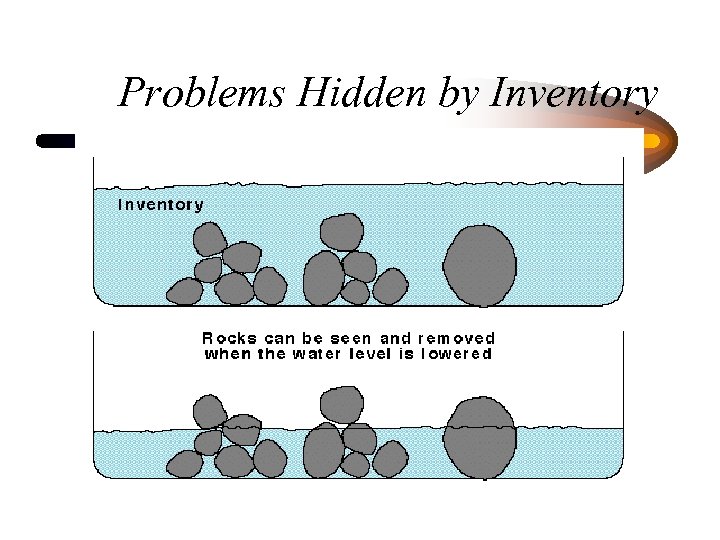 Problems Hidden by Inventory
Problems Hidden by Inventory
 Simplifying the Process • • • Plant layout Group technology U-shaped layout Reducing setup time Total preventive maintenance Simplified Process
Simplifying the Process • • • Plant layout Group technology U-shaped layout Reducing setup time Total preventive maintenance Simplified Process
 Strategy and JIT • Quality and reliability • Flexibility – product – volume • • Dependability Asset utilization People utilization Cost minimization
Strategy and JIT • Quality and reliability • Flexibility – product – volume • • Dependability Asset utilization People utilization Cost minimization
 Internally Oriented Definitions of Quality l l Quality is the degree to which a specific product conforms to a design or specification Differences in quality amount to differences in the quantity of some desired ingredient or attribute
Internally Oriented Definitions of Quality l l Quality is the degree to which a specific product conforms to a design or specification Differences in quality amount to differences in the quantity of some desired ingredient or attribute
