3cbd7afa2bb2485b23ea9df2dc7a76d9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Chapter 10 Supply Chain Management Operations Management - 5 th Edition Roberta Russell & Bernard W. Taylor, III Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Beni Asllani University of Tennessee at Chattanooga
Chapter 10 Supply Chain Management Operations Management - 5 th Edition Roberta Russell & Bernard W. Taylor, III Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Beni Asllani University of Tennessee at Chattanooga
 Lecture Outline w w w w Supply Chain Management Information Technology: A Supply Chain Enabler Suppliers E-Procurement (overview) Distribution (overview) Supply Chain Management Software Measuring Supply Chain Performance Global Supply Chain (overview) Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2
Lecture Outline w w w w Supply Chain Management Information Technology: A Supply Chain Enabler Suppliers E-Procurement (overview) Distribution (overview) Supply Chain Management Software Measuring Supply Chain Performance Global Supply Chain (overview) Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2
 Supply Chain § All facilities, functions, activities, associated with flow and transformation of goods and services from raw materials to customer, as well as the associated information flows § An integrated group of processes to “source, ” “make, ” and “deliver” products Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 3
Supply Chain § All facilities, functions, activities, associated with flow and transformation of goods and services from raw materials to customer, as well as the associated information flows § An integrated group of processes to “source, ” “make, ” and “deliver” products Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 3
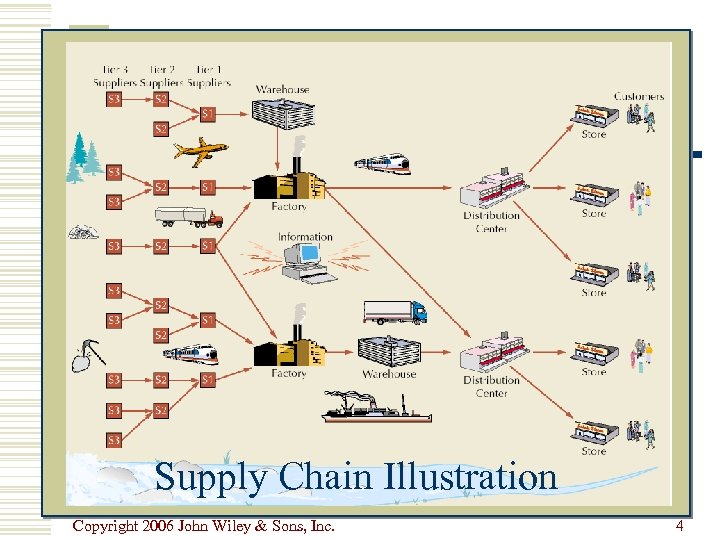 Supply Chain Illustration Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 4
Supply Chain Illustration Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 4
 Supply Chain Management (SCM) w Managing flow of information through supply chain in order to attain the level of synchronization that will make it more responsive to customer needs while lowering costs w Keys to effective SCM n n information communication cooperation trust Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5
Supply Chain Management (SCM) w Managing flow of information through supply chain in order to attain the level of synchronization that will make it more responsive to customer needs while lowering costs w Keys to effective SCM n n information communication cooperation trust Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5
 Supply Chain Uncertainty w One goal in SCM: n respond to uncertainty in customer demand without creating costly excess inventory w Negative effects of uncertainty n n lateness incomplete orders w Inventory n insurance against supply chain uncertainty Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w Factors that contribute to uncertainty n n n n inaccurate demand forecasting long variable lead times late deliveries incomplete shipments product changes batch ordering price fluctuations and discounts inflated orders 6
