6e7e43fa0efbc0e3655388353dcb6073.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 CHAPTER 10 Decision Support Systems and Management Information Systems 1
CHAPTER 10 Decision Support Systems and Management Information Systems 1
 Decision Support Systems • Are oriented toward assisting in solving both semi-structured and unstructured problems. Can be used for structured problems, too. • Offer the potential for higher profits, lower costs, and better products and services. Structured Problem When to reorder … Unstructured Problem Where to a relocate plant. . . 2
Decision Support Systems • Are oriented toward assisting in solving both semi-structured and unstructured problems. Can be used for structured problems, too. • Offer the potential for higher profits, lower costs, and better products and services. Structured Problem When to reorder … Unstructured Problem Where to a relocate plant. . . 2
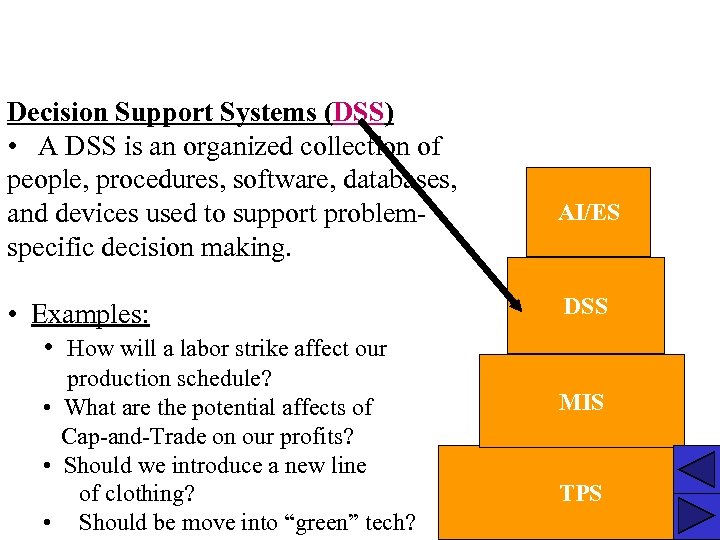 Decision Support Systems (DSS) • A DSS is an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices used to support problemspecific decision making. • Examples: • How will a labor strike affect our production schedule? • What are the potential affects of Cap-and-Trade on our profits? • Should we introduce a new line of clothing? • Should be move into “green” tech? AI/ES DSS MIS TPS 3
Decision Support Systems (DSS) • A DSS is an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices used to support problemspecific decision making. • Examples: • How will a labor strike affect our production schedule? • What are the potential affects of Cap-and-Trade on our profits? • Should we introduce a new line of clothing? • Should be move into “green” tech? AI/ES DSS MIS TPS 3
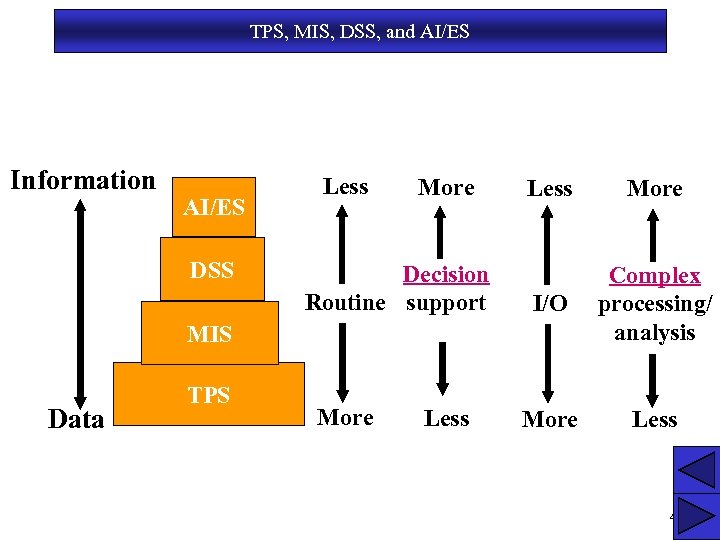 TPS, MIS, DSS, and AI/ES Information AI/ES DSS Less More Decision Routine support Less More I/O Complex processing/ analysis More Less MIS Data TPS More Less 4
TPS, MIS, DSS, and AI/ES Information AI/ES DSS Less More Decision Routine support Less More I/O Complex processing/ analysis More Less MIS Data TPS More Less 4
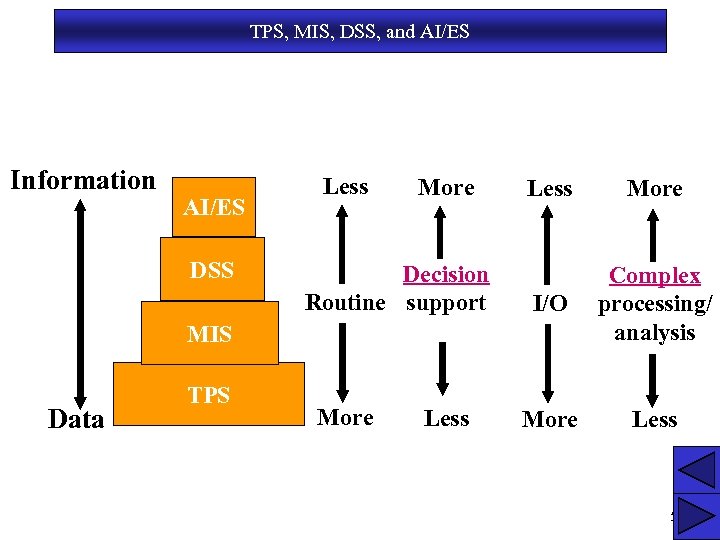 TPS, MIS, DSS, and AI/ES Information AI/ES DSS Less More Decision Routine support Less More I/O Complex processing/ analysis More Less MIS Data TPS More Less 5
TPS, MIS, DSS, and AI/ES Information AI/ES DSS Less More Decision Routine support Less More I/O Complex processing/ analysis More Less MIS Data TPS More Less 5
 Terms • Optimization Model • Finding the best solution to a problem or opportunity. • Satisficing Model • Finding a good -- but not necessarily the best -solution to a problem or opportunity. . • Heuristics (rules of thumb) • Commonly accepted guidelines or procedures that usually find a good solution to a problem or opportunity. • Time is money. • It’s not how much you know, but who you know. • The most affective propaganda (PR) takes advantage of peoples laziness. • Never show Microsoft your new product. 6 • If you repeat a lie often enough it becomes the truth.
