8d8433b1995ec7af1efe0f07caf8a2bf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Chapter 10 Electronic Commerce Payments, Order Fulfillment, and Other Support Services Chapter 11 Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
Chapter 10 Electronic Commerce Payments, Order Fulfillment, and Other Support Services Chapter 11 Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chapter 10 Understand the shifts that are occurring with regard to noncash and online payments. Discuss the Crucial factors that determine whether a method of e-payment achieves critical mass. Discuss the different categories and potential uses of smart cards. Discuss various online alternatives to credit card payments and identify under what circumstances they are best used. Describe the processes and parties involved in e-checking. Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 1
Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chapter 10 Understand the shifts that are occurring with regard to noncash and online payments. Discuss the Crucial factors that determine whether a method of e-payment achieves critical mass. Discuss the different categories and potential uses of smart cards. Discuss various online alternatives to credit card payments and identify under what circumstances they are best used. Describe the processes and parties involved in e-checking. Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 1
 Learning Objectives Describe payment methods in B 2 B EC, including payments for global trade. 7. Define EC order fulfillment and describe the EC order fulfillment process. 8. Describe the major problems of EC order fulfillment. 9. Describe various solutions to EC order fulfillment problems. 10. Discuss support services provided by general consulting and outsourcing firms. 6. Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 2
Learning Objectives Describe payment methods in B 2 B EC, including payments for global trade. 7. Define EC order fulfillment and describe the EC order fulfillment process. 8. Describe the major problems of EC order fulfillment. 9. Describe various solutions to EC order fulfillment problems. 10. Discuss support services provided by general consulting and outsourcing firms. 6. Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 2
 The Payment Revolution l Crucial factors that determine whether a method of epayment achieves critical mass: l Independence – must not need specialized SW l Interoperability and Portability – compatible with many platforms l Security l Anonymity l Divisibility – min/max ranges – credit cards will not do for too small costs l Ease of Use l Transaction Fees – merchant pays 3% + fixed fee l Regulations l International support Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 3
The Payment Revolution l Crucial factors that determine whether a method of epayment achieves critical mass: l Independence – must not need specialized SW l Interoperability and Portability – compatible with many platforms l Security l Anonymity l Divisibility – min/max ranges – credit cards will not do for too small costs l Ease of Use l Transaction Fees – merchant pays 3% + fixed fee l Regulations l International support Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 3
 Using Payment Cards Online l Payment cards —electronic cards that contain information that can be used for payment purposes l Credit cards—provides holder with credit to make purchases up to a limit fixed by the card issuer l Charge cards—balance on a charge card is supposed to be paid in full upon receipt of monthly statement l Debit card—cost of a purchase drawn directly from holder’s checking account (demanddeposit account) Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 4
