b6d28d1fa7e952add385ed6407f2cc27.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 CHAPTER 11 Customer Relationship Management and Supply Chain Management
CHAPTER 11 Customer Relationship Management and Supply Chain Management
 Announcements Today n n n Chapter 11 – CRM and SCM Project 6 – Solver Case due by midnight Review Project 7 – Decision Support n Review of all functions and formulas used Coming Weeks n n n Quiz 3 – Excel Solver Chapter 12 & Tech Guide 4 Final Exam Review
Announcements Today n n n Chapter 11 – CRM and SCM Project 6 – Solver Case due by midnight Review Project 7 – Decision Support n Review of all functions and formulas used Coming Weeks n n n Quiz 3 – Excel Solver Chapter 12 & Tech Guide 4 Final Exam Review
 CHAPTER OUTLINE 11. 1 Defining Customer Relationship Management 11. 2 Operational CRM Systems 11. 3 Analytical CRM Systems 11. 4 Other Types of CRM Systems 11. 5 Supply Chains 11. 6 Supply Chain Management 11. 7 IT Support for Supply Chain Management
CHAPTER OUTLINE 11. 1 Defining Customer Relationship Management 11. 2 Operational CRM Systems 11. 3 Analytical CRM Systems 11. 4 Other Types of CRM Systems 11. 5 Supply Chains 11. 6 Supply Chain Management 11. 7 IT Support for Supply Chain Management
 Chapter Opening Case: The Next Step in Customer Relationship Management Source: Maxx-Studio/Shutterstock Taste Profiling Persuasion Profiling
Chapter Opening Case: The Next Step in Customer Relationship Management Source: Maxx-Studio/Shutterstock Taste Profiling Persuasion Profiling
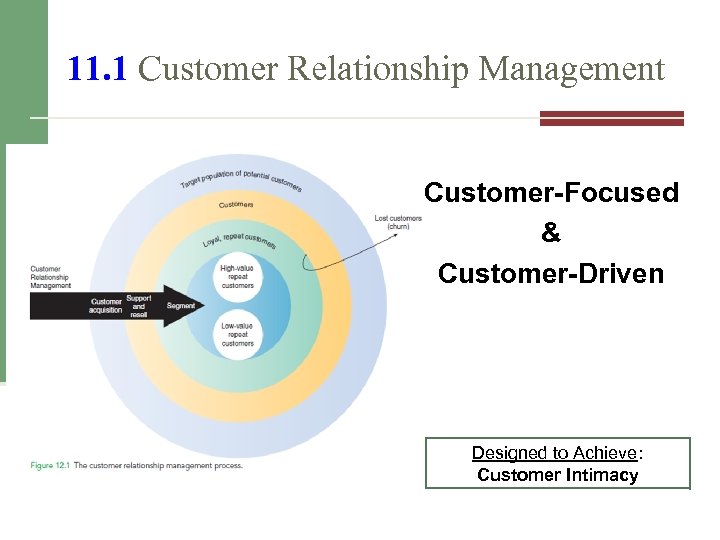 11. 1 Customer Relationship Management Customer-Focused & Customer-Driven Designed to Achieve: Customer Intimacy
11. 1 Customer Relationship Management Customer-Focused & Customer-Driven Designed to Achieve: Customer Intimacy
 From Neighborhood Stores……. © MONKEY BUSINESS-LBR/Age Fotostock America, Inc. Personal
From Neighborhood Stores……. © MONKEY BUSINESS-LBR/Age Fotostock America, Inc. Personal
 …. To Today Mobile population The Web Giant malls Impersonal
…. To Today Mobile population The Web Giant malls Impersonal
 Why do we need CRM? n Cost n Dissatisfied customer impacts n Increasing the customer retention rate n Odds of selling to new customers n Retention of complaining customers
Why do we need CRM? n Cost n Dissatisfied customer impacts n Increasing the customer retention rate n Odds of selling to new customers n Retention of complaining customers
 Why do we need CRM? Value of a customer v. Duration of the relationship v. Number of relationships (e. g. more than one product) v. Profitability of the relationship GOAL of CRM: Maximize lifetime value of a customer
Why do we need CRM? Value of a customer v. Duration of the relationship v. Number of relationships (e. g. more than one product) v. Profitability of the relationship GOAL of CRM: Maximize lifetime value of a customer
 Tenets of CRM n One-to-one relationship between a customer and a seller. n Treat different customers differently. n Keep profitable customers and maximize lifetime revenue from them.