Supply Chain Uncertainty w One goal in SCM: n respond to uncertainty in customer demand without creating costly excess inventory w Negative effects of uncertainty n n lateness incomplete orders w Inventory n insurance against supply chain uncertainty Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w Factors that contribute to uncertainty n n n n inaccurate demand forecasting long variable lead times late deliveries incomplete shipments product changes batch ordering price fluctuations and discounts inflated orders 6
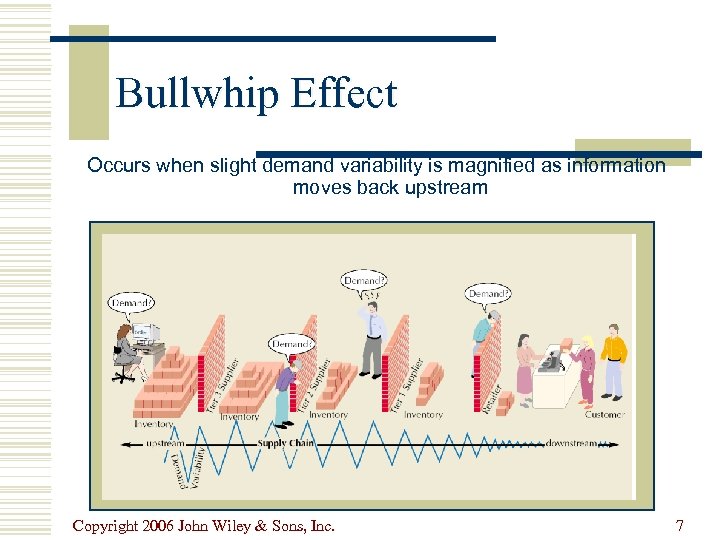 Bullwhip Effect Occurs when slight demand variability is magnified as information moves back upstream Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 7
Bullwhip Effect Occurs when slight demand variability is magnified as information moves back upstream Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 7
 Information Technology: A Supply Chain Enabler w Information links all aspects of supply chain w E-business n replacement of physical business processes with electronic ones w Electronic data interchange (EDI) n a computer-to-computer exchange of business documents Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w Bar code and point-of-sale n data creates an instantaneous computer record of a sale w Radio frequency identification (RFID) n technology can send product data from an item to a reader via radio waves w Internet n allows companies to communicate with suppliers, customers, shippers and other businesses around the world, instantaneously 8
Information Technology: A Supply Chain Enabler w Information links all aspects of supply chain w E-business n replacement of physical business processes with electronic ones w Electronic data interchange (EDI) n a computer-to-computer exchange of business documents Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w Bar code and point-of-sale n data creates an instantaneous computer record of a sale w Radio frequency identification (RFID) n technology can send product data from an item to a reader via radio waves w Internet n allows companies to communicate with suppliers, customers, shippers and other businesses around the world, instantaneously 8
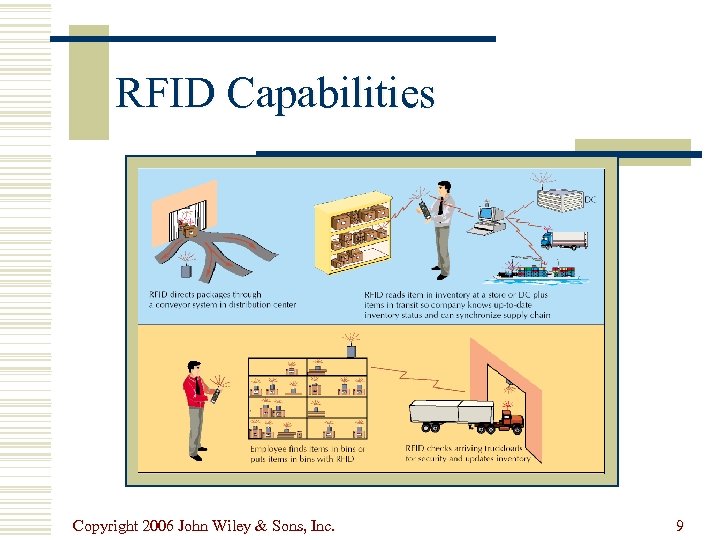 RFID Capabilities Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 9
RFID Capabilities Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 9
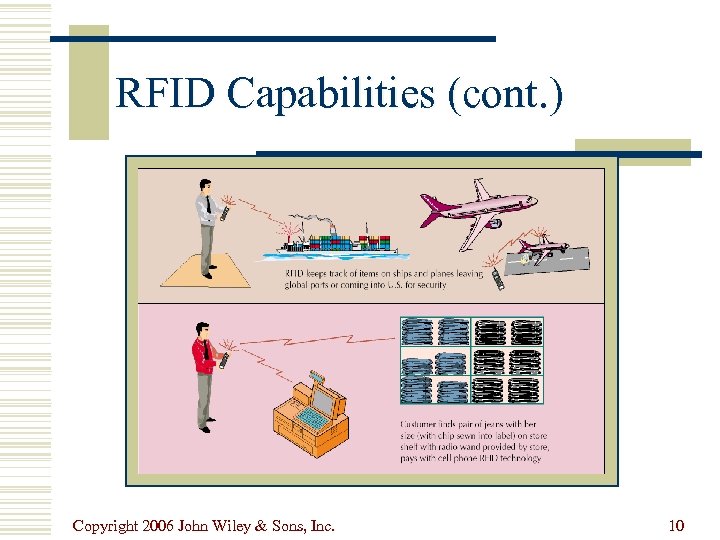 RFID Capabilities (cont. ) Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 10
RFID Capabilities (cont. ) Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 10
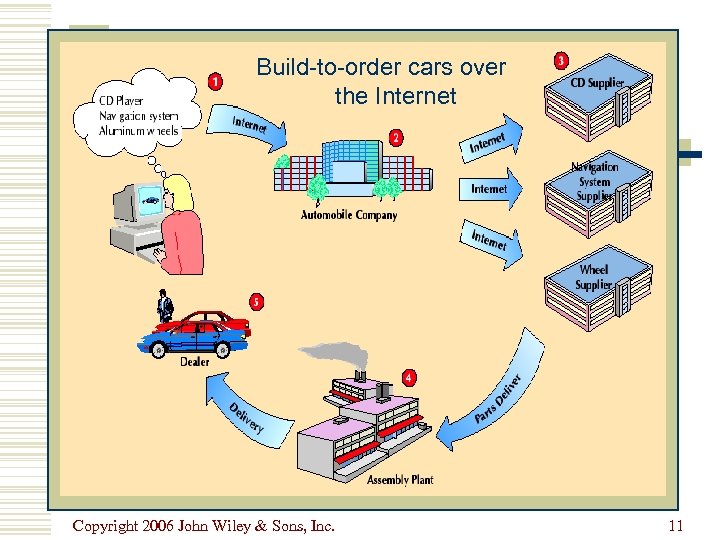 Build-to-order cars over the Internet Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 11
Build-to-order cars over the Internet Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 11
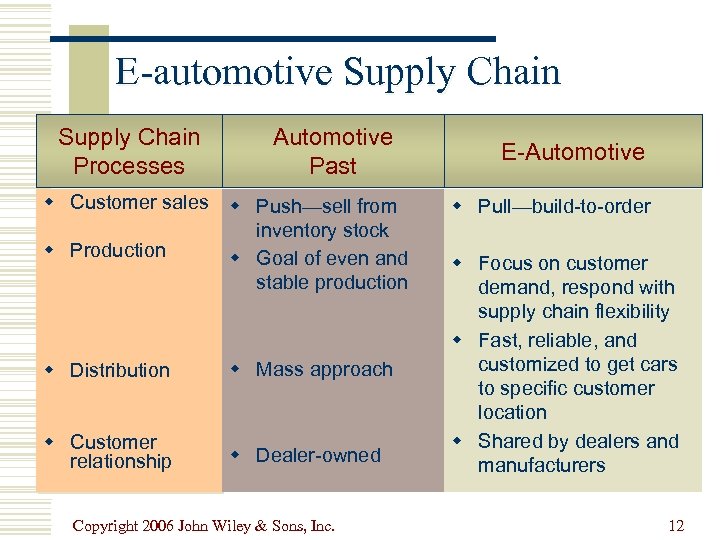 E-automotive Supply Chain Processes Automotive Past w Customer sales w Push—sell from inventory stock w Production w Goal of even and stable production w Distribution w Mass approach w Customer relationship w Dealer-owned Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. E-Automotive w Pull—build-to-order w Focus on customer demand, respond with supply chain flexibility w Fast, reliable, and customized to get cars to specific customer location w Shared by dealers and manufacturers 12
