1d11e7685470e3154f55050b53ac7dc6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 CHAPTER 11 ORGANIZING INTERNATIONAL OPERATIONS 1
CHAPTER 11 ORGANIZING INTERNATIONAL OPERATIONS 1
 Pressure for Globalization Organizational Consequence of Internationalization High Aircraft Cameras Electronics Computers Telecommunications Aerospace Autos Synthetic fibers Steel Clothing Low Cement Low Packaged goods High Pressure for Local Responsiveness 2
Pressure for Globalization Organizational Consequence of Internationalization High Aircraft Cameras Electronics Computers Telecommunications Aerospace Autos Synthetic fibers Steel Clothing Low Cement Low Packaged goods High Pressure for Local Responsiveness 2
 Initial Division Structure Used for Initial Entry into International Markets · Exporting Ø Common first choice for manufacturers of technologically advanced products Ø Firm can charge premium price due to little competition · Subsidiary ØA common for handling finance-related businesses or other operations that require an on-site presence from the start 3
Initial Division Structure Used for Initial Entry into International Markets · Exporting Ø Common first choice for manufacturers of technologically advanced products Ø Firm can charge premium price due to little competition · Subsidiary ØA common for handling finance-related businesses or other operations that require an on-site presence from the start 3
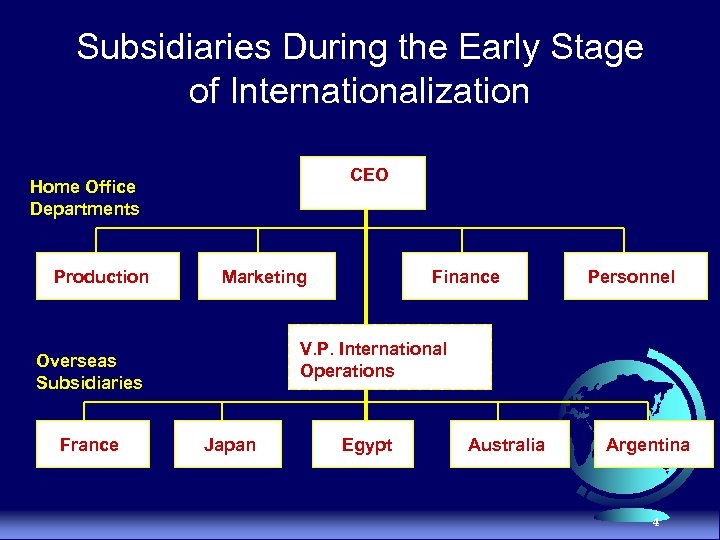 Subsidiaries During the Early Stage of Internationalization CEO Home Office Departments Production Marketing Personnel V. P. International Operations Overseas Subsidiaries France Finance Japan Egypt Australia Argentina 4
Subsidiaries During the Early Stage of Internationalization CEO Home Office Departments Production Marketing Personnel V. P. International Operations Overseas Subsidiaries France Finance Japan Egypt Australia Argentina 4
 International Division Structure u Advantages · · Takes burden off the CEO Receives top management attention Promotes overall unified approach Develops internationally experienced managers u Disadvantages · Separating domestic and international managers may cause differing objectives · Home office may not be able to allocate resources globally, thereby penalizing growth 5
International Division Structure u Advantages · · Takes burden off the CEO Receives top management attention Promotes overall unified approach Develops internationally experienced managers u Disadvantages · Separating domestic and international managers may cause differing objectives · Home office may not be able to allocate resources globally, thereby penalizing growth 5
