66ca7f531e3c82ff868ba9a8cd1cf0ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Chapter 10 Supporting I/O Devices
Chapter 10 Supporting I/O Devices
 You Will Learn… § How to install peripheral I/O devices § How to use ports and expansion slots for add- on devices § About keyboards and how to troubleshoot them § About different types of pointing devices § How monitors and video cards relate to the system, and how to troubleshoot them
You Will Learn… § How to install peripheral I/O devices § How to use ports and expansion slots for add- on devices § About keyboards and how to troubleshoot them § About different types of pointing devices § How monitors and video cards relate to the system, and how to troubleshoot them
 Requirements for a New Device § Device driver or BIOS § System resources (eg, IRQ, DMA channel, I/O addresses, upper memory addresses) § Application software
Requirements for a New Device § Device driver or BIOS § System resources (eg, IRQ, DMA channel, I/O addresses, upper memory addresses) § Application software
 Basic Principles of Peripheral Installations § Peripheral is a hardware device controlled by software; install both hardware and software § Software might be of different types; install levels § More than one peripheral device might attempt to use same computer resources; resolve resource conflicts
Basic Principles of Peripheral Installations § Peripheral is a hardware device controlled by software; install both hardware and software § Software might be of different types; install levels § More than one peripheral device might attempt to use same computer resources; resolve resource conflicts
 Installation Overview 1. 2. 3. Install the device (internal or external) Install the device driver Install the application software
Installation Overview 1. 2. 3. Install the device (internal or external) Install the device driver Install the application software
 Installing a Hardware Device § Turn off PC, plug in the device, and reboot § If device is Pn. P, the Add New Hardware Wizard launches
Installing a Hardware Device § Turn off PC, plug in the device, and reboot § If device is Pn. P, the Add New Hardware Wizard launches
 Installing a Hardware Device
Installing a Hardware Device
 Installing a Hardware Device
Installing a Hardware Device
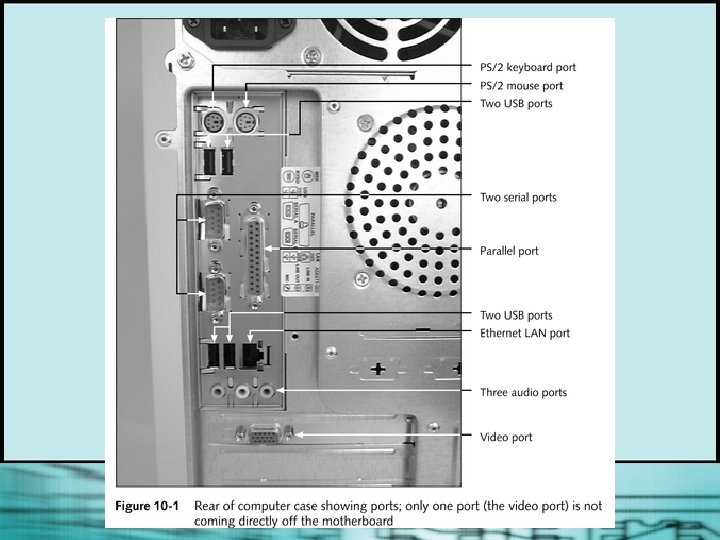
