a457801907accf7ad60bf5c4d9d8d2f9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Chapter 11 -1
Chapter 11 -1
 Conversion Processes and Controls Chapter 11 -2 Accounting Information Systems, 1 st Edition
Conversion Processes and Controls Chapter 11 -2 Accounting Information Systems, 1 st Edition
 Study Objectives 1. Basic features of conversion processes 2. The components of the logistics function 3. Cost accounting reports generated by conversion processes 4. Risks and controls in conversion processes 5. IT systems of conversion processes 6. Ethical issues related to conversion processes 7. Corporate governance in conversion processes Chapter 11 -3
Study Objectives 1. Basic features of conversion processes 2. The components of the logistics function 3. Cost accounting reports generated by conversion processes 4. Risks and controls in conversion processes 5. IT systems of conversion processes 6. Ethical issues related to conversion processes 7. Corporate governance in conversion processes Chapter 11 -3
 Basic Features of Conversion Processes Conversion processes - activities related to the transformation of resources into goods or services. Resources include: Ø Materials Ø Labor Ø Overhead Ø Various other expenses necessary to run the operating facility Chapter 11 -4 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
Basic Features of Conversion Processes Conversion processes - activities related to the transformation of resources into goods or services. Resources include: Ø Materials Ø Labor Ø Overhead Ø Various other expenses necessary to run the operating facility Chapter 11 -4 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
 Basic Features of Conversion Processes Major activities within this process include Ø Operational planning, Ø Optimizing use of employees, property, and inventories, Ø Controlling production flows, Ø Ensuring product quality, and Ø Preparing related cost accounting and financial accounting records. Chapter 11 -5 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
Basic Features of Conversion Processes Major activities within this process include Ø Operational planning, Ø Optimizing use of employees, property, and inventories, Ø Controlling production flows, Ø Ensuring product quality, and Ø Preparing related cost accounting and financial accounting records. Chapter 11 -5 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
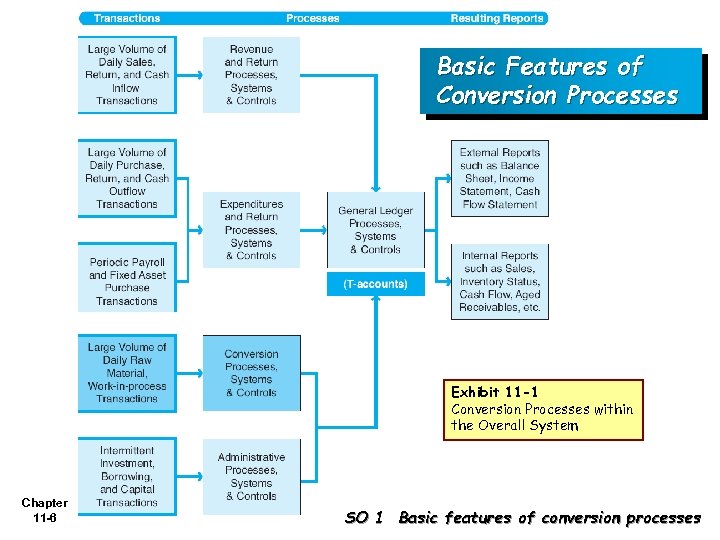 Basic Features of Conversion Processes Exhibit 11 -1 Conversion Processes within the Overall System Chapter 11 -6 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
Basic Features of Conversion Processes Exhibit 11 -1 Conversion Processes within the Overall System Chapter 11 -6 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
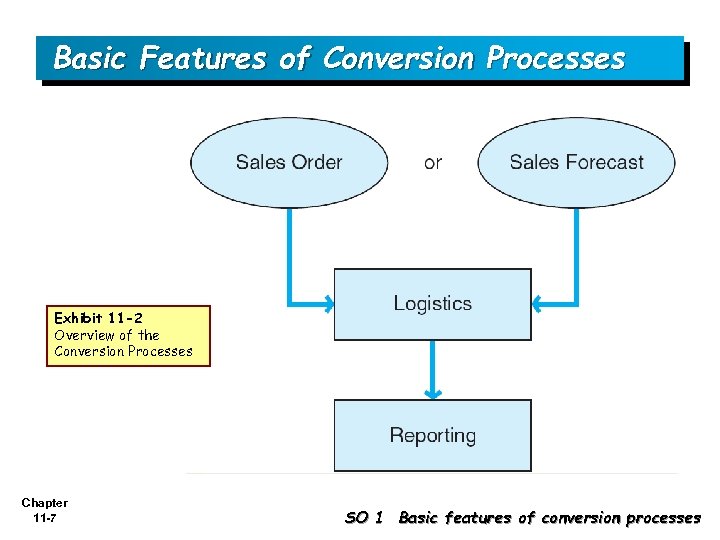 Basic Features of Conversion Processes Exhibit 11 -2 Overview of the Conversion Processes Chapter 11 -7 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
