ce66d4c219b363526001fc37eae35ef8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Chapter 10 Multinational E-Commerce: Strategies and Structures Copyright© 2007 Thomson Learning All rights
Chapter 10 Multinational E-Commerce: Strategies and Structures Copyright© 2007 Thomson Learning All rights
 Learning Objectives • Define the forms of e-commerce • Appreciate the growing presence of ecommerce in the global economy • Understand the structure of the Internet economy • Identify the basic components of successful e-commerce strategy Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Learning Objectives • Define the forms of e-commerce • Appreciate the growing presence of ecommerce in the global economy • Understand the structure of the Internet economy • Identify the basic components of successful e-commerce strategy Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Learning Objectives • Know the basic multinational e-commerce business models • Identify the practicalities of running a multinational e-commerce business • Understand the function of enablers in multinational e-commerce operations Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Learning Objectives • Know the basic multinational e-commerce business models • Identify the practicalities of running a multinational e-commerce business • Understand the function of enablers in multinational e-commerce operations Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 The Internet Economy • Growing faster than any other business trend in history • Companies face issues similar to those faced by traditional multinational companies Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
The Internet Economy • Growing faster than any other business trend in history • Companies face issues similar to those faced by traditional multinational companies Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 What Is E-Commerce? • Refers to the selling of goods or services over the Internet • Includes goods or services delivered offline - E. g. , Amazon. com shipping book via UPS • Also includes goods and services delivered online - E. g. , downloaded computer software Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
What Is E-Commerce? • Refers to the selling of goods or services over the Internet • Includes goods or services delivered offline - E. g. , Amazon. com shipping book via UPS • Also includes goods and services delivered online - E. g. , downloaded computer software Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Types of E-Commerce Transactions • B 2 C: business-to-consumer transactions - Buying toys from e. Toys • B 2 B: business-to-business transactions - Makes up 70 to 85% of current ecommerce business • C 2 C: consumer-to consumer transactions - Anyone selling online • C 2 B: consumer-to-business transactions Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Types of E-Commerce Transactions • B 2 C: business-to-consumer transactions - Buying toys from e. Toys • B 2 B: business-to-business transactions - Makes up 70 to 85% of current ecommerce business • C 2 C: consumer-to consumer transactions - Anyone selling online • C 2 B: consumer-to-business transactions Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
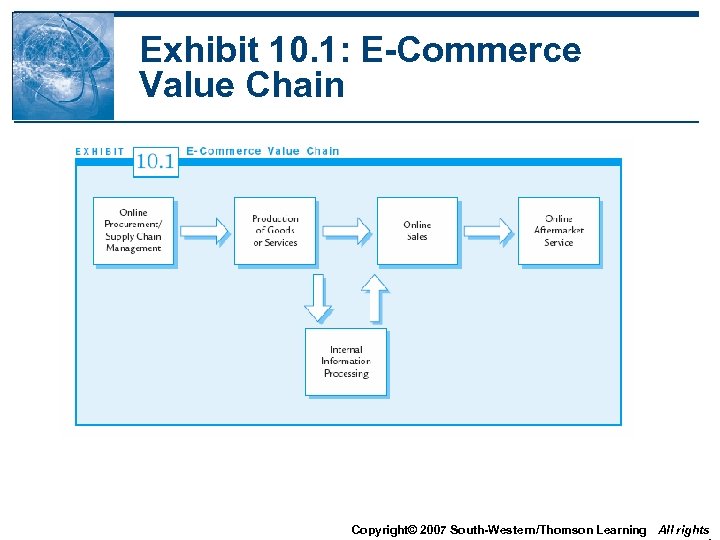 Exhibit 10. 1: E-Commerce Value Chain Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 1: E-Commerce Value Chain Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 The Internet Economy • Two indicators of the global presence of ecommerce - Secure server: an Internet host that allows users to send and receive encrypted data - Internet hosts: computers connected to the Internet with their own IP addresses • OECD dominate the Internet with over 90% of Internet hosts Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
The Internet Economy • Two indicators of the global presence of ecommerce - Secure server: an Internet host that allows users to send and receive encrypted data - Internet hosts: computers connected to the Internet with their own IP addresses • OECD dominate the Internet with over 90% of Internet hosts Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