Tenets of CRM n One-to-one relationship between a customer and a seller. n Treat different customers differently. n Keep profitable customers and maximize lifetime revenue from them.
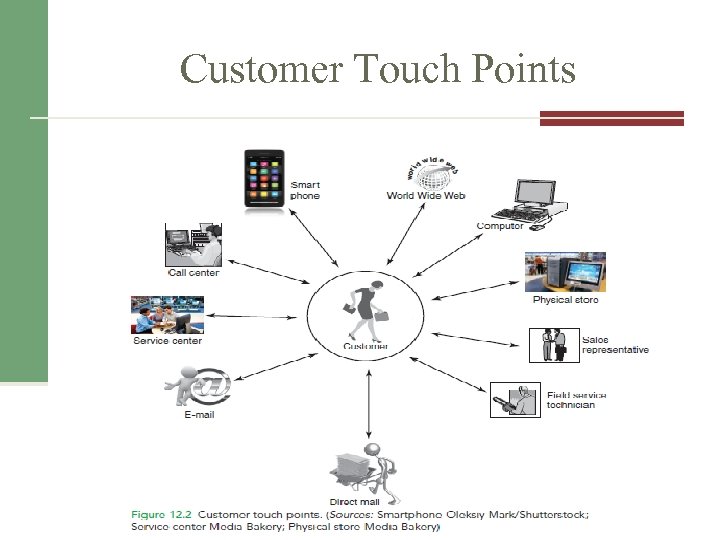 Customer Touch Points
Customer Touch Points
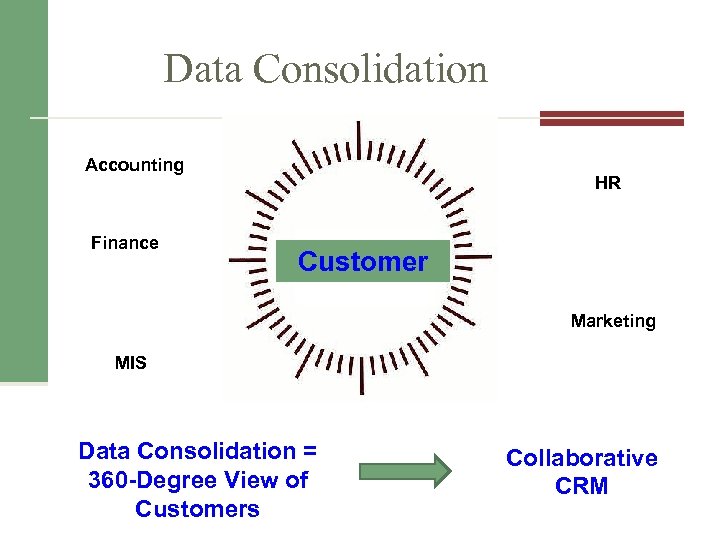 Data Consolidation Accounting Finance HR Customer Marketing MIS Data Consolidation = 360 -Degree View of Customers Collaborative CRM
Data Consolidation Accounting Finance HR Customer Marketing MIS Data Consolidation = 360 -Degree View of Customers Collaborative CRM
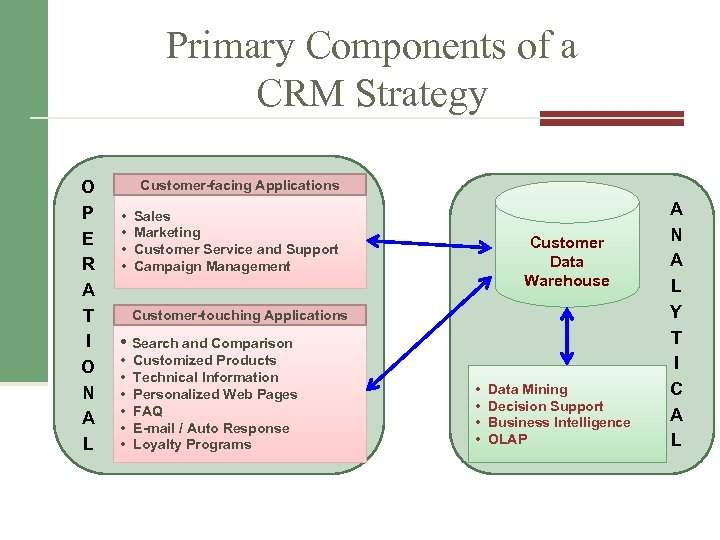 Primary Components of a CRM Strategy O P E R A T I O N A L Customer-facing Applications • • Sales Marketing Customer Service and Support Campaign Management Customer Data Warehouse Customer-touching Applications • Search and Comparison • • • Customized Products Technical Information Personalized Web Pages FAQ E-mail / Auto Response Loyalty Programs • • Data Mining Decision Support Business Intelligence OLAP A N A L Y T I C A L
Primary Components of a CRM Strategy O P E R A T I O N A L Customer-facing Applications • • Sales Marketing Customer Service and Support Campaign Management Customer Data Warehouse Customer-touching Applications • Search and Comparison • • • Customized Products Technical Information Personalized Web Pages FAQ E-mail / Auto Response Loyalty Programs • • Data Mining Decision Support Business Intelligence OLAP A N A L Y T I C A L
 11. 2 Operational CRM Supports the front-office business processes (i. e. those that directly interact w/customers) Marketing List Generator Campaign Mgmt Cross Selling / Up Selling Sales Mgmt Contact Mgmt Opportunity Mgmt Customer Service Contact Center Web-Based Self Service Call Scripting Two major components: 1. 2. Customer-facing applications Customer-touching applications