E-automotive Supply Chain Processes Automotive Past w Customer sales w Push—sell from inventory stock w Production w Goal of even and stable production w Distribution w Mass approach w Customer relationship w Dealer-owned Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. E-Automotive w Pull—build-to-order w Focus on customer demand, respond with supply chain flexibility w Fast, reliable, and customized to get cars to specific customer location w Shared by dealers and manufacturers 12
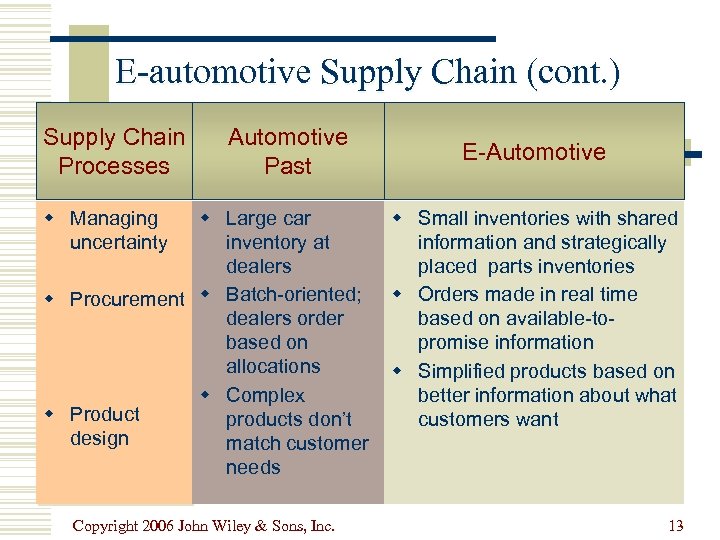 E-automotive Supply Chain (cont. ) Supply Chain Processes Automotive Past w Managing uncertainty w Large car inventory at dealers w Procurement w Batch-oriented; dealers order based on allocations w Complex w Product products don’t design match customer needs Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. E-Automotive w Small inventories with shared information and strategically placed parts inventories w Orders made in real time based on available-topromise information w Simplified products based on better information about what customers want 13
E-automotive Supply Chain (cont. ) Supply Chain Processes Automotive Past w Managing uncertainty w Large car inventory at dealers w Procurement w Batch-oriented; dealers order based on allocations w Complex w Product products don’t design match customer needs Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. E-Automotive w Small inventories with shared information and strategically placed parts inventories w Orders made in real time based on available-topromise information w Simplified products based on better information about what customers want 13
 Suppliers w Procurement n purchase of goods and services from suppliers w On-demand (direct response) delivery n requires supplier to deliver goods when demanded by customer w Continuous replenishment n supplying orders in a short period of time according to a predetermined schedule w Cross-enterprise teams coordinate processes between company and supplier Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 14
Suppliers w Procurement n purchase of goods and services from suppliers w On-demand (direct response) delivery n requires supplier to deliver goods when demanded by customer w Continuous replenishment n supplying orders in a short period of time according to a predetermined schedule w Cross-enterprise teams coordinate processes between company and supplier Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 14
 Outsourcing w Sourcing n selection of suppliers w Outsourcing n purchase of goods and services from an outside supplier w Core competencies n what a company does best w Single sourcing n a company purchases goods and services from only a few (or one) suppliers Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 15
Outsourcing w Sourcing n selection of suppliers w Outsourcing n purchase of goods and services from an outside supplier w Core competencies n what a company does best w Single sourcing n a company purchases goods and services from only a few (or one) suppliers Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 15