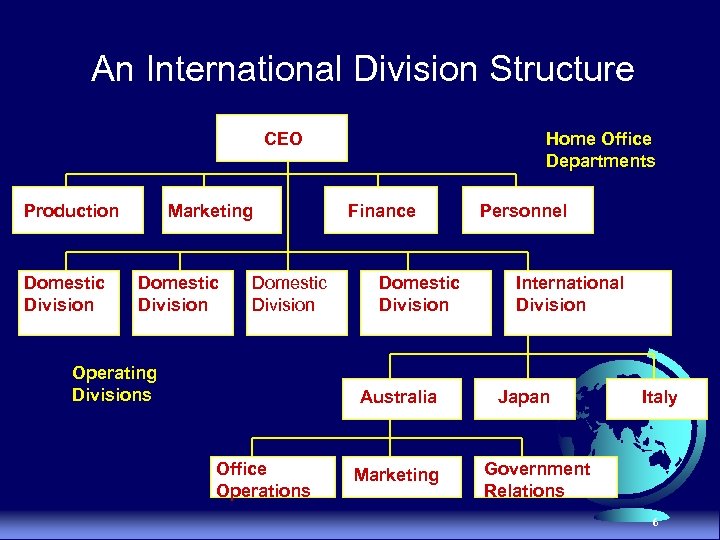 An International Division Structure CEO Production Domestic Division Marketing Domestic Division Operating Divisions Home Office Departments Finance Domestic Division Australia Office Operations Marketing Personnel International Division Japan Italy Government Relations 6
An International Division Structure CEO Production Domestic Division Marketing Domestic Division Operating Divisions Home Office Departments Finance Domestic Division Australia Office Operations Marketing Personnel International Division Japan Italy Government Relations 6
 Global Product Division Domestic divisions are given worldwide responsibility for product groups u Advantages · Helps to manage diversity · Able to cater to local needs · Marketing, production, and finance can be co-ordinated on a product-by-product global basis u Disadvantages · Duplication of facilities and staff personnel · Managers may pursue attractive short-term sites instead of long-term sites · Managers spend to much time trying to tap local instead of international markets 7
Global Product Division Domestic divisions are given worldwide responsibility for product groups u Advantages · Helps to manage diversity · Able to cater to local needs · Marketing, production, and finance can be co-ordinated on a product-by-product global basis u Disadvantages · Duplication of facilities and staff personnel · Managers may pursue attractive short-term sites instead of long-term sites · Managers spend to much time trying to tap local instead of international markets 7
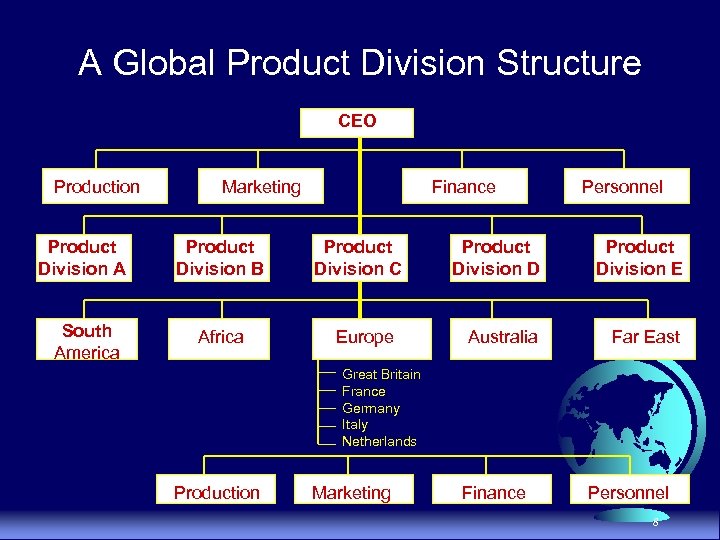 A Global Product Division Structure CEO Production Marketing Product Division A Product Division B South America Africa Finance Product Division C Europe Personnel Product Division D Product Division E Australia Far East Great Britain France Germany Italy Netherlands Production Marketing Finance Personnel 8
A Global Product Division Structure CEO Production Marketing Product Division A Product Division B South America Africa Finance Product Division C Europe Personnel Product Division D Product Division E Australia Far East Great Britain France Germany Italy Netherlands Production Marketing Finance Personnel 8
 Global Area Division Based on geographic rather than product orientation u Advantages · Reduces cost per unit · Caters to local markets · Makes rapid decisions to accommodate environmental changes u Disadvantages · Difficulty reconciling a product emphasis with geographic orientation · Ignores new research and development by division groups 9
Global Area Division Based on geographic rather than product orientation u Advantages · Reduces cost per unit · Caters to local markets · Makes rapid decisions to accommodate environmental changes u Disadvantages · Difficulty reconciling a product emphasis with geographic orientation · Ignores new research and development by division groups 9