Using Payment Cards Online l Payment cards —electronic cards that contain information that can be used for payment purposes l Credit cards—provides holder with credit to make purchases up to a limit fixed by the card issuer l Charge cards—balance on a charge card is supposed to be paid in full upon receipt of monthly statement l Debit card—cost of a purchase drawn directly from holder’s checking account (demanddeposit account) Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 4
 Using Payment Cards Online l PROCESSING CARDS ONLINE authorization Determines whether a buyer’s card is active and whether the customer has sufficient funds. l settlement Transferring money from the buyer’s to the merchant’s account. l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 5
Using Payment Cards Online l PROCESSING CARDS ONLINE authorization Determines whether a buyer’s card is active and whether the customer has sufficient funds. l settlement Transferring money from the buyer’s to the merchant’s account. l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 5
 Using Payment Cards Online l Three basic configurations for processing online payments. Merchants may: l Own the payment software l Use a point of sale system (POS) operated by an acquirer l payment service provider (PSP) A third-party service connecting a merchant’s EC systems to the appropriate acquirers. PSPs must be registered with the various card associations they support l Use a POS operated by a payment service provider Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 6
Using Payment Cards Online l Three basic configurations for processing online payments. Merchants may: l Own the payment software l Use a point of sale system (POS) operated by an acquirer l payment service provider (PSP) A third-party service connecting a merchant’s EC systems to the appropriate acquirers. PSPs must be registered with the various card associations they support l Use a POS operated by a payment service provider Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 6
 Using Payment Cards Online l Fraudulent Card Transactions In the online world, merchants are held liable for fraudulent transactions l Merchants can incur additional fees and penalties imposed by the card associations l Costs associated with combating fraudulent transactions are also the merchant’s responsibility l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 7
Using Payment Cards Online l Fraudulent Card Transactions In the online world, merchants are held liable for fraudulent transactions l Merchants can incur additional fees and penalties imposed by the card associations l Costs associated with combating fraudulent transactions are also the merchant’s responsibility l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 7
 Using Payment Cards Online l FRAUDULENT CARD TRANSACTIONS Key tools used in combating fraud: l Address Verification System (AVS) Detects fraud by comparing the address entered on a Web page with the address information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank. l card verification number (CVN) Detects fraud by comparing the verification number printed on the signature strip on the back of the card with the information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank. Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 8
Using Payment Cards Online l FRAUDULENT CARD TRANSACTIONS Key tools used in combating fraud: l Address Verification System (AVS) Detects fraud by comparing the address entered on a Web page with the address information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank. l card verification number (CVN) Detects fraud by comparing the verification number printed on the signature strip on the back of the card with the information on file with the cardholder’s issuing bank. Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 8
