a6942befe5364a8d623f00b55472f423.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Chapter 11 Marketing Channels and Supply Chain Management 11 -1
Chapter 11 Marketing Channels and Supply Chain Management 11 -1
 Road Map: Previewing the Concepts Explain why companies use distribution channels and discuss the functions these channels perform. Discuss how channel members interact and how they organize to perform the work of the channel. Identify the major channel alternatives open to a company. Explain how companies select, motivate, and evaluate channel members. Discuss the nature and importance of marketing logistics and supply chain management. 2
Road Map: Previewing the Concepts Explain why companies use distribution channels and discuss the functions these channels perform. Discuss how channel members interact and how they organize to perform the work of the channel. Identify the major channel alternatives open to a company. Explain how companies select, motivate, and evaluate channel members. Discuss the nature and importance of marketing logistics and supply chain management. 2
 What is a Distribution Channel? Set of interdependent organizations involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by the consumer or business user. 3
What is a Distribution Channel? Set of interdependent organizations involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by the consumer or business user. 3
 Why are Marketing Intermediaries Used? The use of intermediaries results from their greater efficiency in making goods available to target markets. Offers the firm more than it can achieve on its own through the intermediaries: Contacts, Experience, Specialization, Scale of operation. Purpose: match supply from producers to demand from consumers. 4
Why are Marketing Intermediaries Used? The use of intermediaries results from their greater efficiency in making goods available to target markets. Offers the firm more than it can achieve on its own through the intermediaries: Contacts, Experience, Specialization, Scale of operation. Purpose: match supply from producers to demand from consumers. 4
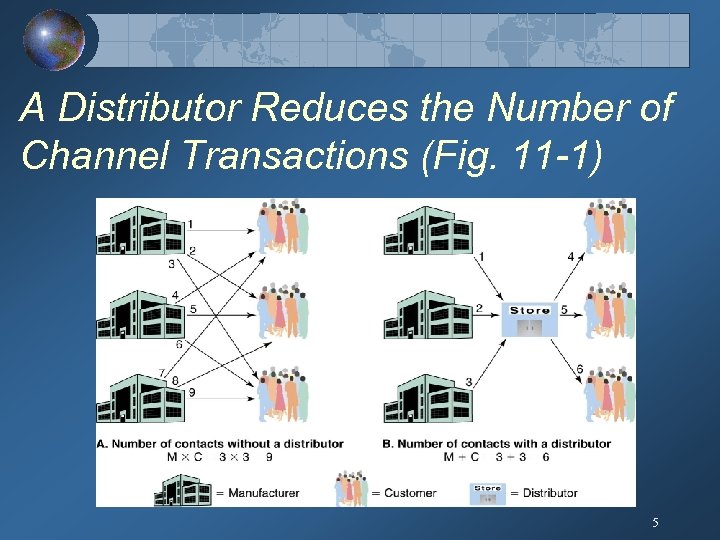 A Distributor Reduces the Number of Channel Transactions (Fig. 11 -1) 5
A Distributor Reduces the Number of Channel Transactions (Fig. 11 -1) 5
