8eaf7a5f349cd5e470413026d0002363.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45

 Chapter 10 Local Marketing in Emerging Markets Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2006 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 10 Local Marketing in Emerging Markets Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2006 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Outline Basic Marketing in Emerging Markets NDCs vs Developing Countries Marketing in Russia Marketing in China Marketing in India Takeaway.
Outline Basic Marketing in Emerging Markets NDCs vs Developing Countries Marketing in Russia Marketing in China Marketing in India Takeaway.
 Marketing in Emerging Markets ESSENTIALLY, EMERGING MARKETS DO NOT USUALLY HAVE AN EFFECTIVE MARKETING INFRASTRUCTURE. IN THE OLD SYSTEM, ESPECIALLY IN NEWLY DEMOCRATIZED COUNTRIES, THERE WAS MUCH MORE VALUE PLACED ON PRODUCTION AND ON INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTS TO THE NEGLECT OF CONSUMER PRODUCTS AND EFFECTIVE DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS. THESE DIFFICIENCIES MAKE IT DIFFICULT TO BE A LOCAL MARKETER IN AN NDC.
Marketing in Emerging Markets ESSENTIALLY, EMERGING MARKETS DO NOT USUALLY HAVE AN EFFECTIVE MARKETING INFRASTRUCTURE. IN THE OLD SYSTEM, ESPECIALLY IN NEWLY DEMOCRATIZED COUNTRIES, THERE WAS MUCH MORE VALUE PLACED ON PRODUCTION AND ON INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTS TO THE NEGLECT OF CONSUMER PRODUCTS AND EFFECTIVE DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS. THESE DIFFICIENCIES MAKE IT DIFFICULT TO BE A LOCAL MARKETER IN AN NDC.
 Marketing Infrastructure THE LOCAL MARKETER MUST DETERMINE WHAT FUNCTIONS CAN BE PERFORMED BY EXISTING CHANNELS OF DISTRIBUTION AND, IF NEED BE, CREATE NEW ONES. THE LOCAL MARKETER HAS TO ADAPT HIS PRODUCT TO LOCAL STANDARDS, EX. BATTERY OPERATED APPLIANCES. SOMETIMES, THE FIRM’S VALUE CHAIN HAS TO BE RECONFIGURED. FOR EXAMPLE, IF THE REQUIRED KNOW-HOW IS NOT AVAILABLE, THE MARKETER MUST CREATE A SERVICE NETWORK AND TRAIN THE SERVICE STAFF.
Marketing Infrastructure THE LOCAL MARKETER MUST DETERMINE WHAT FUNCTIONS CAN BE PERFORMED BY EXISTING CHANNELS OF DISTRIBUTION AND, IF NEED BE, CREATE NEW ONES. THE LOCAL MARKETER HAS TO ADAPT HIS PRODUCT TO LOCAL STANDARDS, EX. BATTERY OPERATED APPLIANCES. SOMETIMES, THE FIRM’S VALUE CHAIN HAS TO BE RECONFIGURED. FOR EXAMPLE, IF THE REQUIRED KNOW-HOW IS NOT AVAILABLE, THE MARKETER MUST CREATE A SERVICE NETWORK AND TRAIN THE SERVICE STAFF.
 “Professor” Marketer IN EMERGING MARKETS, THE ENTERING LOCAL MARKETER NEEDS TO BE A TEACHER AS WELL AS A BUSINESS PERSON. A LOCAL MARKETER NEEDS TO: 1. DEVELOP TRAINING PROGRAMS FOR STORE PERSONNEL, FOCUSING ON CUSTOMER SERVICE. 2. PREPARE MANUALS AND PAMPHLETS DESCRIBING PRODUCTS AND SERVICES AND HELP MIDDLEMEN DEVELOP FACILITIES, INVENTORY, SHIPMENT, SHELVING PROCEDURES FOR THE PRODUCT.
