fad3f59fd922c98f696e1f2586c64052.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 Chapter 11 Conceiving Children: Process and Choice
Chapter 11 Conceiving Children: Process and Choice
 Discussion question Do you want to have children? List the top three or four reasons for your choice.
Discussion question Do you want to have children? List the top three or four reasons for your choice.
 Parenthood as an Option • More people than in the past are choosing to be “kid-free. ” – In 2004, 19. 3% of women age 40 -44 were childless (compared with 9% in 1975) • Advantages of remaining childless – more time for self and companion – more financial resources – marriages less stressful – more spontaneity – more devotion to career
Parenthood as an Option • More people than in the past are choosing to be “kid-free. ” – In 2004, 19. 3% of women age 40 -44 were childless (compared with 9% in 1975) • Advantages of remaining childless – more time for self and companion – more financial resources – marriages less stressful – more spontaneity – more devotion to career
 Parenthood as an Option (cont. ) • Advantages to having children – children give & receive love – may enhance relationship – builds self-esteem, sense of accomplishment – greater meaning & satisfaction
Parenthood as an Option (cont. ) • Advantages to having children – children give & receive love – may enhance relationship – builds self-esteem, sense of accomplishment – greater meaning & satisfaction
 Becoming Pregnant • Enhancing the possibility – intercourse just prior to or at ovulation – predicting ovulation • mucus, calendar, BT methods • ovulation-predictor urine tests--measure the rise in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs before ovulation (available OC). • Children conceived during the months of April and May have a high %age of abnormal genomes. Probable due to pesticides or fertilizers.
Becoming Pregnant • Enhancing the possibility – intercourse just prior to or at ovulation – predicting ovulation • mucus, calendar, BT methods • ovulation-predictor urine tests--measure the rise in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs before ovulation (available OC). • Children conceived during the months of April and May have a high %age of abnormal genomes. Probable due to pesticides or fertilizers.
 Infertility • Defined as inability to conceive after trying for 1 yr – Occurs in approx. 10 -15% of U. S. couples trying to conceive – More than 6 months of trying --> consider consulting a health care practitioner • 60% of couples become pregnant after trying for 6 mos. • Can be due to male or female factors; both partners should be medically evaluated • Causes – Can be complex; often difficult to determine – Remain unidentified in as many as 15% of cases • Can be extremely emotionally painful for couples and pose challenges for their sexual happiness • Secondary infertility: inability to conceive a second child – Occurs in 10% of couples
Infertility • Defined as inability to conceive after trying for 1 yr – Occurs in approx. 10 -15% of U. S. couples trying to conceive – More than 6 months of trying --> consider consulting a health care practitioner • 60% of couples become pregnant after trying for 6 mos. • Can be due to male or female factors; both partners should be medically evaluated • Causes – Can be complex; often difficult to determine – Remain unidentified in as many as 15% of cases • Can be extremely emotionally painful for couples and pose challenges for their sexual happiness • Secondary infertility: inability to conceive a second child – Occurs in 10% of couples
 Female infertility • Problems with ovulation – – – Hormone imbalances, severe vitamin deficiencies, poor nutrition Emotional stress Below-normal % body fat Smoking, substance abuse Can be treated w/medications that stimulate ovulation--can increase chance of multiple births • Damage to fallopian tubes – Previous infection – Endometriosis – Can sometimes be treated by surgery to remove scar tissue • Cervical mucus abnormalities – Presence of antibodies that attack sperm – Can form a plug that blocks passage of sperm – Can be treated by intrauterine injection of sperm
Female infertility • Problems with ovulation – – – Hormone imbalances, severe vitamin deficiencies, poor nutrition Emotional stress Below-normal % body fat Smoking, substance abuse Can be treated w/medications that stimulate ovulation--can increase chance of multiple births • Damage to fallopian tubes – Previous infection – Endometriosis – Can sometimes be treated by surgery to remove scar tissue • Cervical mucus abnormalities – Presence of antibodies that attack sperm – Can form a plug that blocks passage of sperm – Can be treated by intrauterine injection of sperm
 Male infertility • Contributes to 50% of cases; sole cause in 30% of cases • Problems w/sperm number • Abnormal sperm (poor motility, short lifespan) • Causes: – – Inflammation in or abnormal development of testicles Swollen vein in testis or vas deferens (varicocele) Infectious diseases (mumps, STIs) Smoking, alcohol & drug use • Cocaine use decreases spermatogenesis • Marijuana use slows sperm motility – Hormone disorder – Exposure to environmental toxins (chemicals, radiation) • Treatments: decrease frequency of ejaculation ( conc’n. of sperm), no hot baths, no tight shorts or long bike rides
Male infertility • Contributes to 50% of cases; sole cause in 30% of cases • Problems w/sperm number • Abnormal sperm (poor motility, short lifespan) • Causes: – – Inflammation in or abnormal development of testicles Swollen vein in testis or vas deferens (varicocele) Infectious diseases (mumps, STIs) Smoking, alcohol & drug use • Cocaine use decreases spermatogenesis • Marijuana use slows sperm motility – Hormone disorder – Exposure to environmental toxins (chemicals, radiation) • Treatments: decrease frequency of ejaculation ( conc’n. of sperm), no hot baths, no tight shorts or long bike rides
 Reproductive Alternatives & Technologies • Artificial insemination – Semen is mechanically placed in a woman’s vagina, cervis, or uterus (at home, or in a doctor’s office) – Donor semen can be used if woman does not have a male partner or partner’s sperm are inviable • Intrauterine insemination – Sperm is injected directly into uterus (helpful if female cervical mucus is a cause of infertility) • Surrogate mother – Woman who is impregnated (via artificial insemination or IVF) by an infertile or childless couple; carries baby to term and gives it to the couple for adoption
Reproductive Alternatives & Technologies • Artificial insemination – Semen is mechanically placed in a woman’s vagina, cervis, or uterus (at home, or in a doctor’s office) – Donor semen can be used if woman does not have a male partner or partner’s sperm are inviable • Intrauterine insemination – Sperm is injected directly into uterus (helpful if female cervical mucus is a cause of infertility) • Surrogate mother – Woman who is impregnated (via artificial insemination or IVF) by an infertile or childless couple; carries baby to term and gives it to the couple for adoption
 Reproductive Alternatives & Technologies (cont. ) • In vitro fertilization (IVF) – Mature eggs are harvested from woman’s ovary – Eggs are fertilized by sperm in a laboratory – Embryos are introduced into woman’s uterus • Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) – When a single sperm is injected into an egg – May be a part of in vitro fertilization if semen is of poor quality or quantity