 Externally Oriented Definitions of Quality • Quality is fitness for use • Quality consists of the capacity to satisfy wants
Externally Oriented Definitions of Quality • Quality is fitness for use • Quality consists of the capacity to satisfy wants
 A Definition of Quality Used by Many Companies Quality is consistently meeting or exceeding the customer’s needs and expectations.
A Definition of Quality Used by Many Companies Quality is consistently meeting or exceeding the customer’s needs and expectations.
 Dimensions of Service Quality • • • Reliability Responsiveness Assurance Empathy Tangibles
Dimensions of Service Quality • • • Reliability Responsiveness Assurance Empathy Tangibles
 Dimensions of Quality for Goods • • Performance Features Reliability Conformance • • Durability Serviceability Aesthetics Perceived Quality
Dimensions of Quality for Goods • • Performance Features Reliability Conformance • • Durability Serviceability Aesthetics Perceived Quality
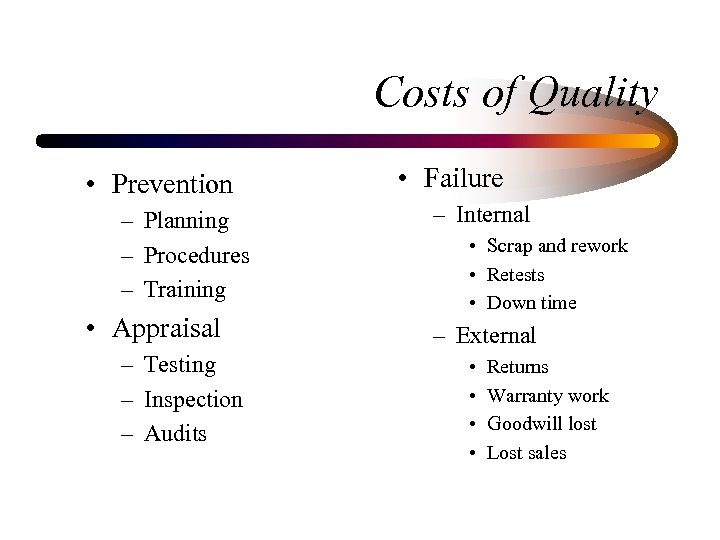 Costs of Quality • Prevention – Planning – Procedures – Training • Appraisal – Testing – Inspection – Audits • Failure – Internal • Scrap and rework • Retests • Down time – External • • Returns Warranty work Goodwill lost Lost sales
