16857c35c28c3d4713b84b1ad0cf3ed7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Chapter 10 Marketing Channels & Supply Chain Management 1
Chapter 10 Marketing Channels & Supply Chain Management 1
 Concept Connections Explain why companies use distribution channels and discuss the functions these channels perform. Identify the major channel alternatives open to a company. Explain how companies select, motivate, and evaluate channel members. Analyze integrated logistics, including how it may be achieved and its benefits to the company. 2
Concept Connections Explain why companies use distribution channels and discuss the functions these channels perform. Identify the major channel alternatives open to a company. Explain how companies select, motivate, and evaluate channel members. Analyze integrated logistics, including how it may be achieved and its benefits to the company. 2
 Issues Concerning Distribution Channels What is the Nature Of Distribution Channels? What Role Does Physical Distribution Play in Attracting and Satisfying Customers? How do Channel What Problems do Firms Interact and Companies Face in Organize to do the Designing and Work of the Managing Their Channel? Channels? 3
Issues Concerning Distribution Channels What is the Nature Of Distribution Channels? What Role Does Physical Distribution Play in Attracting and Satisfying Customers? How do Channel What Problems do Firms Interact and Companies Face in Organize to do the Designing and Work of the Managing Their Channel? Channels? 3
 What’s a Distribution Channel (PLACE) A set of interdependent organizations (intermediaries) involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by the consumer or business user. 4
What’s a Distribution Channel (PLACE) A set of interdependent organizations (intermediaries) involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by the consumer or business user. 4
 Distribution Channel Manufacturer Retailer Distributor Consumers 5
Distribution Channel Manufacturer Retailer Distributor Consumers 5