 Using Ports and Expansion Slots for Add -on Devices § Devices can: • Plug directly into a port (serial, parallel, USB, or IEEE 1394) Use an expansion card plugged into an expansion slot § • All computers come with: • One or two serial ports • One parallel port • One or more USB ports or an IEEE 1394 port (on newer computers)
Using Ports and Expansion Slots for Add -on Devices § Devices can: • Plug directly into a port (serial, parallel, USB, or IEEE 1394) Use an expansion card plugged into an expansion slot § • All computers come with: • One or two serial ports • One parallel port • One or more USB ports or an IEEE 1394 port (on newer computers)
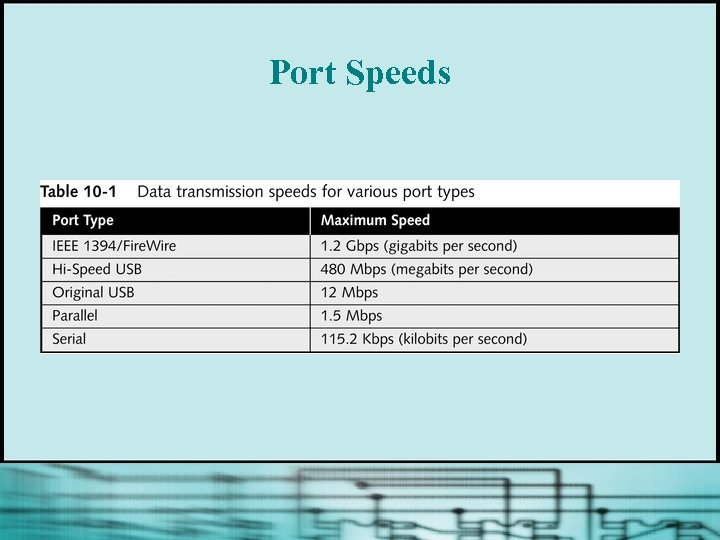 Port Speeds
Port Speeds
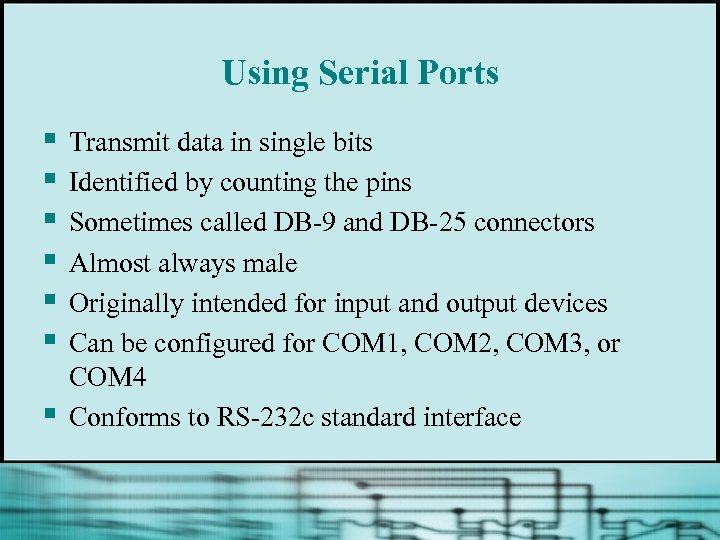 Using Serial Ports § § § § Transmit data in single bits Identified by counting the pins Sometimes called DB-9 and DB-25 connectors Almost always male Originally intended for input and output devices Can be configured for COM 1, COM 2, COM 3, or COM 4 Conforms to RS-232 c standard interface
Using Serial Ports § § § § Transmit data in single bits Identified by counting the pins Sometimes called DB-9 and DB-25 connectors Almost always male Originally intended for input and output devices Can be configured for COM 1, COM 2, COM 3, or COM 4 Conforms to RS-232 c standard interface
 Serial, Parallel, and Game Ports
Serial, Parallel, and Game Ports
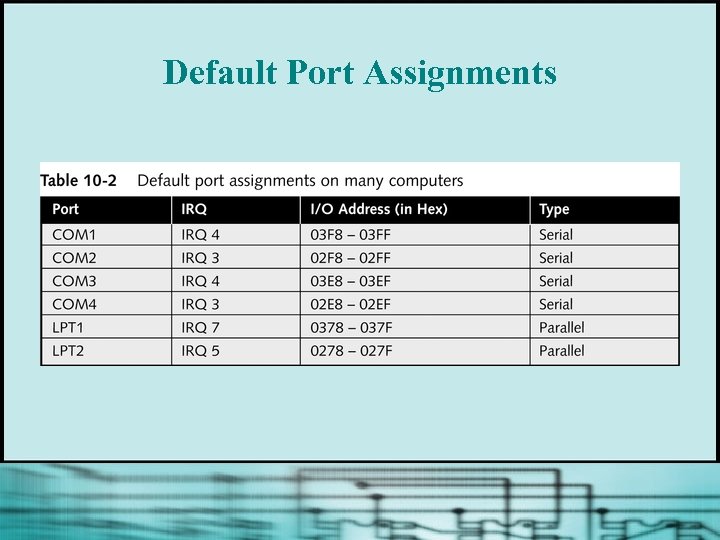 Default Port Assignments
Default Port Assignments
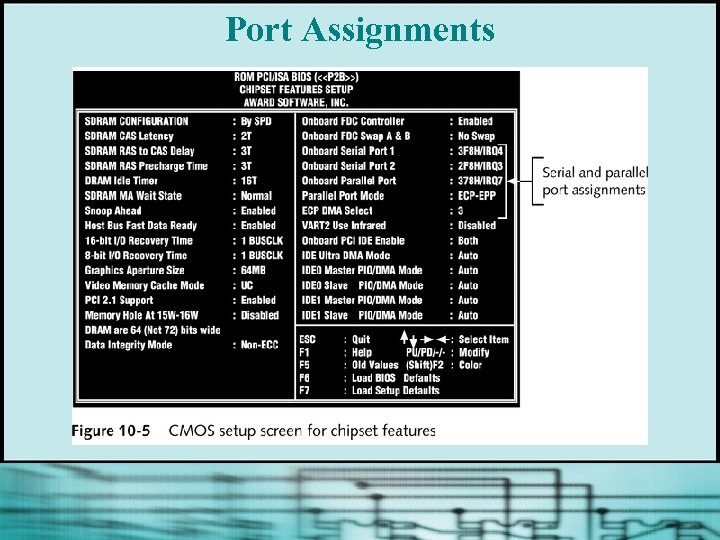 Port Assignments
Port Assignments
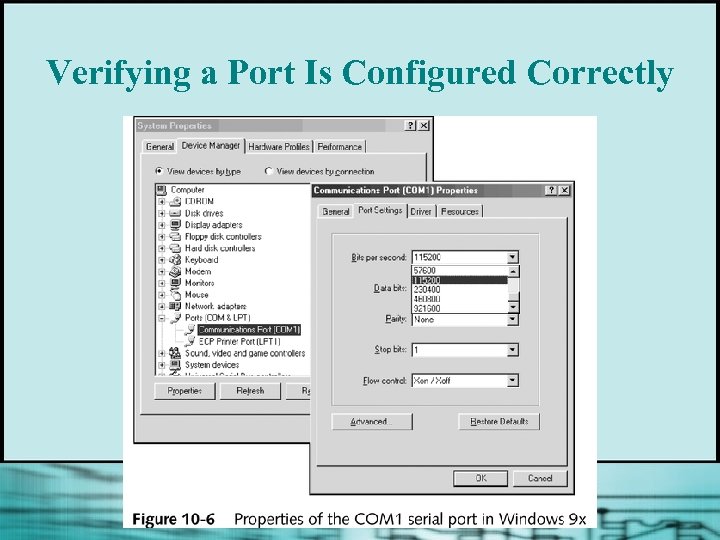 Verifying a Port Is Configured Correctly
Verifying a Port Is Configured Correctly
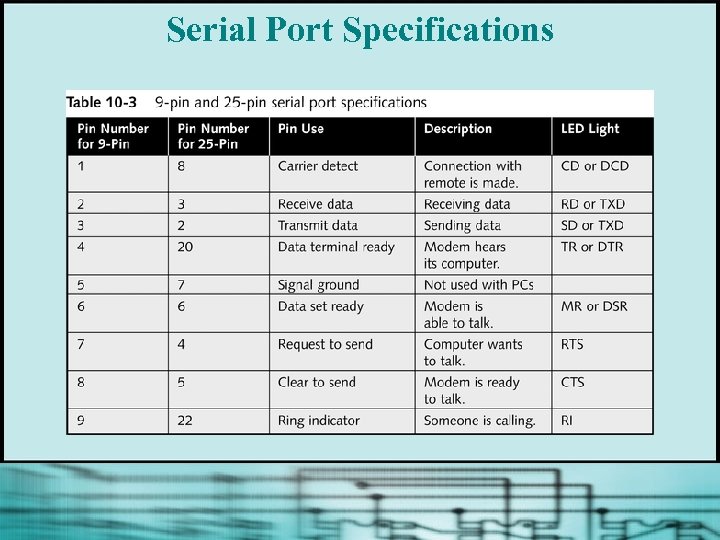 Serial Port Specifications
Serial Port Specifications
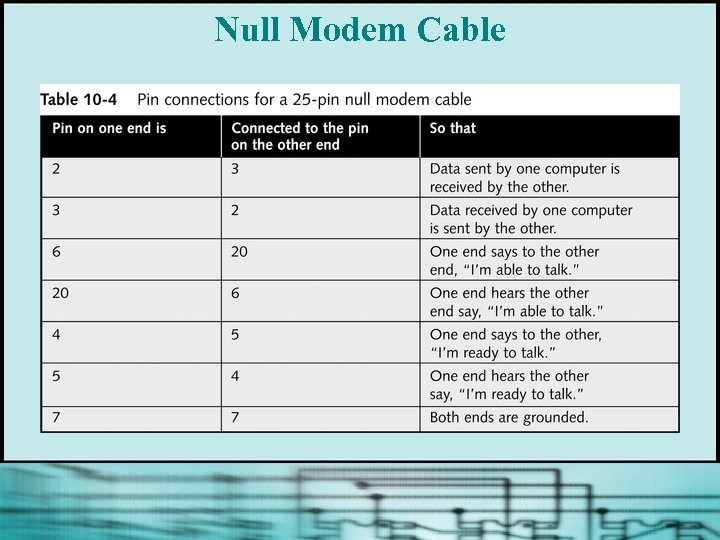
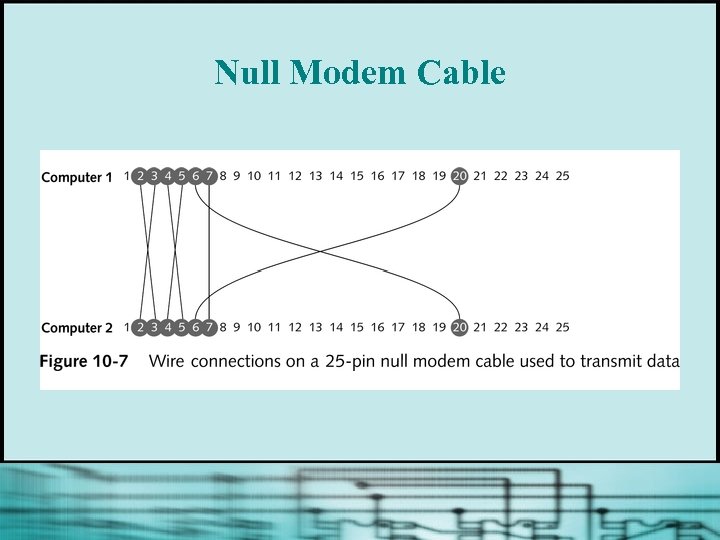
 Null Modem Connection § Special cable (null modem cable or modem eliminator) enables data transmission between two DTE devices without the need for modems § Null modem cable has several wires crossconnected to simulate modem connection
Null Modem Connection § Special cable (null modem cable or modem eliminator) enables data transmission between two DTE devices without the need for modems § Null modem cable has several wires crossconnected to simulate modem connection