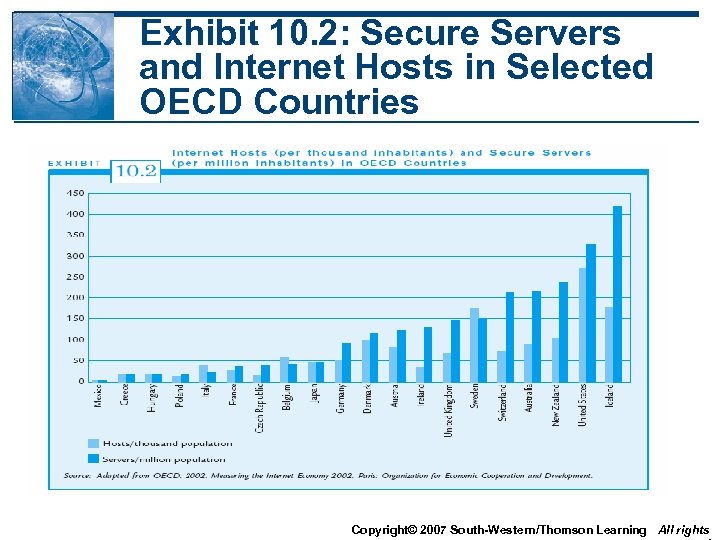 Exhibit 10. 2: Secure Servers and Internet Hosts in Selected OECD Countries Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 2: Secure Servers and Internet Hosts in Selected OECD Countries Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 The Internet Economy • In 1991, 3 million people used the Internet and almost none used it for e-commerce. • The growth in the use of the Internet or the World Wide Web for e-commerce is so dramatic that its impact is difficult to estimate • Some say that the Internet will have more impact on the world than the industrial revolution • Offers tremendous opportunities for Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
The Internet Economy • In 1991, 3 million people used the Internet and almost none used it for e-commerce. • The growth in the use of the Internet or the World Wide Web for e-commerce is so dramatic that its impact is difficult to estimate • Some say that the Internet will have more impact on the world than the industrial revolution • Offers tremendous opportunities for Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
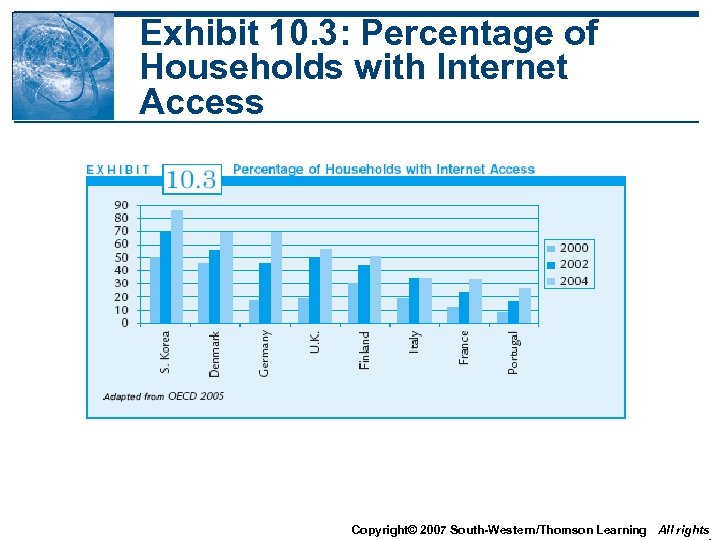 Exhibit 10. 3: Percentage of Households with Internet Access Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 3: Percentage of Households with Internet Access Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
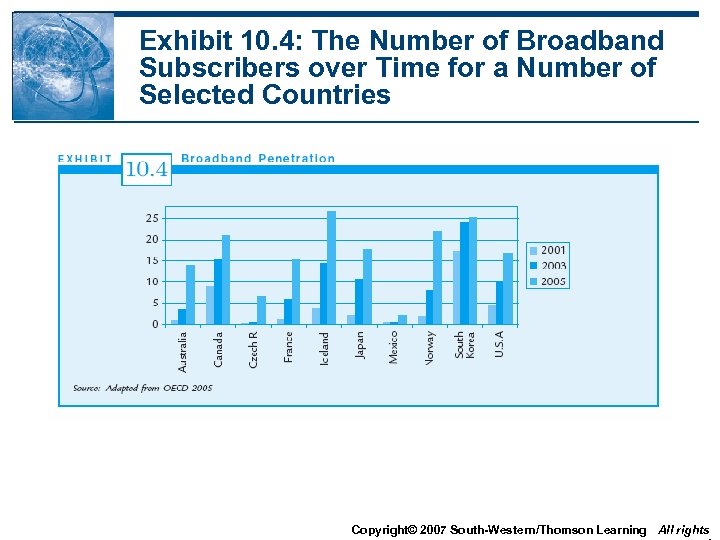 Exhibit 10. 4: The Number of Broadband Subscribers over Time for a Number of Selected Countries Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 4: The Number of Broadband Subscribers over Time for a Number of Selected Countries Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 The Internet Economy • Internet economy has four layers 1. The infrastructure 2. The applications infrastructure 3. The Internet intermediaries 4. The Internet commerce layer Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
The Internet Economy • Internet economy has four layers 1. The infrastructure 2. The applications infrastructure 3. The Internet intermediaries 4. The Internet commerce layer Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Layer 1 • The Internet infrastructure is the backbone of the Internet, including the Internet service providers (ISPs), e. g. , - Communications (Qwest, MCI, World. Com) - Internet service providers (Mindspring, AOL, Earthlink) - Networking (Cisco, Lucent, 3 Com) - Hardware (Dell, Compaq, HP) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Layer 1 • The Internet infrastructure is the backbone of the Internet, including the Internet service providers (ISPs), e. g. , - Communications (Qwest, MCI, World. Com) - Internet service providers (Mindspring, AOL, Earthlink) - Networking (Cisco, Lucent, 3 Com) - Hardware (Dell, Compaq, HP) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Layer 2 • The applications infrastructure - Companies and consultants that build web systems and supporting software • Consultants (Scient) • Commerce applications (Netscape, Sun, IBM) • Web development software (Adobe, Net. Objects) • Search engine software (Verity) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Layer 2 • The applications infrastructure - Companies and consultants that build web systems and supporting software • Consultants (Scient) • Commerce applications (Netscape, Sun, IBM) • Web development software (Adobe, Net. Objects) • Search engine software (Verity) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Layer 3 • The internet intermediaries - Companies that provides linking services on the Internet and derive revenues from commissions, advertising, and membership fees • Online travel agencies (Travelweb, Travelocity. com) • Online brokerages (E*TRADE) • Content aggregators (CNET, ZDNet) • Online advertising (Yahoo!) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Layer 3 • The internet intermediaries - Companies that provides linking services on the Internet and derive revenues from commissions, advertising, and membership fees • Online travel agencies (Travelweb, Travelocity. com) • Online brokerages (E*TRADE) • Content aggregators (CNET, ZDNet) • Online advertising (Yahoo!) