452b4a9d74f77d181b79217527845b56.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Chapter 10 Managing the Information Technology Resource through Strategic Partnerships
Chapter 10 Managing the Information Technology Resource through Strategic Partnerships
 What is Outsourcing? n The phenomenon that appeared in the information systems field in the late 1980 s was outsourcing, which means turning over a firm's computer operations, network operations, or perhaps other information systems functions to a vendor for a specified time - generally, at least for three years. Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -2
What is Outsourcing? n The phenomenon that appeared in the information systems field in the late 1980 s was outsourcing, which means turning over a firm's computer operations, network operations, or perhaps other information systems functions to a vendor for a specified time - generally, at least for three years. Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -2
 Outsourcing in Retrospect Early: computer service bureaus (mid 1960 s) n Major drivers for outsourcing n – access to specialized or occasionally needed computing power or skills – avoidance of building in-house skills – access to special functional capabilities
Outsourcing in Retrospect Early: computer service bureaus (mid 1960 s) n Major drivers for outsourcing n – access to specialized or occasionally needed computing power or skills – avoidance of building in-house skills – access to special functional capabilities
 Outsourcing in the 1990 s Two factors have affected the growth of IT outsourcing n Acceptance of strategic alliances – – – n partner to complement weakness leverage part of value chain “For an alliance to be successful and endure for the long term, both firms must believe that they are winners. ” IT’s changing environment – “The internal IT organization is already a selector of code rather than a developer. ” – low cost maintenance of old systems – transformation to new model Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development N TM -4
Outsourcing in the 1990 s Two factors have affected the growth of IT outsourcing n Acceptance of strategic alliances – – – n partner to complement weakness leverage part of value chain “For an alliance to be successful and endure for the long term, both firms must believe that they are winners. ” IT’s changing environment – “The internal IT organization is already a selector of code rather than a developer. ” – low cost maintenance of old systems – transformation to new model Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development N TM -4
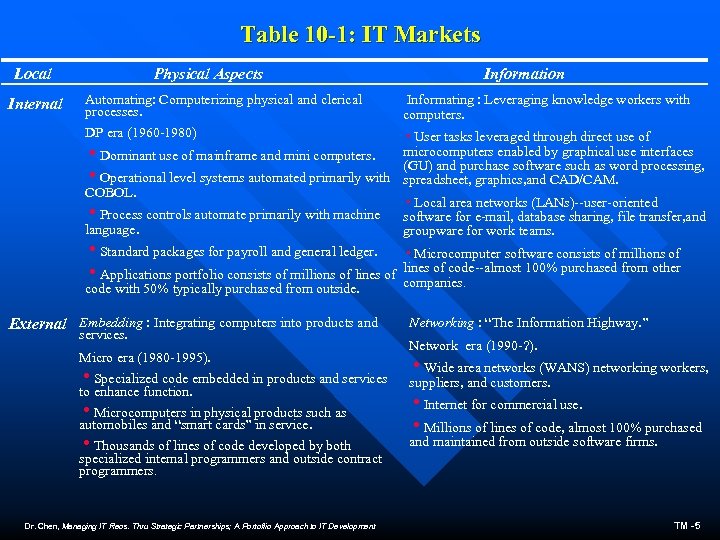 Table 10 -1: IT Markets Local Physical Aspects Information Automating: Computerizing physical and clerical processes. Informating : Leveraging knowledge workers with computers. DP era (1960 -1980) Internal h. User tasks leveraged through direct use of microcomputers enabled by graphical use interfaces h. Dominant use of mainframe and mini computers. (GU) and purchase software such as word processing, h. Operational level systems automated primarily with spreadsheet, graphics, and CAD/CAM. COBOL. h. Local area networks (LANs)--user-oriented h. Process controls automate primarily with machine software for e-mail, database sharing, file transfer, and language. groupware for work teams. h. Standard packages for payroll and general ledger. h. Microcomputer software consists of millions of h. Applications portfolio consists of millions of lines of code--almost 100% purchased from other companies. code with 50% typically purchased from outside. External Embedding : Integrating computers into products and services. Micro era (1980 -1995). h. Specialized code embedded in products and services to enhance function. h. Microcomputers in physical products such as automobiles and “smart cards” in service. h. Thousands of lines of code developed by both specialized internal programmers and outside contract programmers. Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Networking : “The Information Highway. ” Network era (1990 -? ). h. Wide area networks (WANS) networking workers, suppliers, and customers. h. Internet for commercial use. h. Millions of lines of code, almost 100% purchased and maintained from outside software firms. TM -5
Table 10 -1: IT Markets Local Physical Aspects Information Automating: Computerizing physical and clerical processes. Informating : Leveraging knowledge workers with computers. DP era (1960 -1980) Internal h. User tasks leveraged through direct use of microcomputers enabled by graphical use interfaces h. Dominant use of mainframe and mini computers. (GU) and purchase software such as word processing, h. Operational level systems automated primarily with spreadsheet, graphics, and CAD/CAM. COBOL. h. Local area networks (LANs)--user-oriented h. Process controls automate primarily with machine software for e-mail, database sharing, file transfer, and language. groupware for work teams. h. Standard packages for payroll and general ledger. h. Microcomputer software consists of millions of h. Applications portfolio consists of millions of lines of code--almost 100% purchased from other companies. code with 50% typically purchased from outside. External Embedding : Integrating computers into products and services. Micro era (1980 -1995). h. Specialized code embedded in products and services to enhance function. h. Microcomputers in physical products such as automobiles and “smart cards” in service. h. Thousands of lines of code developed by both specialized internal programmers and outside contract programmers. Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Networking : “The Information Highway. ” Network era (1990 -? ). h. Wide area networks (WANS) networking workers, suppliers, and customers. h. Internet for commercial use. h. Millions of lines of code, almost 100% purchased and maintained from outside software firms. TM -5
 The Driving Forces Behind Outsourcing n Two drivers – focus » on core business – value » shareholder Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -6
The Driving Forces Behind Outsourcing n Two drivers – focus » on core business – value » shareholder Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -6
 Pressures (Drivers) to Outsource Concerns about costs and quality n Breakdown in IT performance n Intense supplier pressures n Simplified general management agenda n Financial factors n Corporate culture n Eliminating an internal irritant n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -7