 Null Modem Cable
Null Modem Cable
 Null Modem Cable
Null Modem Cable
 Infrared Transceivers § Use resources of the serial port for communication § Create a virtual infrared serial port and virtual infrared parallel port for infrared devices § Common problem: line-of-sight issue • Radio technology (eg, Bluetooth or 802. 11 b) is most popular way to connect wireless I/O device
Infrared Transceivers § Use resources of the serial port for communication § Create a virtual infrared serial port and virtual infrared parallel port for infrared devices § Common problem: line-of-sight issue • Radio technology (eg, Bluetooth or 802. 11 b) is most popular way to connect wireless I/O device
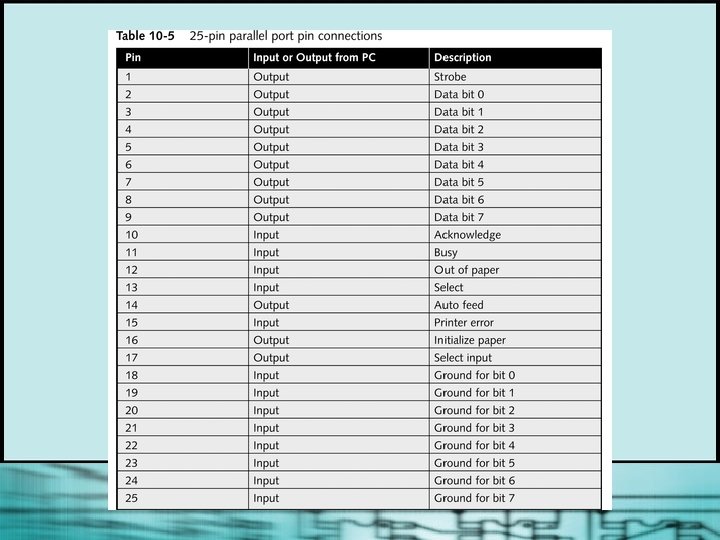
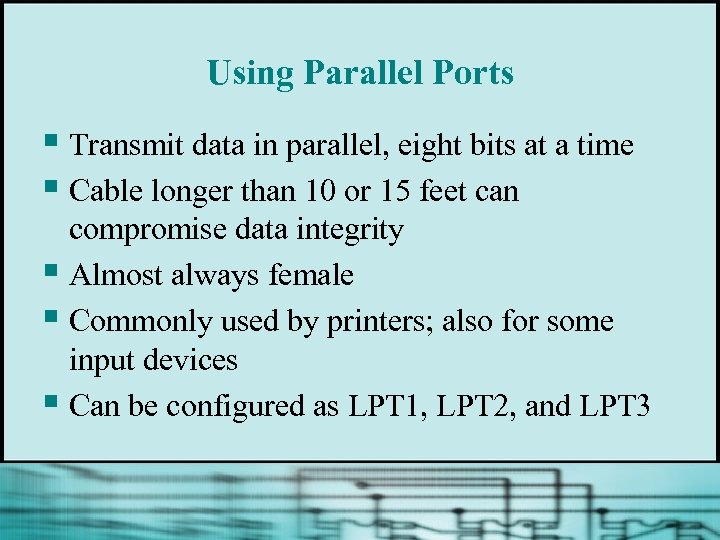 Using Parallel Ports § Transmit data in parallel, eight bits at a time § Cable longer than 10 or 15 feet can compromise data integrity § Almost always female § Commonly used by printers; also for some input devices § Can be configured as LPT 1, LPT 2, and LPT 3
Using Parallel Ports § Transmit data in parallel, eight bits at a time § Cable longer than 10 or 15 feet can compromise data integrity § Almost always female § Commonly used by printers; also for some input devices § Can be configured as LPT 1, LPT 2, and LPT 3
 Types of Parallel Ports § Standard parallel port (SPP) • Data flows in one direction • Comparatively slower § Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) • Bidirectional § Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) • Bidirectional • Uses a DMA channel
Types of Parallel Ports § Standard parallel port (SPP) • Data flows in one direction • Comparatively slower § Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) • Bidirectional § Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) • Bidirectional • Uses a DMA channel
 A Standard Parallel Port
A Standard Parallel Port
 Using USB Ports § Expected to ultimately replace serial and parallel ports • Faster • Use higher quality cabling • Easier to manage § Allows for hot-swapping and is hot-pluggable § Used by many devices (eg, mice, joysticks, keyboards, printers)
Using USB Ports § Expected to ultimately replace serial and parallel ports • Faster • Use higher quality cabling • Easier to manage § Allows for hot-swapping and is hot-pluggable § Used by many devices (eg, mice, joysticks, keyboards, printers)