11. 2 Operational CRM Supports the front-office business processes (i. e. those that directly interact w/customers) Marketing List Generator Campaign Mgmt Cross Selling / Up Selling Sales Mgmt Contact Mgmt Opportunity Mgmt Customer Service Contact Center Web-Based Self Service Call Scripting Two major components: 1. 2. Customer-facing applications Customer-touching applications
 Operational CRM: Customer-Facing Applications Customer service and support Sales force automation Marketing • Cross Selling • Up Selling • Bundling Campaign management © Mustafa Almir Mahmoud/Age Fotostock America, Inc.
Operational CRM: Customer-Facing Applications Customer service and support Sales force automation Marketing • Cross Selling • Up Selling • Bundling Campaign management © Mustafa Almir Mahmoud/Age Fotostock America, Inc.
 Operational CRM: Customer-Touching Applications • Search and comparison capabilities • Technical and other information and services • Customized products and services Source: © Spencer Grant/Photo. Edit • Loyalty programs
Operational CRM: Customer-Touching Applications • Search and comparison capabilities • Technical and other information and services • Customized products and services Source: © Spencer Grant/Photo. Edit • Loyalty programs
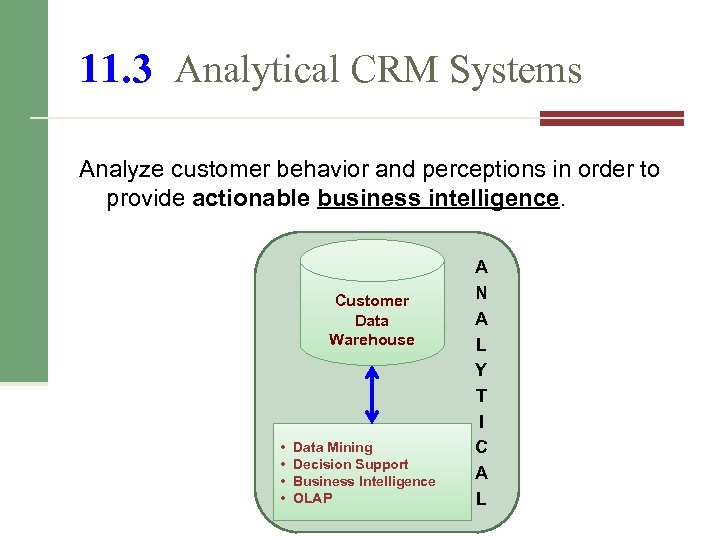 11. 3 Analytical CRM Systems Analyze customer behavior and perceptions in order to provide actionable business intelligence. Customer Data Warehouse • • Data Mining Decision Support Business Intelligence OLAP A N A L Y T I C A L