Basic Features of Conversion Processes Exhibit 11 -2 Overview of the Conversion Processes Chapter 11 -7 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
 Basic Features of Conversion Processes Quick Review Manufacturing has changed in recent years as a result of each of the following factors except: a. globalization b. technological advances c. increased competition d. lack of economic prosperity Chapter 11 -8 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
Basic Features of Conversion Processes Quick Review Manufacturing has changed in recent years as a result of each of the following factors except: a. globalization b. technological advances c. increased competition d. lack of economic prosperity Chapter 11 -8 SO 1 Basic features of conversion processes
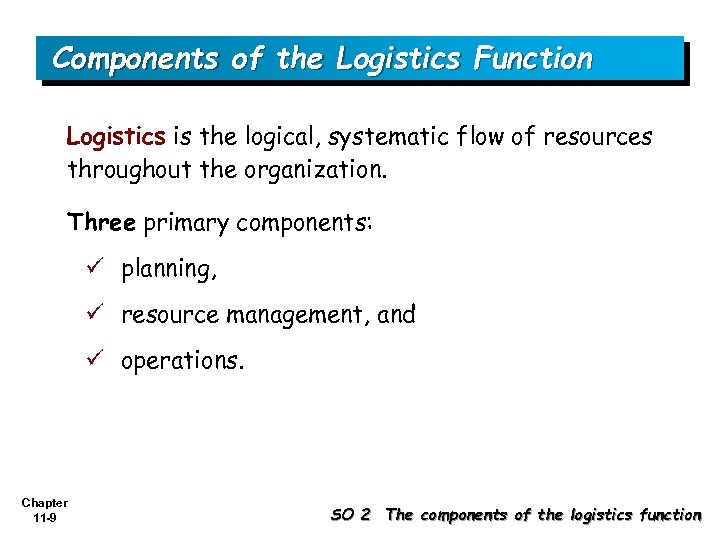 Components of the Logistics Function Logistics is the logical, systematic flow of resources throughout the organization. Three primary components: ü planning, ü resource management, and ü operations. Chapter 11 -9 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Logistics is the logical, systematic flow of resources throughout the organization. Three primary components: ü planning, ü resource management, and ü operations. Chapter 11 -9 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
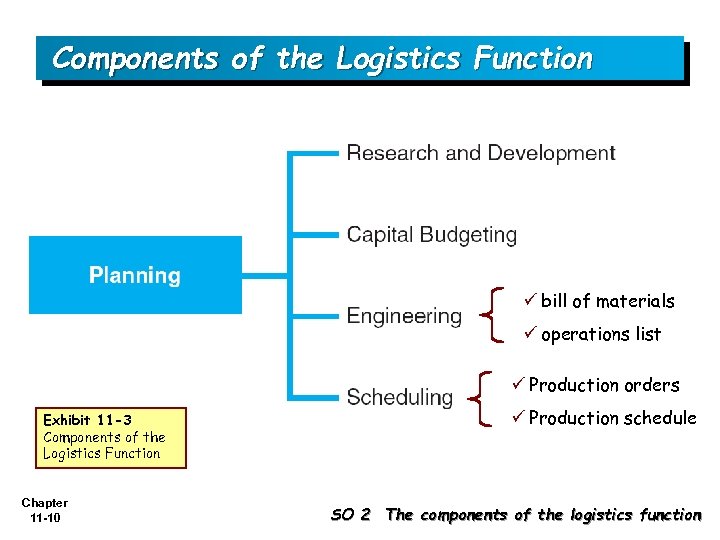 Components of the Logistics Function ü bill of materials ü operations list ü Production orders Exhibit 11 -3 Components of the Logistics Function Chapter 11 -10 ü Production schedule SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function ü bill of materials ü operations list ü Production orders Exhibit 11 -3 Components of the Logistics Function Chapter 11 -10 ü Production schedule SO 2 The components of the logistics function
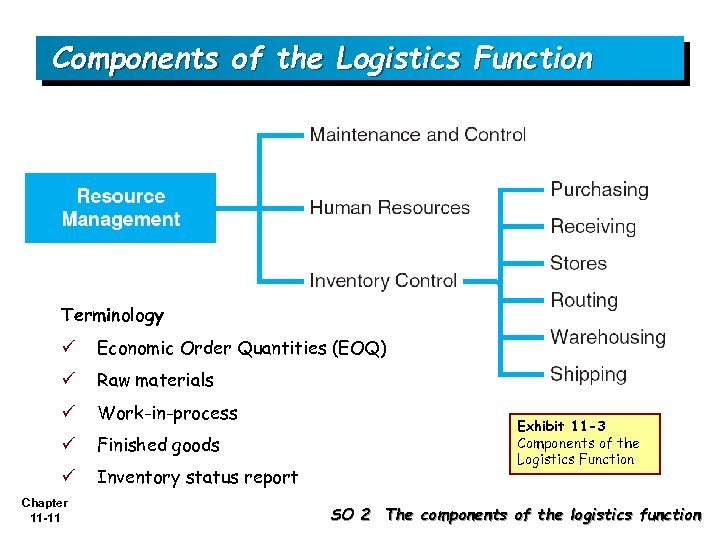 Components of the Logistics Function Terminology ü Economic Order Quantities (EOQ) ü Raw materials ü Work-in-process ü Finished goods ü Inventory status report Chapter 11 -11 Exhibit 11 -3 Components of the Logistics Function SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Terminology ü Economic Order Quantities (EOQ) ü Raw materials ü Work-in-process ü Finished goods ü Inventory status report Chapter 11 -11 Exhibit 11 -3 Components of the Logistics Function SO 2 The components of the logistics function
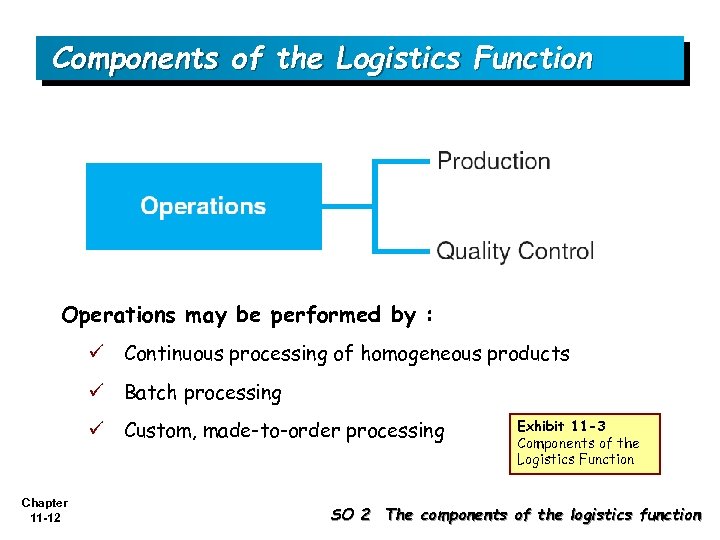 Components of the Logistics Function Operations may be performed by : ü Continuous processing of homogeneous products ü Batch processing ü Custom, made-to-order processing Chapter 11 -12 Exhibit 11 -3 Components of the Logistics Function SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Operations may be performed by : ü Continuous processing of homogeneous products ü Batch processing ü Custom, made-to-order processing Chapter 11 -12 Exhibit 11 -3 Components of the Logistics Function SO 2 The components of the logistics function