 Using USB Ports
Using USB Ports
 Using USB Ports
Using USB Ports
 Using USB Ports
Using USB Ports
 USB Host Controller § Polls each device, asking if data is ready to be sent or requesting to send data to the device § Manages communication to the CPU for all devices, using only a single IRQ, I/O address range, and DMA channel § Automatically assigns system resources at startup (with the OS)
USB Host Controller § Polls each device, asking if data is ready to be sent or requesting to send data to the device § Manages communication to the CPU for all devices, using only a single IRQ, I/O address range, and DMA channel § Automatically assigns system resources at startup (with the OS)
 Requirements for Installing a USB Device § Motherboard or expansion card that provides a USB port § OS that supports USB § USB device driver
Requirements for Installing a USB Device § Motherboard or expansion card that provides a USB port § OS that supports USB § USB device driver
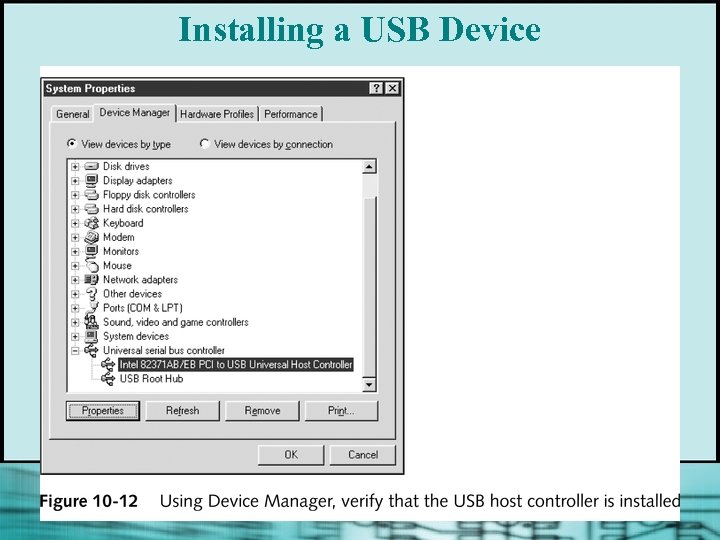 Installing a USB Device
Installing a USB Device
 Using IEEE 1394 Ports § § § Also called Fire. Wire and i. Link Transmits data serially; faster than USB Supports data speeds as high as 1. 2 Gbps Likely to replace SCSI for high-volume, multimedia external devices Devices can be daisy-chained together and managed by a host controller using a single set of system resources Uses isochronous data transfer
Using IEEE 1394 Ports § § § Also called Fire. Wire and i. Link Transmits data serially; faster than USB Supports data speeds as high as 1. 2 Gbps Likely to replace SCSI for high-volume, multimedia external devices Devices can be daisy-chained together and managed by a host controller using a single set of system resources Uses isochronous data transfer
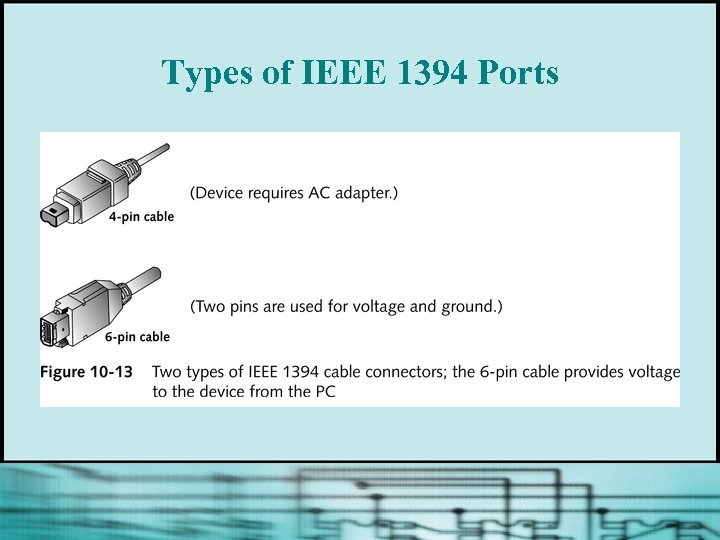 Types of IEEE 1394 Ports
Types of IEEE 1394 Ports
 IEEE 1394 Ports
IEEE 1394 Ports
 Using PCI Expansion Slots § PCI bus is now the standard local I/O bus § Devices connected to it can run at one speed while the CPU runs at a different speed § Often used for fast I/O devices (eg, network cards or SCSI host adapters)
Using PCI Expansion Slots § PCI bus is now the standard local I/O bus § Devices connected to it can run at one speed while the CPU runs at a different speed § Often used for fast I/O devices (eg, network cards or SCSI host adapters)