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Layer 4 • The Internet commerce layer - Companies that conduct commercial transactions on the Web • E-retailers (wine. com, diamond. com) • Manufacturers selling directly (hpshopping. com, Dell) • Subscription-based companies (VRBO. com) • Transportation services (most airlines) • Shipping services (Fed. Ex, UPS) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Layer 4 • The Internet commerce layer - Companies that conduct commercial transactions on the Web • E-retailers (wine. com, diamond. com) • Manufacturers selling directly (hpshopping. com, Dell) • Subscription-based companies (VRBO. com) • Transportation services (most airlines) • Shipping services (Fed. Ex, UPS) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Fundamentals of E-Commerce • E-commerce is evolving quickly. • Failures of many start-ups show it’s not without risks. • E-commerce presents significant opportunities and threats. Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Fundamentals of E-Commerce • E-commerce is evolving quickly. • Failures of many start-ups show it’s not without risks. • E-commerce presents significant opportunities and threats. Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
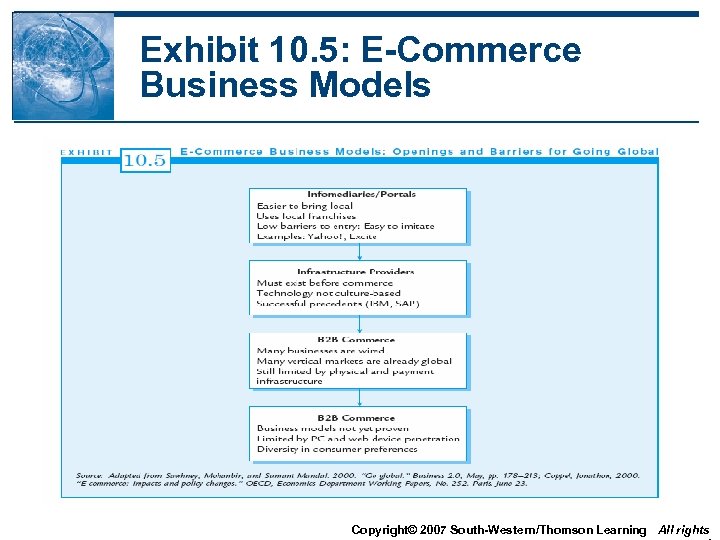 Exhibit 10. 5: E-Commerce Business Models Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 5: E-Commerce Business Models Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Steps for Successful E-Commerce Strategy • Leadership - Successful e-commerce is only possible through dynamic and strong leadership. • Build on current business models and experiment with new e-commerce models - Use e-commerce to search for ways to reduce costs or enhance the business. Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Steps for Successful E-Commerce Strategy • Leadership - Successful e-commerce is only possible through dynamic and strong leadership. • Build on current business models and experiment with new e-commerce models - Use e-commerce to search for ways to reduce costs or enhance the business. Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Steps for Successful E-Commerce Strategy (cont. ) • Meet the challenge of developing an ecommerce organization - Entire firm (not only top management) must be prepared to embrace the e-commerce model. • Allocate resources to the e-commerce business - Commit financial, human, and technological resources to develop e. Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Steps for Successful E-Commerce Strategy (cont. ) • Meet the challenge of developing an ecommerce organization - Entire firm (not only top management) must be prepared to embrace the e-commerce model. • Allocate resources to the e-commerce business - Commit financial, human, and technological resources to develop e. Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Steps for Successful E-Commerce Strategy (cont. ) • Build a superior e-commerce infrastructure as a basis of a differentiation strategy - Provide superior online experiences • Have an e-commerce strategy - Use strategic management to implement a strong and adequate strategic e-commerce plan Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Steps for Successful E-Commerce Strategy (cont. ) • Build a superior e-commerce infrastructure as a basis of a differentiation strategy - Provide superior online experiences • Have an e-commerce strategy - Use strategic management to implement a strong and adequate strategic e-commerce plan Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Steps for Successful ECommerce Strategy (cont. ) • Develop appropriate e-commerce systems - Work hard to remove traditional barriers to ensure that there are increased coordination and information flows among the various functional areas • Measure success - Have metrics in place to measure ecommerce success Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Steps for Successful ECommerce Strategy (cont. ) • Develop appropriate e-commerce systems - Work hard to remove traditional barriers to ensure that there are increased coordination and information flows among the various functional areas • Measure success - Have metrics in place to measure ecommerce success Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Exhibit 10. 