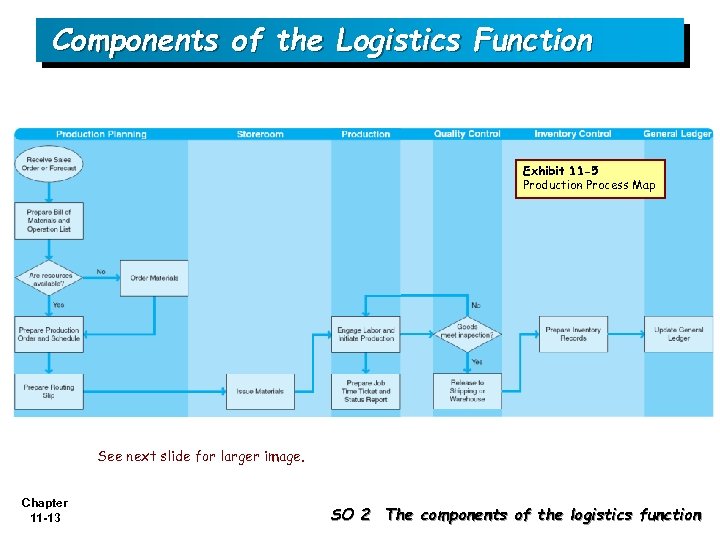 Components of the Logistics Function Exhibit 11 -5 Production Process Map See next slide for larger image. Chapter 11 -13 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Exhibit 11 -5 Production Process Map See next slide for larger image. Chapter 11 -13 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
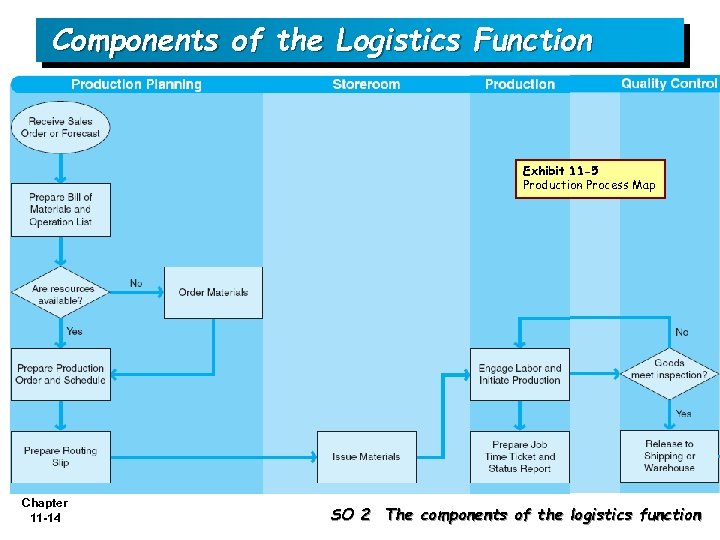 Components of the Logistics Function Exhibit 11 -5 Production Process Map Chapter 11 -14 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Exhibit 11 -5 Production Process Map Chapter 11 -14 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
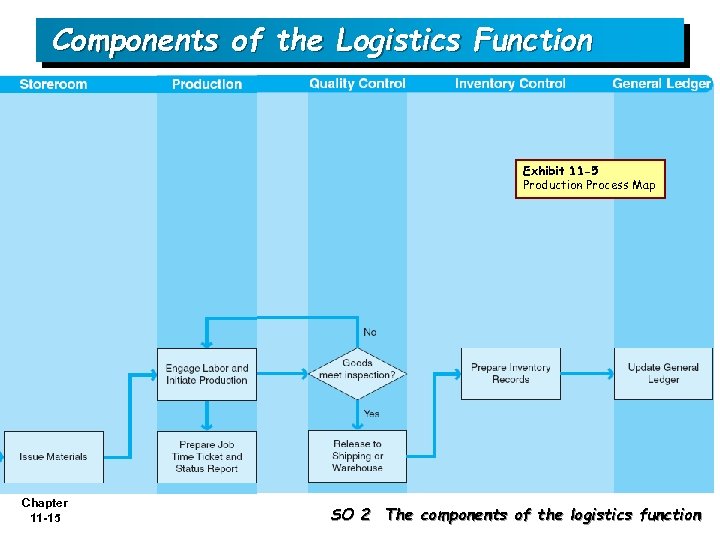 Components of the Logistics Function Exhibit 11 -5 Production Process Map Chapter 11 -15 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Exhibit 11 -5 Production Process Map Chapter 11 -15 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
 Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review The term conversion processes is often used synonymously with a. operations. b. production. c. manufacturing. d. all of the above. Chapter 11 -16 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review The term conversion processes is often used synonymously with a. operations. b. production. c. manufacturing. d. all of the above. Chapter 11 -16 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
 Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review Which of the following activities is not part of the planning component of the logistics function? a. Research and development b. Capital budgeting c. Human resource management d. Scheduling Chapter 11 -17 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review Which of the following activities is not part of the planning component of the logistics function? a. Research and development b. Capital budgeting c. Human resource management d. Scheduling Chapter 11 -17 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
 Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review Which of the following terms relates to the control of materials being held for future production? a. Routing b. Work-in-process c. Stores d. Warehousing Chapter 11 -18 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review Which of the following terms relates to the control of materials being held for future production? a. Routing b. Work-in-process c. Stores d. Warehousing Chapter 11 -18 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
 Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review When additional procedures are necessary to bring a defective product up to its required specifications, this is referred to as a. rework. b. scrap. c. work-in-process. d. variance reporting. Chapter 11 -19 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review When additional procedures are necessary to bring a defective product up to its required specifications, this is referred to as a. rework. b. scrap. c. work-in-process. d. variance reporting. Chapter 11 -19 SO 2 The components of the logistics function
 Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review A firm expects to sell 1000 units of its best-selling product in the coming year. Ordering costs for this product are $100 per order, and carrying costs are $2 per unit. Compute the optimum order size, using the EOQ model. a. 10 units b. 224 units c. 317 units Chapter 11 -20 d. 448 units SO 2 The components of the logistics function
Components of the Logistics Function Quick Review A firm expects to sell 1000 units of its best-selling product in the coming year. Ordering costs for this product are $100 per order, and carrying costs are $2 per unit. Compute the optimum order size, using the EOQ model. a. 10 units b. 224 units c. 317 units Chapter 11 -20 d. 448 units SO 2 The components of the logistics function
 Cost Accounting Reports Generated by Conversion Processes Standard costs are expected costs based on projections of a product’s required resources. Perpetual inventory systems involve Ø recording purchases as raw materials inventory, Ø recording all components of work-in-process for inventories in various stages of production, and Ø recording total cost of sales for products completed and sold. Chapter 11 -21 SO 3 Cost accounting reports generated by conversion processes
Cost Accounting Reports Generated by Conversion Processes Standard costs are expected costs based on projections of a product’s required resources. Perpetual inventory systems involve Ø recording purchases as raw materials inventory, Ø recording all components of work-in-process for inventories in various stages of production, and Ø recording total cost of sales for products completed and sold. Chapter 11 -21 SO 3 Cost accounting reports generated by conversion processes
 Cost Accounting Reports Generated by Conversion Processes Periodic inventory systems involve Ø updating the inventory and Ø cost of sales accounts only at the end of the period. Variances represent the differences between actual costs and the standard costs applied. Chapter 11 -22 SO 3 Cost accounting reports generated by conversion processes
Cost Accounting Reports Generated by Conversion Processes Periodic inventory systems involve Ø updating the inventory and Ø cost of sales accounts only at the end of the period. Variances represent the differences between actual costs and the standard costs applied. Chapter 11 -22 SO 3 Cost accounting reports generated by conversion processes
 Risks and Controls in Conversion Processes Common procedures within the conversion process: Ø Authorization of transactions ü Initiation of production orders ü Issuance of materials into production ü Transfer finished goods to warehouse or shipping areas Ø Segregation of duties Ø Adequate records and documents Chapter 11 -23 SO 4 Risks and controls in conversion processes