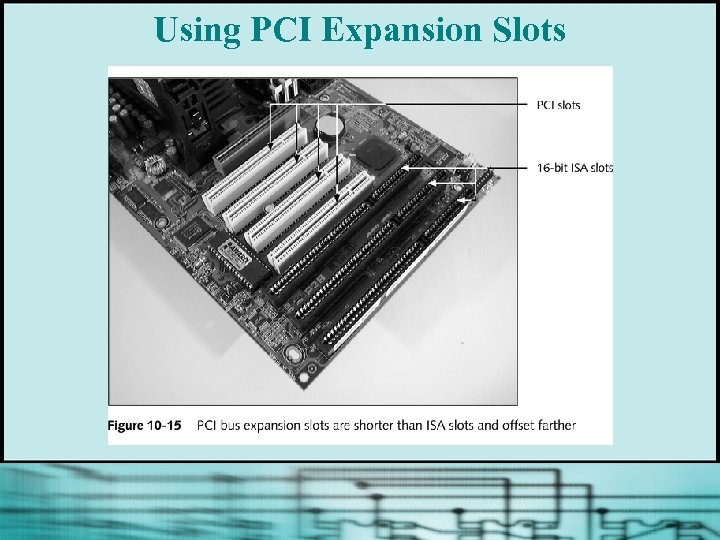 Using PCI Expansion Slots
Using PCI Expansion Slots
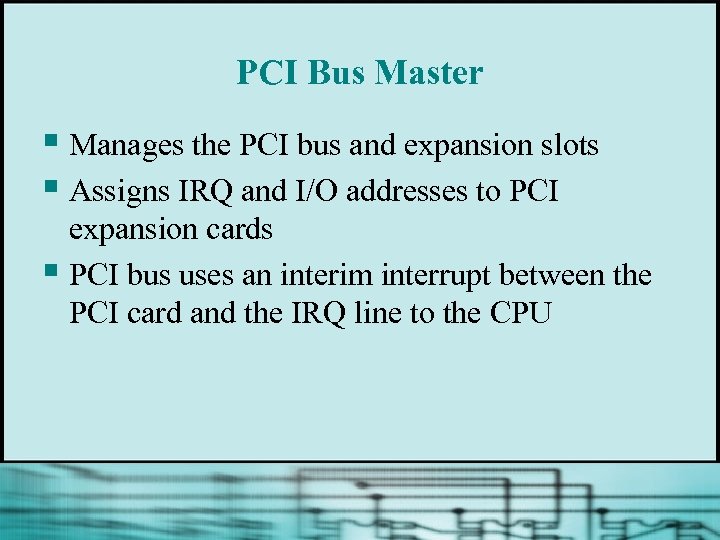 PCI Bus Master § Manages the PCI bus and expansion slots § Assigns IRQ and I/O addresses to PCI expansion cards § PCI bus uses an interim interrupt between the PCI card and the IRQ line to the CPU
PCI Bus Master § Manages the PCI bus and expansion slots § Assigns IRQ and I/O addresses to PCI expansion cards § PCI bus uses an interim interrupt between the PCI card and the IRQ line to the CPU
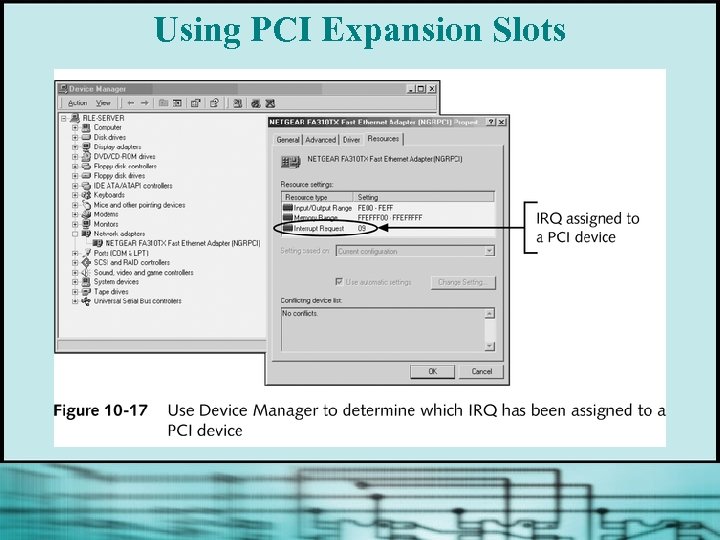 Using PCI Expansion Slots
Using PCI Expansion Slots
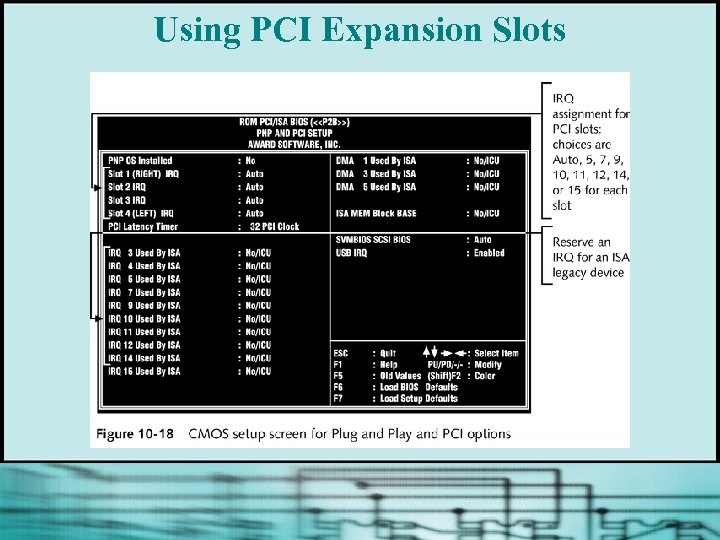 Using PCI Expansion Slots
Using PCI Expansion Slots
 Using ISA Expansion Slots § Configuration is not automated § ISA bus does not manage system resources § ISA device must request system resources at startup
Using ISA Expansion Slots § Configuration is not automated § ISA bus does not manage system resources § ISA device must request system resources at startup
 Keyboards § Traditional straight design or ergonomic design § Two technologies for keys making contact • Foil contact • Metal contact
Keyboards § Traditional straight design or ergonomic design § Two technologies for keys making contact • Foil contact • Metal contact
 An Ergonomic Keyboard
An Ergonomic Keyboard
 Correct Position at the Keyboard
Correct Position at the Keyboard
 Keyboard Connectors § PS/2 connector (mini-DIN) • Small, round, with six pins § DIN connector • Round with five pins § USB port § Wireless connection
Keyboard Connectors § PS/2 connector (mini-DIN) • Small, round, with six pins § DIN connector • Round with five pins § USB port § Wireless connection
 Keyboard Connectors
Keyboard Connectors
 Keyboard Connector Adapter
Keyboard Connector Adapter
 Keyboard Connectors
Keyboard Connectors
 Installing a Keyboard § Usually means plugging it in and turning on the PC § System BIOS manages the keyboard, so no keyboard drivers are necessary (except for wireless keyboards)
Installing a Keyboard § Usually means plugging it in and turning on the PC § System BIOS manages the keyboard, so no keyboard drivers are necessary (except for wireless keyboards)