Terms • Optimization Model • Finding the best solution to a problem or opportunity. • Satisficing Model • Finding a good -- but not necessarily the best -solution to a problem or opportunity. . • Heuristics (rules of thumb) • Commonly accepted guidelines or procedures that usually find a good solution to a problem or opportunity. • Time is money. • It’s not how much you know, but who you know. • The most affective propaganda (PR) takes advantage of peoples laziness. • Never show Microsoft your new product. 6 • If you repeat a lie often enough it becomes the truth.
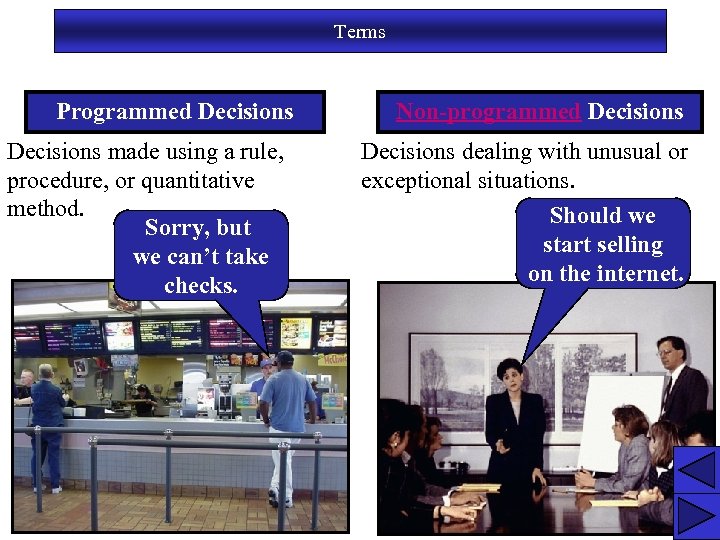 Terms Programmed Decisions made using a rule, procedure, or quantitative method. Sorry, but we can’t take checks. Non-programmed Decisions dealing with unusual or exceptional situations. Should we start selling on the internet. 7
Terms Programmed Decisions made using a rule, procedure, or quantitative method. Sorry, but we can’t take checks. Non-programmed Decisions dealing with unusual or exceptional situations. Should we start selling on the internet. 7
 Real Decision Support Systems Office Depot • They used Essbase from Arbor Software Corporation and Compaq 7000 servers. Cost less than 5 million. • Using this DSS they found they were carrying too much PC stock in the wrong stores. • Using optimizing models, they reduced the number of PC models from 22 to 12. • Eliminated unnecessary inventory. • Avoided costly markdowns on equipment that was not selling. Saved millions. Office Depot’s DSS 8
Real Decision Support Systems Office Depot • They used Essbase from Arbor Software Corporation and Compaq 7000 servers. Cost less than 5 million. • Using this DSS they found they were carrying too much PC stock in the wrong stores. • Using optimizing models, they reduced the number of PC models from 22 to 12. • Eliminated unnecessary inventory. • Avoided costly markdowns on equipment that was not selling. Saved millions. Office Depot’s DSS 8
 Real Decision Support Systems Scotch Maid • They were told by Kmart to use EDI and to ship exactly the right amount of each clothing item to satisfy customer demand--no more and no less. • Using a DSS, Scotch Maid was about 99% effective in keeping 144 different items on the shelves with very little in backroom inventory. Scotch Maid’s DSS K-Mart 9
Real Decision Support Systems Scotch Maid • They were told by Kmart to use EDI and to ship exactly the right amount of each clothing item to satisfy customer demand--no more and no less. • Using a DSS, Scotch Maid was about 99% effective in keeping 144 different items on the shelves with very little in backroom inventory. Scotch Maid’s DSS K-Mart 9
 Real Decision Support Systems Trane Air-conditioning Products • Used a DSS to assess the affects of quickly increasing production by 114 air-conditioning units. • Determined how long it would take to produce the units. • Determined that it would NOT affect existing customers’ delivery schedules. Hurricane Andrew South Florida 10