6: Summary of ECommerce “don’ts” based on Best Practices Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 6: Summary of ECommerce “don’ts” based on Best Practices Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Structure: Integrated or Autonomous • Company needs to decide how e-commerce fits into existing design • Right mixture of bricks and clicks - How much to integrate Internet into traditional businesses • Brick-and-mortar: traditional or non-virtual business operation Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Structure: Integrated or Autonomous • Company needs to decide how e-commerce fits into existing design • Right mixture of bricks and clicks - How much to integrate Internet into traditional businesses • Brick-and-mortar: traditional or non-virtual business operation Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Structure: Integrated or Autonomous • Degree of interaction between brick-andmortar operations can occur anywhere in the value chain • Can range from near seamless operations (e. g. , Office Depot) to the mostly independent operations (e. g. , Barnes & Noble and Barnesandnoble. com) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Structure: Integrated or Autonomous • Degree of interaction between brick-andmortar operations can occur anywhere in the value chain • Can range from near seamless operations (e. g. , Office Depot) to the mostly independent operations (e. g. , Barnes & Noble and Barnesandnoble. com) Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Structure: Integrated or Autonomous • The independent benefits - Faster and more entrepreneurial - Freed from corporate bureaucracy • The integrated benefits - Cross-promotion, shared information, increased quantity purchases, use of same distribution channels Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Structure: Integrated or Autonomous • The independent benefits - Faster and more entrepreneurial - Freed from corporate bureaucracy • The integrated benefits - Cross-promotion, shared information, increased quantity purchases, use of same distribution channels Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
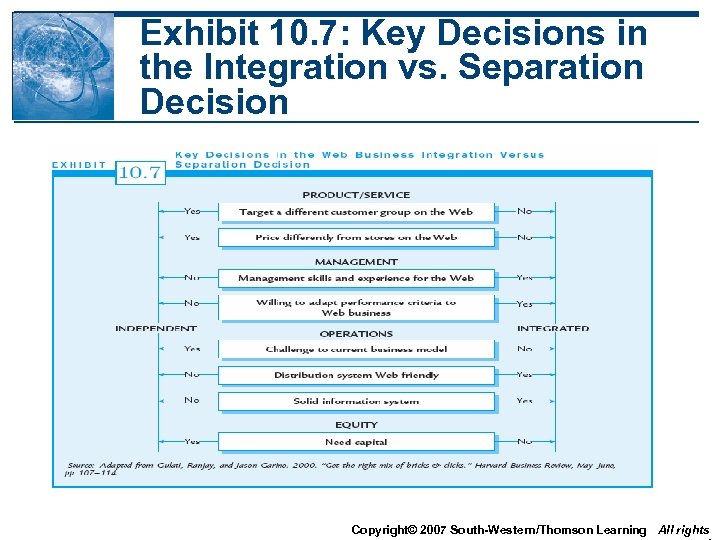 Exhibit 10. 7: Key Decisions in the Integration vs. Separation Decision Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 7: Key Decisions in the Integration vs. Separation Decision Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Structure: Integrated or Autonomous • Ways companies can integrate their online and offline operations - Keep customers informed - Integrate business operations - Share customer data across channels Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Structure: Integrated or Autonomous • Ways companies can integrate their online and offline operations - Keep customers informed - Integrate business operations - Share customer data across channels Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Additional Operational Challenges for an E-Commerce Business • Finding partnerships and alliances with customers or third parties • Attracting, retaining, and developing employees in the e-commerce unit • Inadequate e-commerce training • E-commerce employee retention • Deciding what e-commerce functions to outsource Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Additional Operational Challenges for an E-Commerce Business • Finding partnerships and alliances with customers or third parties • Attracting, retaining, and developing employees in the e-commerce unit • Inadequate e-commerce training • E-commerce employee retention • Deciding what e-commerce functions to outsource Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Pure E-business Company Tasks to Face Challenges • Develop information and management systems to respond to growth • Maintain rapid decision making, creativity, innovation, and flexibility • Build relationships with e-commerce support companies and customers • Attract and retain e-commerce–capable talent • Develop an effective management team Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Pure E-business Company Tasks to Face Challenges • Develop information and management systems to respond to growth • Maintain rapid decision making, creativity, innovation, and flexibility • Build relationships with e-commerce support companies and customers • Attract and retain e-commerce–capable talent • Develop an effective management team Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Tasks for Traditional