 Troubleshooting Keyboard § A few keys don’t work § The keyboard does not work at all § Key continues to repeat after being released § Keys produce wrong characters § Major spills on the keyboard
Troubleshooting Keyboard § A few keys don’t work § The keyboard does not work at all § Key continues to repeat after being released § Keys produce wrong characters § Major spills on the keyboard
 Pointing Devices § Mouse • Wheel mouse • Optical mouse § Trackball § Touch pads
Pointing Devices § Mouse • Wheel mouse • Optical mouse § Trackball § Touch pads
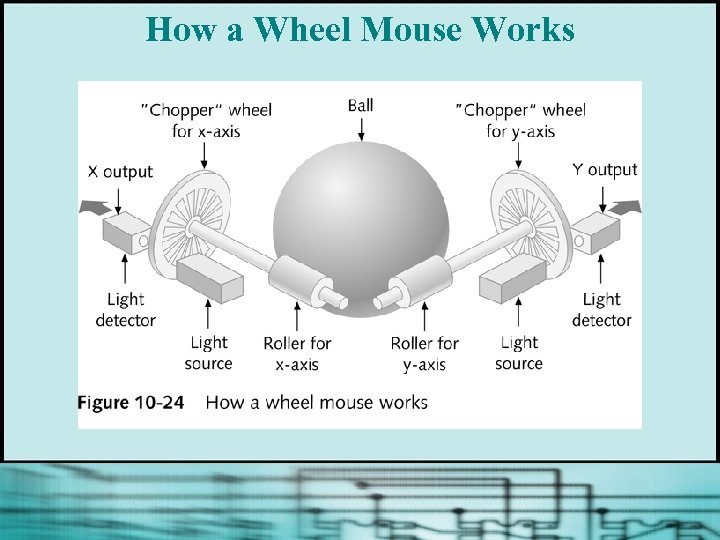 How a Wheel Mouse Works
How a Wheel Mouse Works
 Mouse Connection Types § Serial mouse § Motherboard mouse or PS/2 compatible mouse § Bus mouse § Using a USB port § Using a Y-connection to share a port with a keyboard § Cordless technology
Mouse Connection Types § Serial mouse § Motherboard mouse or PS/2 compatible mouse § Bus mouse § Using a USB port § Using a Y-connection to share a port with a keyboard § Cordless technology
 Cleaning the Mouse § Remove cover § Clean rollers with cotton swab dipped in small amount of liquid soap
Cleaning the Mouse § Remove cover § Clean rollers with cotton swab dipped in small amount of liquid soap
 Manufacturers of Keyboards and Pointing Devices
Manufacturers of Keyboards and Pointing Devices
 Troubleshooting a Mouse § § Check mouse port connection; check for dust or dirt inside; reboot the PC Try a new mouse Using Device Manager and Add New Hardware icon in Control Panel, uninstall then reinstall mouse driver; reboot the PC Reboot PC and select logged option from startup menu to create Bootlog. txt file; continue boot and check log for errors
Troubleshooting a Mouse § § Check mouse port connection; check for dust or dirt inside; reboot the PC Try a new mouse Using Device Manager and Add New Hardware icon in Control Panel, uninstall then reinstall mouse driver; reboot the PC Reboot PC and select logged option from startup menu to create Bootlog. txt file; continue boot and check log for errors
 Computer Video § Necessary components for video output • Video controller • Monitor
Computer Video § Necessary components for video output • Video controller • Monitor
 Monitors § Rated by screen size, resolution, refresh rate, and interlace features § Most meet standards for Super VGA (Video Graphics Adapter) § Use either CRT (cathode-ray tube) technology or LCD (liquid crystal display) technology