Reproductive Alternatives & Technologies (cont. ) • In vitro fertilization (IVF) – Mature eggs are harvested from woman’s ovary – Eggs are fertilized by sperm in a laboratory – Embryos are introduced into woman’s uterus • Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) – When a single sperm is injected into an egg – May be a part of in vitro fertilization if semen is of poor quality or quantity
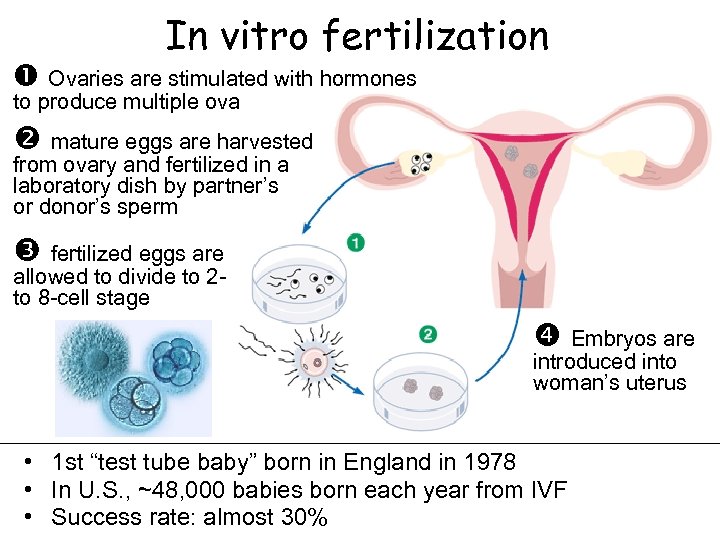 In vitro fertilization Ovaries are stimulated with hormones to produce multiple ova mature eggs are harvested from ovary and fertilized in a laboratory dish by partner’s or donor’s sperm fertilized eggs are allowed to divide to 2 to 8 -cell stage Embryos are introduced into woman’s uterus • 1 st “test tube baby” born in England in 1978 • In U. S. , ~48, 000 babies born each year from IVF • Success rate: almost 30%
In vitro fertilization Ovaries are stimulated with hormones to produce multiple ova mature eggs are harvested from ovary and fertilized in a laboratory dish by partner’s or donor’s sperm fertilized eggs are allowed to divide to 2 to 8 -cell stage Embryos are introduced into woman’s uterus • 1 st “test tube baby” born in England in 1978 • In U. S. , ~48, 000 babies born each year from IVF • Success rate: almost 30%
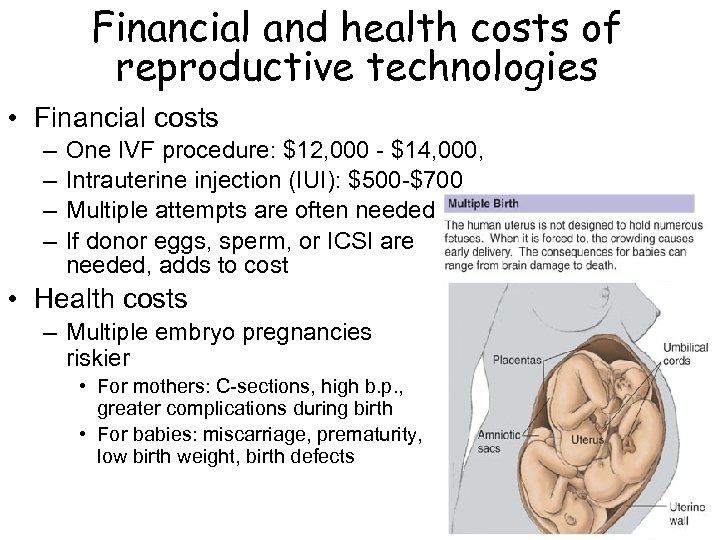 Financial and health costs of reproductive technologies • Financial costs – – One IVF procedure: $12, 000 - $14, 000, Intrauterine injection (IUI): $500 -$700 Multiple attempts are often needed If donor eggs, sperm, or ICSI are needed, adds to cost • Health costs – Multiple embryo pregnancies riskier • For mothers: C-sections, high b. p. , greater complications during birth • For babies: miscarriage, prematurity, low birth weight, birth defects are
Financial and health costs of reproductive technologies • Financial costs – – One IVF procedure: $12, 000 - $14, 000, Intrauterine injection (IUI): $500 -$700 Multiple attempts are often needed If donor eggs, sperm, or ICSI are needed, adds to cost • Health costs – Multiple embryo pregnancies riskier • For mothers: C-sections, high b. p. , greater complications during birth • For babies: miscarriage, prematurity, low birth weight, birth defects are
 Pregnancy detection • First signs: light period, spotting, or no period – Implantation bleeding (6 -12 days post-conception) • Tender breasts • Fatigue • nausea/vomiting; appetite change – “morning sickness” typically begins 2 -8 weeks post-conception and lasts around 6 -8 weeks – Some women feel none; some feel sick their whole pregnancy • blood or urine tests for human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), secreted by placenta – Most sensitive blood tests can detect 7 days post-conception • Headaches, backaches • Food cravings, enhanced odor sensitivity
Pregnancy detection • First signs: light period, spotting, or no period – Implantation bleeding (6 -12 days post-conception) • Tender breasts • Fatigue • nausea/vomiting; appetite change – “morning sickness” typically begins 2 -8 weeks post-conception and lasts around 6 -8 weeks – Some women feel none; some feel sick their whole pregnancy • blood or urine tests for human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), secreted by placenta – Most sensitive blood tests can detect 7 days post-conception • Headaches, backaches • Food cravings, enhanced odor sensitivity
 Spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) • Definition: spontaneous expulsion of fetus from the uterus in 1 st 20 weeks of pregnancy • Frequency – 10 -25% of all known pregnancies – Estimated 50 -75% of unknown pregnancies (miscarriage isn’t felt b/c it occurs before the woman gets her period) • Causes – Rejection of abnormal fetus, implantation problem – Hormonal problem, infection, or other health problem/trauma – Smoking, substance abuse • Timing: usually occur before 13 weeks (in 1 st trimester) • Symptoms: heavier-than-usual menstrual flow (early miscarriage) to cramping, contractions, heavy bleeding (later miscarriage) • Rarely means that a later pregnancy will be unsuccessful – Can be emotionally traumatic; couple may need to grieve
Spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) • Definition: spontaneous expulsion of fetus from the uterus in 1 st 20 weeks of pregnancy • Frequency – 10 -25% of all known pregnancies – Estimated 50 -75% of unknown pregnancies (miscarriage isn’t felt b/c it occurs before the woman gets her period) • Causes – Rejection of abnormal fetus, implantation problem – Hormonal problem, infection, or other health problem/trauma – Smoking, substance abuse • Timing: usually occur before 13 weeks (in 1 st trimester) • Symptoms: heavier-than-usual menstrual flow (early miscarriage) to cramping, contractions, heavy bleeding (later miscarriage) • Rarely means that a later pregnancy will be unsuccessful – Can be emotionally traumatic; couple may need to grieve
 Elective abortion • Decision to terminate a pregnancy by medical procedures • In U. S. , 3 million unplanned pregnancies/yr. – 48% of women w/unintended pregnancies were using contraception during the month they became pregnant (though often not correctly each time) – Of these, 1. 3 million pregnancies result in abortion – 43% of women in U. S. will have had an abortion by age 45 • Socioeconomic factors – Unintended pregnancy has increased by 29% among poor women while decreasing 20% among higher-income women. – Low-income women are >4 x as likely to have an unplanned pregnancy, due to cuts in government-funded contraceptive services
Elective abortion • Decision to terminate a pregnancy by medical procedures • In U. S. , 3 million unplanned pregnancies/yr. – 48% of women w/unintended pregnancies were using contraception during the month they became pregnant (though often not correctly each time) – Of these, 1. 3 million pregnancies result in abortion – 43% of women in U. S. will have had an abortion by age 45 • Socioeconomic factors – Unintended pregnancy has increased by 29% among poor women while decreasing 20% among higher-income women. – Low-income women are >4 x as likely to have an unplanned pregnancy, due to cuts in government-funded contraceptive services
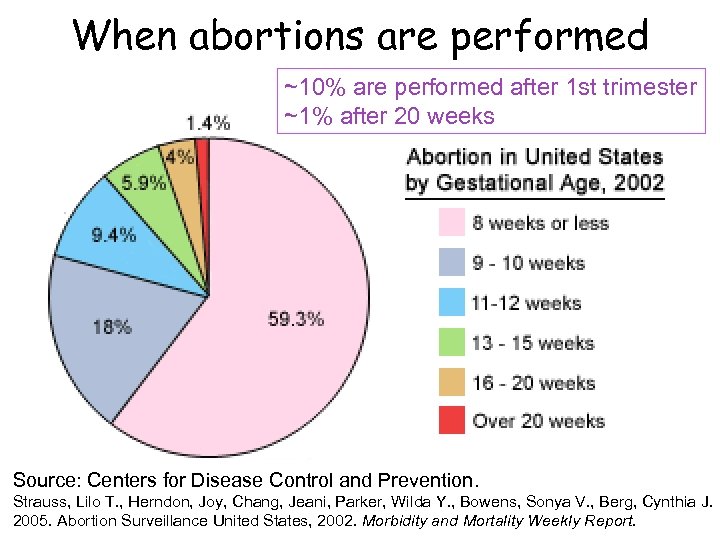 When abortions are performed ~10% are performed after 1 st trimester ~1% after 20 weeks Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Strauss, Lilo T. , Herndon, Joy, Chang, Jeani, Parker, Wilda Y. , Bowens, Sonya V. , Berg, Cynthia J. 2005. Abortion Surveillance United States, 2002. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
When abortions are performed ~10% are performed after 1 st trimester ~1% after 20 weeks Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Strauss, Lilo T. , Herndon, Joy, Chang, Jeani, Parker, Wilda Y. , Bowens, Sonya V. , Berg, Cynthia J. 2005. Abortion Surveillance United States, 2002. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
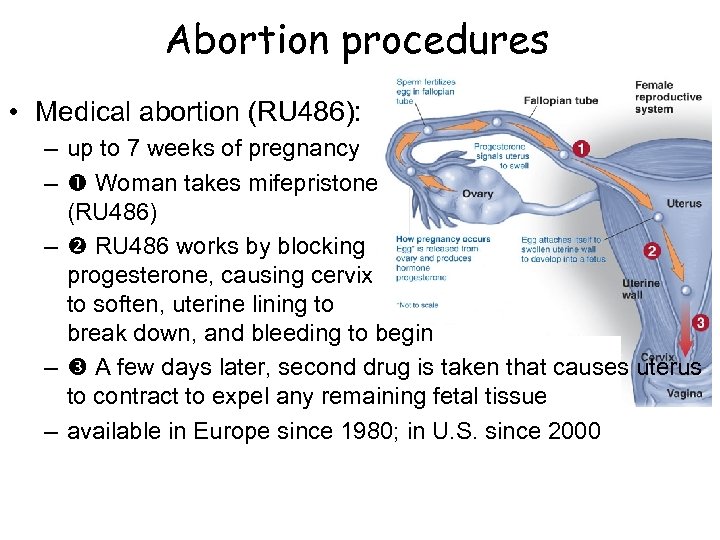 Abortion procedures • Medical abortion (RU 486): – up to 7 weeks of pregnancy – Woman takes mifepristone (RU 486) – RU 486 works by blocking progesterone, causing cervix to soften, uterine lining to break down, and bleeding to begin – A few days later, second drug is taken that causes uterus to contract to expel any remaining fetal tissue – available in Europe since 1980; in U. S. since 2000