“Professor” Marketer IN EMERGING MARKETS, THE ENTERING LOCAL MARKETER NEEDS TO BE A TEACHER AS WELL AS A BUSINESS PERSON. A LOCAL MARKETER NEEDS TO: 1. DEVELOP TRAINING PROGRAMS FOR STORE PERSONNEL, FOCUSING ON CUSTOMER SERVICE. 2. PREPARE MANUALS AND PAMPHLETS DESCRIBING PRODUCTS AND SERVICES AND HELP MIDDLEMEN DEVELOP FACILITIES, INVENTORY, SHIPMENT, SHELVING PROCEDURES FOR THE PRODUCT.
 “Professor” Marketer 3. HELP MIDDLEMEN DEVELOP A TRACKING AND COST ACCOUNTING SYSTEM. 4. MAKE SURE THAT PRODUCT LOCALIZATION IN TERMS OF DESIGN AND PACKAGING ALSO TAKES INTO ACCOUNT THE NEEDS OF THE MIDDLEMEN. 5. DISTRIBUTE INSTRUCTIONAL VIDEOS AND OTHER EDUCATIONAL MATERIAL TO MEMBERS OF THE DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, EXPLAINING THE IMPORTANCE OF CUSTOMERS IN THE FREE MARKET SYSTEM AND IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING.
“Professor” Marketer 3. HELP MIDDLEMEN DEVELOP A TRACKING AND COST ACCOUNTING SYSTEM. 4. MAKE SURE THAT PRODUCT LOCALIZATION IN TERMS OF DESIGN AND PACKAGING ALSO TAKES INTO ACCOUNT THE NEEDS OF THE MIDDLEMEN. 5. DISTRIBUTE INSTRUCTIONAL VIDEOS AND OTHER EDUCATIONAL MATERIAL TO MEMBERS OF THE DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, EXPLAINING THE IMPORTANCE OF CUSTOMERS IN THE FREE MARKET SYSTEM AND IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING.
 Consumers in Emerging Markets Buyer Decision Problems in Emerging Markets 1. LACK OF CASH AND HARD CURRENCY 2. USED TO FEW ALTERNATIVES 3. LACK OF KNOWLEDGE 4. STEREOTYPICAL EVALUATION 5. KNOW MAINLY WHAT THEY DON’T WANT 6. SUSPICION OF THE TRADE 7. DOUBTS ABOUT ADVERTISING CLAIMS 8. UNACCUSTOMED TO FREE CHOICE AND HANDLING COGNITIVE DISSONANCE
Consumers in Emerging Markets Buyer Decision Problems in Emerging Markets 1. LACK OF CASH AND HARD CURRENCY 2. USED TO FEW ALTERNATIVES 3. LACK OF KNOWLEDGE 4. STEREOTYPICAL EVALUATION 5. KNOW MAINLY WHAT THEY DON’T WANT 6. SUSPICION OF THE TRADE 7. DOUBTS ABOUT ADVERTISING CLAIMS 8. UNACCUSTOMED TO FREE CHOICE AND HANDLING COGNITIVE DISSONANCE
 Two Kinds of Emerging Markets NEWLY DEMOCRATIZED COUNTRIES VS. DEVELOPING MARKETS (B 2 -4 B) NDC MARKETS DEVELOPING COUNTRIES Russia & the newly democratized postcommunist nations, China Poor nations of Africa (Nigeria, Zambia, Tanzania), Asia (Pakistan, India, Vietnam), & Central America (Nicaragua, Guatemala). Both are defined primarily by low per capita income levels & severe lack of marketing infrastructure
Two Kinds of Emerging Markets NEWLY DEMOCRATIZED COUNTRIES VS. DEVELOPING MARKETS (B 2 -4 B) NDC MARKETS DEVELOPING COUNTRIES Russia & the newly democratized postcommunist nations, China Poor nations of Africa (Nigeria, Zambia, Tanzania), Asia (Pakistan, India, Vietnam), & Central America (Nicaragua, Guatemala). Both are defined primarily by low per capita income levels & severe lack of marketing infrastructure
 Why NDC Markets Are Different 3 SPECIAL FEATURES OF NEWLY DEMOCRATIZED COUNTRIES • BASIC NEEDS WERE SATISFIED: ESSENTIALLY, NO ONE WAS GOING WITHOUT FOOD, SHELTER, CLOTHING AND OTHER BASIC ITEMS. • EDUCATION AND SOCIAL CONTROL: A GOOD, SOLID BASIC EDUCATION WAS PROVIDED, ALONG WITH SOCIAL CONTROL AND A SECURE LIFE. • NO FREE MARKET: THERE IS A LACK OF UNDERSTANDING OF THE CONCEPT OF A FREE MARKET ECONOMY.