Pressures (Drivers) to Outsource Concerns about costs and quality n Breakdown in IT performance n Intense supplier pressures n Simplified general management agenda n Financial factors n Corporate culture n Eliminating an internal irritant n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -7
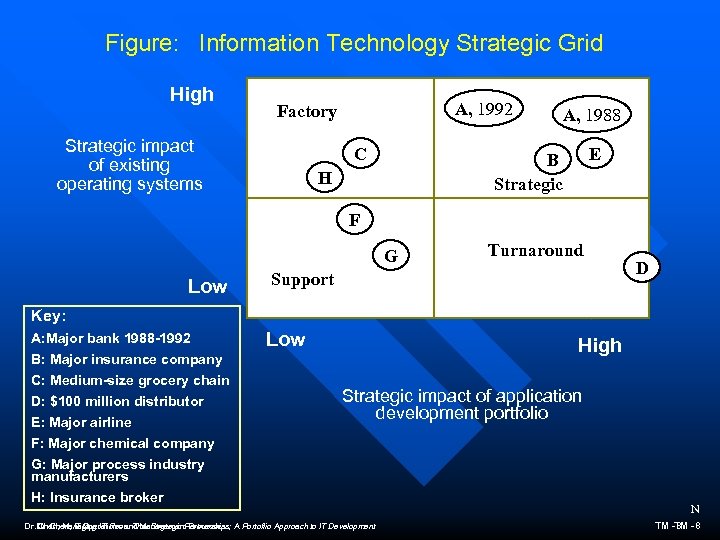 Figure: Information Technology Strategic Grid High A, 1992 Factory Strategic impact of existing operating systems C A, 1988 E B Strategic H F G Low Turnaround Support D Key: A: Major bank 1988 -1992 B: Major insurance company C: Medium-size grocery chain D: $100 million distributor E: Major airline F: Major chemical company G: Major process industry manufacturers H: Insurance broker Low High Strategic impact of application development portfolio Dr. Chen, IT Operations and Management Processes A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; N TM -8 -8 TM
Figure: Information Technology Strategic Grid High A, 1992 Factory Strategic impact of existing operating systems C A, 1988 E B Strategic H F G Low Turnaround Support D Key: A: Major bank 1988 -1992 B: Major insurance company C: Medium-size grocery chain D: $100 million distributor E: Major airline F: Major chemical company G: Major process industry manufacturers H: Insurance broker Low High Strategic impact of application development portfolio Dr. Chen, IT Operations and Management Processes A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; N TM -8 -8 TM
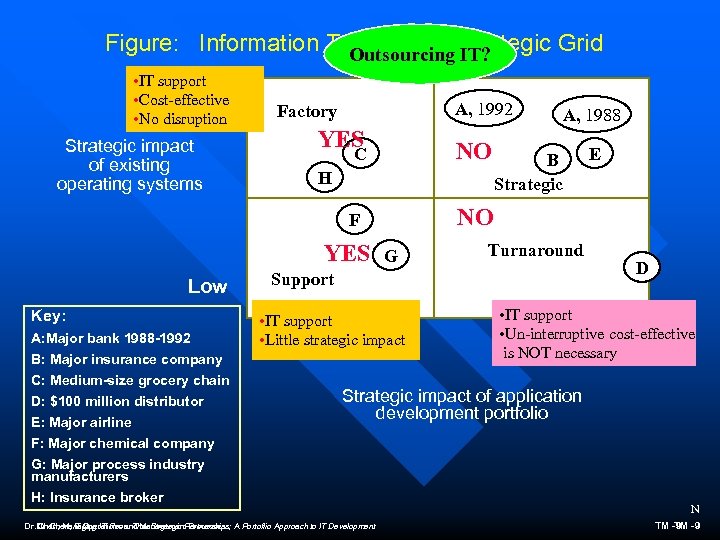 Figure: Information Technology Strategic Grid Outsourcing IT? • IT support High • Cost-effective • No disruption Strategic impact of existing operating systems A, 1992 Factory YES C NO F NO H YES Low Key: A: Major bank 1988 -1992 B: Major insurance company C: Medium-size grocery chain D: $100 million distributor E: Major airline F: Major chemical company G: Major process industry manufacturers H: Insurance broker A, 1988 G B Strategic Turnaround Support • IT support • Little strategic impact Low E D • IT support • Un-interruptive cost-effective High is NOT necessary Strategic impact of application development portfolio Dr. Chen, IT Operations and Management Processes A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; N TM -9 -9 TM
Figure: Information Technology Strategic Grid Outsourcing IT? • IT support High • Cost-effective • No disruption Strategic impact of existing operating systems A, 1992 Factory YES C NO F NO H YES Low Key: A: Major bank 1988 -1992 B: Major insurance company C: Medium-size grocery chain D: $100 million distributor E: Major airline F: Major chemical company G: Major process industry manufacturers H: Insurance broker A, 1988 G B Strategic Turnaround Support • IT support • Little strategic impact Low E D • IT support • Un-interruptive cost-effective High is NOT necessary Strategic impact of application development portfolio Dr. Chen, IT Operations and Management Processes A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; N TM -9 -9 TM
 Outsourcing As an Economic Strategy Core competencies n Which sources are less expensive n How much control is needed n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -10
Outsourcing As an Economic Strategy Core competencies n Which sources are less expensive n How much control is needed n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -10
 When to Outsourcing? Which IS activities are strategic to our company's business? n Will outsourcing save us at least 15 percent? n Does our firm have access to the needed technology and expertise? n – If not, outsourcing may be the answer to acquiring these resources. n Does outsourcing increase our firm's flexibility? Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -11
When to Outsourcing? Which IS activities are strategic to our company's business? n Will outsourcing save us at least 15 percent? n Does our firm have access to the needed technology and expertise? n – If not, outsourcing may be the answer to acquiring these resources. n Does outsourcing increase our firm's flexibility? Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -11
 When to Outsource IT n Position on strategic grid – “The more the firm is operationally dependent on IT, the more sense outsourcing makes. ” – factory: yes strategic: no – support: yes turnaround: no – strategic differentiated outsourcing n Development portfolio – maintenance/high structured projects: yes – low structured projects: no Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -12 N
When to Outsource IT n Position on strategic grid – “The more the firm is operationally dependent on IT, the more sense outsourcing makes. ” – factory: yes strategic: no – support: yes turnaround: no – strategic differentiated outsourcing n Development portfolio – maintenance/high structured projects: yes – low structured projects: no Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -12 N
 When to Outsource IT (Cont. ) Organizational learning n Firm’s “era” n – “The farther a company is from the network era in its internal use of IT, the more useful outsourcing can be to close the gap. ” n Current IT organization – “The more IT development and operations are already segregated, in the organization and in accounting, the easier it is to negotiate an enduring outsourcing contract. ” Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -13 N
When to Outsource IT (Cont. ) Organizational learning n Firm’s “era” n – “The farther a company is from the network era in its internal use of IT, the more useful outsourcing can be to close the gap. ” n Current IT organization – “The more IT development and operations are already segregated, in the organization and in accounting, the easier it is to negotiate an enduring outsourcing contract. ” Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -13 N
 What Activities that Management should not Outsource? strategy n policy role n the decisions about when to introduce information systems into the organization n the management of the vendor n when the system (IS) department is well managed, and where IT is a core competency n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -14
What Activities that Management should not Outsource? strategy n policy role n the decisions about when to introduce information systems into the organization n the management of the vendor n when the system (IS) department is well managed, and where IT is a core competency n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -14