Abortion procedures • Medical abortion (RU 486): – up to 7 weeks of pregnancy – Woman takes mifepristone (RU 486) – RU 486 works by blocking progesterone, causing cervix to soften, uterine lining to break down, and bleeding to begin – A few days later, second drug is taken that causes uterus to contract to expel any remaining fetal tissue – available in Europe since 1980; in U. S. since 2000
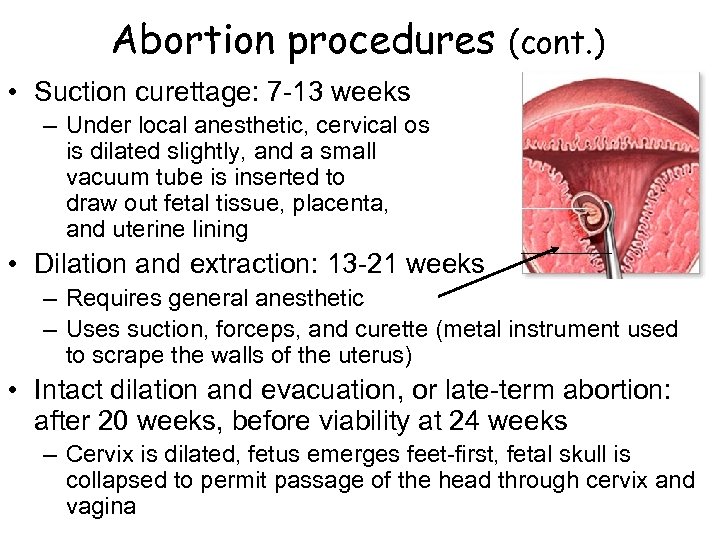 Abortion procedures (cont. ) • Suction curettage: 7 -13 weeks – Under local anesthetic, cervical os is dilated slightly, and a small vacuum tube is inserted to draw out fetal tissue, placenta, and uterine lining • Dilation and extraction: 13 -21 weeks – Requires general anesthetic – Uses suction, forceps, and curette (metal instrument used to scrape the walls of the uterus) • Intact dilation and evacuation, or late-term abortion: after 20 weeks, before viability at 24 weeks – Cervix is dilated, fetus emerges feet-first, fetal skull is collapsed to permit passage of the head through cervix and vagina
Abortion procedures (cont. ) • Suction curettage: 7 -13 weeks – Under local anesthetic, cervical os is dilated slightly, and a small vacuum tube is inserted to draw out fetal tissue, placenta, and uterine lining • Dilation and extraction: 13 -21 weeks – Requires general anesthetic – Uses suction, forceps, and curette (metal instrument used to scrape the walls of the uterus) • Intact dilation and evacuation, or late-term abortion: after 20 weeks, before viability at 24 weeks – Cervix is dilated, fetus emerges feet-first, fetal skull is collapsed to permit passage of the head through cervix and vagina
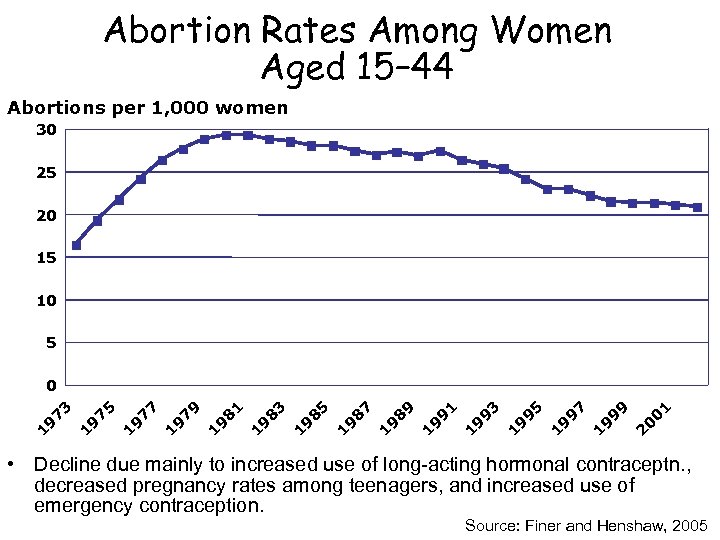 Abortion Rates Among Women Aged 15– 44 Abortions per 1, 000 women 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1 0 2 9 9 9 1 9 7 9 1 9 5 9 1 9 3 9 1 9 1 8 9 9 1 8 7 9 1 8 5 9 1 8 3 9 1 8 1 9 1 7 9 9 1 7 7 9 1 7 5 9 1 1 9 7 3 0 • Decline due mainly to increased use of long-acting hormonal contraceptn. , decreased pregnancy rates among teenagers, and increased use of emergency contraception. Source: Finer and Henshaw, 2005
Abortion Rates Among Women Aged 15– 44 Abortions per 1, 000 women 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1 0 2 9 9 9 1 9 7 9 1 9 5 9 1 9 3 9 1 9 1 8 9 9 1 8 7 9 1 8 5 9 1 8 3 9 1 8 1 9 1 7 9 9 1 7 7 9 1 7 5 9 1 1 9 7 3 0 • Decline due mainly to increased use of long-acting hormonal contraceptn. , decreased pregnancy rates among teenagers, and increased use of emergency contraception. Source: Finer and Henshaw, 2005
 Contraceptive Risk-taking and Abortion • Over half of women who had an abortion were using contraception when they became pregnant • Other unintended pregnancies are often the result of contraceptive risk-taking--not using a contraceptive consistently or reliably • What contributes to contraceptive risk-taking? – Being under influence of alcohol or drugs – Feeling guilty about sex – Women who lack strong self-esteem often fear alienating a partner by asking for his cooperation w/birth control – Women who have experienced abuse are twice as likely to have an unintended pregnancy
Contraceptive Risk-taking and Abortion • Over half of women who had an abortion were using contraception when they became pregnant • Other unintended pregnancies are often the result of contraceptive risk-taking--not using a contraceptive consistently or reliably • What contributes to contraceptive risk-taking? – Being under influence of alcohol or drugs – Feeling guilty about sex – Women who lack strong self-esteem often fear alienating a partner by asking for his cooperation w/birth control – Women who have experienced abuse are twice as likely to have an unintended pregnancy
 Abortion rates in developed world: factors • U. S. has one of the highest abortion rates in the developed world • Factors commonly found in countries w/lower rates of abortion – Comprehensive sex education in schools – Easy access to inexpensive or free birth control and emergency contraception – Social and health services to women and children
Abortion rates in developed world: factors • U. S. has one of the highest abortion rates in the developed world • Factors commonly found in countries w/lower rates of abortion – Comprehensive sex education in schools – Easy access to inexpensive or free birth control and emergency contraception – Social and health services to women and children
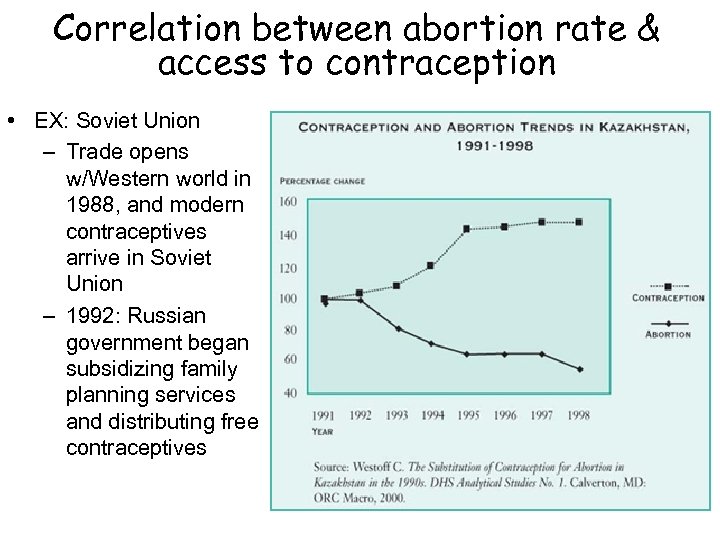 Correlation between abortion rate & access to contraception • EX: Soviet Union – Trade opens w/Western world in 1988, and modern contraceptives arrive in Soviet Union – 1992: Russian government began subsidizing family planning services and distributing free contraceptives
Correlation between abortion rate & access to contraception • EX: Soviet Union – Trade opens w/Western world in 1988, and modern contraceptives arrive in Soviet Union – 1992: Russian government began subsidizing family planning services and distributing free contraceptives
 Abortion legality and rates Source: Guttmacher Institute (www. guttmacher. org)
Abortion legality and rates Source: Guttmacher Institute (www. guttmacher. org)
 Illegal abortion • 25% of women worldwide live in countries where abortion is illegal • Illegal abortion procedures are extremely unsafe – Some women try to self-induce abortions by using enemas, laxatives, pills, herbs, and other substances – Illegal abortionists usually insert a catheter or sharp instrument into the uterus to induce contractions. – Account for 150, 000 -200, 000 maternal deaths/yr. – In Latin America, where legal abortion is restricted to rape or endangerment of woman’s life, almost half of maternal deaths are due to illegal abortion (WHO) – Globally, illegal abortions account for 21% of all maternal deaths
Illegal abortion • 25% of women worldwide live in countries where abortion is illegal • Illegal abortion procedures are extremely unsafe – Some women try to self-induce abortions by using enemas, laxatives, pills, herbs, and other substances – Illegal abortionists usually insert a catheter or sharp instrument into the uterus to induce contractions. – Account for 150, 000 -200, 000 maternal deaths/yr. – In Latin America, where legal abortion is restricted to rape or endangerment of woman’s life, almost half of maternal deaths are due to illegal abortion (WHO) – Globally, illegal abortions account for 21% of all maternal deaths
 Long-Term Safety of Abortion • First trimester abortions pose virtually no future risk of: – Infertility – Ectopic pregnancy – Miscarriage – Birth defect – Preterm or low-birth-weight delivery • There is no association between abortion and breast cancer. • Abortion does not pose a hazard to women’s mental health. – Research studies continue to find that abortion is no more likely to cause mental health problems than is continuing an unwanted pregnancy. Source: Boonstra, 2006