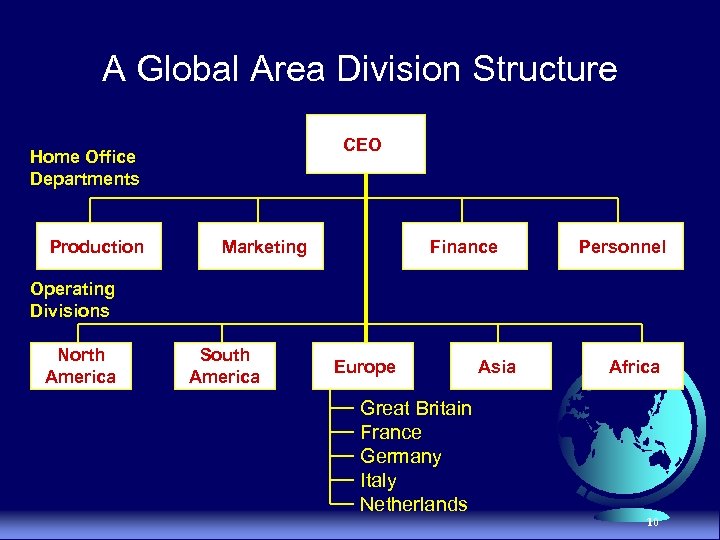 A Global Area Division Structure CEO Home Office Departments Production Marketing Finance Personnel Operating Divisions North America South America Europe Great Britain France Germany Italy Netherlands Asia Africa 10
A Global Area Division Structure CEO Home Office Departments Production Marketing Finance Personnel Operating Divisions North America South America Europe Great Britain France Germany Italy Netherlands Asia Africa 10
 Global Functional Division Worldwide operations based primarily on function and secondarily on product u Advantages · Emphasizes functional expertise · Tight centralized control · Relatively lean managerial staff u Disadvantages · Difficulty co-ordinating manufacturing and marketing · Difficulty managing multiple product lines · Only CEO can be held accountable for profits 11
Global Functional Division Worldwide operations based primarily on function and secondarily on product u Advantages · Emphasizes functional expertise · Tight centralized control · Relatively lean managerial staff u Disadvantages · Difficulty co-ordinating manufacturing and marketing · Difficulty managing multiple product lines · Only CEO can be held accountable for profits 11
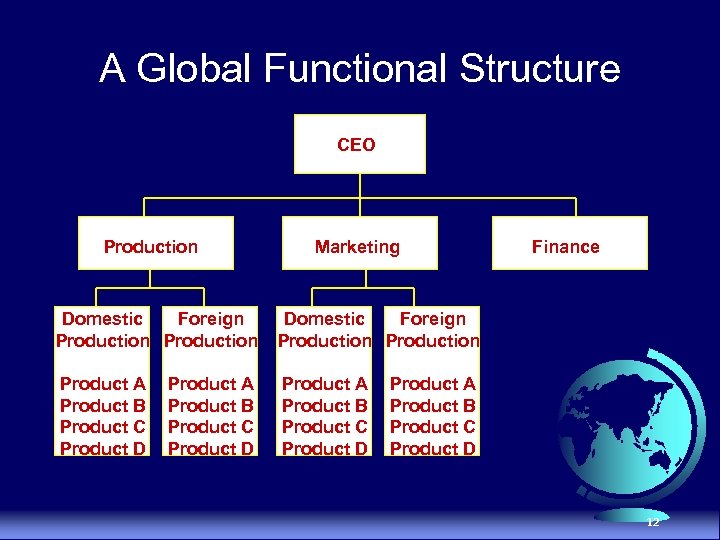 A Global Functional Structure CEO Production Marketing Domestic Foreign Production Product A Product B Product C Product D Finance Product A Product B Product C Product D 12
A Global Functional Structure CEO Production Marketing Domestic Foreign Production Product A Product B Product C Product D Finance Product A Product B Product C Product D 12
 Mixed Organization Structures Combines global product, area, and functional divisions to supplement its primary structure with a secondary one, and perhaps a tertiary (third) one u Advantages · Allows organization to create the specific type of design to meet its needs u Disadvantages · Complexity increases · Difficulty arises in co-ordinating personnel 13
Mixed Organization Structures Combines global product, area, and functional divisions to supplement its primary structure with a secondary one, and perhaps a tertiary (third) one u Advantages · Allows organization to create the specific type of design to meet its needs u Disadvantages · Complexity increases · Difficulty arises in co-ordinating personnel 13
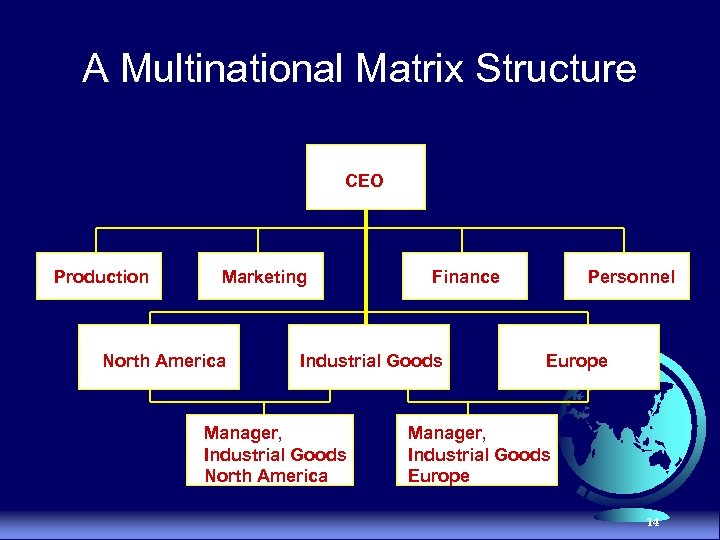 A Multinational Matrix Structure CEO Production Marketing North America Finance Industrial Goods Manager, Industrial Goods North America Personnel Europe Manager, Industrial Goods Europe 14
A Multinational Matrix Structure CEO Production Marketing North America Finance Industrial Goods Manager, Industrial Goods North America Personnel Europe Manager, Industrial Goods Europe 14
