c8c0dc0561b63bba178bd7cff0c704b9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Chapter 10 Supporting Decision Making Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 10 Supporting Decision Making Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Learning Objectives v Identify the changes taking place in the form and use of decision support in business. v Identify the role and reporting alternatives of management information systems. v Describe how online analytical processing can meet key information needs of managers. v Explain the decision support system concept and how it differs from traditional management information systems. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives v Identify the changes taking place in the form and use of decision support in business. v Identify the role and reporting alternatives of management information systems. v Describe how online analytical processing can meet key information needs of managers. v Explain the decision support system concept and how it differs from traditional management information systems. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Learning Objectives v Explain how the following information systems can support the information needs of executives, managers, and business professionals: v. Executive information systems v. Enterprise information portals v. Knowledge management systems Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives v Explain how the following information systems can support the information needs of executives, managers, and business professionals: v. Executive information systems v. Enterprise information portals v. Knowledge management systems Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Learning Objectives v Identify how neural networks, fuzzy logic, genetic algorithms, virtual reality, and intelligent agents can be used in business. v Give examples of several ways expert systems can be used in business decision-making situations. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives v Identify how neural networks, fuzzy logic, genetic algorithms, virtual reality, and intelligent agents can be used in business. v Give examples of several ways expert systems can be used in business decision-making situations. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Section 1 Supporting Decision Making Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Section 1 Supporting Decision Making Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 I. Introduction v An organization is a nexus of decisions with information needs supplied by an Information System v Information, Decisions, and Management – the type of information required by decision makers is directly related to the level of management decision making and the amount of structure in the decision situation v Strategic Management – executive level, long-range plans, organizational goals and policies, and objectives v Tactical Management – mid-level management, medium- and short-range plans to support objectives made by executives, and allocation of resources and performance monitoring of organizational subunits v Operational Management – short-range plans, day-to-day operations, direct the use of resources and performance of tasks Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
I. Introduction v An organization is a nexus of decisions with information needs supplied by an Information System v Information, Decisions, and Management – the type of information required by decision makers is directly related to the level of management decision making and the amount of structure in the decision situation v Strategic Management – executive level, long-range plans, organizational goals and policies, and objectives v Tactical Management – mid-level management, medium- and short-range plans to support objectives made by executives, and allocation of resources and performance monitoring of organizational subunits v Operational Management – short-range plans, day-to-day operations, direct the use of resources and performance of tasks Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 I. Introduction v Information Quality – characteristics of information products v Timeliness – was information present when needed? v Accuracy – was the information correct & error free? v Completeness – was all the needed information there? v Relevance – was the information related to the situation? v Decision Structure v Structured – operational level, occur frequently, much information available v Semistructured – managerial level (most business decisions are here), not as frequent, less information available v Unstructured – executive level, infrequent, little information available Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