Companies with E-Commerce • Build a common vision and commitment to e-commerce • Change the organization structure for quick reconfiguration of assets and capabilities • Change the organization culture to support e-commerce • Attract and retain e-commerce-skilled employees • Alter HR programs to suit skill requirements of Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Tasks for Traditional Companies with E-Commerce • Build a common vision and commitment to e-commerce • Change the organization structure for quick reconfiguration of assets and capabilities • Change the organization culture to support e-commerce • Attract and retain e-commerce-skilled employees • Alter HR programs to suit skill requirements of Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
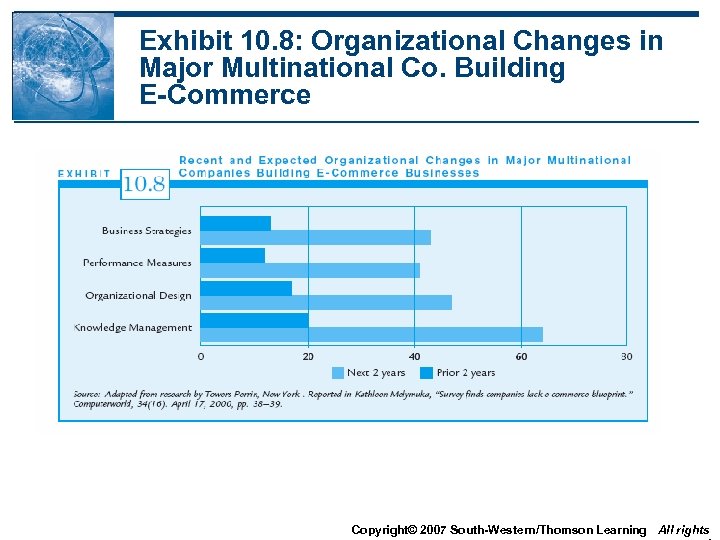 Exhibit 10. 8: Organizational Changes in Major Multinational Co. Building E-Commerce Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 8: Organizational Changes in Major Multinational Co. Building E-Commerce Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Security • E-Commerce security: refers to the degree to which customers feel that their private, personal information can be safeguarded in the hands of online companies collecting such information Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Security • E-Commerce security: refers to the degree to which customers feel that their private, personal information can be safeguarded in the hands of online companies collecting such information Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Security • Companies need to be concerned about a number of information security issues such as - Confidentiality: making sure that private information is protected - Availability: ensuring that information is accessible to authorized users - Integrity: ensuring that the information collected is accurate and reliable - Authentication: having systems in place to ensure that persons using the systems are legitimate Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Security • Companies need to be concerned about a number of information security issues such as - Confidentiality: making sure that private information is protected - Availability: ensuring that information is accessible to authorized users - Integrity: ensuring that the information collected is accurate and reliable - Authentication: having systems in place to ensure that persons using the systems are legitimate Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Security • To ensure that these Internet security issues are addressed, experts suggest the following - Use firewalls, intrusion detection software, and antivirus shields - Encrypt data - Require two-phased authentication - Use web site monitoring tools - Abide by privacy rules Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Security • To ensure that these Internet security issues are addressed, experts suggest the following - Use firewalls, intrusion detection software, and antivirus shields - Encrypt data - Require two-phased authentication - Use web site monitoring tools - Abide by privacy rules Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Globalizing Through the Internet • Internet is enabling the emergence of a new form of multinational, the born-global firms • Born-global firms are able to obtain a significant portion of their revenues from sales in international markets • Born-global firms tend to adopt a global view of markets and develop competitive advantages to succeed in the various markets Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Globalizing Through the Internet • Internet is enabling the emergence of a new form of multinational, the born-global firms • Born-global firms are able to obtain a significant portion of their revenues from sales in international markets • Born-global firms tend to adopt a global view of markets and develop competitive advantages to succeed in the various markets Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Globalizing Through the Internet • A Web site gives the company immediate global access - The challenges of globalization faced by traditional brick-and-mortar companies remain • Managers must still decide whether they want to sell global or local product • Business issues related