 Meeting the Challenges of Globalization u Synergy - (2 + 2 = 5) · whole is greater than the sum of its parts u Organizational Synergy · Pooling knowledge across regions · Sharing resources to meet world-wide needs · Pooling purchases for greater negotiating power · Coordinating strategies to become more efficient · Vertically integrating to be more cost effective · Creating new businesses 15
Meeting the Challenges of Globalization u Synergy - (2 + 2 = 5) · whole is greater than the sum of its parts u Organizational Synergy · Pooling knowledge across regions · Sharing resources to meet world-wide needs · Pooling purchases for greater negotiating power · Coordinating strategies to become more efficient · Vertically integrating to be more cost effective · Creating new businesses 15
 Organizing for Product Integration Strategies: · · · Mutual adjustment Use of direct, technically skilled supervisors Use of integrative leadership Technical training provided in-house Use of standard milestones in work design Flexible design standards 16
Organizing for Product Integration Strategies: · · · Mutual adjustment Use of direct, technically skilled supervisors Use of integrative leadership Technical training provided in-house Use of standard milestones in work design Flexible design standards 16
 Information Technology Key Questions: * Which information systems are needed? * Are investments are worthwhile? * How does technology fit into management’s strategic thinking ? * How should users and specialists connect within the company? * How do you design systems to improve organizational performance? 17
Information Technology Key Questions: * Which information systems are needed? * Are investments are worthwhile? * How does technology fit into management’s strategic thinking ? * How should users and specialists connect within the company? * How do you design systems to improve organizational performance? 17
 Organizational Characteristics u Formalization · The use of defined structures used in decision making, communicating, and controlling Objective - written descriptions u Subjective -informal controls u u Specialization · The assigning of individuals to specific, well-defined tasks Horizontal specialization u Vertical specialization u u Centralization · Management system in which important decisions are made at the top 18
Organizational Characteristics u Formalization · The use of defined structures used in decision making, communicating, and controlling Objective - written descriptions u Subjective -informal controls u u Specialization · The assigning of individuals to specific, well-defined tasks Horizontal specialization u Vertical specialization u u Centralization · Management system in which important decisions are made at the top 18