Costs of Quality • Prevention – Planning – Procedures – Training • Appraisal – Testing – Inspection – Audits • Failure – Internal • Scrap and rework • Retests • Down time – External • • Returns Warranty work Goodwill lost Lost sales
 The Background of TQM • W. Edwards Deming – System causes most defects • Joseph M. Juran – Quality planning, quality control, quality improvement • Philip Crosby – Quality is free, zero defects • Genichi Taguchi – Taguchi methods, robust design
The Background of TQM • W. Edwards Deming – System causes most defects • Joseph M. Juran – Quality planning, quality control, quality improvement • Philip Crosby – Quality is free, zero defects • Genichi Taguchi – Taguchi methods, robust design
 Components of TQM • Focus on the customer • Everyone responsible for quality • Team problem solving • Employee training • Fact-based management • Philosophy of continuous improvement
Components of TQM • Focus on the customer • Everyone responsible for quality • Team problem solving • Employee training • Fact-based management • Philosophy of continuous improvement
 Components of Continuous Improvement • Standardize and document procedures • Assign teams to identify areas for improvement • Use methods analysis and problem-solving tools • Use the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle • Document improved procedures
Components of Continuous Improvement • Standardize and document procedures • Assign teams to identify areas for improvement • Use methods analysis and problem-solving tools • Use the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle • Document improved procedures
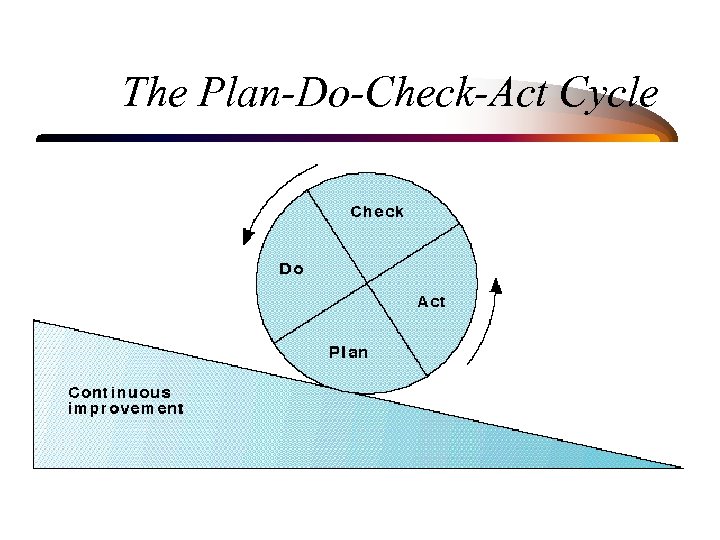 The Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle
The Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle
 Baldridge Award • Baldridge Award Criteria for 00
Baldridge Award • Baldridge Award Criteria for 00
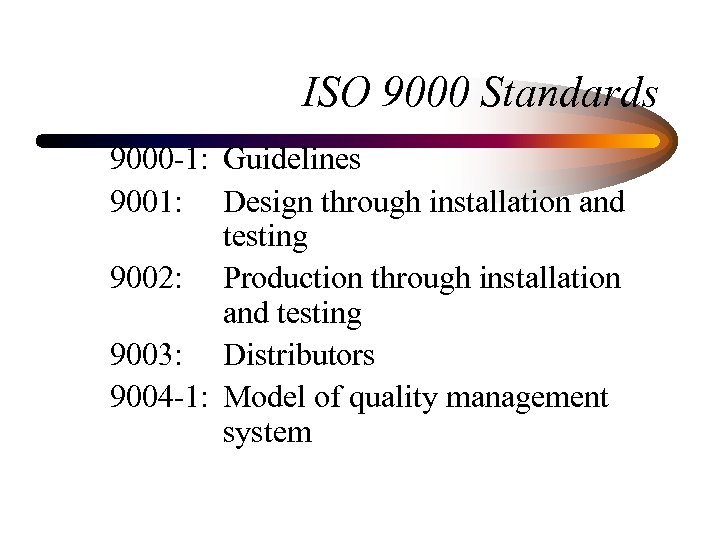 ISO 9000 Standards 9000 -1: Guidelines 9001: Design through installation and testing 9002: Production through installation and testing 9003: Distributors 9004 -1: Model of quality management system
ISO 9000 Standards 9000 -1: Guidelines 9001: Design through installation and testing 9002: Production through installation and testing 9003: Distributors 9004 -1: Model of quality management system