Long-Term Safety of Abortion • First trimester abortions pose virtually no future risk of: – Infertility – Ectopic pregnancy – Miscarriage – Birth defect – Preterm or low-birth-weight delivery • There is no association between abortion and breast cancer. • Abortion does not pose a hazard to women’s mental health. – Research studies continue to find that abortion is no more likely to cause mental health problems than is continuing an unwanted pregnancy. Source: Boonstra, 2006
 U. S. Abortion controversy & legal history • Early American law, based on English common law, allowed abortion until quickening (btwn 18 -24 weeks) • 1860 s: abortion made illegal except to save woman’s life • 1860 -1970 s: – Rich women traveled to country where abortion was legal or paid a U. S. physician to perform an illegal abortion – Women w/o money may have found access to underground skilled abortion providers who worked for free or very little – Otherwise: “back alley” abortions using unsafe procedures, or dangerous self-induced abortions (wire coat hanger, douching w/bleach, swallowing turpentine) • 1973: Roe v. Wade legalized right to abortion before viability (~24 weeks) • 1977: Hyde Amendment: restricted federal Medicaid funds for abortions
U. S. Abortion controversy & legal history • Early American law, based on English common law, allowed abortion until quickening (btwn 18 -24 weeks) • 1860 s: abortion made illegal except to save woman’s life • 1860 -1970 s: – Rich women traveled to country where abortion was legal or paid a U. S. physician to perform an illegal abortion – Women w/o money may have found access to underground skilled abortion providers who worked for free or very little – Otherwise: “back alley” abortions using unsafe procedures, or dangerous self-induced abortions (wire coat hanger, douching w/bleach, swallowing turpentine) • 1973: Roe v. Wade legalized right to abortion before viability (~24 weeks) • 1977: Hyde Amendment: restricted federal Medicaid funds for abortions
 U. S. Abortion controversy & legal history more recent issues • Gag rule: – Banned federal funds for family planning clinics that inform women about abortion as part of counseling – Reversed by Clinton administration • Global gag rule: – Cut off aid to international health programs involved in any abortion-related activities, including info & referral – Establised by Reagan in ‘ 84, reversed by Clinton, reinstated by GW Bush in ‘ 01 • Access to family planning & abortion clinics – Freedom of Access to Clinic Entrances Act (1994): prohibits use/threat of or physical obstruction to prevent access to reproductive health care services
U. S. Abortion controversy & legal history more recent issues • Gag rule: – Banned federal funds for family planning clinics that inform women about abortion as part of counseling – Reversed by Clinton administration • Global gag rule: – Cut off aid to international health programs involved in any abortion-related activities, including info & referral – Establised by Reagan in ‘ 84, reversed by Clinton, reinstated by GW Bush in ‘ 01 • Access to family planning & abortion clinics – Freedom of Access to Clinic Entrances Act (1994): prohibits use/threat of or physical obstruction to prevent access to reproductive health care services
 Abortion controversy in U. S. • 55 -65% of Americans believe women should have access to legal abortion • Public opinion about Roe v. Wade: – 63% want it to remain in place – 23% want it overturned • Anti-abortion/pro-life groups believe that life begins at conception • Pro-choice groups see abortion as a necessary last resort • Many people who believe abortion is wrong also believe that women should still have access to safe, legal abortion (“abortion should be safe, legal, and rare”)
Abortion controversy in U. S. • 55 -65% of Americans believe women should have access to legal abortion • Public opinion about Roe v. Wade: – 63% want it to remain in place – 23% want it overturned • Anti-abortion/pro-life groups believe that life begins at conception • Pro-choice groups see abortion as a necessary last resort • Many people who believe abortion is wrong also believe that women should still have access to safe, legal abortion (“abortion should be safe, legal, and rare”)
 Abortion in the U. S. : current restrictions • Bush administration has supported implementing restrictions on abortion at the state level • Current restrictions as of 2006: – 32 states require mandatory counseling session – 24 states also require 24 -hr waiting period btwn counseling session and abortion – 4 states restrict private insurance from covering abortion unless woman buys additional policy for that purpose – 21 states unnecessarily require abortion to be performed in a hospital instead of a clinic after a certain number of weeks of pregnancy (and in some of these states, only clinics perform abortions, not hospitals) – 34 states have parental consent laws that require a minor to obtain one or both parents’ consent before she can have an abortion
Abortion in the U. S. : current restrictions • Bush administration has supported implementing restrictions on abortion at the state level • Current restrictions as of 2006: – 32 states require mandatory counseling session – 24 states also require 24 -hr waiting period btwn counseling session and abortion – 4 states restrict private insurance from covering abortion unless woman buys additional policy for that purpose – 21 states unnecessarily require abortion to be performed in a hospital instead of a clinic after a certain number of weeks of pregnancy (and in some of these states, only clinics perform abortions, not hospitals) – 34 states have parental consent laws that require a minor to obtain one or both parents’ consent before she can have an abortion
 Discussion question: States with the most restrictions on abortion: - typically provide the fewest resources for mothers and children - often mandate that abstinence be stressed in sex education curricula Why do you think this is the case?
Discussion question: States with the most restrictions on abortion: - typically provide the fewest resources for mothers and children - often mandate that abstinence be stressed in sex education curricula Why do you think this is the case?
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
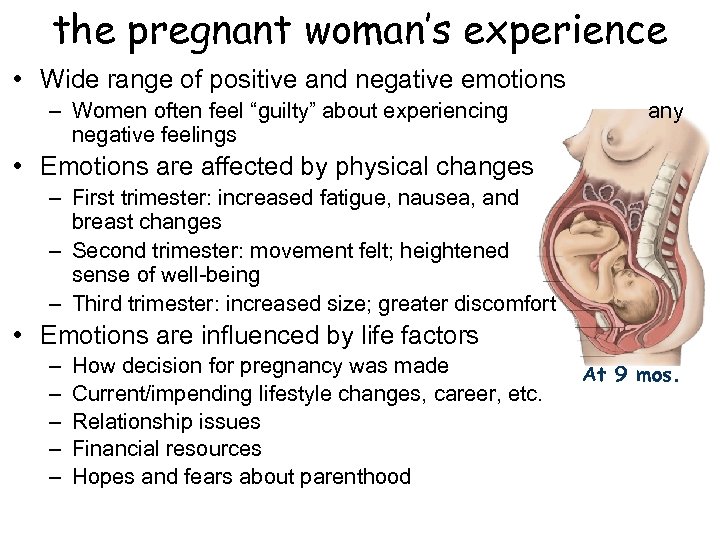 the pregnant woman’s experience • Wide range of positive and negative emotions – Women often feel “guilty” about experiencing negative feelings any • Emotions are affected by physical changes – First trimester: increased fatigue, nausea, and breast changes – Second trimester: movement felt; heightened sense of well-being – Third trimester: increased size; greater discomfort • Emotions are influenced by life factors – – – How decision for pregnancy was made Current/impending lifestyle changes, career, etc. Relationship issues Financial resources Hopes and fears about parenthood At 9 mos.
the pregnant woman’s experience • Wide range of positive and negative emotions – Women often feel “guilty” about experiencing negative feelings any • Emotions are affected by physical changes – First trimester: increased fatigue, nausea, and breast changes – Second trimester: movement felt; heightened sense of well-being – Third trimester: increased size; greater discomfort • Emotions are influenced by life factors – – – How decision for pregnancy was made Current/impending lifestyle changes, career, etc. Relationship issues Financial resources Hopes and fears about parenthood At 9 mos.