 Structuring the Alliance Contract flexibility n Standards and control n Areas to outsource n Cost savings n Supplier stability and quality n Management fit n Conversion problems n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -15 N
Structuring the Alliance Contract flexibility n Standards and control n Areas to outsource n Cost savings n Supplier stability and quality n Management fit n Conversion problems n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -15 N
 Managing the Alliance n The CIO function – “The heart of the CIO’s job is planning …” – partnership/contract management – architecture planning – emerging technologies – continuous learning Performance measurements n Mix and coordination of tasks n Customer-outsourcer interface n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -16 N
Managing the Alliance n The CIO function – “The heart of the CIO’s job is planning …” – partnership/contract management – architecture planning – emerging technologies – continuous learning Performance measurements n Mix and coordination of tasks n Customer-outsourcer interface n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -16 N
 Fig. 15. 10 (Turban) Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -17
Fig. 15. 10 (Turban) Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -17
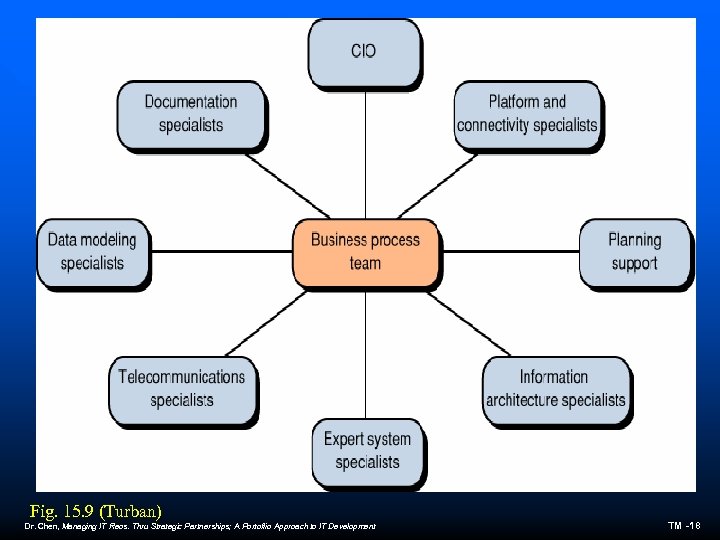 Fig. 15. 9 (Turban) Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -18
Fig. 15. 9 (Turban) Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -18
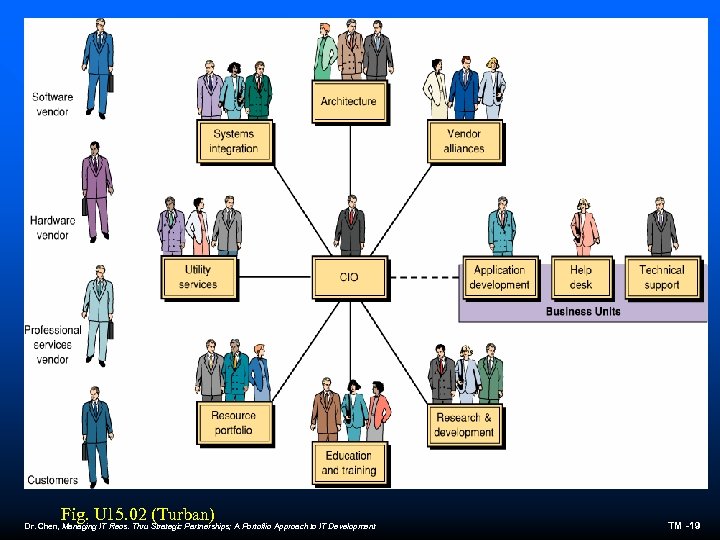 Fig. U 15. 02 (Turban) Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -19
Fig. U 15. 02 (Turban) Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -19
 OUTSOURCING BENEFITS Economy n Service quality n Predictability n Flexibility n Making fixed cost variable n Freeing up human resources for other projects n Freeing up financial capital n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -20
OUTSOURCING BENEFITS Economy n Service quality n Predictability n Flexibility n Making fixed cost variable n Freeing up human resources for other projects n Freeing up financial capital n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -20
 CONS OF OUTSOURCING Loss of control n Vulnerability of strategic information n Dependency n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -21
CONS OF OUTSOURCING Loss of control n Vulnerability of strategic information n Dependency n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -21
 Outsourcing Recommendations Write shorter contracts - less than 5 years n Subcontract control n Selective outsourcing n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -22
Outsourcing Recommendations Write shorter contracts - less than 5 years n Subcontract control n Selective outsourcing n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -22
 Desirable Outcomes and Implementation Issues n n n n n On-time On-budget Full functionality user acceptance Favorable cost-to-benefits ratio Low maintenance Scalability Integration with other systems Reusability Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -23
Desirable Outcomes and Implementation Issues n n n n n On-time On-budget Full functionality user acceptance Favorable cost-to-benefits ratio Low maintenance Scalability Integration with other systems Reusability Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -23
 Chapter 11 A Portfolio Approach to Information Technology Development Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -24
Chapter 11 A Portfolio Approach to Information Technology Development Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -24
 Questions … What is IT Development? n What is a “Portfolio Approach”? n – A profile that aggregates a company’s project information for its portfolio of systems and programming projects. Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -25
Questions … What is IT Development? n What is a “Portfolio Approach”? n – A profile that aggregates a company’s project information for its portfolio of systems and programming projects. Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -25
 Common in “Big Disasters” (both general management and IT management) Failure to consider the implementation risk of a specific project n Failure to consider the aggregate implementation risk of the portfolio of projects n Failure to recognize that different projects require different managerial approaches n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -26
Common in “Big Disasters” (both general management and IT management) Failure to consider the implementation risk of a specific project n Failure to consider the aggregate implementation risk of the portfolio of projects n Failure to recognize that different projects require different managerial approaches n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -26
 Portfolio Risk n What is Portfolio Risk? – A profile that aggregates a company’s project implementation risk for its portfolio of systems and programming projects. n How much portfolio risk is appropriate? N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -27
Portfolio Risk n What is Portfolio Risk? – A profile that aggregates a company’s project implementation risk for its portfolio of systems and programming projects. n How much portfolio risk is appropriate? N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -27
 Project Implementation Risk “Project implementation risk … is what remains after application of proper tools. ” Consequences of Risks: n 1. Anticipated benefits 2. Higher-than-expected implementation costs 3. Longer-than-expected implementation time 4. Technical performance too low 5. System incompatibility N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -28
Project Implementation Risk “Project implementation risk … is what remains after application of proper tools. ” Consequences of Risks: n 1. Anticipated benefits 2. Higher-than-expected implementation costs 3. Longer-than-expected implementation time 4. Technical performance too low 5. System incompatibility N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -28
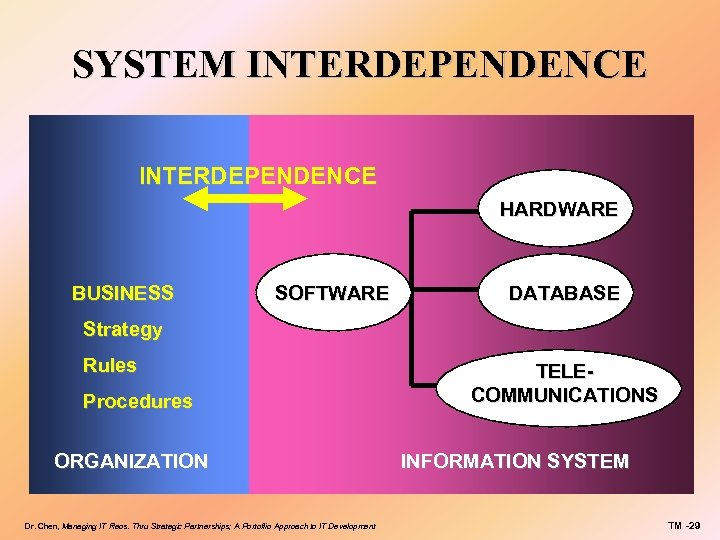 SYSTEM INTERDEPENDENCE HARDWARE BUSINESS SOFTWARE DATABASE Strategy Rules Procedures ORGANIZATION Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TELECOMMUNICATIONS INFORMATION SYSTEM TM -29
SYSTEM INTERDEPENDENCE HARDWARE BUSINESS SOFTWARE DATABASE Strategy Rules Procedures ORGANIZATION Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TELECOMMUNICATIONS INFORMATION SYSTEM TM -29