Real Decision Support Systems Trane Air-conditioning Products • Used a DSS to assess the affects of quickly increasing production by 114 air-conditioning units. • Determined how long it would take to produce the units. • Determined that it would NOT affect existing customers’ delivery schedules. Hurricane Andrew South Florida 10
 Real Decision Support Systems Pitney Bowes ($3. 3 billion company) • Used a DSS to reduce its office equipment inventory reserve from 30 days to 15 days. • Copiers, FAX’s, Mailer, Etc. • Used APS (Advanced Planning System) DSS. • $150, 100 to $1 million. 11
Real Decision Support Systems Pitney Bowes ($3. 3 billion company) • Used a DSS to reduce its office equipment inventory reserve from 30 days to 15 days. • Copiers, FAX’s, Mailer, Etc. • Used APS (Advanced Planning System) DSS. • $150, 100 to $1 million. 11
 Real Decision Support Systems Sikorsky Aircraft • Used a DSS to reduce inventory by 50%, while doubling its business. • Used APS (Advanced Planning System) DSS. • $150, 100 to $1 million. 12
Real Decision Support Systems Sikorsky Aircraft • Used a DSS to reduce inventory by 50%, while doubling its business. • Used APS (Advanced Planning System) DSS. • $150, 100 to $1 million. 12
 Real Decision Support Systems United Airlines • Uses a DSS to schedule arrivals, departures, staffing needs, and gate assignment. • It has reduced gate conflicts, traffic congestion, and staffing problems. 13
Real Decision Support Systems United Airlines • Uses a DSS to schedule arrivals, departures, staffing needs, and gate assignment. • It has reduced gate conflicts, traffic congestion, and staffing problems. 13
 Characteristics of a DSS • Large amounts of data from many sources. • DBMS and data warehouses. • Internets and intranets. • Wide variety of report and presentation formats. • Computer screen or printer output. • Textual or graphical orientations. • Text, tables, line drawings, pie/bar charts, trend lines, etc. Continue 14
Characteristics of a DSS • Large amounts of data from many sources. • DBMS and data warehouses. • Internets and intranets. • Wide variety of report and presentation formats. • Computer screen or printer output. • Textual or graphical orientations. • Text, tables, line drawings, pie/bar charts, trend lines, etc. Continue 14
 Characteristics of a DSS (continued) • Drill-down analyses. • Complex statistical analyses. • Simulation analyses of the real world. • Use models • Financial. • Statistical. • Graphical. • Project management. • Optimization, satisficing, and heuristic approaches. • “What-if” analyses. • Goal-seeking analyses. • If a company wishes to increase sales by 10%, what must it do. 15