 Comparing Baldrige, ISO 9000 and TQM • Baldrige – U. S. Quality Award – Focus on outcomes • ISO 9000 – International standards – Focus on documentation of processes • TQM – Organizational quality philosophy – Foundation of Baldrige criteria
Comparing Baldrige, ISO 9000 and TQM • Baldrige – U. S. Quality Award – Focus on outcomes • ISO 9000 – International standards – Focus on documentation of processes • TQM – Organizational quality philosophy – Foundation of Baldrige criteria
 Chapter 11 – Part II Quality Control COB 300 C - The Operations Dimension Busing
Chapter 11 – Part II Quality Control COB 300 C - The Operations Dimension Busing
 Causes of Variation • Random Causes – difficult or expensive to control – e. g. , outside humidity, line voltage • Assignable Causes – easier to correct – e. g. , employee error, new materials
Causes of Variation • Random Causes – difficult or expensive to control – e. g. , outside humidity, line voltage • Assignable Causes – easier to correct – e. g. , employee error, new materials
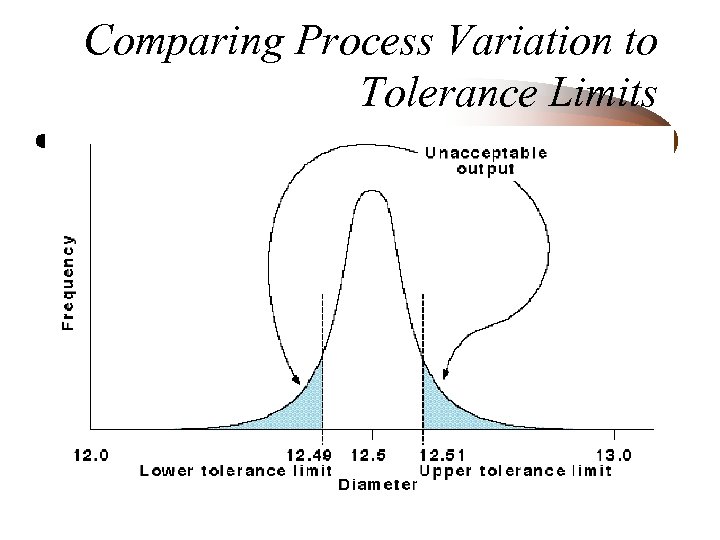 Comparing Process Variation to Tolerance Limits