 SYSTEM FAILURE AN INFORMATION SYSTEM THAT: n DOESN’T PERFORM AS EXPECTED n ISN’T OPERATIONAL AT A SPECIFIED TIME n CANNOT BE USED AS INTENDED * 14. 3 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -30
SYSTEM FAILURE AN INFORMATION SYSTEM THAT: n DOESN’T PERFORM AS EXPECTED n ISN’T OPERATIONAL AT A SPECIFIED TIME n CANNOT BE USED AS INTENDED * 14. 3 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -30
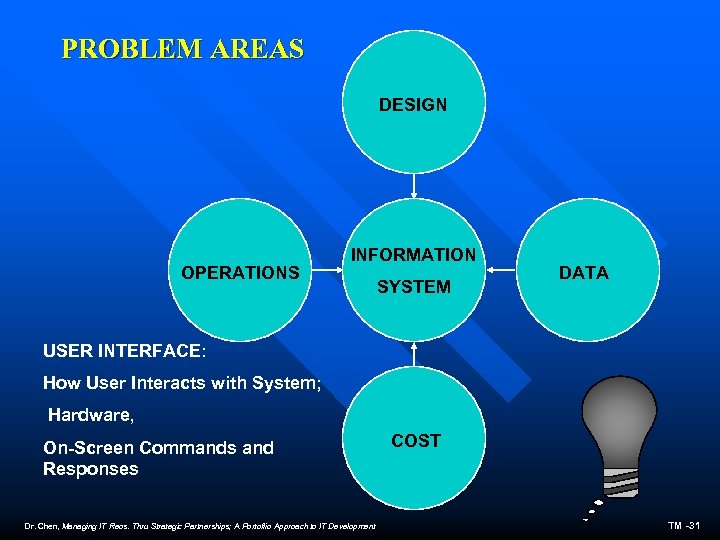 PROBLEM AREAS DESIGN OPERATIONS INFORMATION SYSTEM DATA USER INTERFACE: How User Interacts with System; Hardware, On-Screen Commands and Responses Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development COST TM -31
PROBLEM AREAS DESIGN OPERATIONS INFORMATION SYSTEM DATA USER INTERFACE: How User Interacts with System; Hardware, On-Screen Commands and Responses Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development COST TM -31
 MEASURES OF INFO SYSTEM SUCCESS 1. HIGH LEVELS OF USE 2. USER SATISFACTION 3. FAVORABLE ATTITUDES 4. ACHIEVED OBJECTIVES 5. FINANCIAL PAYOFF * 14. 6 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -32
MEASURES OF INFO SYSTEM SUCCESS 1. HIGH LEVELS OF USE 2. USER SATISFACTION 3. FAVORABLE ATTITUDES 4. ACHIEVED OBJECTIVES 5. FINANCIAL PAYOFF * 14. 6 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -32
 CAUSES OF INFORMATION SYSTEM SUCCESS & FAILURE IMPLEMENTATION n LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY & RISK (Project Dimension that influence risk) n CHALLENGE OF BUSINESS REENGINEERING * n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -33
CAUSES OF INFORMATION SYSTEM SUCCESS & FAILURE IMPLEMENTATION n LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY & RISK (Project Dimension that influence risk) n CHALLENGE OF BUSINESS REENGINEERING * n Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -33
 CHANGE AGENT DURING IMPLEMENTATION, INDIVIDUAL ACTS AS CATALYST DURING CHANGE PROCESS TO ENSURE SUCCESS * 14. 10 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -34
CHANGE AGENT DURING IMPLEMENTATION, INDIVIDUAL ACTS AS CATALYST DURING CHANGE PROCESS TO ENSURE SUCCESS * 14. 10 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -34
 ACTIONS & INDICATORS FOR SUCCESSFUL SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION n n n SUPPORT BY LOCAL FUNDS NEW ORGANIZATIONAL ARRANGEMENTS STABLE SUPPLY & MAINTENANCE NEW PERSONNEL CLASSIFICATIONS CHANGES IN ORGANIZATIONAL AUTHORITY 14. 11 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Source: Yin (1981) TM -35
ACTIONS & INDICATORS FOR SUCCESSFUL SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION n n n SUPPORT BY LOCAL FUNDS NEW ORGANIZATIONAL ARRANGEMENTS STABLE SUPPLY & MAINTENANCE NEW PERSONNEL CLASSIFICATIONS CHANGES IN ORGANIZATIONAL AUTHORITY 14. 11 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Source: Yin (1981) TM -35
 ACTIONS & INDICATORS FOR SUCCESSFUL SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION n n n INTERNALIZATION OF TRAINING PROGRAM CONTINUAL UPDATING OF THE SYSTEM PROMOTION OF KEY PERSONNEL SURVIVAL OF SYSTEM AFTER TURNOVER ATTAINMENT OF WIDESPREAD USE * Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Source: Yin (1981) -36 TM
ACTIONS & INDICATORS FOR SUCCESSFUL SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION n n n INTERNALIZATION OF TRAINING PROGRAM CONTINUAL UPDATING OF THE SYSTEM PROMOTION OF KEY PERSONNEL SURVIVAL OF SYSTEM AFTER TURNOVER ATTAINMENT OF WIDESPREAD USE * Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Source: Yin (1981) -36 TM
 FACTORS IN IMPLEMENTATION OUTCOME DESIGN, COST, OPERATIONS, DATA n n USER INVOLVEMENT & INFLUENCE MANAGEMENT SUPPORT MANAGEMENT OF IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY / RISK (Project Dimension that influence risk) Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -37
FACTORS IN IMPLEMENTATION OUTCOME DESIGN, COST, OPERATIONS, DATA n n USER INVOLVEMENT & INFLUENCE MANAGEMENT SUPPORT MANAGEMENT OF IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY / RISK (Project Dimension that influence risk) Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -37
 MANAGEMENT OF THE IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS n n n DEFINE REQUIREMENTS ASSESS COSTS, BENEFITS, SCHEDULES IDENTIFY INTEREST GROUPS, ACTORS, DETAILS TRAIN END USERS CONTAIN CONFLICTS, UNCERTAINTIES * 14. 19 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -38
MANAGEMENT OF THE IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS n n n DEFINE REQUIREMENTS ASSESS COSTS, BENEFITS, SCHEDULES IDENTIFY INTEREST GROUPS, ACTORS, DETAILS TRAIN END USERS CONTAIN CONFLICTS, UNCERTAINTIES * 14. 19 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -38
 OBSTACLES TO BUSINESS REENGINEERING SUCCESS RESISTANCE TO CHANGE LIMITATIONS TO EXISTING SYSTEMS LACK OF EXECUTIVE CONSENSUS LACK OF SENIOR EXECUTIVE CHAMPION UNREALISTIC EXPECTATIONS LACK OF CROSS-FUNCTIONAL TEAM INADEQUATE TEAM SKILLS I. S. STAFF INVOLVED TOO LATE PROJECT CHARTER TOO NARROW 0 14. 26 Adapted from Caldwell, 1994 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development 20 30 40 % OF RESPONDENTS TM -39
OBSTACLES TO BUSINESS REENGINEERING SUCCESS RESISTANCE TO CHANGE LIMITATIONS TO EXISTING SYSTEMS LACK OF EXECUTIVE CONSENSUS LACK OF SENIOR EXECUTIVE CHAMPION UNREALISTIC EXPECTATIONS LACK OF CROSS-FUNCTIONAL TEAM INADEQUATE TEAM SKILLS I. S. STAFF INVOLVED TOO LATE PROJECT CHARTER TOO NARROW 0 14. 26 Adapted from Caldwell, 1994 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development 20 30 40 % OF RESPONDENTS TM -39
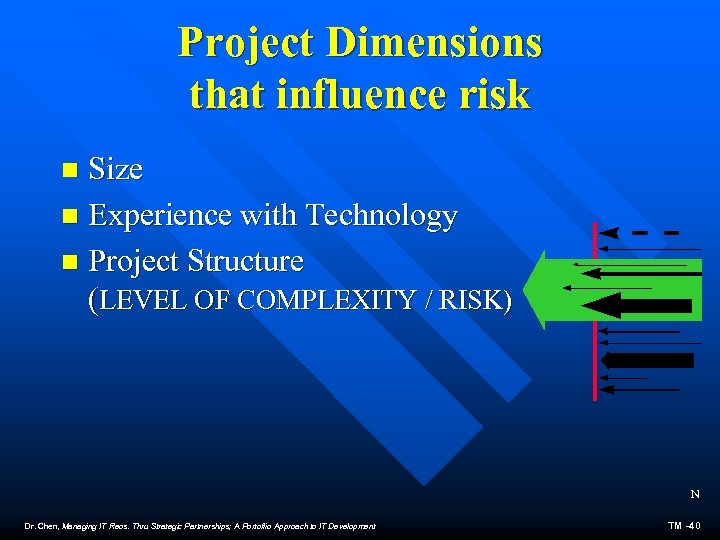 Project Dimensions that influence risk Size n Experience with Technology n Project Structure (LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY / RISK) n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -40
Project Dimensions that influence risk Size n Experience with Technology n Project Structure (LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY / RISK) n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -40
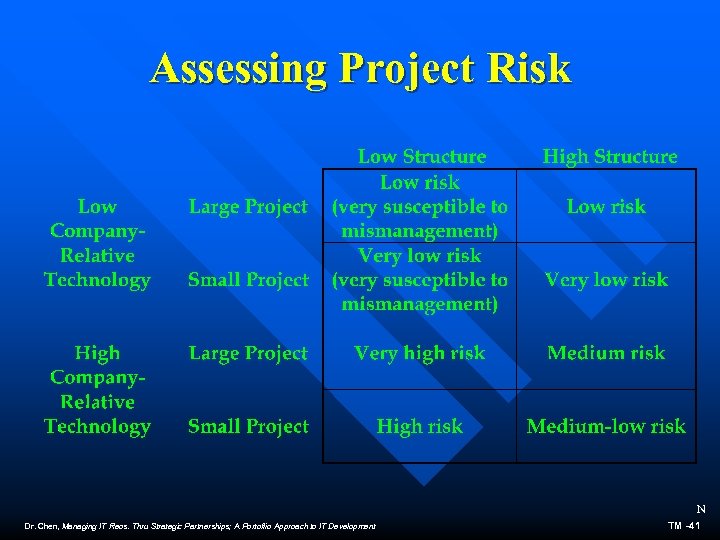 Assessing Project Risk N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -41
Assessing Project Risk N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -41
 MANAGING IMPLEMENTATION CONTROLLING RISK FACTORS n n EXTERNAL INTEGRATION TOOLS: Link work of Implementation Team to Users at all Organizational Levels INTERNAL INTEGRATION TOOLS: Ensure Implementation Team Operates as a Cohesive Unit * 14. 28 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -42