 Using Payment Cards Online Key tools used in combating fraud (cont. ): l Negative lists l Fraud screens and automated decision models l Card association payer authentication services l Manual review Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 9
Using Payment Cards Online Key tools used in combating fraud (cont. ): l Negative lists l Fraud screens and automated decision models l Card association payer authentication services l Manual review Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 9
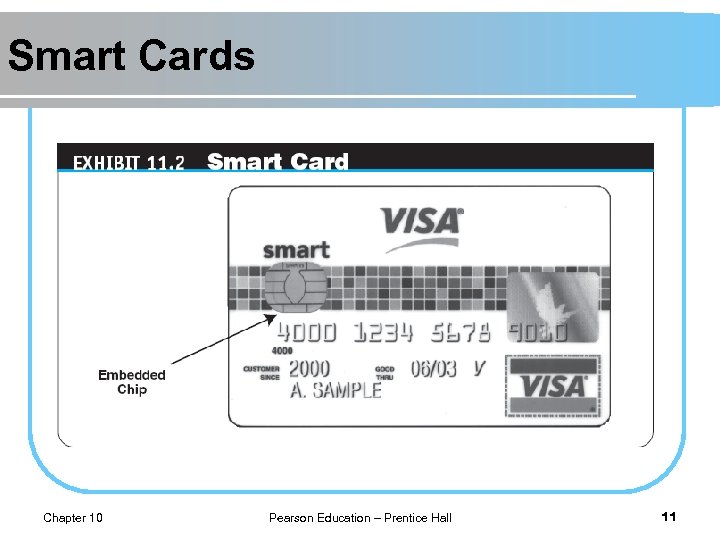
 Smart Cards l SMART CARD An electronic card containing an embedded microchip that enables predefined operations or the addition, deletion, or manipulation of information on the card. l APPLICATIONS OF SMART CARDS Retail Purchases l Transit Fares l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 10
Smart Cards l SMART CARD An electronic card containing an embedded microchip that enables predefined operations or the addition, deletion, or manipulation of information on the card. l APPLICATIONS OF SMART CARDS Retail Purchases l Transit Fares l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 10
 Smart Cards Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 11
Smart Cards Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 11
 Smart Cards l TYPES OF SMART CARDS l l Chapter 10 contact card A smart card containing a small gold plate on the face that when inserted in a smart card reader makes contact and passes data to and from the embedded microchip. contactless (proximity) card A smart card with an embedded antenna, by means of which data and applications are passed to and from a card reader unit or other device without contact between the card and the card reader. Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 12
Smart Cards l TYPES OF SMART CARDS l l Chapter 10 contact card A smart card containing a small gold plate on the face that when inserted in a smart card reader makes contact and passes data to and from the embedded microchip. contactless (proximity) card A smart card with an embedded antenna, by means of which data and applications are passed to and from a card reader unit or other device without contact between the card and the card reader. Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 12
 Smart Cards smart card reader Activates and reads the contents of the chip on a smart card, usually passing the information on to a host system. l smart card operating system Special system that handles file management, security, input/output (I/O), and command execution and provides an application programming interface (API) for a smart card. l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 13
Smart Cards smart card reader Activates and reads the contents of the chip on a smart card, usually passing the information on to a host system. l smart card operating system Special system that handles file management, security, input/output (I/O), and command execution and provides an application programming interface (API) for a smart card. l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 13
 Stored-Value Cards l stored-value card A card that has monetary value loaded onto it and that is usually rechargeable Anyone can obtain a stored-value card without regard to prior financial standing or having an existing bank account as collateral l The stored-value card market is growing rapidly l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 14
Stored-Value Cards l stored-value card A card that has monetary value loaded onto it and that is usually rechargeable Anyone can obtain a stored-value card without regard to prior financial standing or having an existing bank account as collateral l The stored-value card market is growing rapidly l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 14