11. 3 Analytical CRM Systems Analyze customer behavior and perceptions in order to provide actionable business intelligence. Customer Data Warehouse • • Data Mining Decision Support Business Intelligence OLAP A N A L Y T I C A L
 11. 4 Other Types of Customer Relationship Management Systems On-demand CRM Hosted by an external vendor in the vendor’s data center Mobile CRM Interacting directly with customers through mobile devices Open-source CRM Source code openly available to developers and users
11. 4 Other Types of Customer Relationship Management Systems On-demand CRM Hosted by an external vendor in the vendor’s data center Mobile CRM Interacting directly with customers through mobile devices Open-source CRM Source code openly available to developers and users
 Challenges and Future of Customer Relationship Management Systems Challenges • Social Media Future • Supplier Relationship Management • Partner Relationship Management • Employee Relationships Management
Challenges and Future of Customer Relationship Management Systems Challenges • Social Media Future • Supplier Relationship Management • Partner Relationship Management • Employee Relationships Management
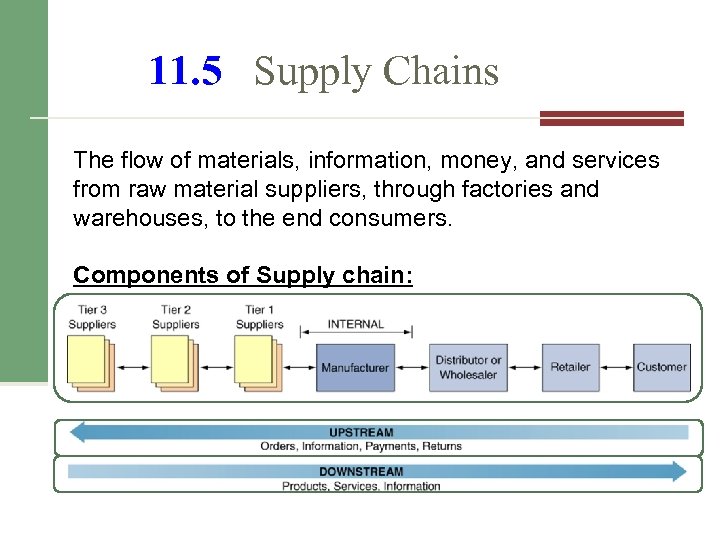 11. 5 Supply Chains The flow of materials, information, money, and services from raw material suppliers, through factories and warehouses, to the end consumers. Components of Supply chain:
11. 5 Supply Chains The flow of materials, information, money, and services from raw material suppliers, through factories and warehouses, to the end consumers. Components of Supply chain:
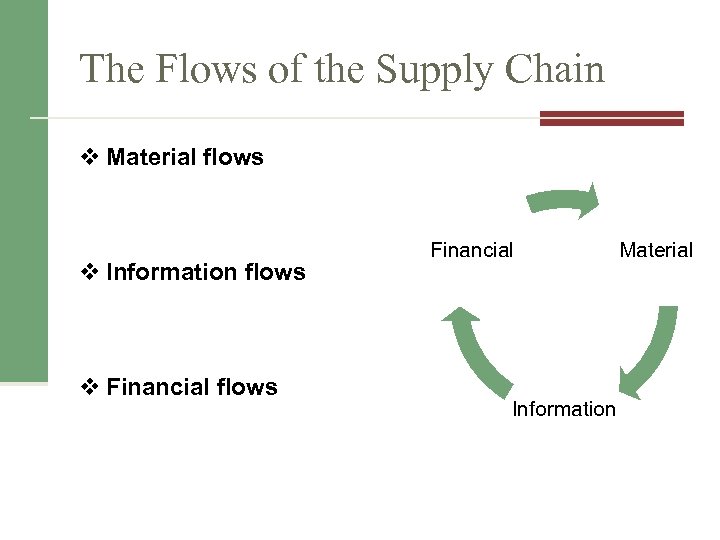 The Flows of the Supply Chain v Material flows v Information flows v Financial flows Financial Information Material
The Flows of the Supply Chain v Material flows v Information flows v Financial flows Financial Information Material