 Pregnancy: the partner’s experience • Also may have a wide range of positive and negative emotions – May feel ecstatic – May feel fearful about future mom’s and baby’s well-being – May feel nervous about impending birth and his/her ability to “keep it together” – Common to feel some concern over impending increase in financial responsibility – Possible feelings of separation from partner, from experience of pregnancy • May experience some psychosympathetic symptoms, such as nausea, fatigue
Pregnancy: the partner’s experience • Also may have a wide range of positive and negative emotions – May feel ecstatic – May feel fearful about future mom’s and baby’s well-being – May feel nervous about impending birth and his/her ability to “keep it together” – Common to feel some concern over impending increase in financial responsibility – Possible feelings of separation from partner, from experience of pregnancy • May experience some psychosympathetic symptoms, such as nausea, fatigue
 Sexual activity during pregnancy • Sexual activity and orgasm are safe throughout pregnancy until labor begins, unless there are risk factors • Pregnant woman’s sexual interest may change during pregnancy – Some women experience increase in desire – Some women experience changes in lubrication, ability to reach orgasm – Nausea and physical discomfort may negatively impact a woman’s desire--especially in 1 st & 3 rd trimesters • Modified sexual positions are often needed – Side-by-side, woman-on-top, sitting, rear-entry are all good options
Sexual activity during pregnancy • Sexual activity and orgasm are safe throughout pregnancy until labor begins, unless there are risk factors • Pregnant woman’s sexual interest may change during pregnancy – Some women experience increase in desire – Some women experience changes in lubrication, ability to reach orgasm – Nausea and physical discomfort may negatively impact a woman’s desire--especially in 1 st & 3 rd trimesters • Modified sexual positions are often needed – Side-by-side, woman-on-top, sitting, rear-entry are all good options
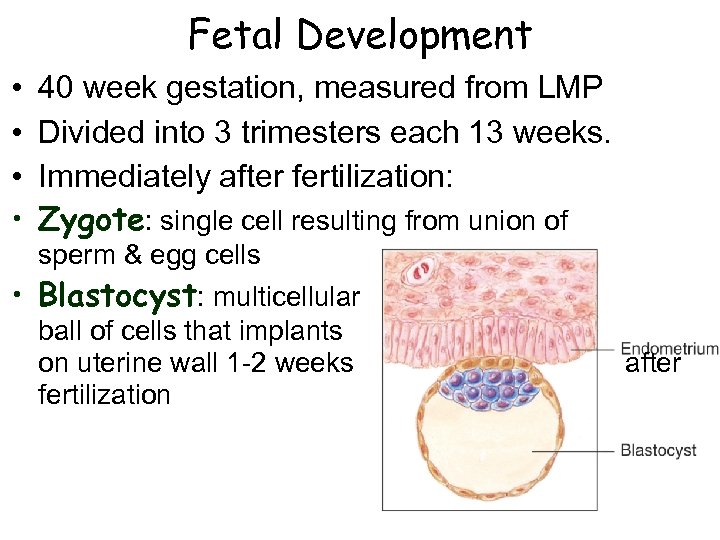 Fetal Development • • 40 week gestation, measured from LMP Divided into 3 trimesters each 13 weeks. Immediately after fertilization: Zygote: single cell resulting from union of sperm & egg cells • Blastocyst: multicellular ball of cells that implants on uterine wall 1 -2 weeks fertilization after
Fetal Development • • 40 week gestation, measured from LMP Divided into 3 trimesters each 13 weeks. Immediately after fertilization: Zygote: single cell resulting from union of sperm & egg cells • Blastocyst: multicellular ball of cells that implants on uterine wall 1 -2 weeks fertilization after
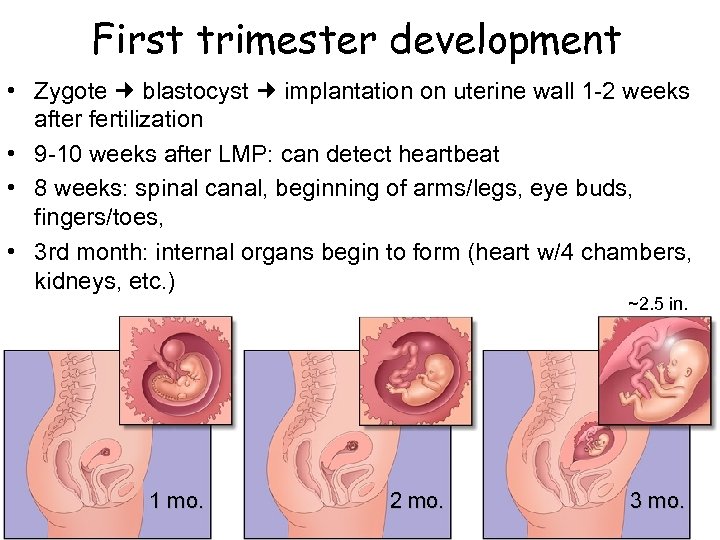 First trimester development • Zygote blastocyst implantation on uterine wall 1 -2 weeks after fertilization • 9 -10 weeks after LMP: can detect heartbeat • 8 weeks: spinal canal, beginning of arms/legs, eye buds, fingers/toes, • 3 rd month: internal organs begin to form (heart w/4 chambers, kidneys, etc. ) ~2. 5 in. 1 mo. 2 mo. 3 mo.
First trimester development • Zygote blastocyst implantation on uterine wall 1 -2 weeks after fertilization • 9 -10 weeks after LMP: can detect heartbeat • 8 weeks: spinal canal, beginning of arms/legs, eye buds, fingers/toes, • 3 rd month: internal organs begin to form (heart w/4 chambers, kidneys, etc. ) ~2. 5 in. 1 mo. 2 mo. 3 mo.
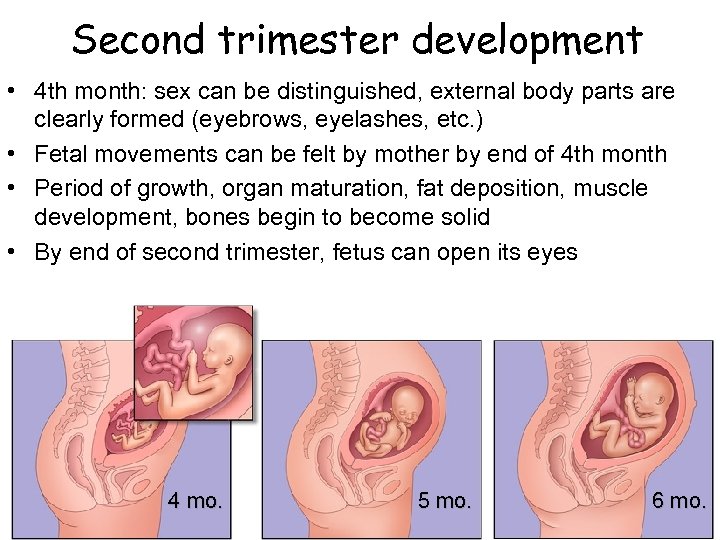 Second trimester development • 4 th month: sex can be distinguished, external body parts are clearly formed (eyebrows, eyelashes, etc. ) • Fetal movements can be felt by mother by end of 4 th month • Period of growth, organ maturation, fat deposition, muscle development, bones begin to become solid • By end of second trimester, fetus can open its eyes 4 mo. 5 mo. 6 mo.
Second trimester development • 4 th month: sex can be distinguished, external body parts are clearly formed (eyebrows, eyelashes, etc. ) • Fetal movements can be felt by mother by end of 4 th month • Period of growth, organ maturation, fat deposition, muscle development, bones begin to become solid • By end of second trimester, fetus can open its eyes 4 mo. 5 mo. 6 mo.
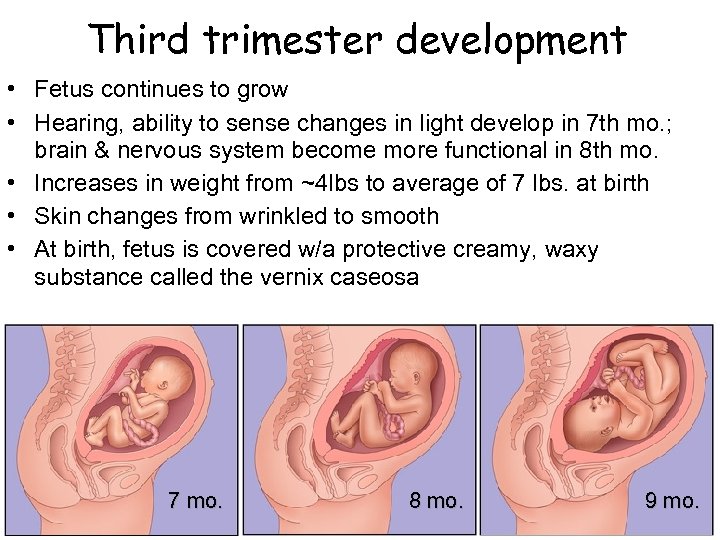 Third trimester development • Fetus continues to grow • Hearing, ability to sense changes in light develop in 7 th mo. ; brain & nervous system become more functional in 8 th mo. • Increases in weight from ~4 lbs to average of 7 lbs. at birth • Skin changes from wrinkled to smooth • At birth, fetus is covered w/a protective creamy, waxy substance called the vernix caseosa 7 mo. 8 mo. 9 mo.
Third trimester development • Fetus continues to grow • Hearing, ability to sense changes in light develop in 7 th mo. ; brain & nervous system become more functional in 8 th mo. • Increases in weight from ~4 lbs to average of 7 lbs. at birth • Skin changes from wrinkled to smooth • At birth, fetus is covered w/a protective creamy, waxy substance called the vernix caseosa 7 mo. 8 mo. 9 mo.