 Why are Marketing Intermediaries Used? Results from their greater efficiency in making goods available to target markets. Offer the firm more than it can achieve on it’s own: n n n Contacts, Experience, Specialization. Purpose: match supply from producers to demand from consumers. 6
Why are Marketing Intermediaries Used? Results from their greater efficiency in making goods available to target markets. Offer the firm more than it can achieve on it’s own: n n n Contacts, Experience, Specialization. Purpose: match supply from producers to demand from consumers. 6
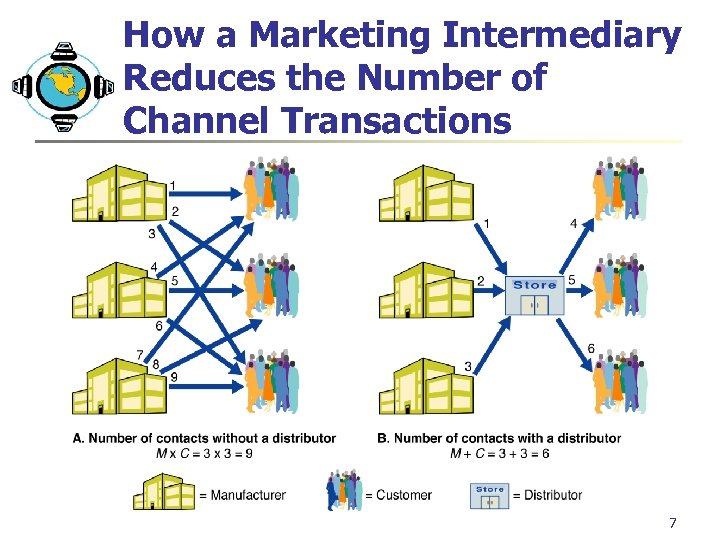 How a Marketing Intermediary Reduces the Number of Channel Transactions 7
How a Marketing Intermediary Reduces the Number of Channel Transactions 7
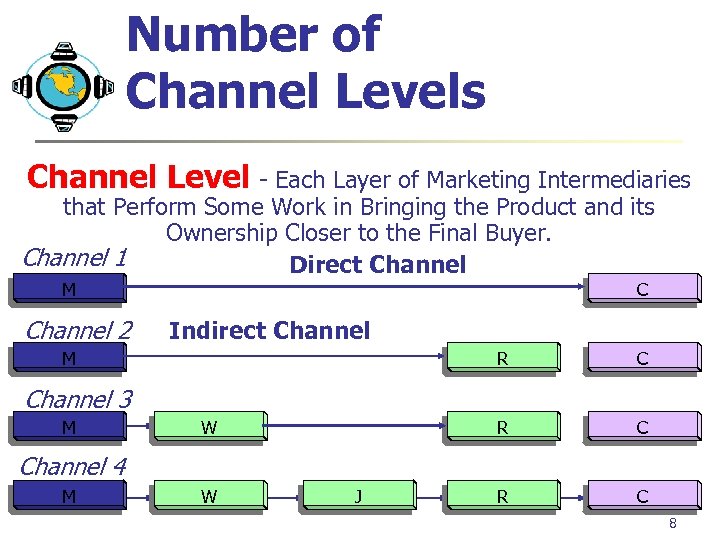 Number of Channel Levels Channel Level - Each Layer of Marketing Intermediaries that Perform Some Work in Bringing the Product and its Ownership Closer to the Final Buyer. Channel 1 Direct Channel M Channel 2 C Indirect Channel R C R M C R C Channel 3 M W Channel 4 M W J 8
Number of Channel Levels Channel Level - Each Layer of Marketing Intermediaries that Perform Some Work in Bringing the Product and its Ownership Closer to the Final Buyer. Channel 1 Direct Channel M Channel 2 C Indirect Channel R C R M C R C Channel 3 M W Channel 4 M W J 8
 Channel Behavior & Conflict Will be effective when n n Each member is assigned tasks it can do best. All members cooperate to attain overall channel goals and satisfy the target market. Conflict occurs: n Horizontal Conflict occurs among firms at the same level of the channel, i. e retailer to retailer. n Vertical Conflict occurs between different levels of the same channel, i. e. wholesaler to retailer. 9
Channel Behavior & Conflict Will be effective when n n Each member is assigned tasks it can do best. All members cooperate to attain overall channel goals and satisfy the target market. Conflict occurs: n Horizontal Conflict occurs among firms at the same level of the channel, i. e retailer to retailer. n Vertical Conflict occurs between different levels of the same channel, i. e. wholesaler to retailer. 9