Why NDC Markets Are Different 3 SPECIAL FEATURES OF NEWLY DEMOCRATIZED COUNTRIES • BASIC NEEDS WERE SATISFIED: ESSENTIALLY, NO ONE WAS GOING WITHOUT FOOD, SHELTER, CLOTHING AND OTHER BASIC ITEMS. • EDUCATION AND SOCIAL CONTROL: A GOOD, SOLID BASIC EDUCATION WAS PROVIDED, ALONG WITH SOCIAL CONTROL AND A SECURE LIFE. • NO FREE MARKET: THERE IS A LACK OF UNDERSTANDING OF THE CONCEPT OF A FREE MARKET ECONOMY.
 Marketing in Developing Countries: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION • Income level represents the basic segmentation criterion • Market for upper-end status products often lucrative due to uneven income distribution • Effective income measure is defined in terms of access to foreign or convertible currency • Most promising market is the urban population of big cities PRODUCT POSITIONING • Customer needs are basic • Domestic alternatives are weak • Upscale positioning can play an important role
Marketing in Developing Countries: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION • Income level represents the basic segmentation criterion • Market for upper-end status products often lucrative due to uneven income distribution • Effective income measure is defined in terms of access to foreign or convertible currency • Most promising market is the urban population of big cities PRODUCT POSITIONING • Customer needs are basic • Domestic alternatives are weak • Upscale positioning can play an important role
 Marketing in Developing Countries: The 4 Ps PRODUCT PRICING • Initial offerings are usually • Policies are dominated by the standardized simpler selections from existing lines balance between affordability & upper end positioning • Limited features make it possible to sell through lowservice outlets • Smaller sizes/smaller packaging • Pricing fluctuates between a skimming price and a lower penetration price • Innovative financing: communal buyers, smaller packaging that’s less expensive, store credit
Marketing in Developing Countries: The 4 Ps PRODUCT PRICING • Initial offerings are usually • Policies are dominated by the standardized simpler selections from existing lines balance between affordability & upper end positioning • Limited features make it possible to sell through lowservice outlets • Smaller sizes/smaller packaging • Pricing fluctuates between a skimming price and a lower penetration price • Innovative financing: communal buyers, smaller packaging that’s less expensive, store credit
 Marketing in Developing Countries: The 4 Ps (cont’d) DISTRIBUTION PROMOTION • Most critical issue • Initially limited due to lack of • Cheap domestic labor offers alternative routes for distribution broadcast media • Personal service is a “convenience good” • Literacy levels differ from more developed nations, promotions must be more visual versus verbal • Weak logistics systems make it difficult for marketing organization & control. • Although limited, this means there will be less clutter
Marketing in Developing Countries: The 4 Ps (cont’d) DISTRIBUTION PROMOTION • Most critical issue • Initially limited due to lack of • Cheap domestic labor offers alternative routes for distribution broadcast media • Personal service is a “convenience good” • Literacy levels differ from more developed nations, promotions must be more visual versus verbal • Weak logistics systems make it difficult for marketing organization & control. • Although limited, this means there will be less clutter
 Marketing in Russia
Marketing in Russia
 Marketing in Russia MARKET BACKGROUND • Russia is a large geographical country, surrounded by previous Soviet member states, now independent but still economically linked, including Belarus, Ukraine and Kazakhstan.
Marketing in Russia MARKET BACKGROUND • Russia is a large geographical country, surrounded by previous Soviet member states, now independent but still economically linked, including Belarus, Ukraine and Kazakhstan.
 Marketing in Russia MARKET BACKGROUND (CONT’D) • The economy of Russia and its role in the global economy is very dependent on its hard currency oil export revenues. • Russia’s population was 145 million in 2003 – but is estimated to be decreasing by about half a percent each year, unusual among countries. • Russia as a market has great potential – but political uncertainty makes it a difficult market to operate in.