to national contexts (e. g. , currencies, local laws, etc. ) have to be Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Globalizing Through the Internet • A Web site gives the company immediate global access - The challenges of globalization faced by traditional brick-and-mortar companies remain • Managers must still decide whether they want to sell global or local product • Business issues related to national contexts (e. g. , currencies, local laws, etc. ) have to be Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Multinational E-Commerce Strategy Formulation • Depends on - Nature of the business - Types of products or services offered through e-commerce • Hierarchy of difficulty depending on infrastructure requirements - Telecommunications infrastructure to move information - Payment infrastructure to move money - Physical infrastructure to deliver products Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Multinational E-Commerce Strategy Formulation • Depends on - Nature of the business - Types of products or services offered through e-commerce • Hierarchy of difficulty depending on infrastructure requirements - Telecommunications infrastructure to move information - Payment infrastructure to move money - Physical infrastructure to deliver products Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Attractions of E-Commerce • Cost reduction - Less expensive to reach international customers • Technology - Already available • Efficiencies - More efficient Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Attractions of E-Commerce • Cost reduction - Less expensive to reach international customers • Technology - Already available • Efficiencies - More efficient Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Attractions of E-commerce (cont. ) • Convenience - Web is operating all the time regardless of location • Speed of access - Company’s products or services can be accessed immediately from anywhere in the world Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Attractions of E-commerce (cont. ) • Convenience - Web is operating all the time regardless of location • Speed of access - Company’s products or services can be accessed immediately from anywhere in the world Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Deterrents/Challenges • Return/receipt burden and cost of delivery - Expect 30 -40% return rate • Costs of site construction, maintenance, upgrades • Channel conflicts • Easily copied models - Competitors can easily see and copy business model Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Deterrents/Challenges • Return/receipt burden and cost of delivery - Expect 30 -40% return rate • Costs of site construction, maintenance, upgrades • Channel conflicts • Easily copied models - Competitors can easily see and copy business model Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 E-Commerce Deterrents • Cultural differences - Web sites must be appropriate culturally • Traditional cross-border complexities remain - Exchange rates, different taxes, and government regulations • Standard or local web sites • Customer trust and satisfaction Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
E-Commerce Deterrents • Cultural differences - Web sites must be appropriate culturally • Traditional cross-border complexities remain - Exchange rates, different taxes, and government regulations • Standard or local web sites • Customer trust and satisfaction Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Picking a Market • Two factors to target countries - Market inefficiencies • E. g. , formerly state-controlled economies - Attractive demographic characteristics • Internet population of at least 5% • High literacy rate • Participation in at least on free trade agreements • Government with viable legal system Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Picking a Market • Two factors to target countries - Market inefficiencies • E. g. , formerly state-controlled economies - Attractive demographic characteristics • Internet population of at least 5% • High literacy rate • Participation in at least on free trade agreements • Government with viable legal system Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Picking a Market (cont. ) • E-commerce potential is substantial in Latin America because of MERCOSUR • Potential exists for Asian countries with membership in ASEAN • Open borders and common currency of European Union is also fertile ground Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Picking a Market (cont. ) • E-commerce potential is substantial in Latin America because of MERCOSUR • Potential exists for Asian countries with membership in ASEAN • Open borders and common currency of European Union is also fertile ground Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