Monitors § Rated by screen size, resolution, refresh rate, and interlace features § Most meet standards for Super VGA (Video Graphics Adapter) § Use either CRT (cathode-ray tube) technology or LCD (liquid crystal display) technology
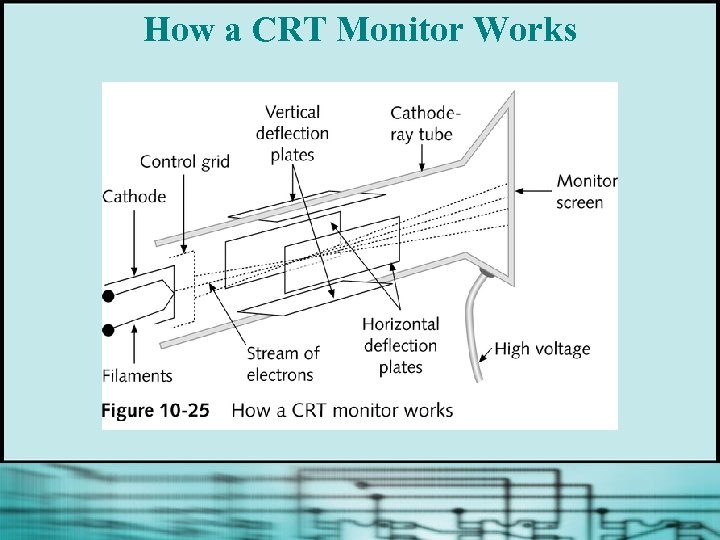 How a CRT Monitor Works
How a CRT Monitor Works
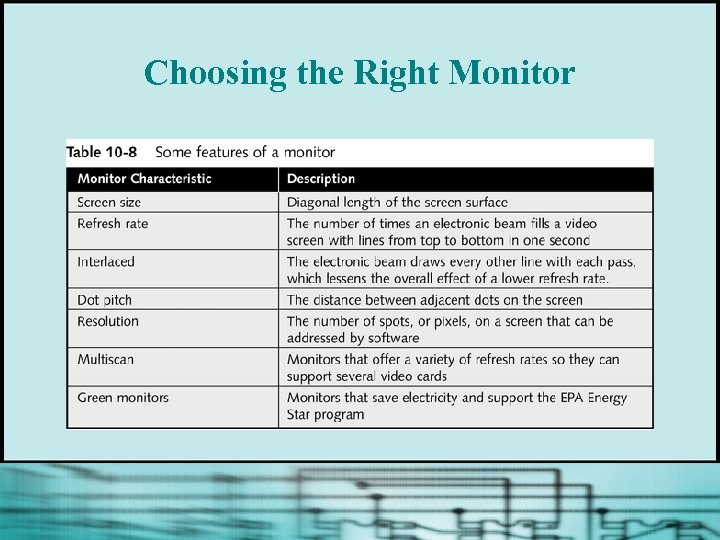 Choosing the Right Monitor
Choosing the Right Monitor
 Monitors § Monitors and ELF (extremely low frequency) emissions § Flat panel monitors • Active-matrix • Dual-scan passive matrix
Monitors § Monitors and ELF (extremely low frequency) emissions § Flat panel monitors • Active-matrix • Dual-scan passive matrix
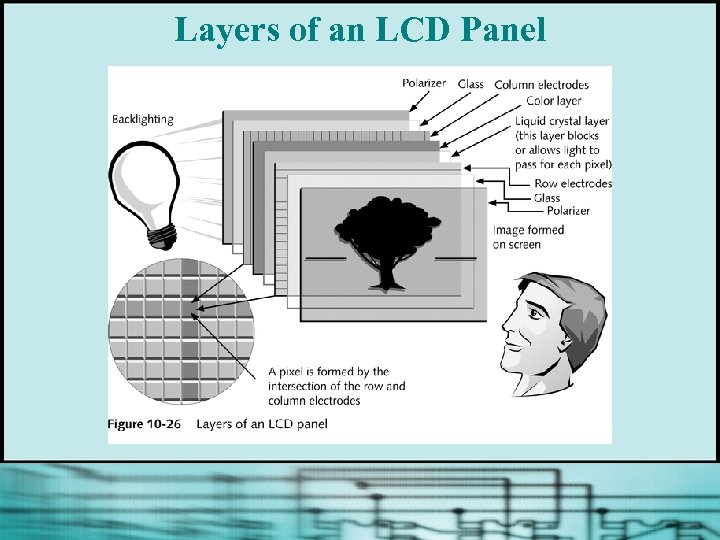 Layers of an LCD Panel
Layers of an LCD Panel
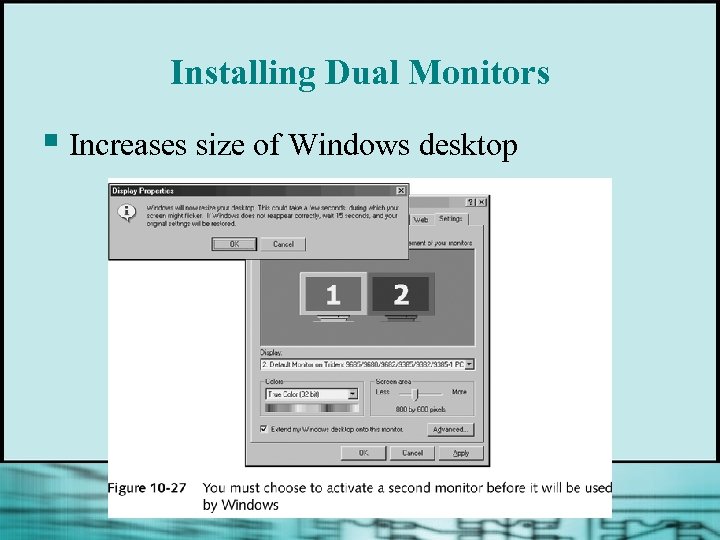 Installing Dual Monitors § Increases size of Windows desktop
Installing Dual Monitors § Increases size of Windows desktop
 Video Cards § § Quality of video subsystem is rated according to how it affects: • Overall system performance • Video quality (eg, resolution and color) • Power-saving features • Ease of use and installation Features to look for: • The bus it uses • Amount of video RAM it has or can support
Video Cards § § Quality of video subsystem is rated according to how it affects: • Overall system performance • Video quality (eg, resolution and color) • Power-saving features • Ease of use and installation Features to look for: • The bus it uses • Amount of video RAM it has or can support
 Buses Used by Video Cards § VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) bus § PCI bus § AGP bus
Buses Used by Video Cards § VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) bus § PCI bus § AGP bus
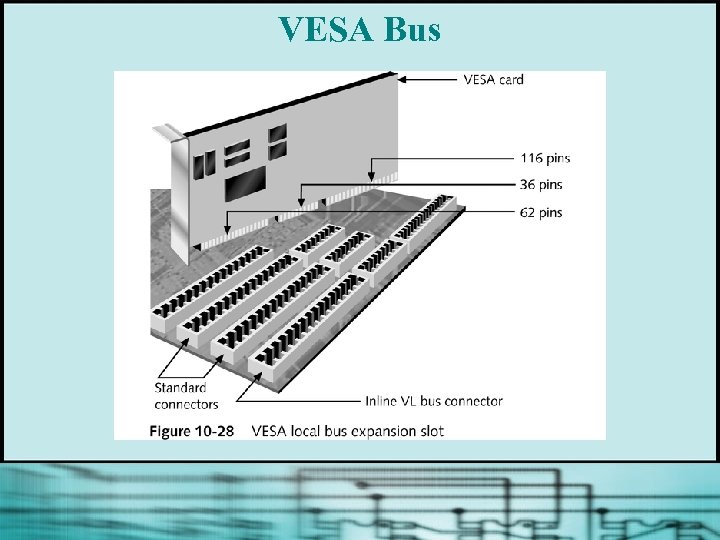 VESA Bus
VESA Bus
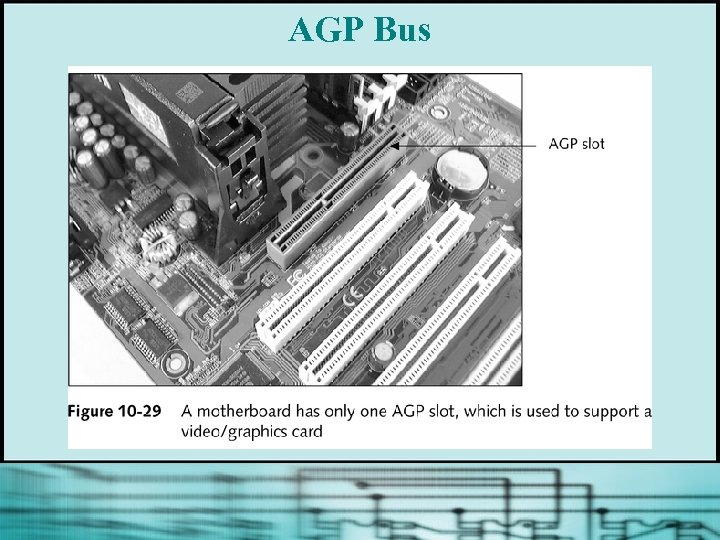 AGP Bus
AGP Bus
 Graphics Accelerators § § Type of video card that has its own processor to boost performance Features reduce burden on motherboard CPU, eg: • MPEG decoding • 3 -D graphics • Dual porting • Color space conversion • Interpolated scaling • EPA Green PC support
Graphics Accelerators § § Type of video card that has its own processor to boost performance Features reduce burden on motherboard CPU, eg: • MPEG decoding • 3 -D graphics • Dual porting • Color space conversion • Interpolated scaling • EPA Green PC support