MANAGING IMPLEMENTATION CONTROLLING RISK FACTORS n n EXTERNAL INTEGRATION TOOLS: Link work of Implementation Team to Users at all Organizational Levels INTERNAL INTEGRATION TOOLS: Ensure Implementation Team Operates as a Cohesive Unit * 14. 28 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -42
 MANAGING IMPLEMENTATION FORMAL PLANNING & CONTROL TOOLS n n FORMAL PLANNING TOOLS: Help Structure, Sequence Tasks; Budget Time, Money, Resources FORMAL CONTROL TOOLS: Help Monitor Progress Toward Completing Tasks, Reaching Goals * 14. 31 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -43
MANAGING IMPLEMENTATION FORMAL PLANNING & CONTROL TOOLS n n FORMAL PLANNING TOOLS: Help Structure, Sequence Tasks; Budget Time, Money, Resources FORMAL CONTROL TOOLS: Help Monitor Progress Toward Completing Tasks, Reaching Goals * 14. 31 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -43
 Project Management: A Contingency Approach (Management Tools) External integration n Internal integration including technical leadership n Formal planning n Formal results-control mechanisms n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -44
Project Management: A Contingency Approach (Management Tools) External integration n Internal integration including technical leadership n Formal planning n Formal results-control mechanisms n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -44
 EXTERNAL INTEGRATION TOOLS n n n n User as Team Leader or Assistant User Steering Committee Users as Active Team Members Require User Approval of Specs Distribute Important Minutes Widely Users can Report to Management; Lead Training Effort and Installation User Responsible for Change Control * 14. 29 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -45
EXTERNAL INTEGRATION TOOLS n n n n User as Team Leader or Assistant User Steering Committee Users as Active Team Members Require User Approval of Specs Distribute Important Minutes Widely Users can Report to Management; Lead Training Effort and Installation User Responsible for Change Control * 14. 29 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -45
 INTERNAL INTEGRATION TOOLS n n n Team Members Highly Experienced Leader has Strong Technical, Project Management Background Frequent Meetings; Distribute Minutes Concerning Key Decisions Regular Technical Status Reviews Members have Good Working Relationships with Others Members help set Goals, Establish Targets 14. 30 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -46
INTERNAL INTEGRATION TOOLS n n n Team Members Highly Experienced Leader has Strong Technical, Project Management Background Frequent Meetings; Distribute Minutes Concerning Key Decisions Regular Technical Status Reviews Members have Good Working Relationships with Others Members help set Goals, Establish Targets 14. 30 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -46
 FORMAL PLANNING TOOLS SELECT MILESTONE PHASES n DEVELOP SPECIFICATIONS FROM FEASIBILITY STUDY n ESTABLISH SPECIFICATION STANDARDS n DEVELOP PROCESS FOR PROJECT APPROVAL * n 14. 32 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -47
FORMAL PLANNING TOOLS SELECT MILESTONE PHASES n DEVELOP SPECIFICATIONS FROM FEASIBILITY STUDY n ESTABLISH SPECIFICATION STANDARDS n DEVELOP PROCESS FOR PROJECT APPROVAL * n 14. 32 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -47
 FORMAL CONTROL TOOLS MAINTAIN DISCIPLINES TO CONTROL, FREEZE DESIGN n SPOT DEVIATIONS FROM PLAN n PERIODIC FORMAL STATUS REPORTS TO SHOW PROGRESS * n 14. 33 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -48
FORMAL CONTROL TOOLS MAINTAIN DISCIPLINES TO CONTROL, FREEZE DESIGN n SPOT DEVIATIONS FROM PLAN n PERIODIC FORMAL STATUS REPORTS TO SHOW PROGRESS * n 14. 33 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -48
 Results-Control Tools Best when … n Clear knowledge of desired results exists n Where the desired result can be controlled n Where the controllable result area can be measured effectively n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -49
Results-Control Tools Best when … n Clear knowledge of desired results exists n Where the desired result can be controlled n Where the controllable result area can be measured effectively n N Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -49
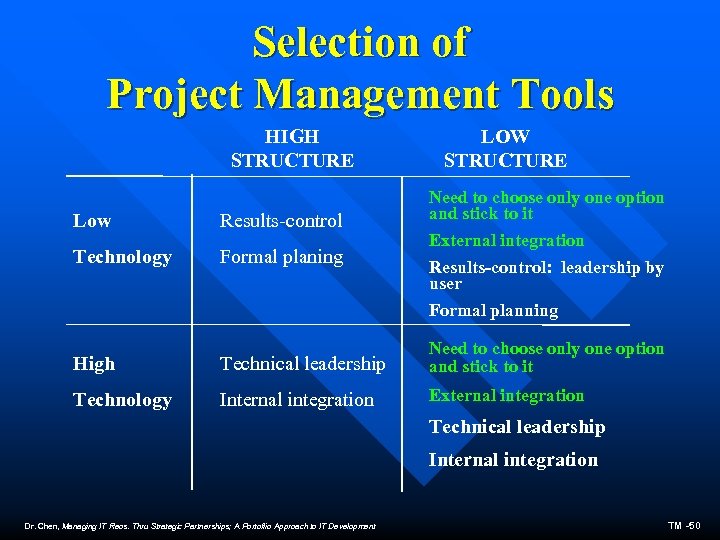 Selection of Project Management Tools HIGH STRUCTURE Low Results-control Technology Formal planing LOW STRUCTURE Need to choose only one option and stick to it External integration Results-control: leadership by user Formal planning High Technical leadership Need to choose only one option and stick to it Technology Internal integration External integration Technical leadership Internal integration Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -50
Selection of Project Management Tools HIGH STRUCTURE Low Results-control Technology Formal planing LOW STRUCTURE Need to choose only one option and stick to it External integration Results-control: leadership by user Formal planning High Technical leadership Need to choose only one option and stick to it Technology Internal integration External integration Technical leadership Internal integration Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -50
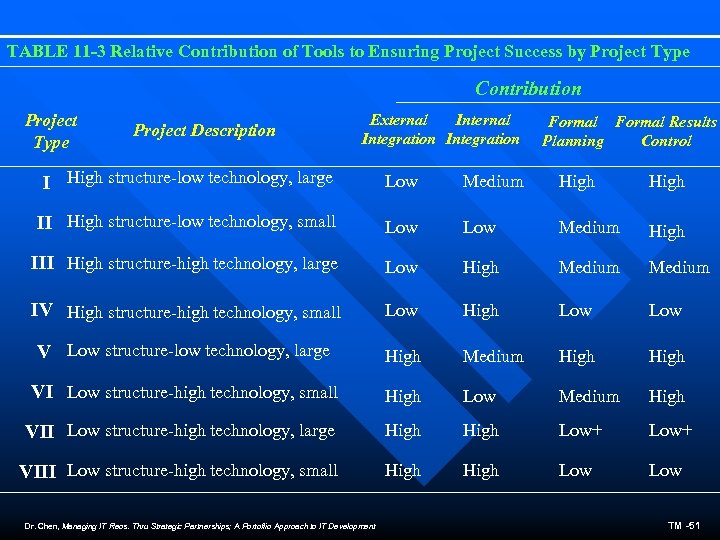 TABLE 11 -3 Relative Contribution of Tools to Ensuring Project Success by Project Type Contribution Project Type Project Description External Integration Formal Results Planning Control I High structure-low technology, large Low Medium High II High structure-low technology, small Low Medium High III High structure-high technology, large Low High Medium IV High structure-high technology, small Low High Low V Low structure-low technology, large High Medium High VI Low structure-high technology, small High Low Medium High VII Low structure-high technology, large High Low+ VIII Low structure-high technology, small High Low Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -51
TABLE 11 -3 Relative Contribution of Tools to Ensuring Project Success by Project Type Contribution Project Type Project Description External Integration Formal Results Planning Control I High structure-low technology, large Low Medium High II High structure-low technology, small Low Medium High III High structure-high technology, large Low High Medium IV High structure-high technology, small Low High Low V Low structure-low technology, large High Medium High VI Low structure-high technology, small High Low Medium High VII Low structure-high technology, large High Low+ VIII Low structure-high technology, small High Low Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -51