 Distribution Channel Functions These Functions Should be Assigned to the Channel Member Who Can Perform Them Most Efficiently and Effectively. Risk Taking Information Financing Promotion Physical Distribution Contact Negotiation Matching 6
Distribution Channel Functions These Functions Should be Assigned to the Channel Member Who Can Perform Them Most Efficiently and Effectively. Risk Taking Information Financing Promotion Physical Distribution Contact Negotiation Matching 6
 List and briefly discuss the marketing channel functions that are involved in completing and fulfilling transactions. Which functions apply most in each of the following situations? A retailer puts in a rush re-order for a needed Christmas item that is in short supply. An Internet marketer seeks ways to identify and contact its market. 7
List and briefly discuss the marketing channel functions that are involved in completing and fulfilling transactions. Which functions apply most in each of the following situations? A retailer puts in a rush re-order for a needed Christmas item that is in short supply. An Internet marketer seeks ways to identify and contact its market. 7
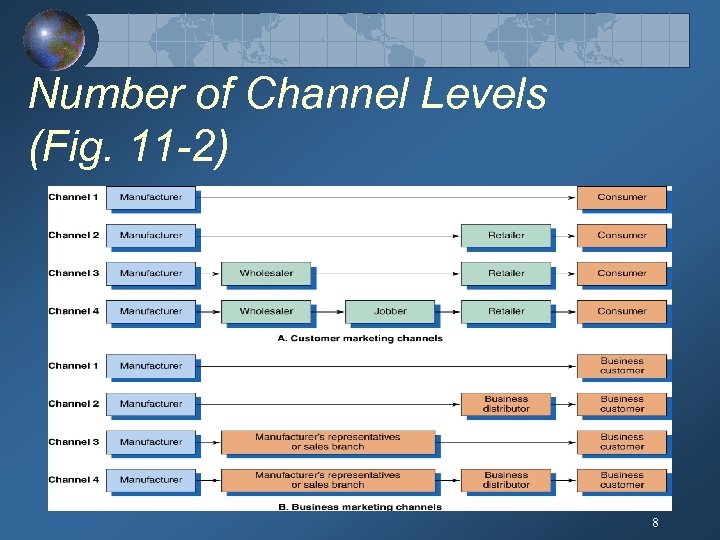 Number of Channel Levels (Fig. 11 -2) 8
Number of Channel Levels (Fig. 11 -2) 8
 Channel Behavior & Organization The channel will be most effective when: each member is assigned tasks it can do best. all members cooperate to attain overall channel goals and satisfy the target market. When this doesn’t happen, conflict occurs: Horizontal Conflict occurs among firms at the same level of the channel, i. e retailer to retailer. Vertical Conflict occurs between different levels of the same channel, i. e. wholesaler to retailer. Each channel member’s role must be specified and conflict must be managed. 9
Channel Behavior & Organization The channel will be most effective when: each member is assigned tasks it can do best. all members cooperate to attain overall channel goals and satisfy the target market. When this doesn’t happen, conflict occurs: Horizontal Conflict occurs among firms at the same level of the channel, i. e retailer to retailer. Vertical Conflict occurs between different levels of the same channel, i. e. wholesaler to retailer. Each channel member’s role must be specified and conflict must be managed. 9