 E-Procurement w Direct purchase from suppliers over the Internet w Direct products go directly into production process a product, indirect products not w E-marketplaces n web sites where companies and suppliers conduct business-to-business activities w Reverse auction n a company posts orders on the Internet for suppliers to bid on Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 16
E-Procurement w Direct purchase from suppliers over the Internet w Direct products go directly into production process a product, indirect products not w E-marketplaces n web sites where companies and suppliers conduct business-to-business activities w Reverse auction n a company posts orders on the Internet for suppliers to bid on Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 16
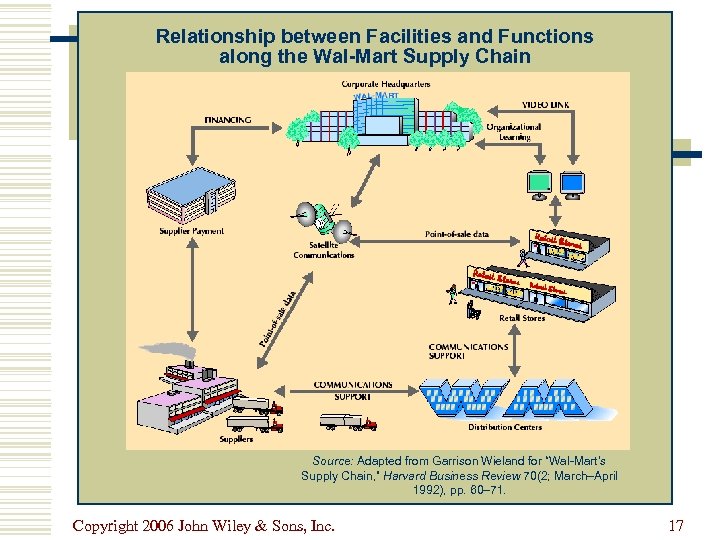 Relationship between Facilities and Functions along the Wal-Mart Supply Chain Source: Adapted from Garrison Wieland for “Wal-Mart’s Supply Chain, ” Harvard Business Review 70(2; March–April 1992), pp. 60– 71. Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 17
Relationship between Facilities and Functions along the Wal-Mart Supply Chain Source: Adapted from Garrison Wieland for “Wal-Mart’s Supply Chain, ” Harvard Business Review 70(2; March–April 1992), pp. 60– 71. Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 17
 Distribution § Encompasses all channels, processes, and functions, including warehousing and transportation, that a product passes on its way to final customer § Often called logistics § Logistics § transportation and distribution of goods and services § Driving force today is speed § Particularly important for Internet dot-coms Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 18
Distribution § Encompasses all channels, processes, and functions, including warehousing and transportation, that a product passes on its way to final customer § Often called logistics § Logistics § transportation and distribution of goods and services § Driving force today is speed § Particularly important for Internet dot-coms Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 18
 Warehouse Management Systems § Highly automated system that runs day-to-day operations of a DC § Controls item putaway, picking, packing, and shipping § Features § transportation management § order management § yard management § labor management § warehouse optimization Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 19
Warehouse Management Systems § Highly automated system that runs day-to-day operations of a DC § Controls item putaway, picking, packing, and shipping § Features § transportation management § order management § yard management § labor management § warehouse optimization Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 19
 SCM Software w Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) n n n software that integrates components of a company by sharing and organizing information and data SAP was first ERP software my. SAP. com l web enabled modules that allow collaboration between companies along the supply chain Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 20