 MANAGING IMPLEMENTATION OVERCOMING USER RESISTANCE COUNTERIMPLEMENTATION: Deliberate attempt to Thwart Implementation. Countered by: n PEOPLE-ORIENTED THEORY n SYSTEM-ORIENTED THEORY n INTERACTION THEORY * 14. 34 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development N TM -52
MANAGING IMPLEMENTATION OVERCOMING USER RESISTANCE COUNTERIMPLEMENTATION: Deliberate attempt to Thwart Implementation. Countered by: n PEOPLE-ORIENTED THEORY n SYSTEM-ORIENTED THEORY n INTERACTION THEORY * 14. 34 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development N TM -52
 MANAGING IMPLEMENTATION DESIGNING FOR THE ORGANIZATION n n n ORGANIZATIONAL IMPACT ANALYSIS ERGONOMICS SOCIOTECHNICAL DESIGN * 14. 38 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -53
MANAGING IMPLEMENTATION DESIGNING FOR THE ORGANIZATION n n n ORGANIZATIONAL IMPACT ANALYSIS ERGONOMICS SOCIOTECHNICAL DESIGN * 14. 38 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -53
 ORGANIZATIONAL IMPACT ANALYSIS : HOW WILL PROPOSED SYSTEM AFFECT ORIENTATIONAL: n STRUCTURE n ATTITUDES n DECISION MAKING n OPERATIONS ? 14. 39 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -54
ORGANIZATIONAL IMPACT ANALYSIS : HOW WILL PROPOSED SYSTEM AFFECT ORIENTATIONAL: n STRUCTURE n ATTITUDES n DECISION MAKING n OPERATIONS ? 14. 39 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -54
 ERGONOMICS: INTERACTION OF PEOPLE & MACHINES, INCLUDING: n DESIGN OF JOBS n HEALTH ISSUES n END-USER INTERFACES * 14. 40 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -55
ERGONOMICS: INTERACTION OF PEOPLE & MACHINES, INCLUDING: n DESIGN OF JOBS n HEALTH ISSUES n END-USER INTERFACES * 14. 40 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -55
 SOCIOTECHNICAL DESIGN: DESIGN TO PRODUCE INFORMATION SYSTEMS THAT BLEND: n TECHNICAL EFFICIENCY n SENSITIVITY TO ORGANIZATIONAL NEEDS n SENSITIVITY TO HUMAN NEEDS * 14. 41 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -56
SOCIOTECHNICAL DESIGN: DESIGN TO PRODUCE INFORMATION SYSTEMS THAT BLEND: n TECHNICAL EFFICIENCY n SENSITIVITY TO ORGANIZATIONAL NEEDS n SENSITIVITY TO HUMAN NEEDS * 14. 41 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -56
 POOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT COST OVERRUNS n TIME SLIPPAGE n TECHNICAL SHORTFALLS IMPAIR PERFORMANCE n FAILURE TO OBTAIN ANTICIPATED BENEFITS * n 14. 20 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -57
POOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT COST OVERRUNS n TIME SLIPPAGE n TECHNICAL SHORTFALLS IMPAIR PERFORMANCE n FAILURE TO OBTAIN ANTICIPATED BENEFITS * n 14. 20 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -57
 WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n ANALYSIS: Incorrect allocation of Time, Money Resources; Too Little Preliminary Planning; Improper Staffing; Excessive Promises; Incomplete Requirements; Users Spend Insufficient Time Helping Team Gather Information; Poor User Interviews * 14. 21 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -58
WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n ANALYSIS: Incorrect allocation of Time, Money Resources; Too Little Preliminary Planning; Improper Staffing; Excessive Promises; Incomplete Requirements; Users Spend Insufficient Time Helping Team Gather Information; Poor User Interviews * 14. 21 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -58
 WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n DESIGN: Little or no User Input to Design; No built-in Flexibility; Lack of Organizational Impact Analysis; Functional Specifications Inadequately Documented * 14. 22 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -59
WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n DESIGN: Little or no User Input to Design; No built-in Flexibility; Lack of Organizational Impact Analysis; Functional Specifications Inadequately Documented * 14. 22 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -59
 WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n PROGRAMMING: Underestimated Time, Cost; Incomplete Specifications; Not Enough Time for Program Logic; Time Wasted on Writing Code; Insufficient use of Structured Design, Object-Oriented Techniques; Programs Inadequately Documented; Requisite Resources not Scheduled * 14. 23 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -60
WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n PROGRAMMING: Underestimated Time, Cost; Incomplete Specifications; Not Enough Time for Program Logic; Time Wasted on Writing Code; Insufficient use of Structured Design, Object-Oriented Techniques; Programs Inadequately Documented; Requisite Resources not Scheduled * 14. 23 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -60
 WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n TESTING: Underestimated Time & Cost; Disorganized Test Plan; All Direct Users not Involved until Conversion; Inappropriate Acceptance Tests; Management Doesn’t Sign Off on Test Results * 14. 24 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -61
WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n TESTING: Underestimated Time & Cost; Disorganized Test Plan; All Direct Users not Involved until Conversion; Inappropriate Acceptance Tests; Management Doesn’t Sign Off on Test Results * 14. 24 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -61
 WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n CONVERSION: Insufficient Time & Money; All Direct Users not Involved until Conversion; Delayed Training; To Reduce Cost Overruns & Delays System Goes Online too soon; Inadequate System & Use Documentation; No Performance Evaluation or Standards; Insufficient System Maintenance Plans or Training * 14. 25 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -62
WHAT CAN GO WRONG? n CONVERSION: Insufficient Time & Money; All Direct Users not Involved until Conversion; Delayed Training; To Reduce Cost Overruns & Delays System Goes Online too soon; Inadequate System & Use Documentation; No Performance Evaluation or Standards; Insufficient System Maintenance Plans or Training * 14. 25 Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -62