 Prenatal care • Before pregnancy: – HIV test, German measles (rubella) immunity • During pregnancy: – Good nutrition, adequate rest, routine check-ups, exercise, childbirth education • Risks of poor prenatal care: – Low birth weight, lung disorders, brain damage, abnormal growth patterns – Lifelong effects – Increased chance of maternal complications • In U. S. , 4 x as many African American women as white women die from childbirth complications due to poor access to prenatal care • Risk of dying from pregnancy/childbirth in N. America: 1 in 3, 700 (0. 02%) • Risk of dying from pregnancy/childbirth in Asia: 1 in 65 (1. 5%) • Risk of dying from pregnancy/childbirth in Africa: 1 in 6 (16. 7%)
Prenatal care • Before pregnancy: – HIV test, German measles (rubella) immunity • During pregnancy: – Good nutrition, adequate rest, routine check-ups, exercise, childbirth education • Risks of poor prenatal care: – Low birth weight, lung disorders, brain damage, abnormal growth patterns – Lifelong effects – Increased chance of maternal complications • In U. S. , 4 x as many African American women as white women die from childbirth complications due to poor access to prenatal care • Risk of dying from pregnancy/childbirth in N. America: 1 in 3, 700 (0. 02%) • Risk of dying from pregnancy/childbirth in Asia: 1 in 65 (1. 5%) • Risk of dying from pregnancy/childbirth in Africa: 1 in 6 (16. 7%)
 Risks to fetal development • Fetus depends on mother for nutrients, oxygen, and waste elimination--substances pass through the placenta: – Disk-shaped organ attached to the uterine wall and connected to fetus by the umbilical cord; substances pass btwn mother and fetus through the placental cell walls • Placenta prevents some, but not all, bacteria and viruses from passing into fetus circulatory system--many, include HIV, can cross • Nicotine, prescription & nonprescription drugs, alcohol – Alcohol can cause birth defects. • Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): syndrome in infants caused by heavy maternal prenatal alcohol use; characterized by heart defects, brain damage, physical malformations, and below-normal IQ • Babies can be born addicted to alcohol/drugs • Toxic chemicals and pollutants in the environment – Nicotine/smoking reduces oxygen, increases the chance of miscarriage & pregnancy complications
Risks to fetal development • Fetus depends on mother for nutrients, oxygen, and waste elimination--substances pass through the placenta: – Disk-shaped organ attached to the uterine wall and connected to fetus by the umbilical cord; substances pass btwn mother and fetus through the placental cell walls • Placenta prevents some, but not all, bacteria and viruses from passing into fetus circulatory system--many, include HIV, can cross • Nicotine, prescription & nonprescription drugs, alcohol – Alcohol can cause birth defects. • Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): syndrome in infants caused by heavy maternal prenatal alcohol use; characterized by heart defects, brain damage, physical malformations, and below-normal IQ • Babies can be born addicted to alcohol/drugs • Toxic chemicals and pollutants in the environment – Nicotine/smoking reduces oxygen, increases the chance of miscarriage & pregnancy complications
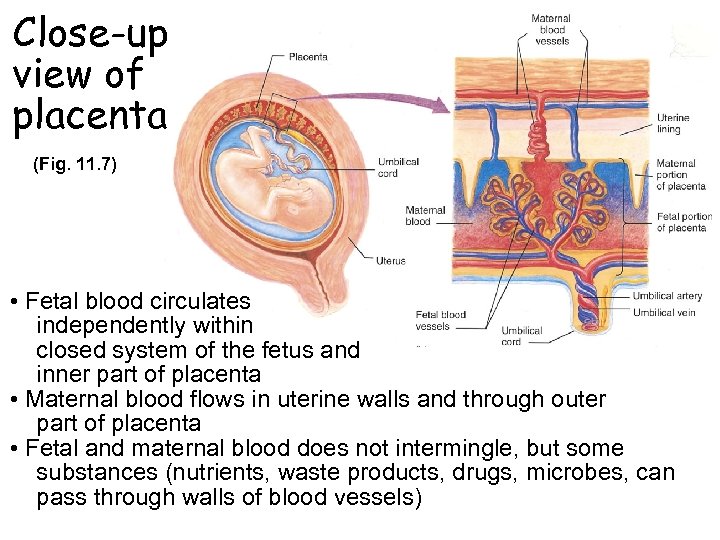 Close-up view of placenta (Fig. 11. 7) • Fetal blood circulates independently within closed system of the fetus and inner part of placenta • Maternal blood flows in uterine walls and through outer part of placenta • Fetal and maternal blood does not intermingle, but some substances (nutrients, waste products, drugs, microbes, can pass through walls of blood vessels)
Close-up view of placenta (Fig. 11. 7) • Fetal blood circulates independently within closed system of the fetus and inner part of placenta • Maternal blood flows in uterine walls and through outer part of placenta • Fetal and maternal blood does not intermingle, but some substances (nutrients, waste products, drugs, microbes, can pass through walls of blood vessels)
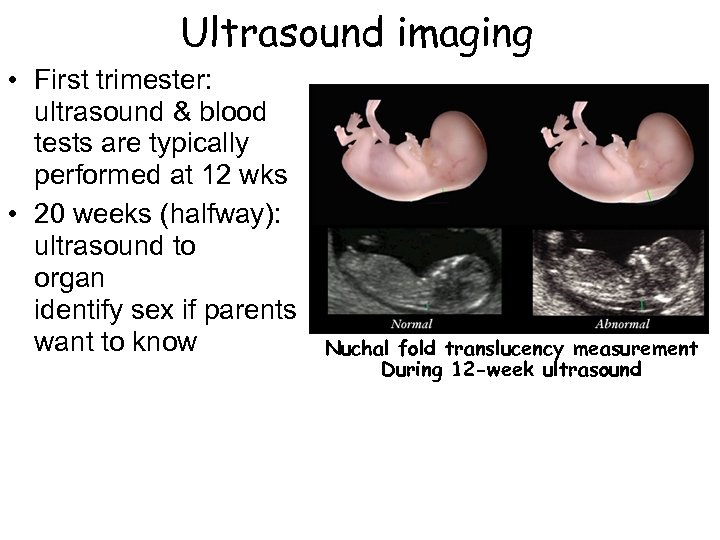 Ultrasound imaging • First trimester: ultrasound & blood tests are typically performed at 12 wks • 20 weeks (halfway): ultrasound to organ identify sex if parents want to know 2 nd examine development; can Nuchal fold translucency measurement During 12 -week ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging • First trimester: ultrasound & blood tests are typically performed at 12 wks • 20 weeks (halfway): ultrasound to organ identify sex if parents want to know 2 nd examine development; can Nuchal fold translucency measurement During 12 -week ultrasound
 Pregnancy after 35 • Most healthy women from age 35 into their 40 s have healthy pregnancies--if problems do arise, they can usually be successfully treated. – Quite common now--20% of all childbearing women in U. S. • Women over age 35 have an increased risk of: – Fertility problems – Multiple pregnancy (twins or more) – Fetus w/abnormal chromosome # (often results in miscarriage-see slide on abnormal chromosome #) – Premature delivery – Cesarean section delivery – Placenta previa, a condition in which the placenta is in the wrong place and covers the cervix – Chronic illnesses such as high blood pressure or diabetes that are important factors during pregnancy
Pregnancy after 35 • Most healthy women from age 35 into their 40 s have healthy pregnancies--if problems do arise, they can usually be successfully treated. – Quite common now--20% of all childbearing women in U. S. • Women over age 35 have an increased risk of: – Fertility problems – Multiple pregnancy (twins or more) – Fetus w/abnormal chromosome # (often results in miscarriage-see slide on abnormal chromosome #) – Premature delivery – Cesarean section delivery – Placenta previa, a condition in which the placenta is in the wrong place and covers the cervix – Chronic illnesses such as high blood pressure or diabetes that are important factors during pregnancy
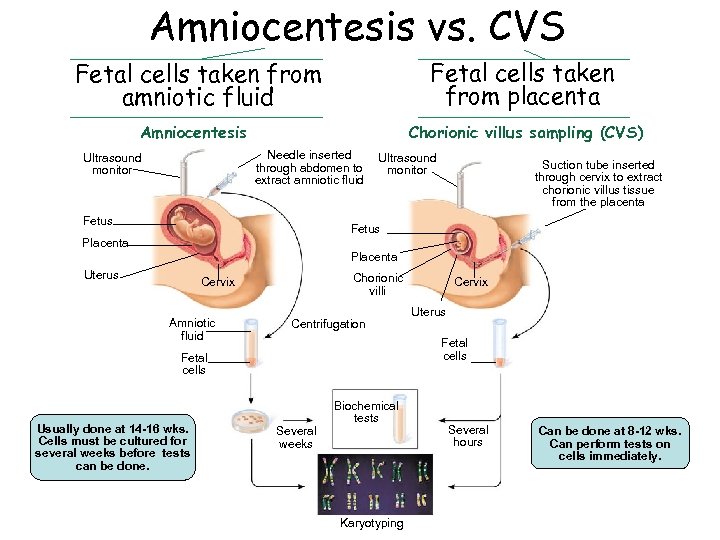 Amniocentesis vs. CVS Fetal cells taken from amniotic fluid Fetal cells taken from placenta Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) Needle inserted through abdomen to extract amniotic fluid Ultrasound monitor Fetus Ultrasound monitor Suction tube inserted through cervix to extract chorionic villus tissue from the placenta Fetus Placenta Uterus Chorionic villi Cervix Amniotic fluid Centrifugation Uterus Fetal cells Usually done at 14 -16 wks. Cells must be cultured for several weeks before tests can be done. Cervix Several weeks Biochemical tests Karyotyping Several hours Can be done at 8 -12 wks. Can perform tests on cells immediately.
Amniocentesis vs. CVS Fetal cells taken from amniotic fluid Fetal cells taken from placenta Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) Needle inserted through abdomen to extract amniotic fluid Ultrasound monitor Fetus Ultrasound monitor Suction tube inserted through cervix to extract chorionic villus tissue from the placenta Fetus Placenta Uterus Chorionic villi Cervix Amniotic fluid Centrifugation Uterus Fetal cells Usually done at 14 -16 wks. Cells must be cultured for several weeks before tests can be done. Cervix Several weeks Biochemical tests Karyotyping Several hours Can be done at 8 -12 wks. Can perform tests on cells immediately.