Marketing in Russia MARKET BACKGROUND (CONT’D) • The economy of Russia and its role in the global economy is very dependent on its hard currency oil export revenues. • Russia’s population was 145 million in 2003 – but is estimated to be decreasing by about half a percent each year, unusual among countries. • Russia as a market has great potential – but political uncertainty makes it a difficult market to operate in.
 Marketing in Russia POLITICAL & LEGAL FACTORS • Assistance from international agencies plays an important role in economic progress, but the government policies have made such assistance difficult to render • It is necessary to treat centralizing and authoritarian political and legal forces as integral parts of the economic landscape and obstacles to exploiting the large market potential • Export controls at home can also a problem area for the Western marketer • Politics influences peoples’ attitude toward the free market system
Marketing in Russia POLITICAL & LEGAL FACTORS • Assistance from international agencies plays an important role in economic progress, but the government policies have made such assistance difficult to render • It is necessary to treat centralizing and authoritarian political and legal forces as integral parts of the economic landscape and obstacles to exploiting the large market potential • Export controls at home can also a problem area for the Western marketer • Politics influences peoples’ attitude toward the free market system
 Marketing in Russia: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION • Based on ethnicity • National borders can be less important than ethnicity. • Western-oriented younger segments. PRODUCT POSITIONING • High-end positioning may yield first mover advantage • Low-end positioning places firm in direct competition with strong domestic brands
Marketing in Russia: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION • Based on ethnicity • National borders can be less important than ethnicity. • Western-oriented younger segments. PRODUCT POSITIONING • High-end positioning may yield first mover advantage • Low-end positioning places firm in direct competition with strong domestic brands
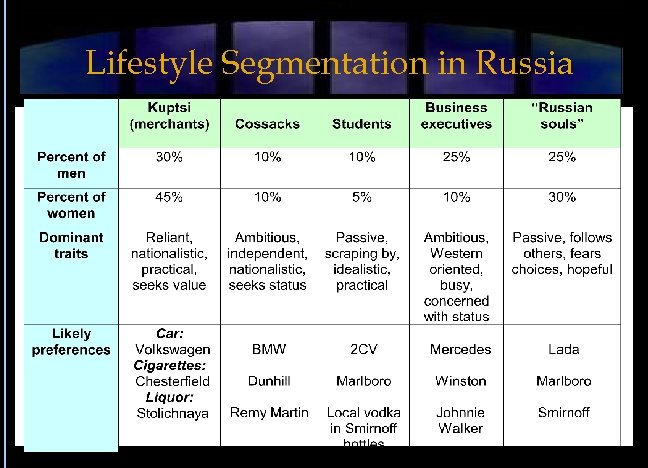 Lifestyle Segmentation in Russia
Lifestyle Segmentation in Russia
 Marketing in Russia: The 4 Ps PRODUCT Customers initially feel ambivalent about their domestic products • • But as domestic producers improve quality, gradually a prodomestic sentiment sets in PRICING Entering global brands will be able to command a price premium over existing local brands • • Long-term prospects of these markets matter much more than short-term payoffs
Marketing in Russia: The 4 Ps PRODUCT Customers initially feel ambivalent about their domestic products • • But as domestic producers improve quality, gradually a prodomestic sentiment sets in PRICING Entering global brands will be able to command a price premium over existing local brands • • Long-term prospects of these markets matter much more than short-term payoffs
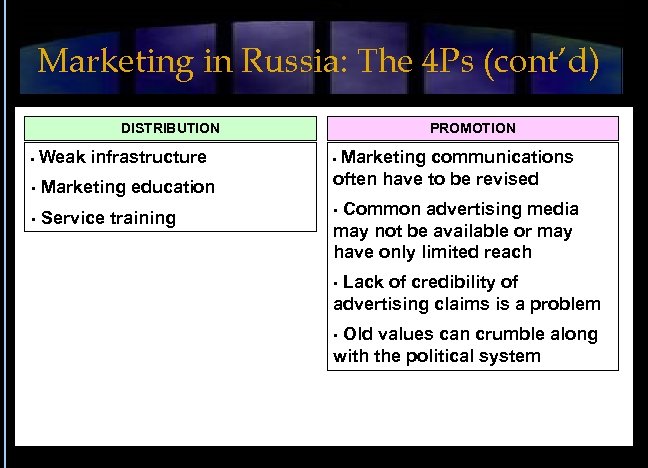 Marketing in Russia: The 4 Ps (cont’d) DISTRIBUTION • Weak infrastructure • Marketing education • Service training PROMOTION Marketing communications often have to be revised • • Common advertising media may not be available or may have only limited reach • Lack of credibility of advertising claims is a problem • Old values can crumble along with the political system
Marketing in Russia: The 4 Ps (cont’d) DISTRIBUTION • Weak infrastructure • Marketing education • Service training PROMOTION Marketing communications often have to be revised • • Common advertising media may not be available or may have only limited reach • Lack of credibility of advertising claims is a problem • Old values can crumble along with the political system
 Marketing in Russia 2005: RUSSIA AT THE CROSSROADS • Despite an abundance of natural resources & a highly educated labor force, progress is slow due to corruption, mismanagement & centralization • Development is skewed, prioritizing heavy industry over consumer goods & agriculture • Large income disparities make people doubt democracy • Prospect of WTO membership in 2006 questionable • Ruble devalued - Barter-style economy prevalent in some parts of the country • Internal political problems, including terrorism.