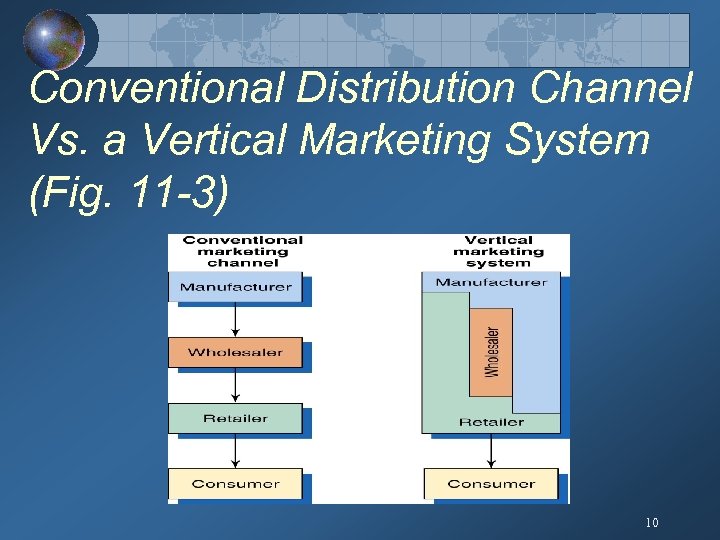 Conventional Distribution Channel Vs. a Vertical Marketing System (Fig. 11 -3) 10
Conventional Distribution Channel Vs. a Vertical Marketing System (Fig. 11 -3) 10
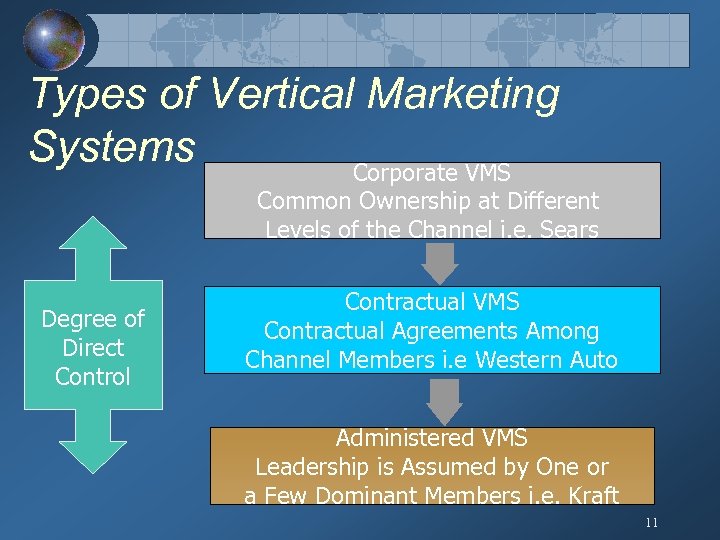 Types of Vertical Marketing Systems Corporate VMS Common Ownership at Different Levels of the Channel i. e. Sears Degree of Direct Control Contractual VMS Contractual Agreements Among Channel Members i. e Western Auto Administered VMS Leadership is Assumed by One or a Few Dominant Members i. e. Kraft 11
Types of Vertical Marketing Systems Corporate VMS Common Ownership at Different Levels of the Channel i. e. Sears Degree of Direct Control Contractual VMS Contractual Agreements Among Channel Members i. e Western Auto Administered VMS Leadership is Assumed by One or a Few Dominant Members i. e. Kraft 11
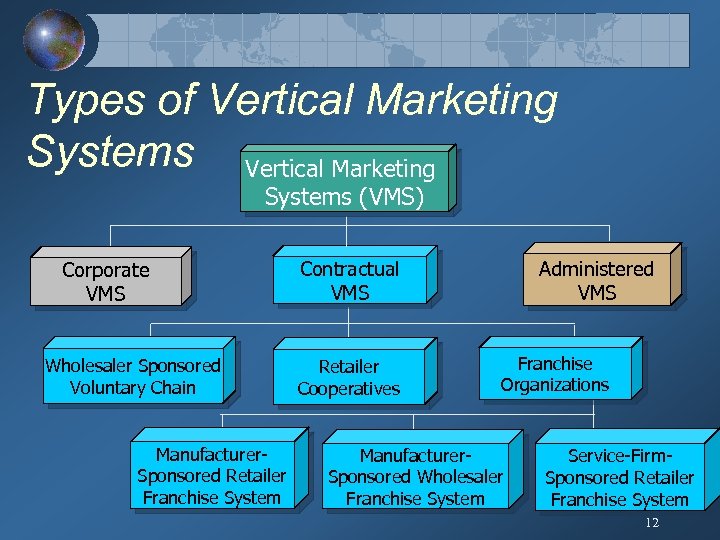 Types of Vertical Marketing Systems (VMS) Corporate VMS Wholesaler Sponsored Voluntary Chain Manufacturer. Sponsored Retailer Franchise System Administered VMS Contractual VMS Retailer Cooperatives Franchise Organizations Manufacturer. Sponsored Wholesaler Franchise System Service-Firm. Sponsored Retailer Franchise System 12
Types of Vertical Marketing Systems (VMS) Corporate VMS Wholesaler Sponsored Voluntary Chain Manufacturer. Sponsored Retailer Franchise System Administered VMS Contractual VMS Retailer Cooperatives Franchise Organizations Manufacturer. Sponsored Wholesaler Franchise System Service-Firm. Sponsored Retailer Franchise System 12
 Innovations in Marketing Systems Horizontal Marketing System Hybrid Marketing System Two or More Companies at One Channel Level Join Together to Follow a New Marketing Opportunity. A Single Firm Sets Up Two or More Marketing Channels to Reach One or More Customer Segments. Example: Banks in Grocery Stores Retailers, Catalogs, and Sales Force 13
Innovations in Marketing Systems Horizontal Marketing System Hybrid Marketing System Two or More Companies at One Channel Level Join Together to Follow a New Marketing Opportunity. A Single Firm Sets Up Two or More Marketing Channels to Reach One or More Customer Segments. Example: Banks in Grocery Stores Retailers, Catalogs, and Sales Force 13