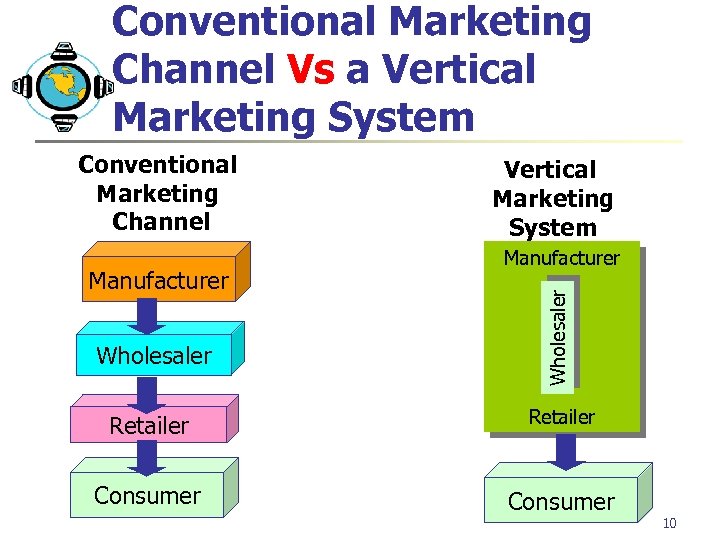 Conventional Marketing Channel Vs a Vertical Marketing System Manufacturer Wholesaler Conventional Marketing Channel Retailer Consumer 10
Conventional Marketing Channel Vs a Vertical Marketing System Manufacturer Wholesaler Conventional Marketing Channel Retailer Consumer 10
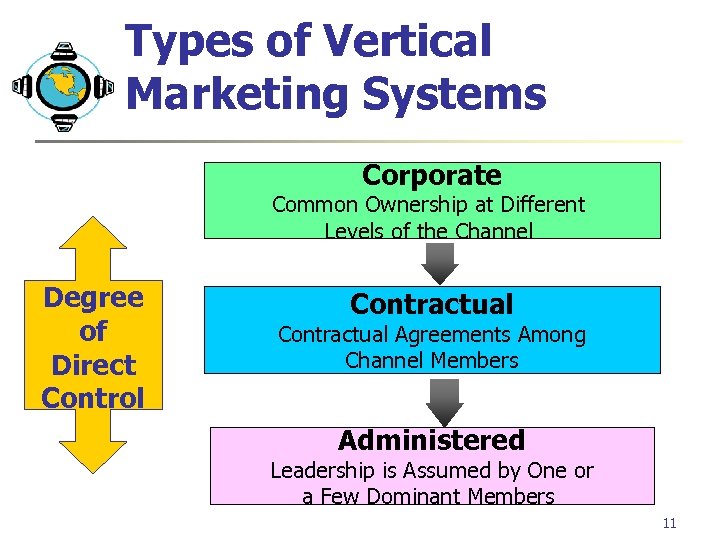 Types of Vertical Marketing Systems Corporate Common Ownership at Different Levels of the Channel Degree of Direct Control Contractual Agreements Among Channel Members Administered Leadership is Assumed by One or a Few Dominant Members 11
Types of Vertical Marketing Systems Corporate Common Ownership at Different Levels of the Channel Degree of Direct Control Contractual Agreements Among Channel Members Administered Leadership is Assumed by One or a Few Dominant Members 11
 Changing Channel Organization A Major Trend is Toward Disintermediation Which Means Producers are Bypassing Intermediaries and Going Directly to Final Buyers That New Types of Channel Intermediaries are Emerging to Displace Traditional Ones. 12
Changing Channel Organization A Major Trend is Toward Disintermediation Which Means Producers are Bypassing Intermediaries and Going Directly to Final Buyers That New Types of Channel Intermediaries are Emerging to Displace Traditional Ones. 12
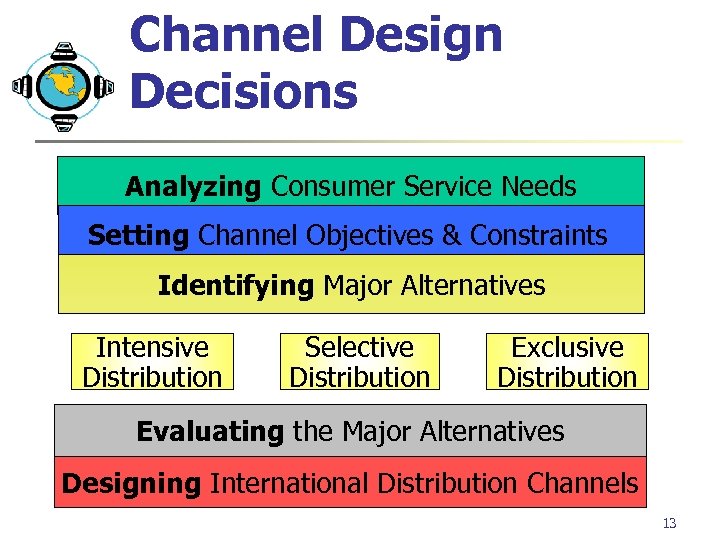 Channel Design Decisions Analyzing Consumer Service Needs Setting Channel Objectives & Constraints Identifying Major Alternatives Intensive Distribution Selective Distribution Exclusive Distribution Evaluating the Major Alternatives Designing International Distribution Channels 13
Channel Design Decisions Analyzing Consumer Service Needs Setting Channel Objectives & Constraints Identifying Major Alternatives Intensive Distribution Selective Distribution Exclusive Distribution Evaluating the Major Alternatives Designing International Distribution Channels 13
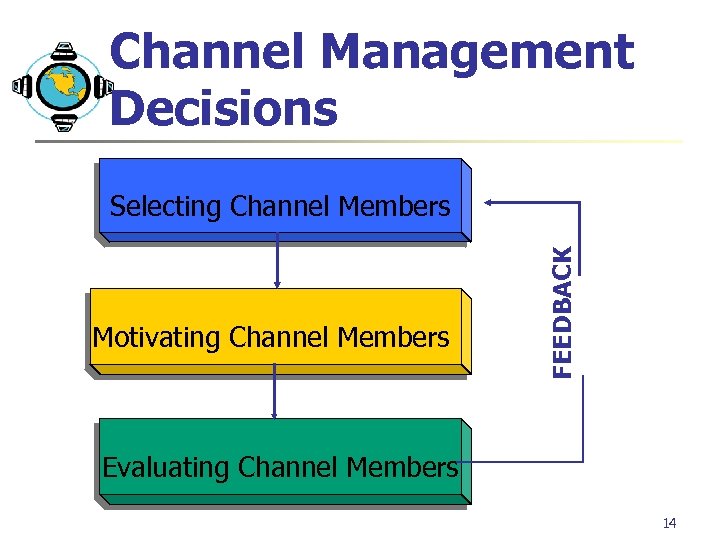 Channel Management Decisions Motivating Channel Members FEEDBACK Selecting Channel Members Evaluating Channel Members 14