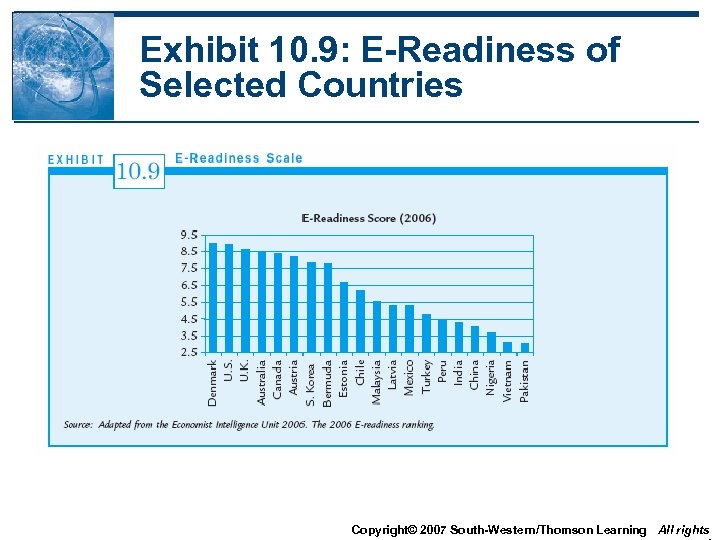 Exhibit 10. 9: E-Readiness of Selected Countries Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 9: E-Readiness of Selected Countries Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Multinational E-Commerce Strategy Implementation • Requires building an appropriate organization and developing the necessary technical capabilities to conduct electronic transactions Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Multinational E-Commerce Strategy Implementation • Requires building an appropriate organization and developing the necessary technical capabilities to conduct electronic transactions Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 The Multinational E-Commerce Organization • Three-tiered mixing of global and local functions • Headquarters - Vision, strategy, leadership for worldwide electronic marketing - Also provide shared services such as network infrastructure Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
The Multinational E-Commerce Organization • Three-tiered mixing of global and local functions • Headquarters - Vision, strategy, leadership for worldwide electronic marketing - Also provide shared services such as network infrastructure Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 The Multinational E-Commerce Organization (cont. ) • Shared functional services - Provide HRM, marketing, partner management to regions • Local subsidiaries - Deliver goods, manage functions better done locally such as the supply chain Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
The Multinational E-Commerce Organization (cont. ) • Shared functional services - Provide HRM, marketing, partner management to regions • Local subsidiaries - Deliver goods, manage functions better done locally such as the supply chain Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
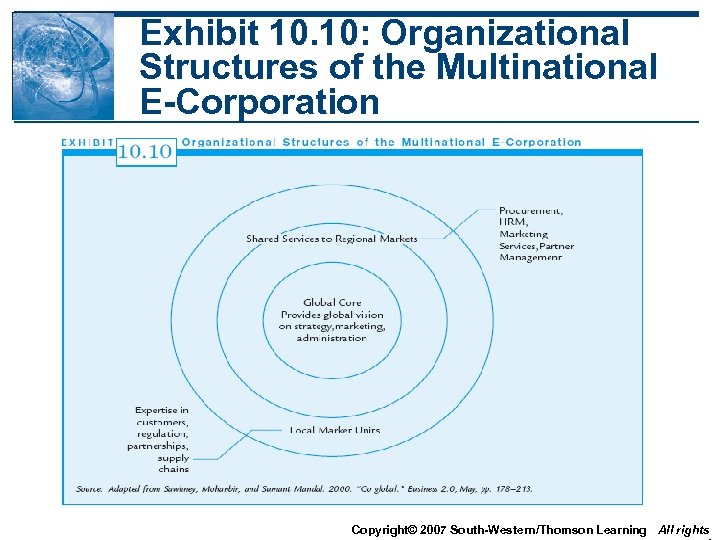 Exhibit 10. 10: Organizational Structures of the Multinational E-Corporation Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 10: Organizational Structures of the Multinational E-Corporation Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Technical Capabilities for Multinational E-commerce • Ability to process multiple currencies • Ability to calculate/show purchase information on international shipping, duties, and local taxes such as VAT • Systems that check compliance with local and international laws Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Technical Capabilities for Multinational E-commerce • Ability to process multiple currencies • Ability to calculate/show purchase information on international shipping, duties, and local taxes such as VAT • Systems that check compliance with local and international laws Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Technical Capabilities for Multinational E-commerce • Ability to provide support in multilingual service centers • Fraud protection • Electronic payment models in addition to credit cards Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Technical Capabilities for Multinational E-commerce • Ability to provide support in multilingual service centers • Fraud protection • Electronic payment models in addition to credit cards Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Web Sites: To Localize or Standardize • Standardized web site: companies’ web sites are fairly similar in layout and design around the world • Localized web site: values, appeals, symbols, and even themes in the communication content is adapted to the local culture Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Web Sites: To Localize or Standardize • Standardized web site: companies’ web sites are fairly similar in layout and design around the world • Localized web site: values, appeals, symbols, and even themes in the communication content is adapted to the local culture Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