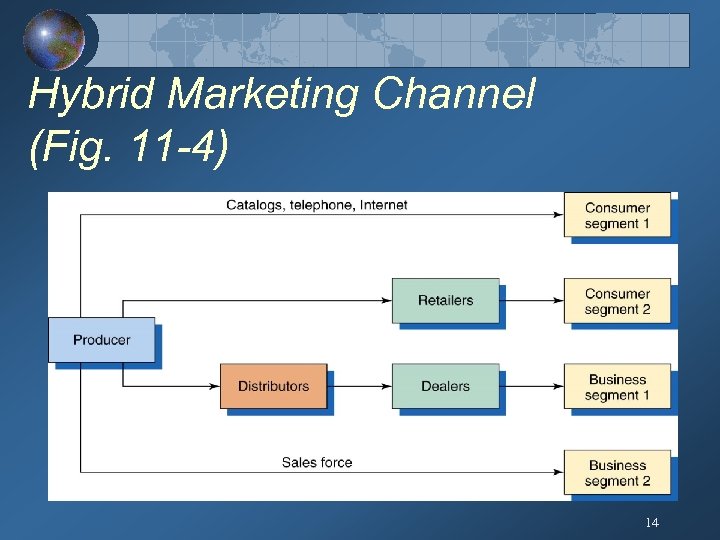 Hybrid Marketing Channel (Fig. 11 -4) 14
Hybrid Marketing Channel (Fig. 11 -4) 14
 Changing Channel Organization A Major Trend is Toward Disintermediation Which Means that Product and Service Producers are Bypassing Intermediaries and Going Directly to Final Buyers or That New Types of Channel Intermediaries are Emerging to Displace Traditional Ones. 15
Changing Channel Organization A Major Trend is Toward Disintermediation Which Means that Product and Service Producers are Bypassing Intermediaries and Going Directly to Final Buyers or That New Types of Channel Intermediaries are Emerging to Displace Traditional Ones. 15
 Channel Design Decisions Analyzing Consumer Service Needs Setting Channel Objectives & Constraints Identifying Major Alternatives Types of Intermediaries Number of Intermediaries Responsibilities of Intermediaries Evaluating the Major Alternatives Designing International Distribution Channels 16
Channel Design Decisions Analyzing Consumer Service Needs Setting Channel Objectives & Constraints Identifying Major Alternatives Types of Intermediaries Number of Intermediaries Responsibilities of Intermediaries Evaluating the Major Alternatives Designing International Distribution Channels 16
 Number of Marketing Intermediaries Intensive Distribution Selective Distribution Exclusive Distribution 17
Number of Marketing Intermediaries Intensive Distribution Selective Distribution Exclusive Distribution 17
 Decide which distribution strategy-intensive, selective, or exclusive--is used for the following products, and why: Piaget watches, Acura automobiles, Snickers candy bars. 18
Decide which distribution strategy-intensive, selective, or exclusive--is used for the following products, and why: Piaget watches, Acura automobiles, Snickers candy bars. 18
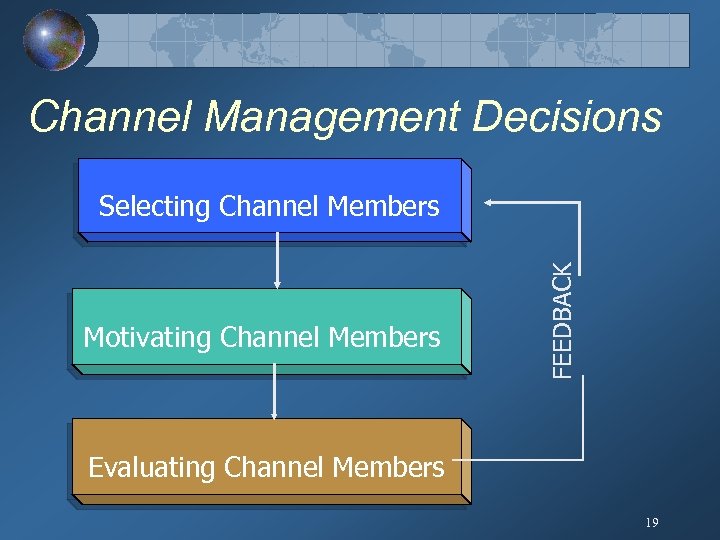 Channel Management Decisions Motivating Channel Members FEEDBACK Selecting Channel Members Evaluating Channel Members 19
Channel Management Decisions Motivating Channel Members FEEDBACK Selecting Channel Members Evaluating Channel Members 19
