464234b354c9eebc618ab81b1c9862f3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Chapter 10 Publishing and Maintaining Your Web Site Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Objectives • • Publish your Web site Test your Web site Refine and update your content Attract notice to your Web site Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 2

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Publishing Your Site • To make your site live, you transfer your Web site files to a Web server • Unless your company or organization has a Web server, you’ll have to use the services of a Web hosting provider • After you choose a server to host your files, you’ll need to select file transfer software and upload the Web site files from your development machine to the Web server Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 3

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Choosing an ISP • One of the most important decisions you’ll make is your choice of Web hosting service or Internet Service Provider (ISP). This is the company that hosts your Web pages on a Web server, making them available to anyone who knows your URL. • Web hosting services provide Web server space only, and may be more capable of hosting a complex commercial site Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 4

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design ISP Checklist • Is the ISP local or national? • Does the ISP have enough local Points Of Presence (POPs) in my area code? • Does the ISP offer technical support? When is support staff available? • How many e-mail address do I get with an account? • Does the ISP provide software, such as an FTP client? Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 5

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design ISP Checklist • Does the ISP support the latest connection technologies? • Does the ISP offer enhanced services, such as SQL database support, Secure Socket Layer, CGI scripting, and multimedia technology? Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 6
Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Using CGI Scripts • The Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is the communications “bridge” between the Internet and the server • Using programs called scripts, CGI can collect data sent by a user via the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and transfer it to a variety of data processing programs including spreadsheets, databases, or other software running on the server Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 7

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Using FTP • To publish your pages on the Web, you must send your HTML, image, and other files to the Web server • To do this, you need File Transfer Protocol (FTP) software, often called an FTP client Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 8

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Using FTP • To upload your files, start your FTP program and connect to your Web server using the FTP information provided by your service provider • Select the files that you want to upload in your local directory listing and transfer them to the server • Once the files have reached the Web server, they are immediately available for access on the Web Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 9

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design • Figure 10 -1 Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 10

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Testing Your Site Remember to test for the following Web design variables: • • Multiple browsers Multiple operating systems Connection speeds Display types Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 11

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design User Testing • Vary your subjects • Formalize your testing • Develop a feedback form Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 12

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design User Feedback Questions • Did you find the information you needed? • Was it easy or difficult to find the information you needed? • Did you find the site visually attractive? • Did you find the content easy to read? • Did you find the site easy to navigate? Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 13

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design User Feedback Questions • Did you think the information was presented correctly? • Did the information have enough depth? • What area of the site did you like the best? • What area of the site did you like the least? • Would you recommend the site to others? Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 14

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Refining and Updating Content • Refine your content and presentation based on your user’s feedback • Analyze your visitors and their preferences when they visit • Plan for ongoing maintenance of your site • Plan for major site design changes on a regular basis Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 15

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Working with Search Engines • Search engines are software programs that search out and index Web sites in a catalog • Not all search engines are alike, so the way they search and catalog differs greatly Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 16

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Working with Search Engines • • • Use meaningful titles Use META elements Be careful with frames Use ALT text with images Submit your URL to different search engines Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 17

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Working with <meta> Tags • You can use the <meta> elements on your site to possibly raise your Web site listing with certain search engines • The <meta> tags will get you results with Alta Vista, Excite, Inktomi, and Hot. Bot • The <meta> element is an empty element that resides in the <head> section of the HTML document • <meta> allows you to specify information about a document that is invisible to the user Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 18

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design • Table 10 -1 Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 19
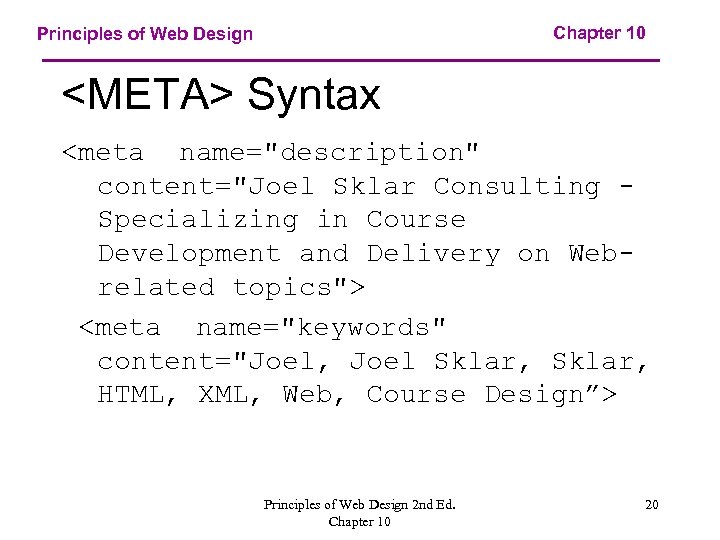
Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design <META> Syntax <meta name="description" content="Joel Sklar Consulting Specializing in Course Development and Delivery on Webrelated topics"> <meta name="keywords" content="Joel, Joel Sklar, HTML, XML, Web, Course Design”> Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 20
Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Frames and Search Engines • Since frame set files contain no content, they lack the information that many search engines look for • Use both <meta> tags and information in the noframes element Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 21

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design <noframes> Syntax <frameset cols="150, *"> <frame src="navcol. htm"> <frame src="article 1. htm" name="content"> <noframes> <body> <p>The Joel Sklar Consulting Web site is a resource for HTML authors and students. </P> <p>You can view a <a href=”index 2. htm”>nonframed</a> version of the site. </p> </body> </noframes> </frameset> Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. 22 Chapter 10

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Summary • Publishing your Web site involves transferring files to a Web server. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) provide space on their Web server if you are one of their subscribers. You can use an FTP application to transfer the files. • Shop carefully and compare features when you are looking for an Internet Service Provider or Web host. Consider the future disk space and technology needs of your content. Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 23

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Summary • Download and learn to use an FTP client. You transfer files to your site often and you need to know how to do this. • After your site is live, test it against the basic Web variables of browser, operating system, display resolution, and connection speed • Test your site with a variety of users. Listen carefully to their feedback to determine trouble spots in your information design. Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 24

Chapter 10 Principles of Web Design Summary • Plan for the maintenance, upkeep, and redesign of your site. Keep your content fresh! Let users know when you have made updates to the site. • Enhance your site to take advantage of search engine behavior Principles of Web Design 2 nd Ed. Chapter 10 25
464234b354c9eebc618ab81b1c9862f3.ppt