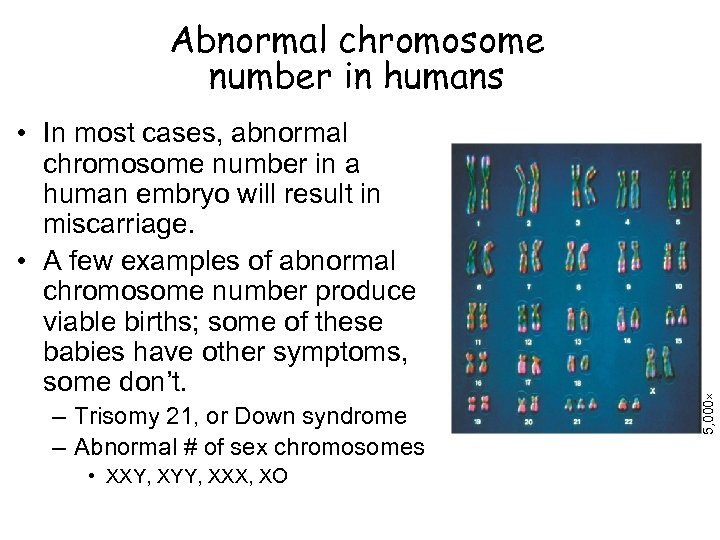 • In most cases, abnormal chromosome number in a human embryo will result in miscarriage. • A few examples of abnormal chromosome number produce viable births; some of these babies have other symptoms, some don’t. – Trisomy 21, or Down syndrome – Abnormal # of sex chromosomes • XXY, XYY, XXX, XO 5, 000 Abnormal chromosome number in humans
• In most cases, abnormal chromosome number in a human embryo will result in miscarriage. • A few examples of abnormal chromosome number produce viable births; some of these babies have other symptoms, some don’t. – Trisomy 21, or Down syndrome – Abnormal # of sex chromosomes • XXY, XYY, XXX, XO 5, 000 Abnormal chromosome number in humans
 An extra copy of chromosome 21 causes Down syndrome (trisomy 21) • Trisomy 21 is the most common chromosome # abnormality (~1 in 700). • Symptoms: – – characteristic facial features. short stature. heart defects. susceptibility to respiratory infections, leukemia, and Alzheimer’s disease. – Reduced life span. – Varying degrees of mental retardation.
An extra copy of chromosome 21 causes Down syndrome (trisomy 21) • Trisomy 21 is the most common chromosome # abnormality (~1 in 700). • Symptoms: – – characteristic facial features. short stature. heart defects. susceptibility to respiratory infections, leukemia, and Alzheimer’s disease. – Reduced life span. – Varying degrees of mental retardation.
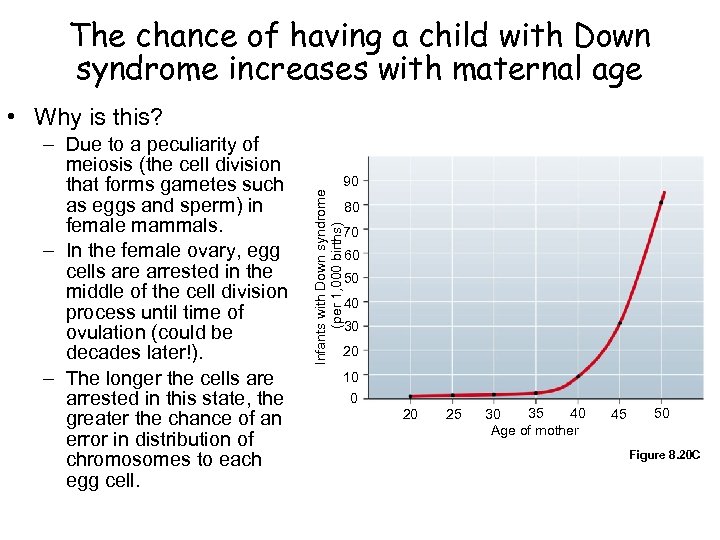 The chance of having a child with Down syndrome increases with maternal age • Why is this? 90 Infants with Down syndrome (per 1, 000 births) – Due to a peculiarity of meiosis (the cell division that forms gametes such as eggs and sperm) in female mammals. – In the female ovary, egg cells are arrested in the middle of the cell division process until time of ovulation (could be decades later!). – The longer the cells are arrested in this state, the greater the chance of an error in distribution of chromosomes to each egg cell. 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 20 25 35 40 30 Age of mother 45 50 Figure 8. 20 C
The chance of having a child with Down syndrome increases with maternal age • Why is this? 90 Infants with Down syndrome (per 1, 000 births) – Due to a peculiarity of meiosis (the cell division that forms gametes such as eggs and sperm) in female mammals. – In the female ovary, egg cells are arrested in the middle of the cell division process until time of ovulation (could be decades later!). – The longer the cells are arrested in this state, the greater the chance of an error in distribution of chromosomes to each egg cell. 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 20 25 35 40 30 Age of mother 45 50 Figure 8. 20 C
 Contemporary childbirth • Parents-to-be work as a team • Childbirth education classes provide information about what to expect in labor and birth, breathing/relaxation techniques, and possible medical interventions • Women assisted by a birth attendant during labor had fewer C-sections, less pain medication, shorter labor, and greater satisfaction w/birth experience • Birthplace options: home, birthing center, hospital w/midwife or w/ob-gyn
Contemporary childbirth • Parents-to-be work as a team • Childbirth education classes provide information about what to expect in labor and birth, breathing/relaxation techniques, and possible medical interventions • Women assisted by a birth attendant during labor had fewer C-sections, less pain medication, shorter labor, and greater satisfaction w/birth experience • Birthplace options: home, birthing center, hospital w/midwife or w/ob-gyn
 Labor • Walking during labor can help progression of labor • Positions: – Lying on back is the worst • Birthing balls, warm bath, massage can help • Episiotomy: – surgical incision in the perineum to enlarge the vagina during birth – Previously thought to be easier to sew up than a “natural tear” – Now shown to be associated w/greater tearing – Medically unnecessary, cause more harm than good.
Labor • Walking during labor can help progression of labor • Positions: – Lying on back is the worst • Birthing balls, warm bath, massage can help • Episiotomy: – surgical incision in the perineum to enlarge the vagina during birth – Previously thought to be easier to sew up than a “natural tear” – Now shown to be associated w/greater tearing – Medically unnecessary, cause more harm than good.
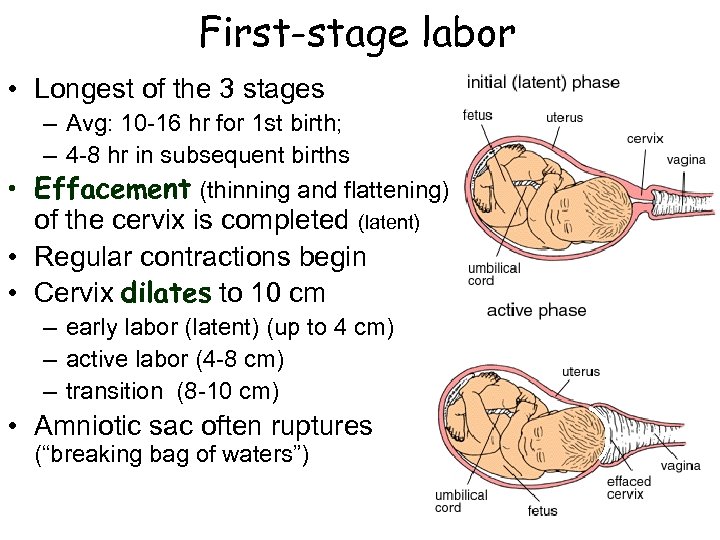 First-stage labor • Longest of the 3 stages – Avg: 10 -16 hr for 1 st birth; – 4 -8 hr in subsequent births • Effacement (thinning and flattening) of the cervix is completed (latent) • Regular contractions begin • Cervix dilates to 10 cm – early labor (latent) (up to 4 cm) – active labor (4 -8 cm) – transition (8 -10 cm) • Amniotic sac often ruptures (“breaking bag of waters”)
First-stage labor • Longest of the 3 stages – Avg: 10 -16 hr for 1 st birth; – 4 -8 hr in subsequent births • Effacement (thinning and flattening) of the cervix is completed (latent) • Regular contractions begin • Cervix dilates to 10 cm – early labor (latent) (up to 4 cm) – active labor (4 -8 cm) – transition (8 -10 cm) • Amniotic sac often ruptures (“breaking bag of waters”)
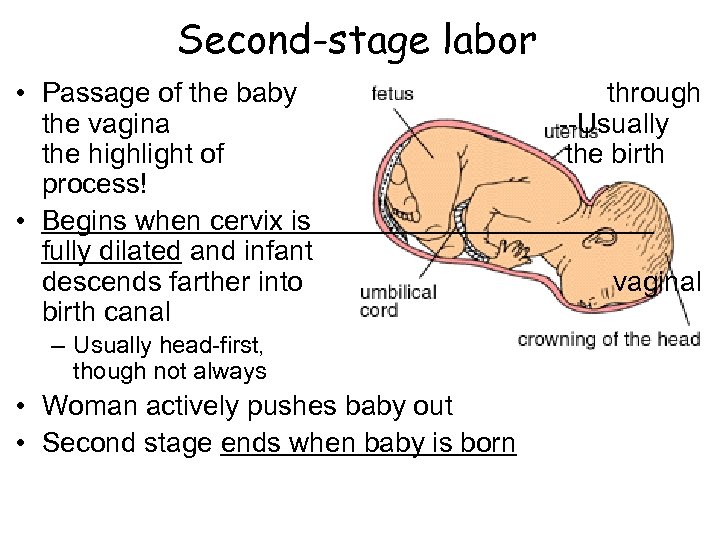 Second-stage labor • Passage of the baby the vagina the highlight of process! • Begins when cervix is fully dilated and infant descends farther into birth canal – Usually head-first, though not always • Woman actively pushes baby out • Second stage ends when baby is born through --Usually the birth vaginal
Second-stage labor • Passage of the baby the vagina the highlight of process! • Begins when cervix is fully dilated and infant descends farther into birth canal – Usually head-first, though not always • Woman actively pushes baby out • Second stage ends when baby is born through --Usually the birth vaginal
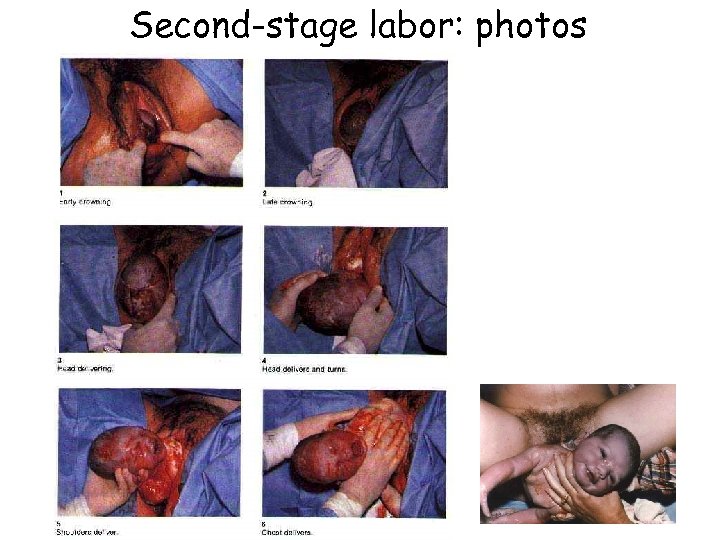 Second-stage labor: photos
Second-stage labor: photos
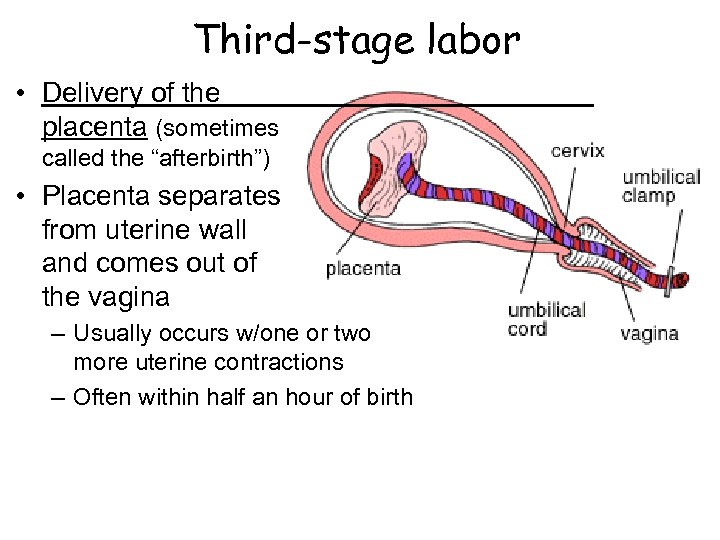 Third-stage labor • Delivery of the placenta (sometimes called the “afterbirth”) • Placenta separates from uterine wall and comes out of the vagina – Usually occurs w/one or two more uterine contractions – Often within half an hour of birth
Third-stage labor • Delivery of the placenta (sometimes called the “afterbirth”) • Placenta separates from uterine wall and comes out of the vagina – Usually occurs w/one or two more uterine contractions – Often within half an hour of birth
 Delivery by Cesarean section (“C-section”) • Baby is removed through an incision made in the abdominal wall and uterus • Can be a lifesaving surgery for mother and child • Recommended when there are indications of fetal distress during labor or when there are complications, such as breech presentation (feet or bottom first) • Rate of C-sections in the U. S. has increased from 5. 5% in 1970 to ~30% in 2004 – Analysis of birth data found that 11% of C-sections for a first pregnancy and 65% of repeat C-sections may not have been necessary – Increase is thought to be due to intensive fetal monitoring, aggressive malpractice lawsuits, and physician or maternal preference