I. Introduction v Information Quality – characteristics of information products v Timeliness – was information present when needed? v Accuracy – was the information correct & error free? v Completeness – was all the needed information there? v Relevance – was the information related to the situation? v Decision Structure v Structured – operational level, occur frequently, much information available v Semistructured – managerial level (most business decisions are here), not as frequent, less information available v Unstructured – executive level, infrequent, little information available Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
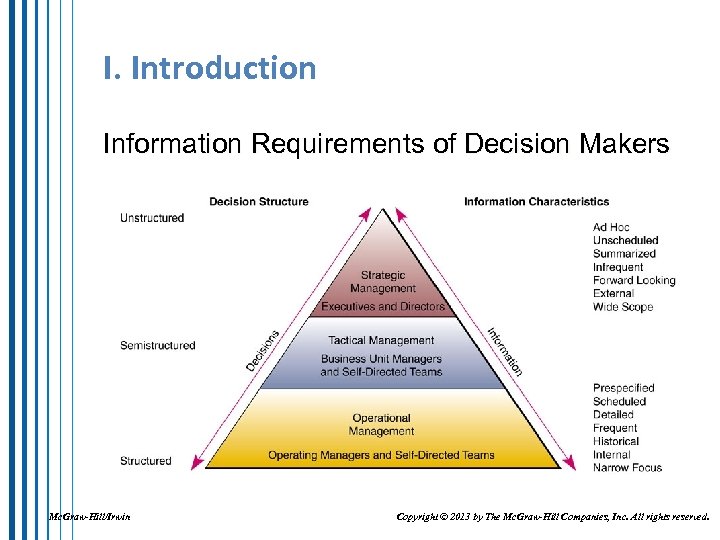 I. Introduction Information Requirements of Decision Makers Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
I. Introduction Information Requirements of Decision Makers Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
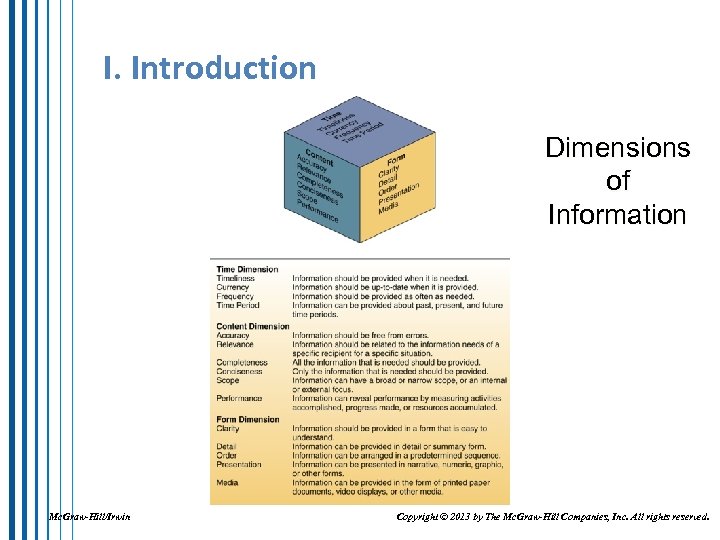 I. Introduction Dimensions of Information Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
I. Introduction Dimensions of Information Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Section 2 Advanced Technologies for Decision Support Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Advanced Technologies for Decision Support Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 II. An Overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) v Goal of AI is to simulate the ability to think – reasoning, learning, problem solving v Turing Test – if a human communicates with a computer and does not know it is a computer, the computer is exhibiting artificial intelligence v CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing Test) – a test to tell people from computers – a distorted graphic with letters/numbers; a human can see the letters/numbers a computer cannot Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
II. An Overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) v Goal of AI is to simulate the ability to think – reasoning, learning, problem solving v Turing Test – if a human communicates with a computer and does not know it is a computer, the computer is exhibiting artificial intelligence v CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing Test) – a test to tell people from computers – a distorted graphic with letters/numbers; a human can see the letters/numbers a computer cannot Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
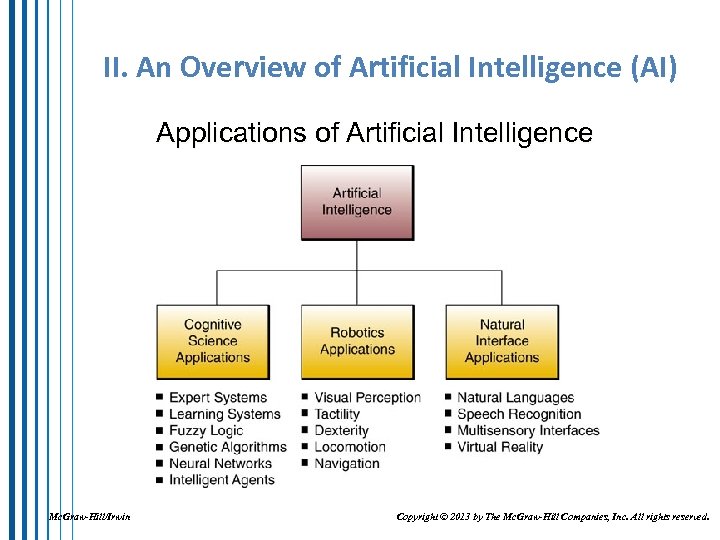 II. An Overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications of Artificial Intelligence Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
II. An Overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications of Artificial Intelligence Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 III. Expert Systems v Components of an Expert System v Knowledge Base – contains facts and the heuristics (rules) to express the reasoning procedures the expert uses v Software Resources – v. Inference Engine – the program that processes the knowledge (rules and facts) v. Interface – the way the user communicates with the system Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
III. Expert Systems v Components of an Expert System v Knowledge Base – contains facts and the heuristics (rules) to express the reasoning procedures the expert uses v Software Resources – v. Inference Engine – the program that processes the knowledge (rules and facts) v. Interface – the way the user communicates with the system Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 VI. Fuzzy Logic Systems v. Reasoning with incomplete or ambiguous data v. Fuzzy Logic in Business – rare in the U. S. (preferring expert systems), but popular in Japan VII. Genetic Algorithms v. Simulates evolutionary processes that yield increasingly better solutions Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
VI. Fuzzy Logic Systems v. Reasoning with incomplete or ambiguous data v. Fuzzy Logic in Business – rare in the U. S. (preferring expert systems), but popular in Japan VII. Genetic Algorithms v. Simulates evolutionary processes that yield increasingly better solutions Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 VIII. Virtual Reality (VR) v. Computer-simulated reality v. VR Applications – CAD, medical diagnostics, flight simulation, entertainment IX. Intelligent Agents v. Use built-in and learned knowledge to make decisions and accomplish tasks that fulfill the intentions of the user Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
VIII. Virtual Reality (VR) v. Computer-simulated reality v. VR Applications – CAD, medical diagnostics, flight simulation, entertainment IX. Intelligent Agents v. Use built-in and learned knowledge to make decisions and accomplish tasks that fulfill the intentions of the user Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.