Marketing in Russia 2005: RUSSIA AT THE CROSSROADS • Despite an abundance of natural resources & a highly educated labor force, progress is slow due to corruption, mismanagement & centralization • Development is skewed, prioritizing heavy industry over consumer goods & agriculture • Large income disparities make people doubt democracy • Prospect of WTO membership in 2006 questionable • Ruble devalued - Barter-style economy prevalent in some parts of the country • Internal political problems, including terrorism.
 Marketing in China
Marketing in China
 Marketing in China MARKET BACKGROUND • China has 1. 2 billion people, largest country in the world. • It has become the new economic superpower in Asia, challenging the preeminence of Japan.
Marketing in China MARKET BACKGROUND • China has 1. 2 billion people, largest country in the world. • It has become the new economic superpower in Asia, challenging the preeminence of Japan.
 Marketing in China MARKET BACKGROUND (CONT’D) • In 2001, China overtook Italy to become 6 th largest world economy • The growth rate of the economy has been around 10% annually for the last several years. • China became a WTO member in December 2001 • The policy towards Hong Kong, its new territory since the 1997 takeover, has been relatively "handsoff. “
Marketing in China MARKET BACKGROUND (CONT’D) • In 2001, China overtook Italy to become 6 th largest world economy • The growth rate of the economy has been around 10% annually for the last several years. • China became a WTO member in December 2001 • The policy towards Hong Kong, its new territory since the 1997 takeover, has been relatively "handsoff. “
 Marketing in China ENTRY BARRIERS • Import license controls – the Ministry of Foreign Trade & Economic Cooperation (MOFTEC) is the main regulatory organization • Protective tariffs – with WTO entry, tariff reduction gradually in place • Foreign exchange control – new exchange rate system since 1994
Marketing in China ENTRY BARRIERS • Import license controls – the Ministry of Foreign Trade & Economic Cooperation (MOFTEC) is the main regulatory organization • Protective tariffs – with WTO entry, tariff reduction gradually in place • Foreign exchange control – new exchange rate system since 1994
 Marketing in China TRADE REGIONS • SPECIAL ECONOMIC ZONES (SEZ’s) to attract foreign investment in production for export • These areas are Shenzen, Zhuhai, Shantou, Xiamen, Hainen, & Pudong New Area in Shanghai • Corporate tax rate in SEZs is only 15% versus 33% national rate • Some zones have additional tax exemptions • Piracy and counterfeits still prevalent
Marketing in China TRADE REGIONS • SPECIAL ECONOMIC ZONES (SEZ’s) to attract foreign investment in production for export • These areas are Shenzen, Zhuhai, Shantou, Xiamen, Hainen, & Pudong New Area in Shanghai • Corporate tax rate in SEZs is only 15% versus 33% national rate • Some zones have additional tax exemptions • Piracy and counterfeits still prevalent
 Marketing in China HONG KONG’S ROLE • HK handover had little impact on economic policy – so far. • Many western firms enter China through HK, where sophisticated HK trading companies are familiar with western business practices • Joint ventures with Chinese partners usually done through HK intermediaries. • Gradually, however, as more experience is gained, Western companies are moving beyond Hong Kong, dealing with mainland China directly.