 E-Micropayments e-micropayments Small online payments, typically under $10. l Five basic micropayment models that do not depend solely or directly on credit or debit cards: l l l Chapter 10 Aggregation Direct payment Stored value Subscriptions Á la carte Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 15
E-Micropayments e-micropayments Small online payments, typically under $10. l Five basic micropayment models that do not depend solely or directly on credit or debit cards: l l l Chapter 10 Aggregation Direct payment Stored value Subscriptions Á la carte Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 15
 E-Checking e-check A legally valid electronic version or representation of a paper check. l Automated Clearing House (ACH) Network A nationwide batch-oriented electronic funds transfer system that provides for the interbank clearing of electronic payments for participating financial institutions. l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 16
E-Checking e-check A legally valid electronic version or representation of a paper check. l Automated Clearing House (ACH) Network A nationwide batch-oriented electronic funds transfer system that provides for the interbank clearing of electronic payments for participating financial institutions. l Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 16
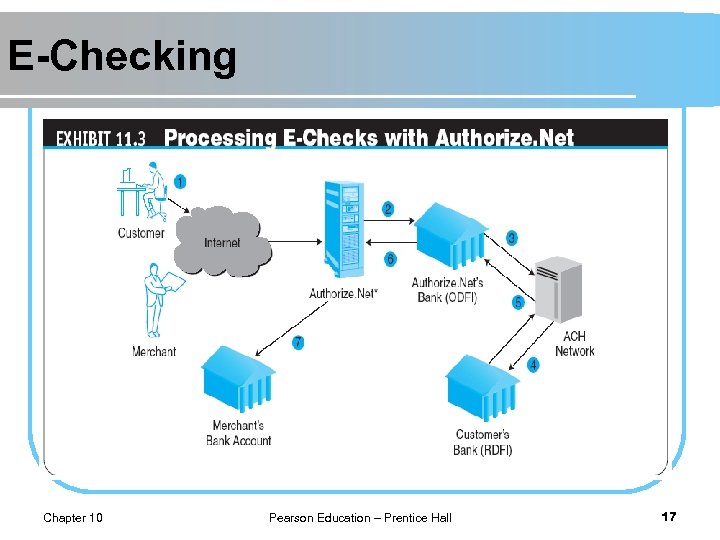 E-Checking Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 17
E-Checking Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 17
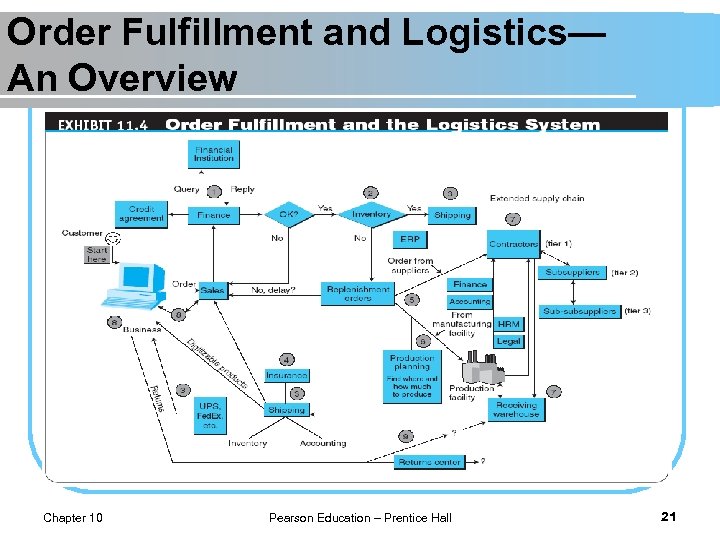
 Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview l order fulfillment All the activities needed to provide customers with their ordered goods and services, including related customer services. l l Chapter 10 back-office operations The activities that support fulfillment of orders, such as packing, delivery, accounting, inventory management and shipping front-office operations The business processes, such as sales and advertising, that are visible to customers. Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 18
Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview l order fulfillment All the activities needed to provide customers with their ordered goods and services, including related customer services. l l Chapter 10 back-office operations The activities that support fulfillment of orders, such as packing, delivery, accounting, inventory management and shipping front-office operations The business processes, such as sales and advertising, that are visible to customers. Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 18
 Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview l logistics The operations involved in the efficient and effective flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from point of origin to point of consumption. Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 19
Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview l logistics The operations involved in the efficient and effective flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from point of origin to point of consumption. Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 19
 Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview l THE EC ORDER FULFILLMENT PROCESS Step 1: Making sure the customer will pay Step 2: Checking for in-stock availability Step 3: Arranging shipments Step 4: Insurance Step 5: Replenishment Step 6: In-house production Step 7: Use contractors Step 8: Contacts with customers Step 9: Returns Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 20
Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview l THE EC ORDER FULFILLMENT PROCESS Step 1: Making sure the customer will pay Step 2: Checking for in-stock availability Step 3: Arranging shipments Step 4: Insurance Step 5: Replenishment Step 6: In-house production Step 7: Use contractors Step 8: Contacts with customers Step 9: Returns Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 20
 Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 21
Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 21
 Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview reverse logistics The movement of returns from customers to vendors. l Traditional versus EC Logistics l l Chapter 10 e-logistics The logistics of EC systems, typically involving small parcels sent to many customers’ homes (in B 2 C). Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 22
Order Fulfillment and Logistics— An Overview reverse logistics The movement of returns from customers to vendors. l Traditional versus EC Logistics l l Chapter 10 e-logistics The logistics of EC systems, typically involving small parcels sent to many customers’ homes (in B 2 C). Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 22
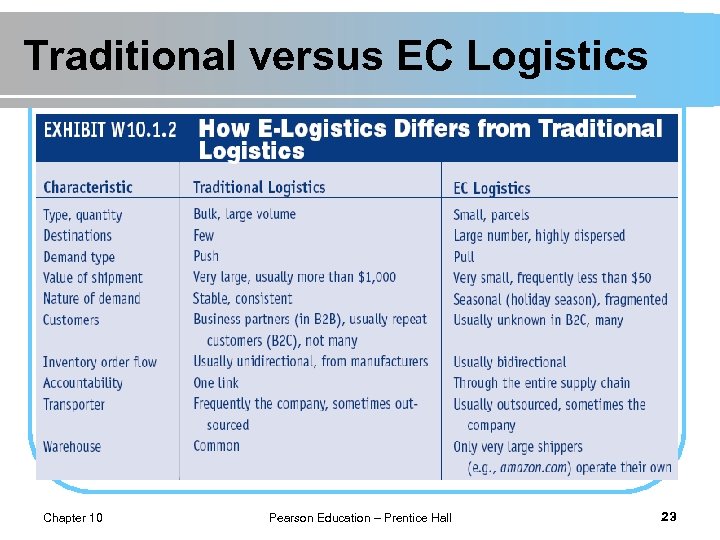 Traditional versus EC Logistics Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 23
Traditional versus EC Logistics Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 23
 Order Fulfillment and the Supply Chain Order fulfillment and order taking are integral parts of the supply chain. l Flows of orders, payments, and materials and parts need to be coordinated among l l Company’s internal participants External partners The principles of supply chain management must be considered in planning and managing the order fulfillment process Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 24
Order Fulfillment and the Supply Chain Order fulfillment and order taking are integral parts of the supply chain. l Flows of orders, payments, and materials and parts need to be coordinated among l l Company’s internal participants External partners The principles of supply chain management must be considered in planning and managing the order fulfillment process Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 24
 Problems in Order Fulfillment and the Supply Chain l Typical Supply Chain Problems l Demand forecasting is difficult l Many of the problems along the EC supply chain stem from the need to coordinate several activities, internal units, and business partners in the face of uncertainties, caused by demand forecast. l third-party logistics suppliers (3 PL) External, rather than in-house, providers of logistics services. Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 25
Problems in Order Fulfillment and the Supply Chain l Typical Supply Chain Problems l Demand forecasting is difficult l Many of the problems along the EC supply chain stem from the need to coordinate several activities, internal units, and business partners in the face of uncertainties, caused by demand forecast. l third-party logistics suppliers (3 PL) External, rather than in-house, providers of logistics services. Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 25
 Other EC Support Services CONSULTING SERVICES l EC OUTSOURCING SERVICES l l Major reasons why many companies outsource: l l l Chapter 10 A desire to concentrate on the core business The need to have services up and running rapidly Lack of expertise for many of the required support services The inability to have the economy of scale enjoyed by outsourcers Inability to keep up with rapidly fluctuating demands if an in -house option is used The number of required services, which usually are simply too many for one company to handle Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 26