Comparing Process Variation to Tolerance Limits
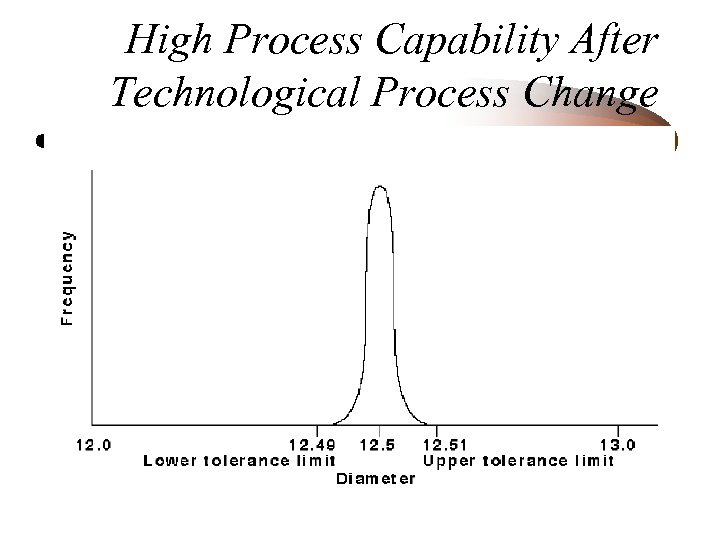 High Process Capability After Technological Process Change
High Process Capability After Technological Process Change
 Control Charts • Variables - concentrates on mean for some measurable characteristic. – diameter – length • Attribute - data is based on counts or the number of times we observe a particular event. – proportion defective/non-defective – go/no go – proportion pass/fail
Control Charts • Variables - concentrates on mean for some measurable characteristic. – diameter – length • Attribute - data is based on counts or the number of times we observe a particular event. – proportion defective/non-defective – go/no go – proportion pass/fail
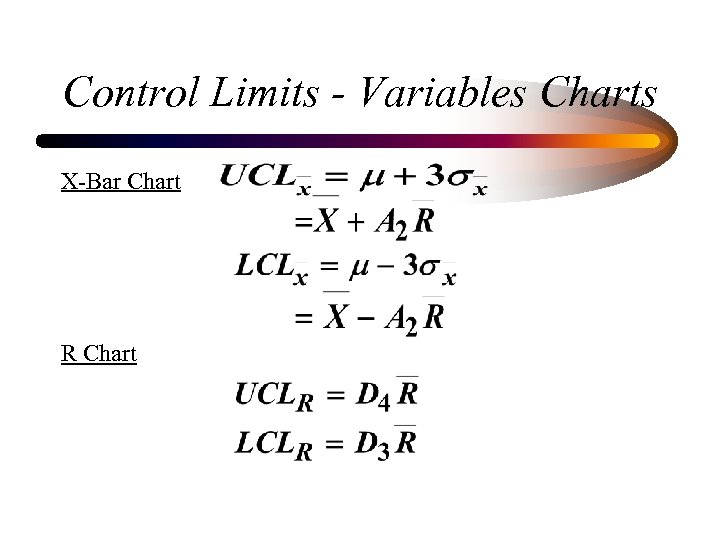 Control Limits - Variables Charts X-Bar Chart R Chart
Control Limits - Variables Charts X-Bar Chart R Chart
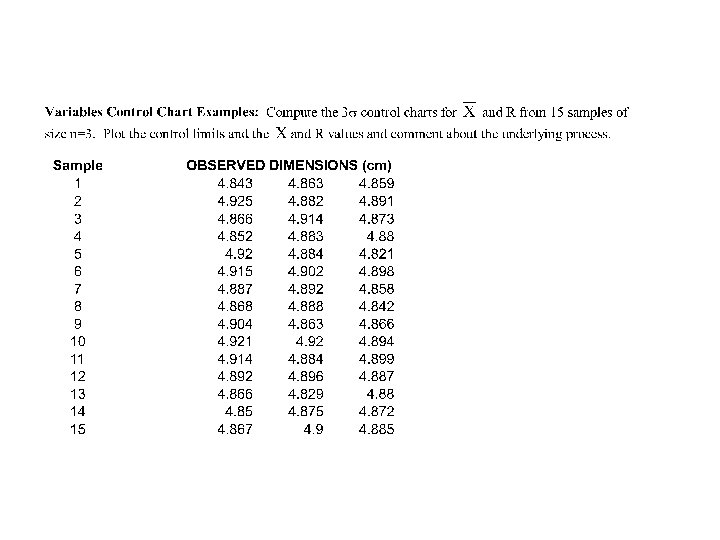
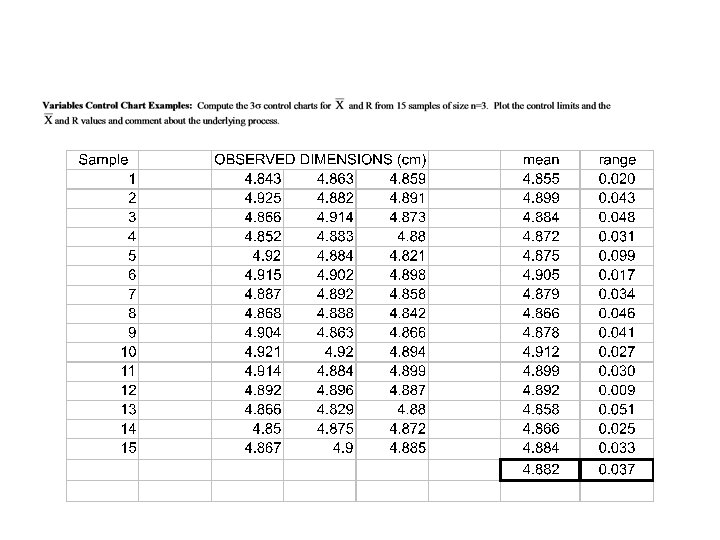
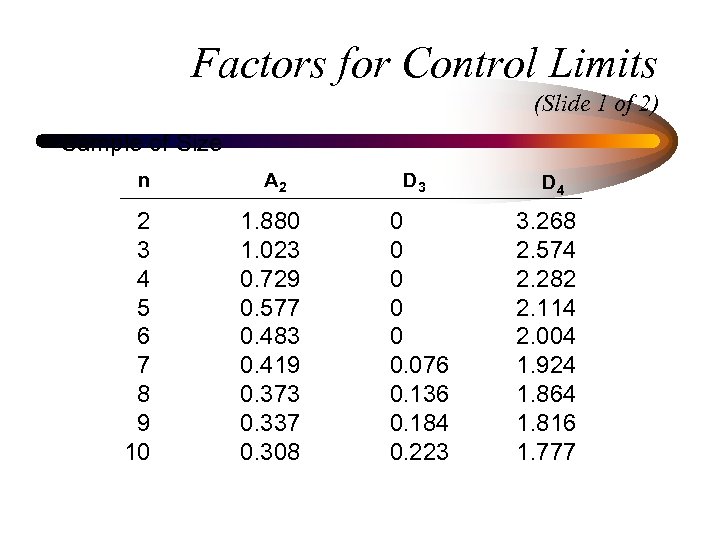 Factors for Control Limits (Slide 1 of 2) Sample of Size n 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 A 2 D 3 1. 880 1. 023 0. 729 0. 577 0. 483 0. 419 0. 373 0. 337 0. 308 0 0 0. 076 0. 136 0. 184 0. 223 D 4 3. 268 2. 574 2. 282 2. 114 2. 004 1. 924 1. 864 1. 816 1. 777