Risks and Controls in Conversion Processes Common procedures within the conversion process: Ø Authorization of transactions ü Initiation of production orders ü Issuance of materials into production ü Transfer finished goods to warehouse or shipping areas Ø Segregation of duties Ø Adequate records and documents Chapter 11 -23 SO 4 Risks and controls in conversion processes
 Risks and Controls in Conversion Processes Common procedures within the conversion process: Ø Security of assets and documents Ø Independent checks and reconciliation ü Physical inventory count ü Physical inventory reconciliation Ø Cost-benefit considerations Chapter 11 -24 SO 4 Risks and controls in conversion processes
Risks and Controls in Conversion Processes Common procedures within the conversion process: Ø Security of assets and documents Ø Independent checks and reconciliation ü Physical inventory count ü Physical inventory reconciliation Ø Cost-benefit considerations Chapter 11 -24 SO 4 Risks and controls in conversion processes
 Risks and Controls in Conversion Processes Quick Review Which of the following internal controls is typically associated with the maintenance of accurate inventory records? a. Performing regular comparisons of perpetual records with recent costs of inventory items b. Using a just-in-time system to keep inventory levels at a minimum c. Performing a match of the purchase request, receiving report, and purchase order before payment is approved Chapter 11 -25 d. Using physical inventory counts as a basis for adjusting the perpetual records 4 Risks and controls in conversion processes SO
Risks and Controls in Conversion Processes Quick Review Which of the following internal controls is typically associated with the maintenance of accurate inventory records? a. Performing regular comparisons of perpetual records with recent costs of inventory items b. Using a just-in-time system to keep inventory levels at a minimum c. Performing a match of the purchase request, receiving report, and purchase order before payment is approved Chapter 11 -25 d. Using physical inventory counts as a basis for adjusting the perpetual records 4 Risks and controls in conversion processes SO
 Risks and Controls in Conversion Processes Quick Review The goal of a physical inventory reconciliation is to a. determine the quantity of inventory sold. b. compare the physical count with the perpetual records. c. compare the physical count with the periodic records. d. determine the quantity of inventory in process. Chapter 11 -26 SO 4 Risks and controls in conversion processes
Risks and Controls in Conversion Processes Quick Review The goal of a physical inventory reconciliation is to a. determine the quantity of inventory sold. b. compare the physical count with the perpetual records. c. compare the physical count with the periodic records. d. determine the quantity of inventory in process. Chapter 11 -26 SO 4 Risks and controls in conversion processes