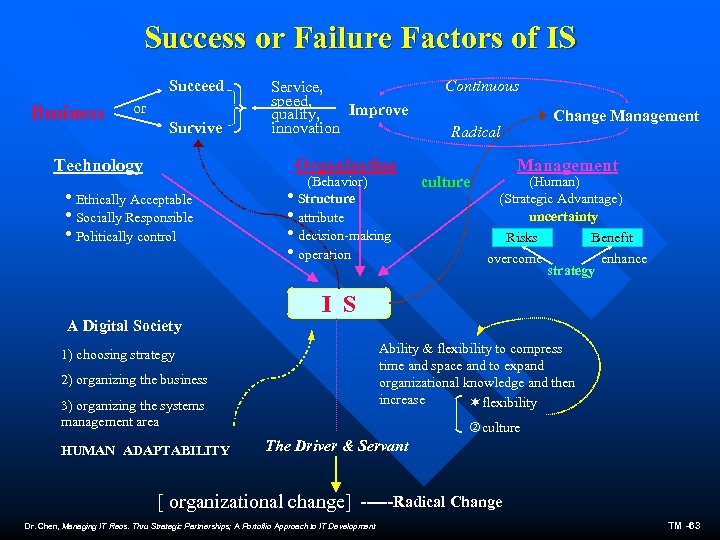 Success or Failure Factors of IS Succeed Business or Survive Service, speed, Improve quality, innovation Organization Technology i. Ethically Acceptable i. Socially Responsible i. Politically control A Digital Society (Behavior) i. Structure iattribute idecision-making ioperation Change Management Radical culture Management (Human) (Strategic Advantage) uncertainty Risks Benefit overcome strategy enhance I S Ability & flexibility to compress time and space and to expand organizational knowledge and then increase flexibility 1) choosing strategy 2) organizing the business 3) organizing the systems management area HUMAN ADAPTABILITY Continuous culture The Driver & Servant [ organizational change] ------Radical Change Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -63
Success or Failure Factors of IS Succeed Business or Survive Service, speed, Improve quality, innovation Organization Technology i. Ethically Acceptable i. Socially Responsible i. Politically control A Digital Society (Behavior) i. Structure iattribute idecision-making ioperation Change Management Radical culture Management (Human) (Strategic Advantage) uncertainty Risks Benefit overcome strategy enhance I S Ability & flexibility to compress time and space and to expand organizational knowledge and then increase flexibility 1) choosing strategy 2) organizing the business 3) organizing the systems management area HUMAN ADAPTABILITY Continuous culture The Driver & Servant [ organizational change] ------Radical Change Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -63
![Success or Failure Factors of IS (Cont’d) [ organizational change] A FIRM/ORGANIZATION: Efficiency ------Radical Success or Failure Factors of IS (Cont’d) [ organizational change] A FIRM/ORGANIZATION: Efficiency ------Radical](https://present5.com/presentation/452b4a9d74f77d181b79217527845b56/image-64.jpg) Success or Failure Factors of IS (Cont’d) [ organizational change] A FIRM/ORGANIZATION: Efficiency ------Radical Change Evolution of change Effectiveness (Automate) Innovation (Informate) (Innovate) [Doing the things right] [Doing the right things] - creativity -Proper utilization of resource {Save Money} -Attainment of goals - property of culture {Make Money} Restructuring Competitive Advantage Re-engineering Cooperative Advantage Electronic Market: flatten the organizational hierarchical structure “ Revolutionary significance lies in generality” e. g. , steam engineers--triggered the first Industrial Revolution Computers--Seem to be triggering a second one. Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -64
Success or Failure Factors of IS (Cont’d) [ organizational change] A FIRM/ORGANIZATION: Efficiency ------Radical Change Evolution of change Effectiveness (Automate) Innovation (Informate) (Innovate) [Doing the things right] [Doing the right things] - creativity -Proper utilization of resource {Save Money} -Attainment of goals - property of culture {Make Money} Restructuring Competitive Advantage Re-engineering Cooperative Advantage Electronic Market: flatten the organizational hierarchical structure “ Revolutionary significance lies in generality” e. g. , steam engineers--triggered the first Industrial Revolution Computers--Seem to be triggering a second one. Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -64
 IT Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Yesterday Tomorrow Computer age Computer proc. Computing Accuracy Automation Efficiency Information age People proc. Communication Perspective Information Effectiveness Knowledge age Knowledge proc. Connectivity Reality Innovation Performance/ Innovation “doing things right” “doing the right things” “creativity” Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -65
IT Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Yesterday Tomorrow Computer age Computer proc. Computing Accuracy Automation Efficiency Information age People proc. Communication Perspective Information Effectiveness Knowledge age Knowledge proc. Connectivity Reality Innovation Performance/ Innovation “doing things right” “doing the right things” “creativity” Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -65
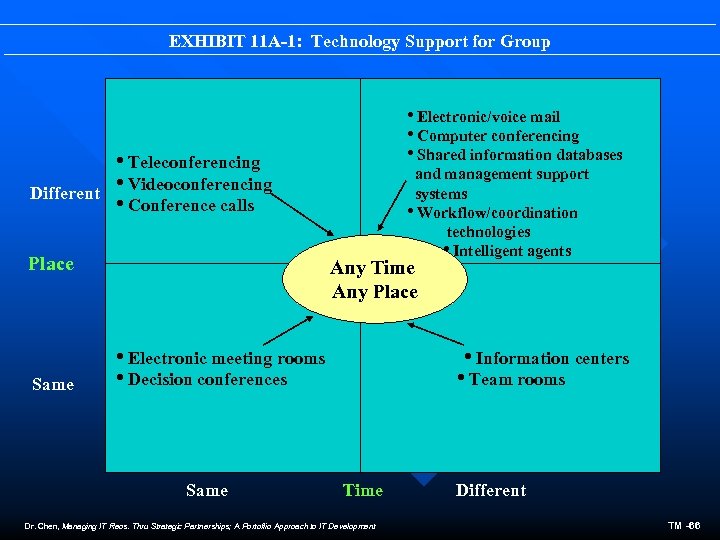 EXHIBIT 11 A-1: Technology Support for Group i. Electronic/voice mail i. Computer conferencing i. Shared information databases i. Teleconferencing i. Videoconferencing Different i. Conference calls Place Same and management support systems i. Workflow/coordination technologies i. Intelligent agents Any Time Any Place i. Electronic meeting rooms i. Decision conferences Same i. Information centers i. Team rooms Time Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Different TM -66
EXHIBIT 11 A-1: Technology Support for Group i. Electronic/voice mail i. Computer conferencing i. Shared information databases i. Teleconferencing i. Videoconferencing Different i. Conference calls Place Same and management support systems i. Workflow/coordination technologies i. Intelligent agents Any Time Any Place i. Electronic meeting rooms i. Decision conferences Same i. Information centers i. Team rooms Time Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Different TM -66
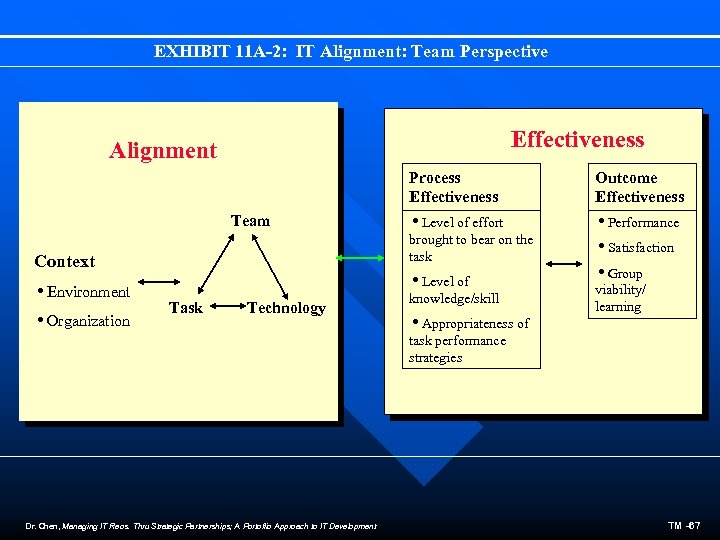 EXHIBIT 11 A-2: IT Alignment: Team Perspective Effectiveness Alignment Process Effectiveness Team i. Organization i. Level of effort i. Performance brought to bear on the task Context i. Environment Outcome Effectiveness i. Level of Task Technology knowledge/skill i. Satisfaction i. Group viability/ learning i. Appropriateness of task performance strategies Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -67
EXHIBIT 11 A-2: IT Alignment: Team Perspective Effectiveness Alignment Process Effectiveness Team i. Organization i. Level of effort i. Performance brought to bear on the task Context i. Environment Outcome Effectiveness i. Level of Task Technology knowledge/skill i. Satisfaction i. Group viability/ learning i. Appropriateness of task performance strategies Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development TM -67
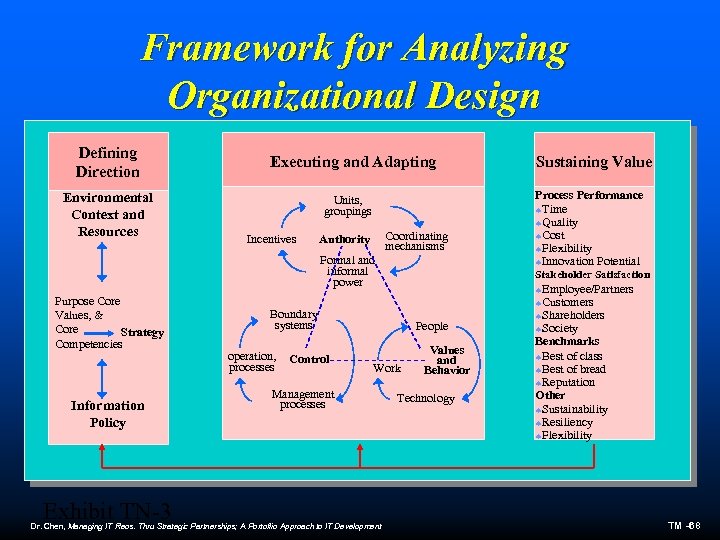 Framework for Analyzing Organizational Design Defining Direction Environmental Context and Resources Executing and Adapting Units, groupings Incentives Coordinating mechanisms Authority Formal and informal power Purpose Core Values, & Core Strategy Competencies Information Policy Exhibit TN-3 Control People Work Management processes Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Process Performance ªTime ªQuality ªCost ªFlexibility ªInnovation Potential Stakeholder Satisfaction Boundary systems operation, processes Sustaining Values and Behavior Technology ªEmployee/Partners ªCustomers ªShareholders ªSociety Benchmarks ªBest of class ªBest of bread ªReputation Other ªSustainability ªResiliency ªFlexibility TM -68