 Marketing Logistics and Supply Chain Management Involves getting the right product to the right customers in the right place at the right time. Marketing logistics addresses: Outbound distribution, Inbound distribution, Reverse distribution, Entire supply chain management. 20
Marketing Logistics and Supply Chain Management Involves getting the right product to the right customers in the right place at the right time. Marketing logistics addresses: Outbound distribution, Inbound distribution, Reverse distribution, Entire supply chain management. 20
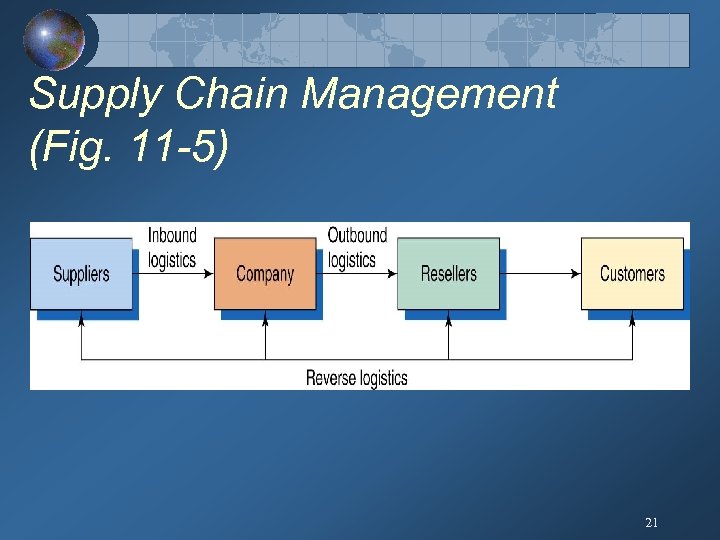 Supply Chain Management (Fig. 11 -5) 21
Supply Chain Management (Fig. 11 -5) 21
 Goals of the Logistics System Higher Distribution Costs; Higher Customer Service Levels Goal: To Provide a Targeted Level of Customer Service at the Least Cost. Lower Distribution Costs; Lower Customer Service Levels 22
Goals of the Logistics System Higher Distribution Costs; Higher Customer Service Levels Goal: To Provide a Targeted Level of Customer Service at the Least Cost. Lower Distribution Costs; Lower Customer Service Levels 22
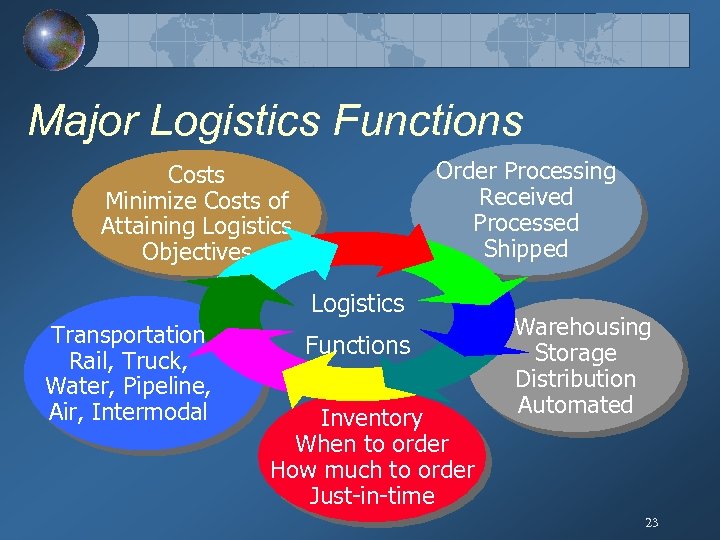 Major Logistics Functions Order Processing Received Processed Shipped Costs Minimize Costs of Attaining Logistics Objectives Logistics Transportation Rail, Truck, Water, Pipeline, Air, Intermodal Functions Inventory When to order How much to order Just-in-time Warehousing Storage Distribution Automated 23
Major Logistics Functions Order Processing Received Processed Shipped Costs Minimize Costs of Attaining Logistics Objectives Logistics Transportation Rail, Truck, Water, Pipeline, Air, Intermodal Functions Inventory When to order How much to order Just-in-time Warehousing Storage Distribution Automated 23
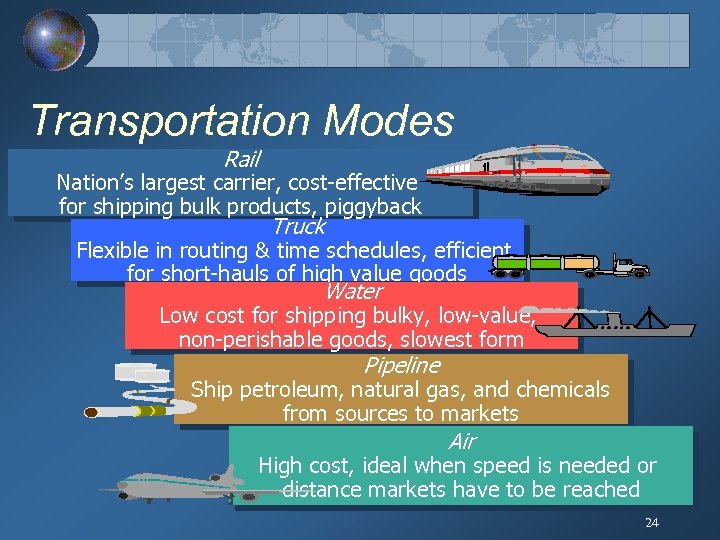 Transportation Modes Rail Nation’s largest carrier, cost-effective for shipping bulk products, piggyback Truck Flexible in routing & time schedules, efficient for short-hauls of high value goods Water Low cost for shipping bulky, low-value, non-perishable goods, slowest form Pipeline Ship petroleum, natural gas, and chemicals from sources to markets Air High cost, ideal when speed is needed or distance markets have to be reached 24