 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Computerized systems may provide the following benefits: Ø Automatic computation of materials requirements Ø Systematic scheduling that allows for greater flexibility and increased efficiencies Ø Timely transfer of inventories due to the automatic notification features Ø Validation of data entries Ø Automatic updating of inventory status reports Ø Automatic preparation of financial accounting entries and cost accounting reports Chapter 11 -27 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Computerized systems may provide the following benefits: Ø Automatic computation of materials requirements Ø Systematic scheduling that allows for greater flexibility and increased efficiencies Ø Timely transfer of inventories due to the automatic notification features Ø Validation of data entries Ø Automatic updating of inventory status reports Ø Automatic preparation of financial accounting entries and cost accounting reports Chapter 11 -27 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Additional trends that enhance the conversion process: Ø Computer-aided design (CAD) Ø Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) ü Industrial robots Ø Materials resource planning (MRP) Ø Manufacturing resource planning (MRP-II) Ø Enterprise-wide resource planning (ERP) Ø Computer-integrated manufacturing systems (CIMs) Ø Just-in-time (JIT) production systems Chapter 11 -28 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Additional trends that enhance the conversion process: Ø Computer-aided design (CAD) Ø Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) ü Industrial robots Ø Materials resource planning (MRP) Ø Manufacturing resource planning (MRP-II) Ø Enterprise-wide resource planning (ERP) Ø Computer-integrated manufacturing systems (CIMs) Ø Just-in-time (JIT) production systems Chapter 11 -28 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
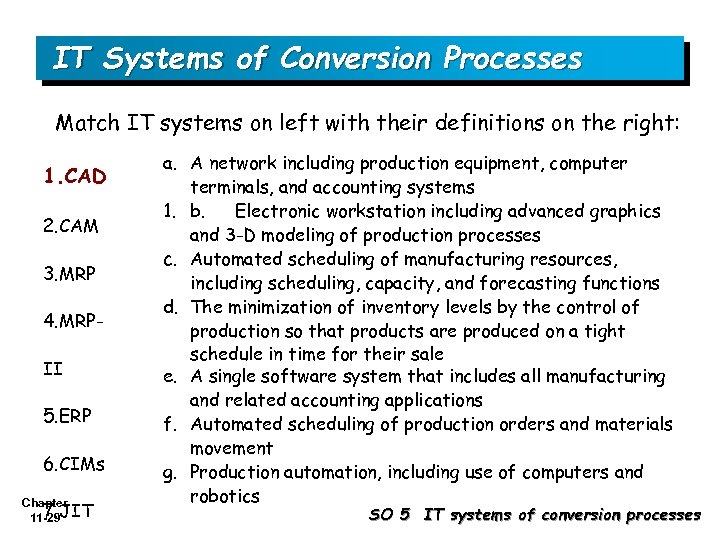 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRPII 5. ERP 6. CIMs Chapter 7. 11 -29 JIT a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRPII 5. ERP 6. CIMs Chapter 7. 11 -29 JIT a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
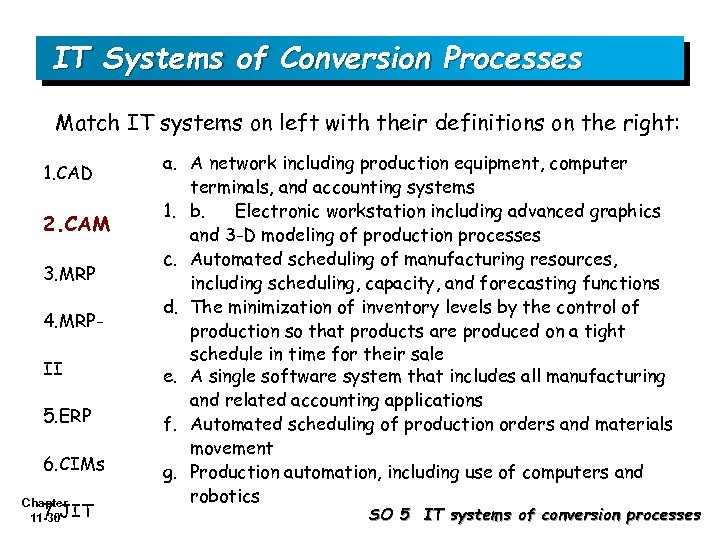 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRPII 5. ERP 6. CIMs Chapter 7. 11 -30 JIT a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRPII 5. ERP 6. CIMs Chapter 7. 11 -30 JIT a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
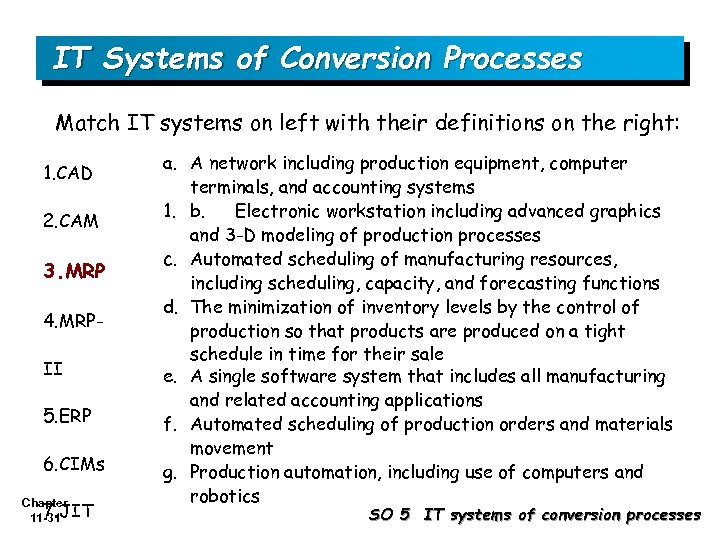 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRPII 5. ERP 6. CIMs Chapter 7. 11 -31 JIT a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRPII 5. ERP 6. CIMs Chapter 7. 11 -31 JIT a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
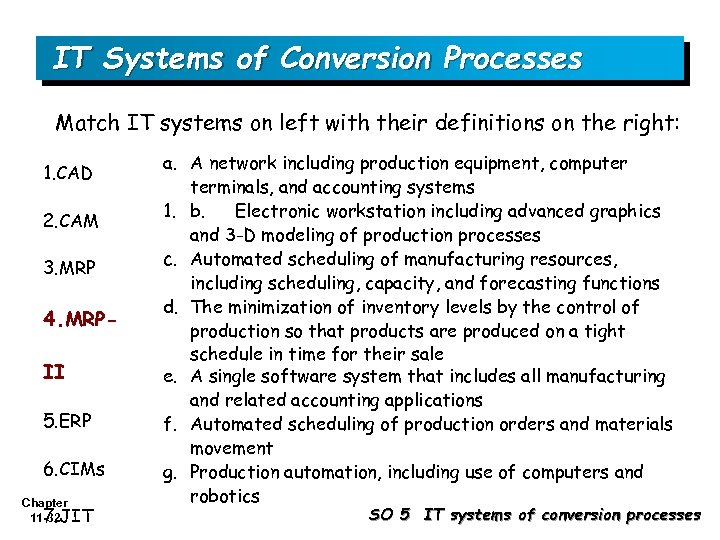 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRPII 5. ERP 6. CIMs Chapter 11 -32 JIT 7. a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRPII 5. ERP 6. CIMs Chapter 11 -32 JIT 7. a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