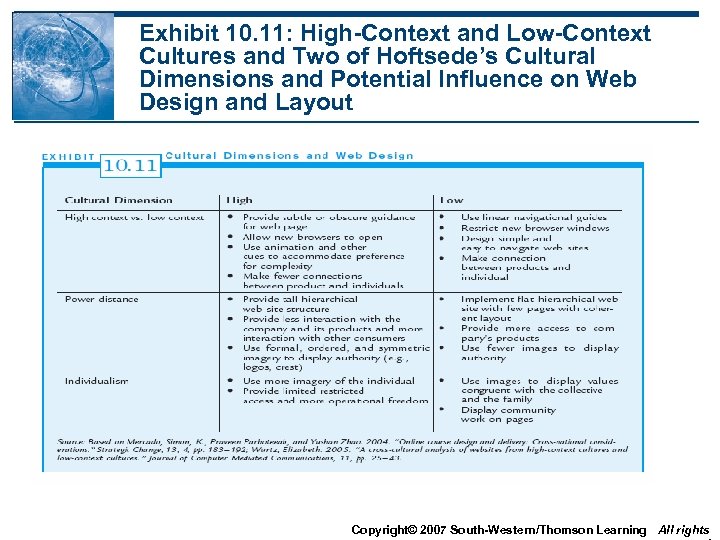 Exhibit 10. 11: High-Context and Low-Context Cultures and Two of Hoftsede’s Cultural Dimensions and Potential Influence on Web Design and Layout Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 11: High-Context and Low-Context Cultures and Two of Hoftsede’s Cultural Dimensions and Potential Influence on Web Design and Layout Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 “Mission-Critical” Factors to Communicate to Global Audience 1. Link all Web sites to corporate Web site 2. Web site should contain all nonelectronic local contact information for feedback or comment 3. Provide a prominent list of languages used by the company’s Web site 4. Use different languages for downloads Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
“Mission-Critical” Factors to Communicate to Global Audience 1. Link all Web sites to corporate Web site 2. Web site should contain all nonelectronic local contact information for feedback or comment 3. Provide a prominent list of languages used by the company’s Web site 4. Use different languages for downloads Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 “Mission-Critical” Factors to Communicate to Global Audience (cont. ) 5. Localize by language the parts of the parent company Web site that receive the most access 6. Provide a site map 7. Provide the firm’s privacy statement in all local languages Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
“Mission-Critical” Factors to Communicate to Global Audience (cont. ) 5. Localize by language the parts of the parent company Web site that receive the most access 6. Provide a site map 7. Provide the firm’s privacy statement in all local languages Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 “Mission-Critical” Factors to Communicate to Global Audience (cont. ) 8. Guard against local piracy by putting your policies in local languages 9. Localize your graphics and written material 10. Localize content management Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
“Mission-Critical” Factors to Communicate to Global Audience (cont. ) 8. Guard against local piracy by putting your policies in local languages 9. Localize your graphics and written material 10. Localize content management Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
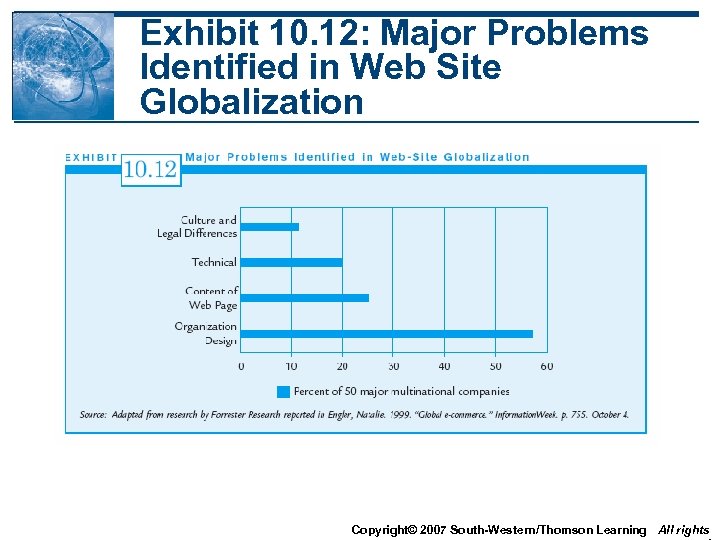 Exhibit 10. 12: Major Problems Identified in Web Site Globalization Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Exhibit 10. 12: Major Problems Identified in Web Site Globalization Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 To Build or Outsource Technical Capabilities? • Two options - Run all e-commerce functions internally or outsource to e-commerce enablers • E-commerce enablers: fulfillment specialists that provide services such as Web site translation - Provide services and software that translate Web sites, calculate shipping, value-added taxes, duties, and other Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
To Build or Outsource Technical Capabilities? • Two options - Run all e-commerce functions internally or outsource to e-commerce enablers • E-commerce enablers: fulfillment specialists that provide services such as Web site translation - Provide services and software that translate Web sites, calculate shipping, value-added taxes, duties, and other Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
 Conclusion • Internet and e-commerce becoming an increasingly important component of any multinational’s strategy • Chapter introduced the basic concepts of ecommerce • Comparison of traditional vs. e-commerce companies discussed • Many of the same challenges are faced • Chapter provides solid background on key Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights
Conclusion • Internet and e-commerce becoming an increasingly important component of any multinational’s strategy • Chapter introduced the basic concepts of ecommerce • Comparison of traditional vs. e-commerce companies discussed • Many of the same challenges are faced • Chapter provides solid background on key Copyright© 2007 South-Western/Thomson Learning All rights