Other EC Support Services CONSULTING SERVICES l EC OUTSOURCING SERVICES l l Major reasons why many companies outsource: l l l Chapter 10 A desire to concentrate on the core business The need to have services up and running rapidly Lack of expertise for many of the required support services The inability to have the economy of scale enjoyed by outsourcers Inability to keep up with rapidly fluctuating demands if an in -house option is used The number of required services, which usually are simply too many for one company to handle Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 26
 Solutions to Order Fulfillment Problems l Improvements in the Order-Taking Process l Warehouse management system (WMS) A software system that helps in managing warehouses. l Automated Chapter 10 Warehouses Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 27
Solutions to Order Fulfillment Problems l Improvements in the Order-Taking Process l Warehouse management system (WMS) A software system that helps in managing warehouses. l Automated Chapter 10 Warehouses Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 27
 Solutions to Order Fulfillment Problems l Other inventory management improvements l Reducing inventory and decreasing the incidence of out-of-stocks l Maintaining an inventory of repair items l Picking items out of inventory in the warehouse l Communicating l Managing product inventory l Receiving items at the warehouse automating the warehouse Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 28
Solutions to Order Fulfillment Problems l Other inventory management improvements l Reducing inventory and decreasing the incidence of out-of-stocks l Maintaining an inventory of repair items l Picking items out of inventory in the warehouse l Communicating l Managing product inventory l Receiving items at the warehouse automating the warehouse Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 28
 Solutions to Order Fulfillment Problems l Partnering Efforts and Outsourcing Logistics l Comprehensive Logistics Services l l l Outsourcing logistics Speeding Deliveries - same day, even same hour Handling Returns (Reverse Logistics) l Return the item to the place of purchase l Separate the logistics of returns from the logistics of delivery l Completely outsource returns l Allow the customer to physically drop the returned item at a collection station l Auction the returned items Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 29
Solutions to Order Fulfillment Problems l Partnering Efforts and Outsourcing Logistics l Comprehensive Logistics Services l l l Outsourcing logistics Speeding Deliveries - same day, even same hour Handling Returns (Reverse Logistics) l Return the item to the place of purchase l Separate the logistics of returns from the logistics of delivery l Completely outsource returns l Allow the customer to physically drop the returned item at a collection station l Auction the returned items Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 29
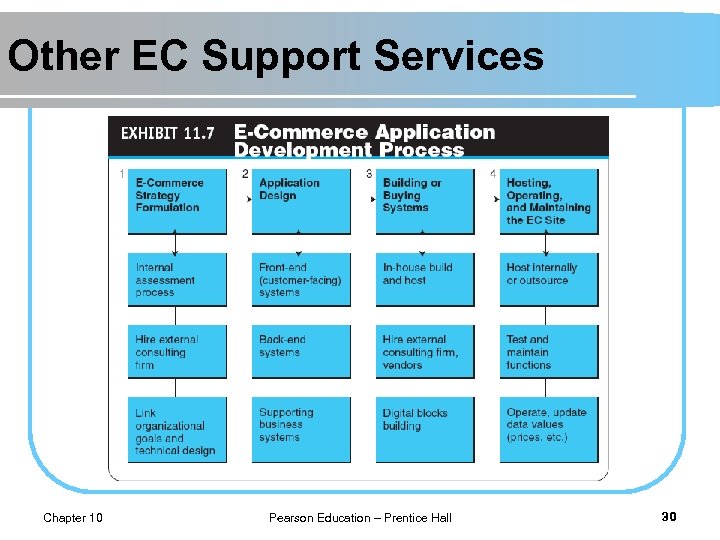 Other EC Support Services Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 30
Other EC Support Services Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 30
 Solutions to Order Fulfillment Problems l Order Fulfillment in B 2 B l Using BPM to improve order fulfillment l Using e-marketplaces and exchanges to ease order fulfillment l Order fulfillment in services Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 31
Solutions to Order Fulfillment Problems l Order Fulfillment in B 2 B l Using BPM to improve order fulfillment l Using e-marketplaces and exchanges to ease order fulfillment l Order fulfillment in services Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 31
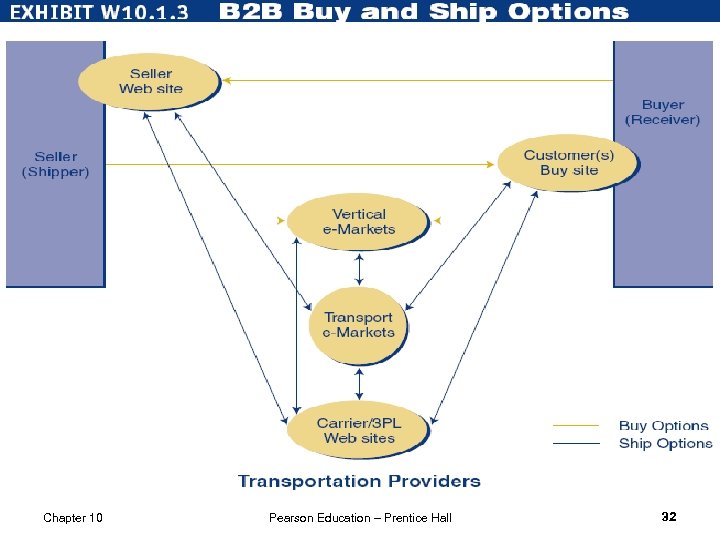 Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 32
Chapter 10 Pearson Education – Prentice Hall 32