Marketing in China HONG KONG’S ROLE • HK handover had little impact on economic policy – so far. • Many western firms enter China through HK, where sophisticated HK trading companies are familiar with western business practices • Joint ventures with Chinese partners usually done through HK intermediaries. • Gradually, however, as more experience is gained, Western companies are moving beyond Hong Kong, dealing with mainland China directly.
 Marketing in China: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION • Geographic region. E. g. four regions: Eastern China (with Shanghai as the center), Northern China (Beijing the center), Southern China (with Guangzhou as the center) and Western China (with Chengdu as the center). • Languages & dialects, food and drink preferences, and even ethnic roots vary across the regions. • Urban/rural split in the typical emerging market pattern, weak infrastructure in rural areas. • Emerging middle class, rise in per capita income most rapid in Shanghai, Beijing, Guangzhou
Marketing in China: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION • Geographic region. E. g. four regions: Eastern China (with Shanghai as the center), Northern China (Beijing the center), Southern China (with Guangzhou as the center) and Western China (with Chengdu as the center). • Languages & dialects, food and drink preferences, and even ethnic roots vary across the regions. • Urban/rural split in the typical emerging market pattern, weak infrastructure in rural areas. • Emerging middle class, rise in per capita income most rapid in Shanghai, Beijing, Guangzhou
 Marketing in China: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION (cont’d) • Chinese talk about "Four big things" (shi da zen), the four products everyone aspires to. In the 1970 s, they were a bicycle, a black & white television set, a refrigerator, and a washing machine. In the 1990 s they have become a video camera, a CD hi-fi system, a personal computer, and an air conditioner. • Teenagers/college age people represent the Chinese version of the global youth segment.
Marketing in China: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION (cont’d) • Chinese talk about "Four big things" (shi da zen), the four products everyone aspires to. In the 1970 s, they were a bicycle, a black & white television set, a refrigerator, and a washing machine. In the 1990 s they have become a video camera, a CD hi-fi system, a personal computer, and an air conditioner. • Teenagers/college age people represent the Chinese version of the global youth segment.
 Marketing in China: MSPP (cont’d) PRODUCT POSITIONING • Global brands confer status. Domestic products still suffer from negative image. • Need to accommodate translation of brand names. Coca Cola had to change its original transliteration from one meaning "dry mouth full of wax" to one signifying "happiness in the mouth" when read and spoken. • Foreign competition in sales promotion, after-sale service, product delivery, and price. • Quality differences between foreign companies are perceived as small. • Consumers are brand loyal, making for definite first-mover advantages.
Marketing in China: MSPP (cont’d) PRODUCT POSITIONING • Global brands confer status. Domestic products still suffer from negative image. • Need to accommodate translation of brand names. Coca Cola had to change its original transliteration from one meaning "dry mouth full of wax" to one signifying "happiness in the mouth" when read and spoken. • Foreign competition in sales promotion, after-sale service, product delivery, and price. • Quality differences between foreign companies are perceived as small. • Consumers are brand loyal, making for definite first-mover advantages.