Delivery by Cesarean section (“C-section”) • Baby is removed through an incision made in the abdominal wall and uterus • Can be a lifesaving surgery for mother and child • Recommended when there are indications of fetal distress during labor or when there are complications, such as breech presentation (feet or bottom first) • Rate of C-sections in the U. S. has increased from 5. 5% in 1970 to ~30% in 2004 – Analysis of birth data found that 11% of C-sections for a first pregnancy and 65% of repeat C-sections may not have been necessary – Increase is thought to be due to intensive fetal monitoring, aggressive malpractice lawsuits, and physician or maternal preference
 After childbirth • Postpartum period = first several weeks after birth – Time of intensified emotion, physical and psychological adjustment – Partners may feel increased closeness, non-mom partner may feel jealous of close relationship btwn mom & child – Time and energy demands of a new infant can contribute to stress • Postpartum depression (PPD) – More serious than “baby blues” (tearfulness and mood swings that last a couple of weeks in 75% of new moms) – Classic symptoms of clinical depression, such as insomnia, anxiety, panic attacks, hopelessness – Women may lose interest in or develop obsessive thoughts about harming themselves or their babies
After childbirth • Postpartum period = first several weeks after birth – Time of intensified emotion, physical and psychological adjustment – Partners may feel increased closeness, non-mom partner may feel jealous of close relationship btwn mom & child – Time and energy demands of a new infant can contribute to stress • Postpartum depression (PPD) – More serious than “baby blues” (tearfulness and mood swings that last a couple of weeks in 75% of new moms) – Classic symptoms of clinical depression, such as insomnia, anxiety, panic attacks, hopelessness – Women may lose interest in or develop obsessive thoughts about harming themselves or their babies
 Sexual activity after childbirth • Intercourse can safely be resumed after approx. 46 weeks (sometimes longer if there were complications during birth) – Lochia (reddish uterine discharge) should have stopped – Vaginal tears (or episiotomy) need to heal – For C-section, incision needs to heal • Estrogen levels are reduced by nursing (especially in beginning)--can reduce vaginal lubrication, sometimes desire • Fatigue is a major factor affecting sexuality after birth
Sexual activity after childbirth • Intercourse can safely be resumed after approx. 46 weeks (sometimes longer if there were complications during birth) – Lochia (reddish uterine discharge) should have stopped – Vaginal tears (or episiotomy) need to heal – For C-section, incision needs to heal • Estrogen levels are reduced by nursing (especially in beginning)--can reduce vaginal lubrication, sometimes desire • Fatigue is a major factor affecting sexuality after birth
 Breastfeeding • Colostrum: produced before milk comes in – Thin yellowish fluid – Contains antibodies and protein • Milk production occurs b/c pituitary secretes hormones in response to nipple stimulation by infant sucking – If new mother doesn’t begin or continue to nurse, milk production stops in a matter of days • Medical recommendations: (AAP, WHO): Exclusive b. -f. for first 6 months, continued b. -f. w/other food for at least 1 yr. – Survey in U. S. : only 47% of 1 -week-old infants had been exclusively breast-fed, and that only 10% of 6 -month-old infants were breast-fed. • May be related to women going back to work--of all industrialized countries, only U. S. and Australia lack laws that require paid parental leave w/a guaranteed return to work.
Breastfeeding • Colostrum: produced before milk comes in – Thin yellowish fluid – Contains antibodies and protein • Milk production occurs b/c pituitary secretes hormones in response to nipple stimulation by infant sucking – If new mother doesn’t begin or continue to nurse, milk production stops in a matter of days • Medical recommendations: (AAP, WHO): Exclusive b. -f. for first 6 months, continued b. -f. w/other food for at least 1 yr. – Survey in U. S. : only 47% of 1 -week-old infants had been exclusively breast-fed, and that only 10% of 6 -month-old infants were breast-fed. • May be related to women going back to work--of all industrialized countries, only U. S. and Australia lack laws that require paid parental leave w/a guaranteed return to work.
 Benefits of breastfeeding • Benefits to baby: – Antibodies are passed from mother to baby to protect from illness – Breast-fed babies have lower rates of asthma and allergies – Breast milk is ultimate complete nutrition for baby, changes composition as baby grows • Breast-fed babies have been shown to be leaner as older children and have reduced rates of obesity in adulthood – – Many babies have easier time digesting breast milk than formula Promotes good jaw development and healthy, straight teeth Associated w/ decreased risk of SIDS (sudden Inf. death syndrome) Neurological and cognitive benefits • Breast-fed babies score higher on IQ tests at age 8 • Benefits to mom: – – – Burns lots of calories and fat, helps mom lose pregnancy weight Lowers risk of breast, ovarian, uterine, and endometrial cancers Lowers risk of osteoporosis Practicality: saves money, always have food with you Increased feelings of bonding with baby
Benefits of breastfeeding • Benefits to baby: – Antibodies are passed from mother to baby to protect from illness – Breast-fed babies have lower rates of asthma and allergies – Breast milk is ultimate complete nutrition for baby, changes composition as baby grows • Breast-fed babies have been shown to be leaner as older children and have reduced rates of obesity in adulthood – – Many babies have easier time digesting breast milk than formula Promotes good jaw development and healthy, straight teeth Associated w/ decreased risk of SIDS (sudden Inf. death syndrome) Neurological and cognitive benefits • Breast-fed babies score higher on IQ tests at age 8 • Benefits to mom: – – – Burns lots of calories and fat, helps mom lose pregnancy weight Lowers risk of breast, ovarian, uterine, and endometrial cancers Lowers risk of osteoporosis Practicality: saves money, always have food with you Increased feelings of bonding with baby
 Discussion question: Women are often made to feel uncomfortable about nursing their babies in public places, and sometimes are even asked to “cover up” or to nurse elsewhere. Read the articles about the ‘nursing at Starbucks’ story. Why do you think some people feel that women should not nurse their babies in public? How do such attitudes affect rates of breastfeeding in the U. S. ?
Discussion question: Women are often made to feel uncomfortable about nursing their babies in public places, and sometimes are even asked to “cover up” or to nurse elsewhere. Read the articles about the ‘nursing at Starbucks’ story. Why do you think some people feel that women should not nurse their babies in public? How do such attitudes affect rates of breastfeeding in the U. S. ?