Transportation Modes Rail Nation’s largest carrier, cost-effective for shipping bulk products, piggyback Truck Flexible in routing & time schedules, efficient for short-hauls of high value goods Water Low cost for shipping bulky, low-value, non-perishable goods, slowest form Pipeline Ship petroleum, natural gas, and chemicals from sources to markets Air High cost, ideal when speed is needed or distance markets have to be reached 24
 Integrated Logistics Management Concept Recognizes that Providing Better Customer Service and Trimming Distribution Costs Requires Teamwork, Both Inside the Company and Among All the Marketing Channel Organizations. Involves: Cross-functional teamwork inside the company Building channel partnerships Third-party logistics 25
Integrated Logistics Management Concept Recognizes that Providing Better Customer Service and Trimming Distribution Costs Requires Teamwork, Both Inside the Company and Among All the Marketing Channel Organizations. Involves: Cross-functional teamwork inside the company Building channel partnerships Third-party logistics 25
 Toys “R” Us Partner Western Publishing Group partners with Toys “R” Us to create mini-bookstore sections – called Books “R” Us – within each store. This helps to build channel partnerships that benefit both companies. 26
Toys “R” Us Partner Western Publishing Group partners with Toys “R” Us to create mini-bookstore sections – called Books “R” Us – within each store. This helps to build channel partnerships that benefit both companies. 26
 Rest Stop: Reviewing the Concept Explain why companies use distribution channels and discuss the functions these channels perform. Discuss how channel members interact and how they organize to perform the work of the channel. Identify the major channel alternatives open to a company. Explain how companies select, motivate, and evaluate channel members. Discuss the nature and importance of marketing logistics and supply chain management. 27
Rest Stop: Reviewing the Concept Explain why companies use distribution channels and discuss the functions these channels perform. Discuss how channel members interact and how they organize to perform the work of the channel. Identify the major channel alternatives open to a company. Explain how companies select, motivate, and evaluate channel members. Discuss the nature and importance of marketing logistics and supply chain management. 27