 Marketing in China: The 4 Ps PRODUCT POLICIES • Quality gap between foreign & local products still large • High tariffs make it hard foreign brands to compete with lower quality domestic brands • For most Chinese, acquiring foreign made products are a novel experience PRICING • Chinese are very price- sensitive consumers (due to low income and due to habit) • Prices still high for imported products • Low priced- products have an inherently assumed low quality
Marketing in China: The 4 Ps PRODUCT POLICIES • Quality gap between foreign & local products still large • High tariffs make it hard foreign brands to compete with lower quality domestic brands • For most Chinese, acquiring foreign made products are a novel experience PRICING • Chinese are very price- sensitive consumers (due to low income and due to habit) • Prices still high for imported products • Low priced- products have an inherently assumed low quality
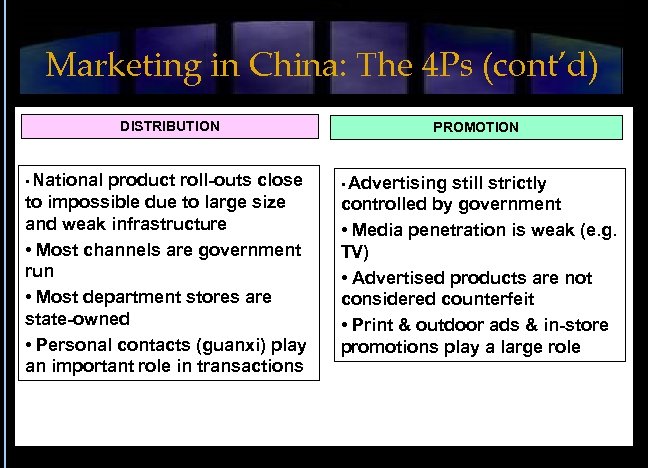 Marketing in China: The 4 Ps (cont’d) DISTRIBUTION • National product roll-outs close to impossible due to large size and weak infrastructure • Most channels are government run • Most department stores are state-owned • Personal contacts (guanxi) play an important role in transactions PROMOTION • Advertising still strictly controlled by government • Media penetration is weak (e. g. TV) • Advertised products are not considered counterfeit • Print & outdoor ads & in-store promotions play a large role
Marketing in China: The 4 Ps (cont’d) DISTRIBUTION • National product roll-outs close to impossible due to large size and weak infrastructure • Most channels are government run • Most department stores are state-owned • Personal contacts (guanxi) play an important role in transactions PROMOTION • Advertising still strictly controlled by government • Media penetration is weak (e. g. TV) • Advertised products are not considered counterfeit • Print & outdoor ads & in-store promotions play a large role
 Service in the new China: Outlawed comments • If you don’t like it, go somewhere else. • Ask someone else. • Take a taxi if you don’t like the bus. • I don’t care whom you complain to. • If you’re not buying, what are you looking at? • Buy it if you can afford it, otherwise get out of here. • Are you buying or not? Have you made up your mind? • Don’t you see I’m busy? What’s the hurry? • I just told you. Why are you asking again? • Why didn’t you choose well when you bought it? Go ask the person who sold it to you.
Service in the new China: Outlawed comments • If you don’t like it, go somewhere else. • Ask someone else. • Take a taxi if you don’t like the bus. • I don’t care whom you complain to. • If you’re not buying, what are you looking at? • Buy it if you can afford it, otherwise get out of here. • Are you buying or not? Have you made up your mind? • Don’t you see I’m busy? What’s the hurry? • I just told you. Why are you asking again? • Why didn’t you choose well when you bought it? Go ask the person who sold it to you.
 Marketing in India
Marketing in India
 Marketing in India MARKET BACKGROUND • Close to 1 billion citizens. British colony until 1947. The world's largest democracy. • Religious and ethnic violence. High political risk, with religious rifts and Pakistan problem. • During the 1990 s socialist policies and government controls are gradually giving way to privatization and free markets.
Marketing in India MARKET BACKGROUND • Close to 1 billion citizens. British colony until 1947. The world's largest democracy. • Religious and ethnic violence. High political risk, with religious rifts and Pakistan problem. • During the 1990 s socialist policies and government controls are gradually giving way to privatization and free markets.
 Marketing in India MARKET BACKGROUND (cont’d) • Excellent educational system introduced by the British. • By 2000, the annual growth rate was a strong 6. 5%. Western outsourcing FDI very strong. • With liberalization, foreign firms enter via FDI, usually as a joint venture with local partners who better understand the marketplace. • Domestic firms are forced to become more efficient, and can draw upon a large and well educated pool of workers.
Marketing in India MARKET BACKGROUND (cont’d) • Excellent educational system introduced by the British. • By 2000, the annual growth rate was a strong 6. 5%. Western outsourcing FDI very strong. • With liberalization, foreign firms enter via FDI, usually as a joint venture with local partners who better understand the marketplace. • Domestic firms are forced to become more efficient, and can draw upon a large and well educated pool of workers.