Characteristics of a DSS (continued) • Drill-down analyses. • Complex statistical analyses. • Simulation analyses of the real world. • Use models • Financial. • Statistical. • Graphical. • Project management. • Optimization, satisficing, and heuristic approaches. • “What-if” analyses. • Goal-seeking analyses. • If a company wishes to increase sales by 10%, what must it do. 15
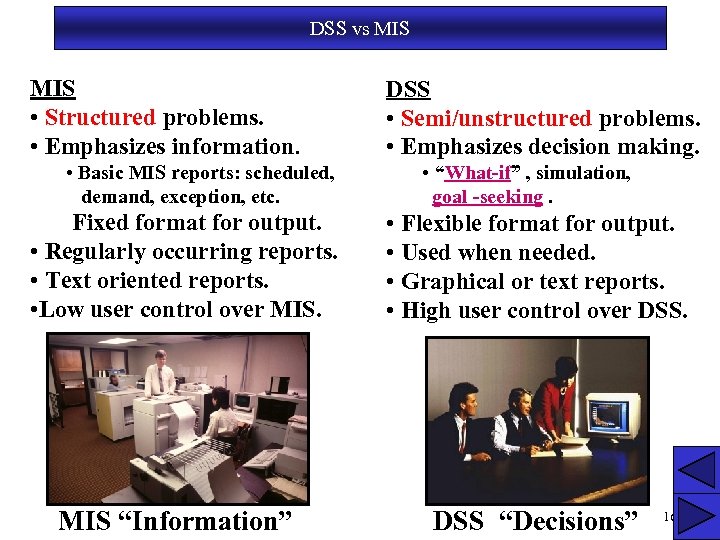 DSS vs MIS • Structured problems. • Emphasizes information. • Basic MIS reports: scheduled, demand, exception, etc. Fixed format for output. • Regularly occurring reports. • Text oriented reports. • Low user control over MIS “Information” DSS • Semi/unstructured problems. • Emphasizes decision making. • “What-if” , simulation, goal -seeking. • Flexible format for output. • Used when needed. • Graphical or text reports. • High user control over DSS “Decisions” 16
DSS vs MIS • Structured problems. • Emphasizes information. • Basic MIS reports: scheduled, demand, exception, etc. Fixed format for output. • Regularly occurring reports. • Text oriented reports. • Low user control over MIS “Information” DSS • Semi/unstructured problems. • Emphasizes decision making. • “What-if” , simulation, goal -seeking. • Flexible format for output. • Used when needed. • Graphical or text reports. • High user control over DSS “Decisions” 16
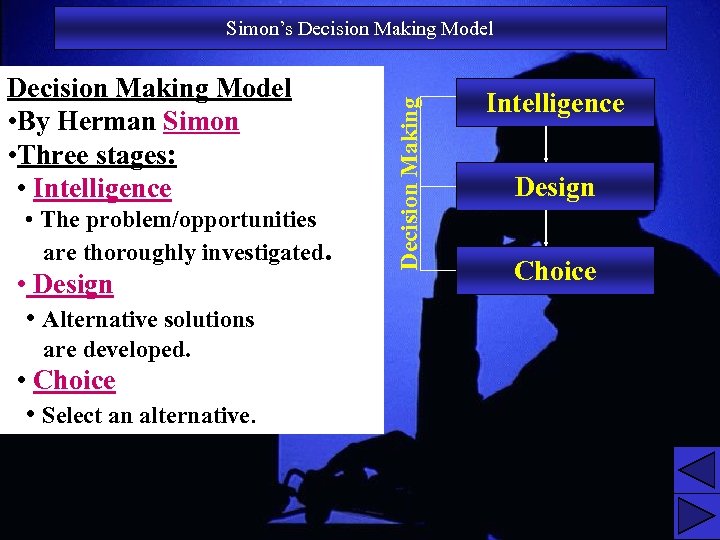 Decision Making Model • By Herman Simon • Three stages: • Intelligence • The problem/opportunities are thoroughly investigated. • Design • Alternative solutions Decision Making Simon’s Decision Making Model Intelligence Design Choice are developed. • Choice • Select an alternative. 17
Decision Making Model • By Herman Simon • Three stages: • Intelligence • The problem/opportunities are thoroughly investigated. • Design • Alternative solutions Decision Making Simon’s Decision Making Model Intelligence Design Choice are developed. • Choice • Select an alternative. 17
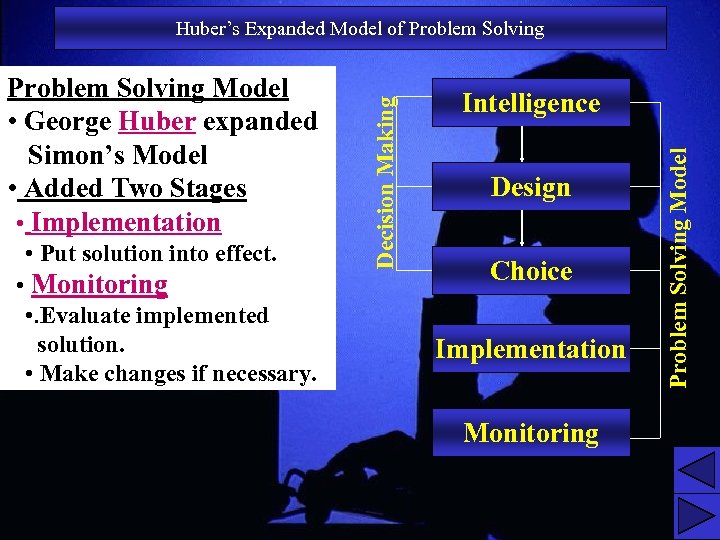 • Put solution into effect. • Monitoring • . Evaluate implemented solution. • Make changes if necessary. Intelligence Design Choice Implementation Problem Solving Model • George Huber expanded Simon’s Model • Added Two Stages • Implementation Decision Making Huber’s Expanded Model of Problem Solving Monitoring 18
• Put solution into effect. • Monitoring • . Evaluate implemented solution. • Make changes if necessary. Intelligence Design Choice Implementation Problem Solving Model • George Huber expanded Simon’s Model • Added Two Stages • Implementation Decision Making Huber’s Expanded Model of Problem Solving Monitoring 18
 Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) GDSS • Group decision room. • Has the components of a DSS. • Group. Ware: software designed specifically for decisions made by groups. 19
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) GDSS • Group decision room. • Has the components of a DSS. • Group. Ware: software designed specifically for decisions made by groups. 19
 Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) Some GDSS Characteristics: • Special Design to foster: • Creative thinking. • Effective communication. • Good group decision making techniques. • Reduction of negative group behavior. • Dominant individuals taking over the discussion. • Ease of use and flexibility. • Anonymous input. • Parallel communication. Group Decision Room • Two or more individuals can type comments at the same time. • Comments instantly seen by all. • Automatic record keeping for: • voting. • detailed comments. Continue 20
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) Some GDSS Characteristics: • Special Design to foster: • Creative thinking. • Effective communication. • Good group decision making techniques. • Reduction of negative group behavior. • Dominant individuals taking over the discussion. • Ease of use and flexibility. • Anonymous input. • Parallel communication. Group Decision Room • Two or more individuals can type comments at the same time. • Comments instantly seen by all. • Automatic record keeping for: • voting. • detailed comments. Continue 20
 Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) Some GDSS Characteristics: • Supports different decision making approaches: Brainstorming Delphi Approach Continue 21
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) Some GDSS Characteristics: • Supports different decision making approaches: Brainstorming Delphi Approach Continue 21
 Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) Continue 22
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) Continue 22
 Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) Some GDSS Characteristics (Continued): • Supports different decision making approaches: Group Consensus Approach (Forces Unanimous Decision) Nominal Group Technique (Group Members Vote) 23
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS) Some GDSS Characteristics (Continued): • Supports different decision making approaches: Group Consensus Approach (Forces Unanimous Decision) Nominal Group Technique (Group Members Vote) 23
 Executive Support Systems (ESS) ESS • A specialized DSS for executives. • Individualized for each executive. • High ability to analyze, compare, and highlight trends. • Mostly used to track critical success factors and for strategic planning. 24
Executive Support Systems (ESS) ESS • A specialized DSS for executives. • Individualized for each executive. • High ability to analyze, compare, and highlight trends. • Mostly used to track critical success factors and for strategic planning. 24
 Pratt & Whitney’s ESS • Tracked key-indicators of strategic plan success: • Used to track engine quality and reliability by customer. • Used to track the quality of service given to individual customers. • Commander EIS by Comshare. 25
Pratt & Whitney’s ESS • Tracked key-indicators of strategic plan success: • Used to track engine quality and reliability by customer. • Used to track the quality of service given to individual customers. • Commander EIS by Comshare. 25
 26
26