 11. 6 Supply Chain Management The function of planning, organizing, and optimizing the various activities performed along the supply chain These systems are considered to be a type of Interorganizational information system (IOS). Goal of an SCM System: Reduce problems along supply chain
11. 6 Supply Chain Management The function of planning, organizing, and optimizing the various activities performed along the supply chain These systems are considered to be a type of Interorganizational information system (IOS). Goal of an SCM System: Reduce problems along supply chain
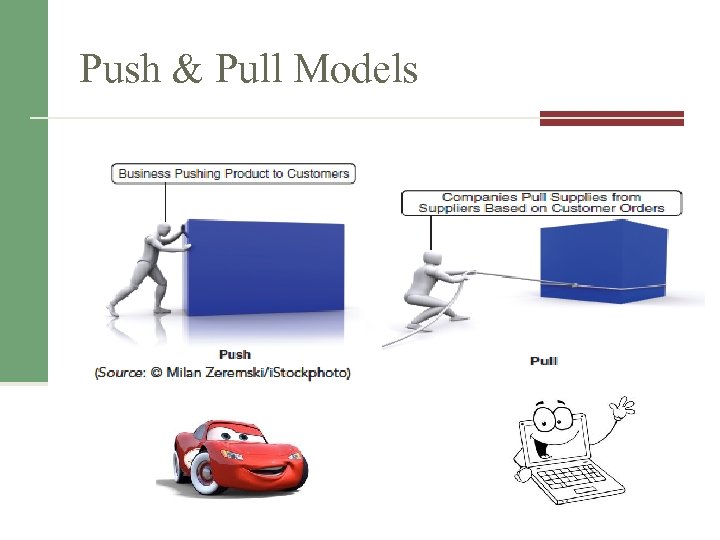 Push & Pull Models
Push & Pull Models
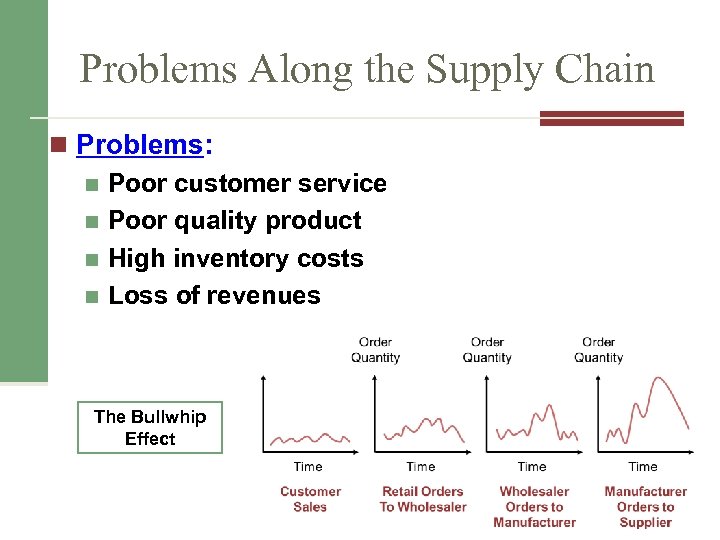 Problems Along the Supply Chain n Problems: n Poor customer service n Poor quality product n High inventory costs n Loss of revenues The Bullwhip Effect
Problems Along the Supply Chain n Problems: n Poor customer service n Poor quality product n High inventory costs n Loss of revenues The Bullwhip Effect
 Solutions to Supply Chain Problems n Using inventories: n Just-in-time inventory n Information sharing: n Vendor-managed inventory
Solutions to Supply Chain Problems n Using inventories: n Just-in-time inventory n Information sharing: n Vendor-managed inventory
 11. 7 Information Technology Support for Supply Chain Management Electronic data interchange (EDI) Enables business partners to exchange routing documents electronically n Example n EDI is accomplished through the use of Extranets The main goal of extranets is to foster collaboration between business partners. n An extranet is open to selected B 2 B suppliers, customers and other business partners. n