Factors for Control Limits (Slide 1 of 2) Sample of Size n 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 A 2 D 3 1. 880 1. 023 0. 729 0. 577 0. 483 0. 419 0. 373 0. 337 0. 308 0 0 0. 076 0. 136 0. 184 0. 223 D 4 3. 268 2. 574 2. 282 2. 114 2. 004 1. 924 1. 864 1. 816 1. 777
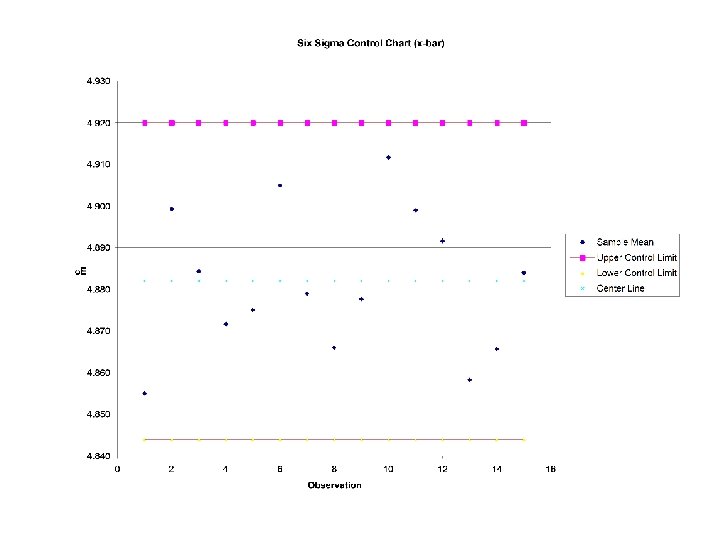
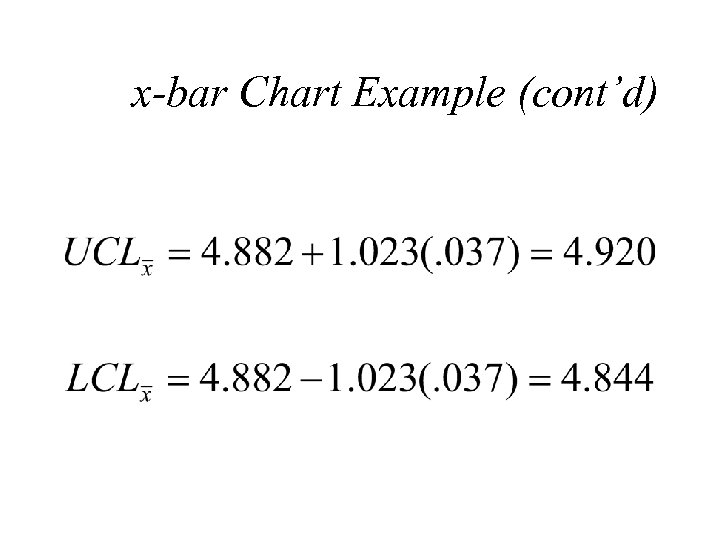 x-bar Chart Example (cont’d)
x-bar Chart Example (cont’d)
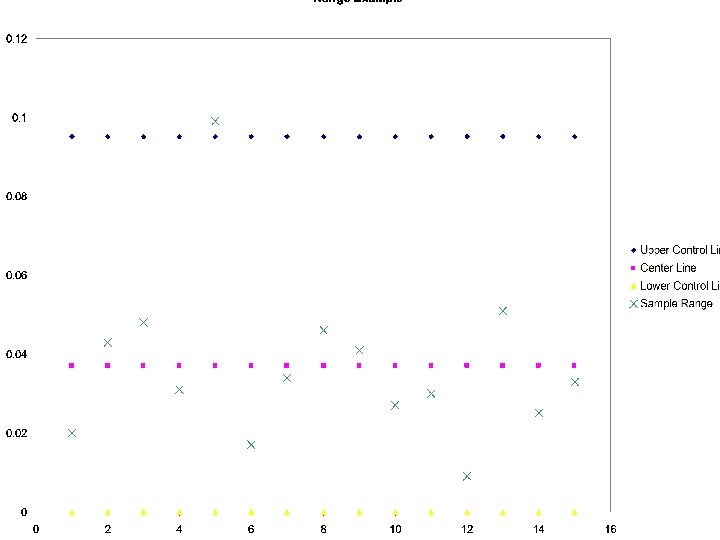
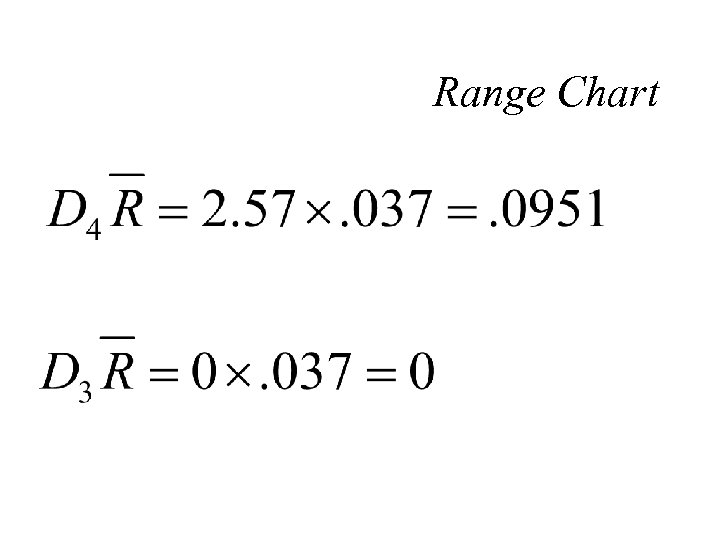 Range Chart
Range Chart
 Warning Conditions • Two successive points near limit • Run of five above or below mean • Trend • Erratic behavior
Warning Conditions • Two successive points near limit • Run of five above or below mean • Trend • Erratic behavior
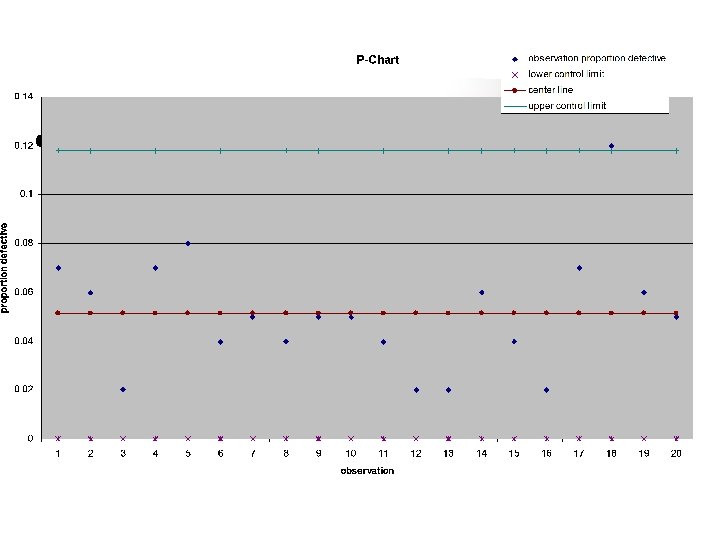
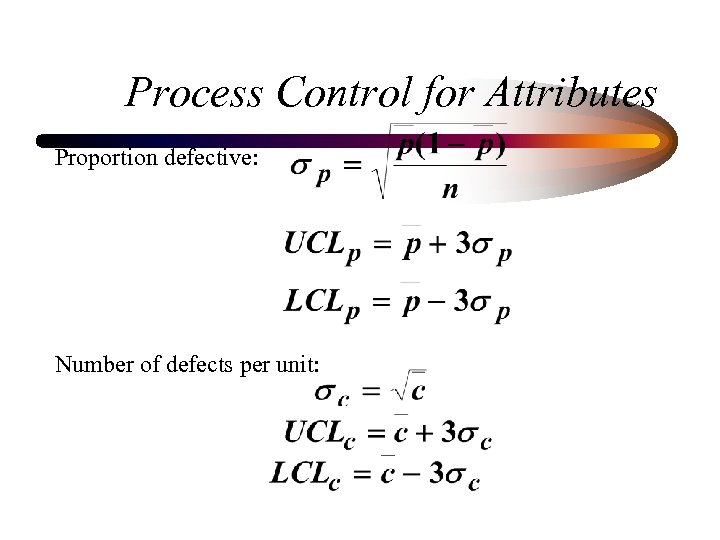 Process Control for Attributes Proportion defective: Number of defects per unit:
Process Control for Attributes Proportion defective: Number of defects per unit:
 Homework • Chapter 11 – 4, 8, 9
Homework • Chapter 11 – 4, 8, 9