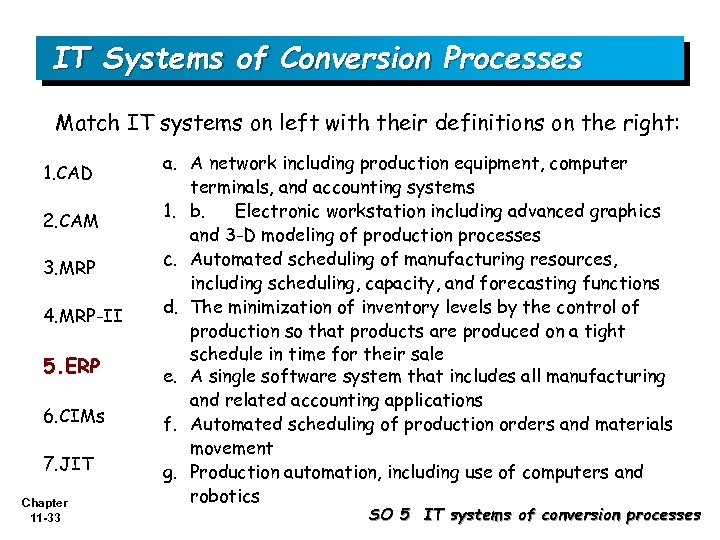 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRP-II 5. ERP 6. CIMs 7. JIT Chapter 11 -33 a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRP-II 5. ERP 6. CIMs 7. JIT Chapter 11 -33 a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
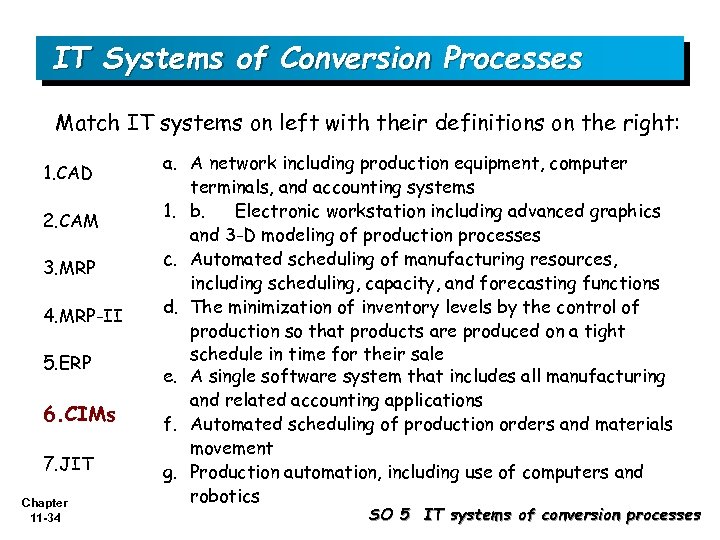 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRP-II 5. ERP 6. CIMs 7. JIT Chapter 11 -34 a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRP-II 5. ERP 6. CIMs 7. JIT Chapter 11 -34 a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
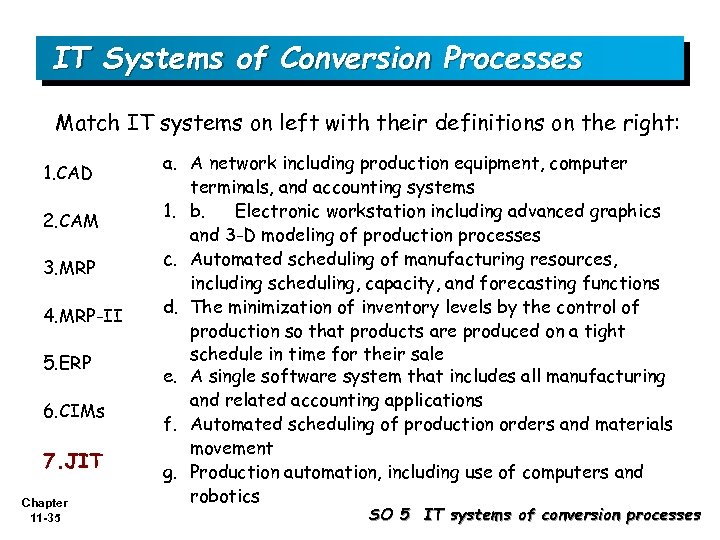 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRP-II 5. ERP 6. CIMs 7. JIT Chapter 11 -35 a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: 1. CAD 2. CAM 3. MRP 4. MRP-II 5. ERP 6. CIMs 7. JIT Chapter 11 -35 a. A network including production equipment, computer terminals, and accounting systems 1. b. Electronic workstation including advanced graphics and 3 -D modeling of production processes c. Automated scheduling of manufacturing resources, including scheduling, capacity, and forecasting functions d. The minimization of inventory levels by the control of production so that products are produced on a tight schedule in time for their sale e. A single software system that includes all manufacturing and related accounting applications f. Automated scheduling of production orders and materials movement g. Production automation, including use of computers and robotics SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
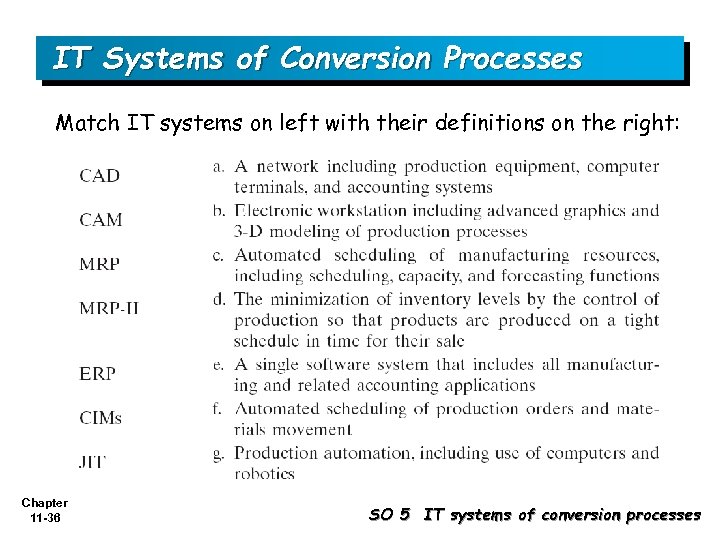 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: Chapter 11 -36 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Match IT systems on left with their definitions on the right: Chapter 11 -36 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Quick Review Which of the following is not considered a benefit of using computerized conversion systems? a. Automatic computation of materials requirements b. Increased sales and cost of sales c. Increased efficiency and flexibility d. Early error detection and increased accuracy Chapter 11 -37 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Quick Review Which of the following is not considered a benefit of using computerized conversion systems? a. Automatic computation of materials requirements b. Increased sales and cost of sales c. Increased efficiency and flexibility d. Early error detection and increased accuracy Chapter 11 -37 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Quick Review Which of the following represents a method of managing inventory designed to minimize a company’s investment in inventories by scheduling materials to arrive at the time they are needed for production? a. The economic order quantity (EOQ) b. Material resource planning (MRP) c. First-in, first-out (FIFO) d. Just-in-time (JIT) Chapter 11 -38 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Quick Review Which of the following represents a method of managing inventory designed to minimize a company’s investment in inventories by scheduling materials to arrive at the time they are needed for production? a. The economic order quantity (EOQ) b. Material resource planning (MRP) c. First-in, first-out (FIFO) d. Just-in-time (JIT) Chapter 11 -38 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
 IT Systems of Conversion Processes Quick Review For which of the following computerized conversion systems is Wal-Mart well known? a. CAD/CAM b. MRP-II c. CIMs d. JIT Chapter 11 -39 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
IT Systems of Conversion Processes Quick Review For which of the following computerized conversion systems is Wal-Mart well known? a. CAD/CAM b. MRP-II c. CIMs d. JIT Chapter 11 -39 SO 5 IT systems of conversion processes
 Ethical Issues Related to Conversion Processes Earnings management is the act of misstating financial information in order to improve financial statement results. Absorption costing involves the inclusion of both variable and fixed costs in the determination of unit costs for ending inventories and cost of goods sold. Chapter 11 -40 SO 6 Ethical issues related to conversion processes
Ethical Issues Related to Conversion Processes Earnings management is the act of misstating financial information in order to improve financial statement results. Absorption costing involves the inclusion of both variable and fixed costs in the determination of unit costs for ending inventories and cost of goods sold. Chapter 11 -40 SO 6 Ethical issues related to conversion processes
 Corporate Governance in Conversion Processes The internal controls and ethical tone and procedures within the conversion process are also part of the corporate governance structure. Establishing and maintaining reliable inventory management processes, internal controls, and ethical practices help ensure proper financial stewardship. Chapter 11 -41 SO 7 Corporate governance in conversion processes
Corporate Governance in Conversion Processes The internal controls and ethical tone and procedures within the conversion process are also part of the corporate governance structure. Establishing and maintaining reliable inventory management processes, internal controls, and ethical practices help ensure proper financial stewardship. Chapter 11 -41 SO 7 Corporate governance in conversion processes
 Copyright © 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the express written permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the information contained herein. Chapter 11 -42
Copyright © 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the express written permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the information contained herein. Chapter 11 -42