Channel Management Decisions Motivating Channel Members FEEDBACK Selecting Channel Members Evaluating Channel Members 14
 Nature and Importance of Marketing Logistics Involves getting the right product to the right customers in the right place at the right time. Companies place greater emphasis on logistics because: n n n customer service and satisfaction have become the cornerstone of marketing strategy. logistics is a major cost element for most companies. . Improvements in information technology has created opportunities for major gains in distribution efficiency. 15
Nature and Importance of Marketing Logistics Involves getting the right product to the right customers in the right place at the right time. Companies place greater emphasis on logistics because: n n n customer service and satisfaction have become the cornerstone of marketing strategy. logistics is a major cost element for most companies. . Improvements in information technology has created opportunities for major gains in distribution efficiency. 15
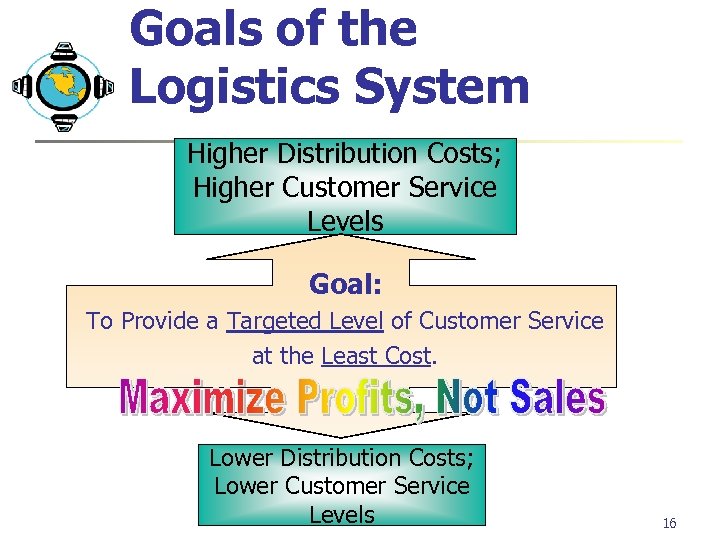 Goals of the Logistics System Higher Distribution Costs; Higher Customer Service Levels Goal: To Provide a Targeted Level of Customer Service at the Least Cost. Lower Distribution Costs; Lower Customer Service Levels 16
Goals of the Logistics System Higher Distribution Costs; Higher Customer Service Levels Goal: To Provide a Targeted Level of Customer Service at the Least Cost. Lower Distribution Costs; Lower Customer Service Levels 16
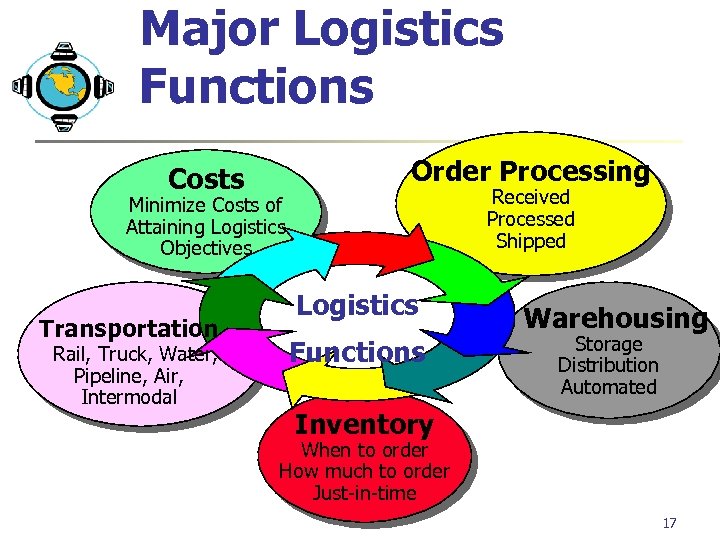 Major Logistics Functions Costs Order Processing Received Processed Shipped Minimize Costs of Attaining Logistics Objectives Transportation Rail, Truck, Water, Pipeline, Air, Intermodal Logistics Functions Warehousing Storage Distribution Automated Inventory When to order How much to order Just-in-time 17
Major Logistics Functions Costs Order Processing Received Processed Shipped Minimize Costs of Attaining Logistics Objectives Transportation Rail, Truck, Water, Pipeline, Air, Intermodal Logistics Functions Warehousing Storage Distribution Automated Inventory When to order How much to order Just-in-time 17