 Marketing in India: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION PRODUCT POSITIONING • Two large segments: an • Exposure to new products & impoverished rural population and an increasingly well-off urban middle class. services has increased the appetite for further purchases • Huge metropolitan markets, increased purchasing power, family planning and women working. • Traditional habits are changing as the middle class becomes more Westernized. • Consumers are more demanding • Products are bought for status • Firms being forced to become more efficient as the economic liberalization continues
Marketing in India: MSPP MARKET SEGMENTATION PRODUCT POSITIONING • Two large segments: an • Exposure to new products & impoverished rural population and an increasingly well-off urban middle class. services has increased the appetite for further purchases • Huge metropolitan markets, increased purchasing power, family planning and women working. • Traditional habits are changing as the middle class becomes more Westernized. • Consumers are more demanding • Products are bought for status • Firms being forced to become more efficient as the economic liberalization continues
 Marketing in India: The 4 Ps PRODUCT POLICIES PRICING • With increasing maturity, the • Global brands can no longer market can support a full line of products also from foreign firms. • First-mover effects are significant, favoring multinationals which are "old India hands. " count on an automatic price premium. • Middle-income group of consumers are price sensitive. • Price level is especially important when brand name is less known. Some MNC’s acquire and use well established local brands.
Marketing in India: The 4 Ps PRODUCT POLICIES PRICING • With increasing maturity, the • Global brands can no longer market can support a full line of products also from foreign firms. • First-mover effects are significant, favoring multinationals which are "old India hands. " count on an automatic price premium. • Middle-income group of consumers are price sensitive. • Price level is especially important when brand name is less known. Some MNC’s acquire and use well established local brands.
 Marketing in India: The 4 Ps (cont’d) DISTRIBUTION PROMOTION • Infrastructure is still weak in • Advertising agencies are a vast country. Entering companies are assisting with structural improvements. • Urban distribution channels are becoming more efficient. Capacity is expanded. booming. • Global advertising campaigns are adapted to meet local Indian tastes and localized to India's many dialects. • TV advertising very popular, but print and outdoor are more cost effective.
Marketing in India: The 4 Ps (cont’d) DISTRIBUTION PROMOTION • Infrastructure is still weak in • Advertising agencies are a vast country. Entering companies are assisting with structural improvements. • Urban distribution channels are becoming more efficient. Capacity is expanded. booming. • Global advertising campaigns are adapted to meet local Indian tastes and localized to India's many dialects. • TV advertising very popular, but print and outdoor are more cost effective.
 Takeaways To take advantage of the opportunities in emerging markets, the marketer needs to get back to the basics of what marketing is supposed to bring to people.
Takeaways To take advantage of the opportunities in emerging markets, the marketer needs to get back to the basics of what marketing is supposed to bring to people.
 Takeaways Emerging countries are usually characterized by political uncertainty, and direct foreign investment can be very risky. It is useful to distinguish between the newly democratized countries that were part of the Soviet sphere of influence where education was strong but free markets did not exist and the typical developing countries which are defined mostly by poverty.
Takeaways Emerging countries are usually characterized by political uncertainty, and direct foreign investment can be very risky. It is useful to distinguish between the newly democratized countries that were part of the Soviet sphere of influence where education was strong but free markets did not exist and the typical developing countries which are defined mostly by poverty.
 Takeaways A functioning marketing infrastructure, especially an effective distribution, is crucial in emerging markets. When one is lacking, the local marketing effort has to help build it.
Takeaways A functioning marketing infrastructure, especially an effective distribution, is crucial in emerging markets. When one is lacking, the local marketing effort has to help build it.
 Takeaways The political heritage of the newly democratized countries means that middlemen & consumers have a very ambivalent feeling about free markets. They may expect too much while not wanting to accept the uncertainties that free markets bring. The local marketer from abroad becomes an educator about free markets.
Takeaways The political heritage of the newly democratized countries means that middlemen & consumers have a very ambivalent feeling about free markets. They may expect too much while not wanting to accept the uncertainties that free markets bring. The local marketer from abroad becomes an educator about free markets.
 Takeaways Emerging markets are not all the same and do not even necessarily move in tandem. For example, in the new millennium as Russia has faltered, China & India still more than hold their own.
Takeaways Emerging markets are not all the same and do not even necessarily move in tandem. For example, in the new millennium as Russia has faltered, China & India still more than hold their own.