Framework for Analyzing Organizational Design Defining Direction Environmental Context and Resources Executing and Adapting Units, groupings Incentives Coordinating mechanisms Authority Formal and informal power Purpose Core Values, & Core Strategy Competencies Information Policy Exhibit TN-3 Control People Work Management processes Dr. Chen, Managing IT Reos. Thru Strategic Partnerships; A Portoflio Approach to IT Development Process Performance ªTime ªQuality ªCost ªFlexibility ªInnovation Potential Stakeholder Satisfaction Boundary systems operation, processes Sustaining Values and Behavior Technology ªEmployee/Partners ªCustomers ªShareholders ªSociety Benchmarks ªBest of class ªBest of bread ªReputation Other ªSustainability ªResiliency ªFlexibility TM -68
 End of Chapters 10, 11
End of Chapters 10, 11
 Pressures to Outsource (Ch. 10) Financial factors Strengthening the balance sheet and avoiding a 1) To liquefy the firm’s intangible IT asset, and stream of sporadic (small pieces and successive) Hardware/Software Asset capital investments in the future 2) Outsourcing can turn a largely fixed-cost business into one with variable costs 3) A third-party relationship brings an entirely different set of dynamics to a firm’s view of IT expenditures Corporate culture 1) A company’s values can make it very hard for managers to take appropriate action. 2) However, outsourcing driven by very senior management, provided the fulcrum for overcoming this impasses, since it was not directly associated with any division or corporate staff. 3) An internal IT organization may fall behind the state of the art without being immediately attacked while an outsourcers is forced to keep up with the latest technology to be successful. Eliminating an internal irritant 1) No matter how competent and adaptive existing IT management and staff are (and usually they are very good), there is usually tension between the end users of the resources and the IT staff. 2) Often the tension is exacerbated by the different language IT professional use, and 3) lack of career paths for users and IT staff across the organization, 4) perceived high IT costs, perceived unresponsiveness to urgent requests, and 5) perceived technical obsolescence. In this context, the notion of a remote, efficient, experienced outsourcer is particularly compelling, even though the internal perceptions are not necessarily realistic. N
Pressures to Outsource (Ch. 10) Financial factors Strengthening the balance sheet and avoiding a 1) To liquefy the firm’s intangible IT asset, and stream of sporadic (small pieces and successive) Hardware/Software Asset capital investments in the future 2) Outsourcing can turn a largely fixed-cost business into one with variable costs 3) A third-party relationship brings an entirely different set of dynamics to a firm’s view of IT expenditures Corporate culture 1) A company’s values can make it very hard for managers to take appropriate action. 2) However, outsourcing driven by very senior management, provided the fulcrum for overcoming this impasses, since it was not directly associated with any division or corporate staff. 3) An internal IT organization may fall behind the state of the art without being immediately attacked while an outsourcers is forced to keep up with the latest technology to be successful. Eliminating an internal irritant 1) No matter how competent and adaptive existing IT management and staff are (and usually they are very good), there is usually tension between the end users of the resources and the IT staff. 2) Often the tension is exacerbated by the different language IT professional use, and 3) lack of career paths for users and IT staff across the organization, 4) perceived high IT costs, perceived unresponsiveness to urgent requests, and 5) perceived technical obsolescence. In this context, the notion of a remote, efficient, experienced outsourcer is particularly compelling, even though the internal perceptions are not necessarily realistic. N
 Selection of Project Management Tools n High Structure – Low Technology – results-control – formal planning n High Structure – High Technology – technical leadership – internal integration
Selection of Project Management Tools n High Structure – Low Technology – results-control – formal planning n High Structure – High Technology – technical leadership – internal integration
 Selection of Project Management Tools n Low Structure – Low Technology – need to choose only one option and stick to it – external integration – formal planning – results-control — leadership by user n Low Structure – High Technology – need to choose only one option and stick to it – external integration – technical leadership – internal integration
Selection of Project Management Tools n Low Structure – Low Technology – need to choose only one option and stick to it – external integration – formal planning – results-control — leadership by user n Low Structure – High Technology – need to choose only one option and stick to it – external integration – technical leadership – internal integration
 USER-DESIGNER COMMUNICATIONS GAP DIFFERENCES IN BACKGROUNDS, INTERESTS, PRIORITIES IMPEDE COMMUNICATION AND PROBLEM SOLVING AMONG END USERS AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS SPECIALISTS *
USER-DESIGNER COMMUNICATIONS GAP DIFFERENCES IN BACKGROUNDS, INTERESTS, PRIORITIES IMPEDE COMMUNICATION AND PROBLEM SOLVING AMONG END USERS AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS SPECIALISTS *
 USER CONCERNS: WILL SYSTEM DELIVER INFORMATION I NEED? HOW QUICKLY CAN I ACCESS DATA? HOW EASILY CAN I RECEIVE DATA? HOW MUCH CLERICAL SUPPORT WILL I NEED FOR DATA ENTRY? HOW WILL SYSTEM OPERATION FIT INTO MY DAILY BUSINESS SCHEDULE? * 14. 15
USER CONCERNS: WILL SYSTEM DELIVER INFORMATION I NEED? HOW QUICKLY CAN I ACCESS DATA? HOW EASILY CAN I RECEIVE DATA? HOW MUCH CLERICAL SUPPORT WILL I NEED FOR DATA ENTRY? HOW WILL SYSTEM OPERATION FIT INTO MY DAILY BUSINESS SCHEDULE? * 14. 15
 DESIGNER CONCERNS: HOW MUCH DISK SPACE WILL MASTER FILE CONSUME? HOW MANY LINES OF PROGRAM CODE WILL THIS FUNCTION TAKE? HOW CAN WE REDUCE CPU TIME? WHAT IS THE MOST EFFICIENT WAY OF STORING THIS DATA? WHAT DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM SHOULD WE USE? *
DESIGNER CONCERNS: HOW MUCH DISK SPACE WILL MASTER FILE CONSUME? HOW MANY LINES OF PROGRAM CODE WILL THIS FUNCTION TAKE? HOW CAN WE REDUCE CPU TIME? WHAT IS THE MOST EFFICIENT WAY OF STORING THIS DATA? WHAT DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM SHOULD WE USE? *