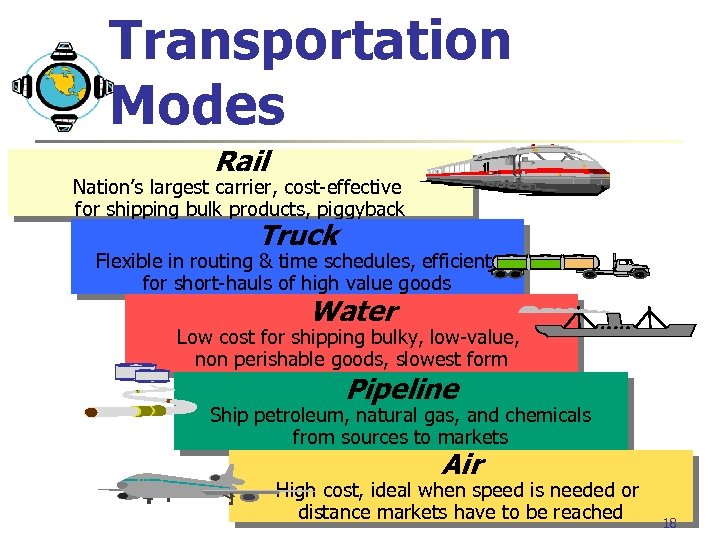 Transportation Modes Rail Nation’s largest carrier, cost-effective for shipping bulk products, piggyback Truck Flexible in routing & time schedules, efficient for short-hauls of high value goods Water Low cost for shipping bulky, low-value, non perishable goods, slowest form Pipeline Ship petroleum, natural gas, and chemicals from sources to markets Air High cost, ideal when speed is needed or distance markets have to be reached 18
Transportation Modes Rail Nation’s largest carrier, cost-effective for shipping bulk products, piggyback Truck Flexible in routing & time schedules, efficient for short-hauls of high value goods Water Low cost for shipping bulky, low-value, non perishable goods, slowest form Pipeline Ship petroleum, natural gas, and chemicals from sources to markets Air High cost, ideal when speed is needed or distance markets have to be reached 18
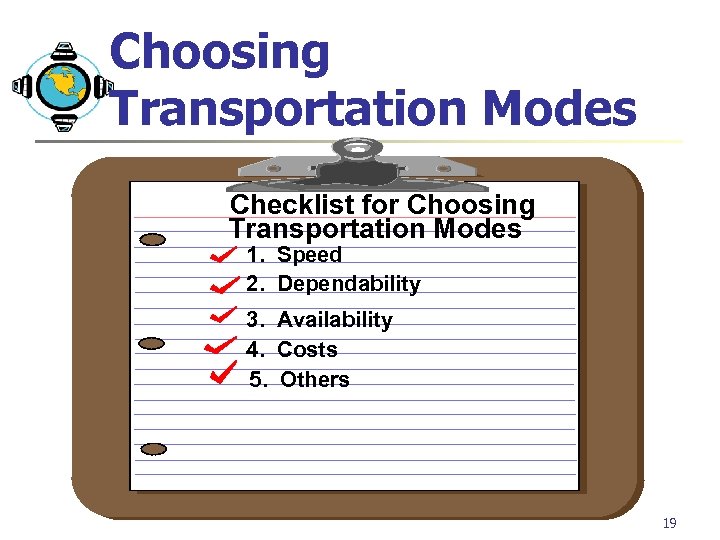 Choosing Transportation Modes Checklist for Choosing Transportation Modes 1. Speed 2. Dependability 3. Availability 4. Costs 5. Others 19
Choosing Transportation Modes Checklist for Choosing Transportation Modes 1. Speed 2. Dependability 3. Availability 4. Costs 5. Others 19
 Review of Concept Connections Explain why companies use distribution channels and discuss the functions these channels perform. Identify the major channel alternatives open to a company. Explain how companies select, motivate, and evaluate channel members. Analyze integrated logistics, including how it may be achieved and its benefits to the company. 20
Review of Concept Connections Explain why companies use distribution channels and discuss the functions these channels perform. Identify the major channel alternatives open to a company. Explain how companies select, motivate, and evaluate channel members. Analyze integrated logistics, including how it may be achieved and its benefits to the company. 20