SCM Software w Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) n n n software that integrates components of a company by sharing and organizing information and data SAP was first ERP software my. SAP. com l web enabled modules that allow collaboration between companies along the supply chain Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 20
 Measuring Supply Chain Performance w Key performance indicators n inventory turnover l n inventory days of supply l n cost of annual sales per inventory unit total value of all items being held in inventory fill rate l fraction of orders filled by a distribution center within a specific time period Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 21
Measuring Supply Chain Performance w Key performance indicators n inventory turnover l n inventory days of supply l n cost of annual sales per inventory unit total value of all items being held in inventory fill rate l fraction of orders filled by a distribution center within a specific time period Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 21
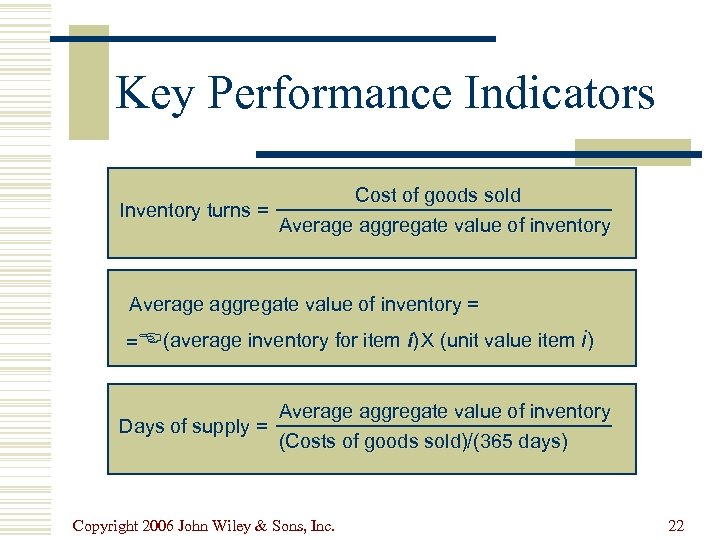 Key Performance Indicators Cost of goods sold Inventory turns = Average aggregate value of inventory = = (average inventory for item i) X (unit value item i) Average aggregate value of inventory Days of supply = (Costs of goods sold)/(365 days) Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 22
Key Performance Indicators Cost of goods sold Inventory turns = Average aggregate value of inventory = = (average inventory for item i) X (unit value item i) Average aggregate value of inventory Days of supply = (Costs of goods sold)/(365 days) Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 22
 Global Supply Chain § To compete globally requires an effective supply chain § Information technology is an “enabler” of global trade § Nations form trading groups § No tariffs or duties Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 23
Global Supply Chain § To compete globally requires an effective supply chain § Information technology is an “enabler” of global trade § Nations form trading groups § No tariffs or duties Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 23
 Effects of 9/11 on Global Chains w Increase security measures n n added time to supply chain schedules Increased supply chain costs w 24 hours rules for “risk screening” n n w w extended documentation extend time by 3 -4 days Inventory levels have increased 5% Other costs include: n new people, technologies, equipment, surveillance, communication, and security systems, and training necessary for screening at airports and seaports around the world Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 24
Effects of 9/11 on Global Chains w Increase security measures n n added time to supply chain schedules Increased supply chain costs w 24 hours rules for “risk screening” n n w w extended documentation extend time by 3 -4 days Inventory levels have increased 5% Other costs include: n new people, technologies, equipment, surveillance, communication, and security systems, and training necessary for screening at airports and seaports around the world Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 24