 Video Memory § VRAM (Video RAM) § SGRAM (synchronous graphics RAM) § WRAM (window RAM) § 3 -D RAM
Video Memory § VRAM (Video RAM) § SGRAM (synchronous graphics RAM) § WRAM (window RAM) § 3 -D RAM
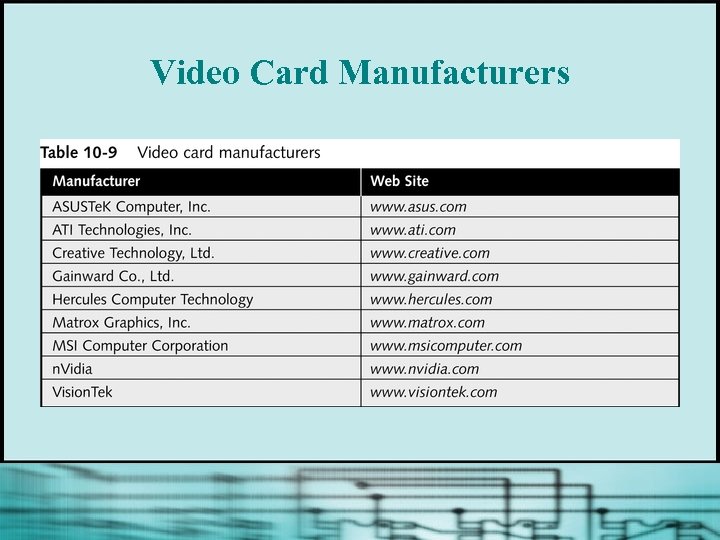 Video Card Manufacturers
Video Card Manufacturers
 Troubleshooting Video Problems § Power light (LED) does not go on; no picture § Power LED light is on; no picture on power-up § Power on; monitor displays wrong characters § Monitor flickers and/or has wavy lines § No graphics display or screen goes blank when loading certain programs continued…
Troubleshooting Video Problems § Power light (LED) does not go on; no picture § Power LED light is on; no picture on power-up § Power on; monitor displays wrong characters § Monitor flickers and/or has wavy lines § No graphics display or screen goes blank when loading certain programs continued…
 Troubleshooting Video Problems § Screen goes blank 30 seconds or one minute after keyboard is left untouched § Poor quality color display § Picture out of focus or out of adjustment § Crackling sound
Troubleshooting Video Problems § Screen goes blank 30 seconds or one minute after keyboard is left untouched § Poor quality color display § Picture out of focus or out of adjustment § Crackling sound
 Video Problems § To configure or change monitor settings and drivers in Windows § To change the video driver configuration § Returning to standard VGA settings
Video Problems § To configure or change monitor settings and drivers in Windows § To change the video driver configuration § Returning to standard VGA settings
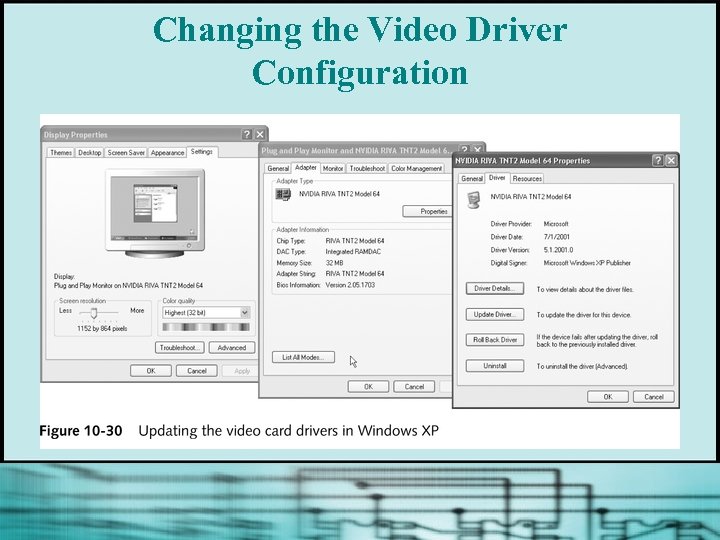 Changing the Video Driver Configuration
Changing the Video Driver Configuration
 Chapter Summary § Installing and supporting I/O devices § Procedures and guidelines common to most installations § How to use serial, parallel, UB, and IEEE 1394 ports, and expansions slots § Essential I/O devices for a PC: keyboard, mouse, and video
Chapter Summary § Installing and supporting I/O devices § Procedures and guidelines common to most installations § How to use serial, parallel, UB, and IEEE 1394 ports, and expansions slots § Essential I/O devices for a PC: keyboard, mouse, and video