11. 7 Information Technology Support for Supply Chain Management Electronic data interchange (EDI) Enables business partners to exchange routing documents electronically n Example n EDI is accomplished through the use of Extranets The main goal of extranets is to foster collaboration between business partners. n An extranet is open to selected B 2 B suppliers, customers and other business partners. n
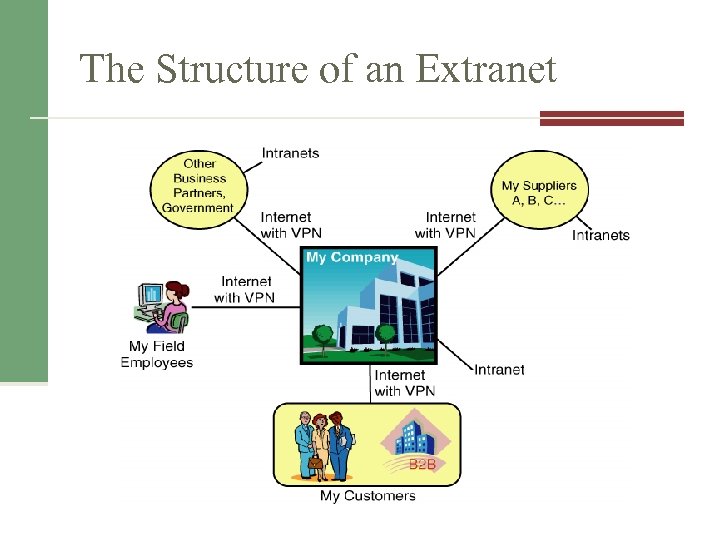 The Structure of an Extranet
The Structure of an Extranet
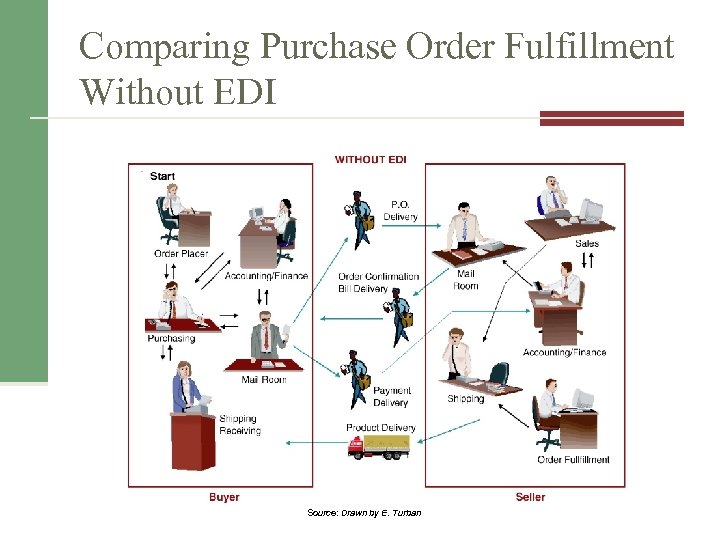 Comparing Purchase Order Fulfillment Without EDI Source: Drawn by E. Turban
Comparing Purchase Order Fulfillment Without EDI Source: Drawn by E. Turban
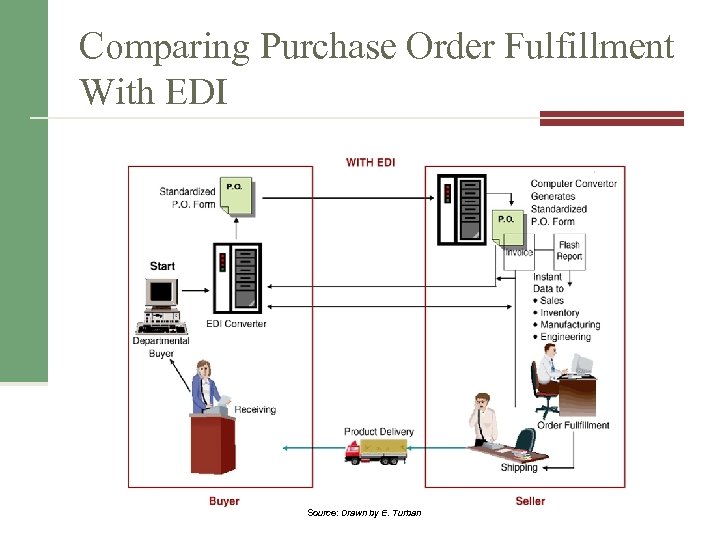 Comparing Purchase Order Fulfillment With EDI Source: Drawn by E. Turban
Comparing Purchase Order Fulfillment With EDI Source: Drawn by E. Turban
 EDI Benefits n Minimize data entry errors n Length of messages are shorter n Messages are secured n Reduces cycle time n Increases productivity n Enhances customer service n Minimizes paper usage and storage
EDI Benefits n Minimize data entry errors n Length of messages are shorter n Messages are secured n Reduces cycle time n Increases productivity n Enhances customer service n Minimizes paper usage and storage
 EDI Limitations n Significant initial investment to implement n Ongoing operating costs are high due to the use of expensive, private VANs n Traditional EDI system is inflexible n Long startup period n Multiple EDI standards exist
EDI Limitations n Significant initial investment to implement n Ongoing operating costs are high due to the use of expensive, private VANs n Traditional EDI system is inflexible n Long startup period n Multiple EDI standards exist


