 Chapter 10 Conventional Practice in Section View
Chapter 10 Conventional Practice in Section View
 TOPICS Section view representation of rib, web, spoke and lug. Aligned section Conventional break
TOPICS Section view representation of rib, web, spoke and lug. Aligned section Conventional break
 Section view representation of rib, web, spoke and lug
Section view representation of rib, web, spoke and lug
 CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE There are some exceptions to the general rules of sectioning: v Webs, ribs, lugs, spokes, v Shafts, rods, spindles, v Bolts, nuts and thin washers. v Rivets, dowels, pins and cotters.
CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE There are some exceptions to the general rules of sectioning: v Webs, ribs, lugs, spokes, v Shafts, rods, spindles, v Bolts, nuts and thin washers. v Rivets, dowels, pins and cotters.
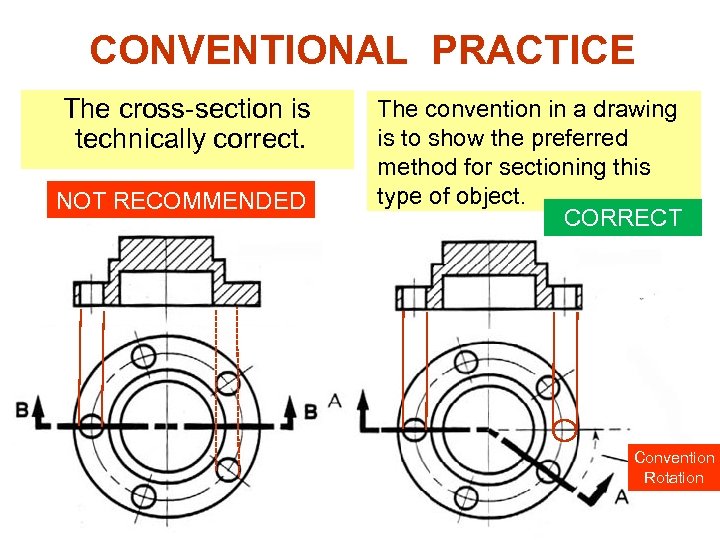 CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE The cross-section is technically correct. NOT RECOMMENDED The convention in a drawing is to show the preferred method for sectioning this type of object. CORRECT Convention Rotation
CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE The cross-section is technically correct. NOT RECOMMENDED The convention in a drawing is to show the preferred method for sectioning this type of object. CORRECT Convention Rotation
 TERMINOLOGY Rib and Web are thin, flat feature of an object that acts as a structural support. Rib
TERMINOLOGY Rib and Web are thin, flat feature of an object that acts as a structural support. Rib
 TERMINOLOGY A web or rib is a strengthining or supporting part of a component. Web
TERMINOLOGY A web or rib is a strengthining or supporting part of a component. Web
 TERMINOLOGY Spoke is the rod radiating from the hub to the rim of a wheel. Hub Spoke Rim Spoke
TERMINOLOGY Spoke is the rod radiating from the hub to the rim of a wheel. Hub Spoke Rim Spoke
 TERMINOLOGY Lug is an ear which is built as portion of an object for attachment.
TERMINOLOGY Lug is an ear which is built as portion of an object for attachment.
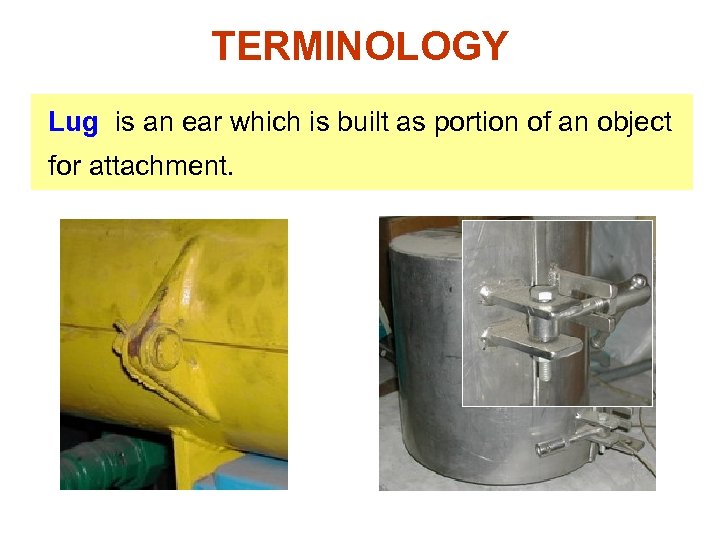 TERMINOLOGY Lug is an ear which is built as portion of an object for attachment.
TERMINOLOGY Lug is an ear which is built as portion of an object for attachment.
 CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE Omit the section lines on the section view of v Rib, Web and Lug, if the cutting plane is passed flatwise through. v Spoke, if the cutting plane is passed longwise through.
CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE Omit the section lines on the section view of v Rib, Web and Lug, if the cutting plane is passed flatwise through. v Spoke, if the cutting plane is passed longwise through.
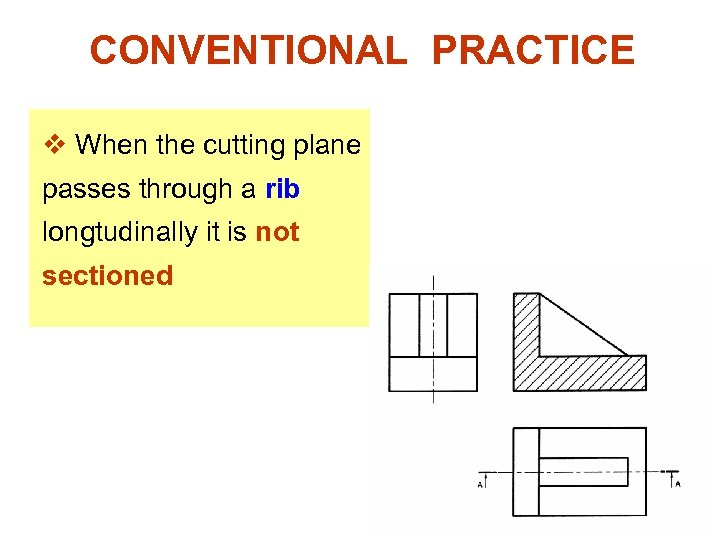 CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE v When the cutting plane passes through a rib longtudinally it is not sectioned
CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE v When the cutting plane passes through a rib longtudinally it is not sectioned
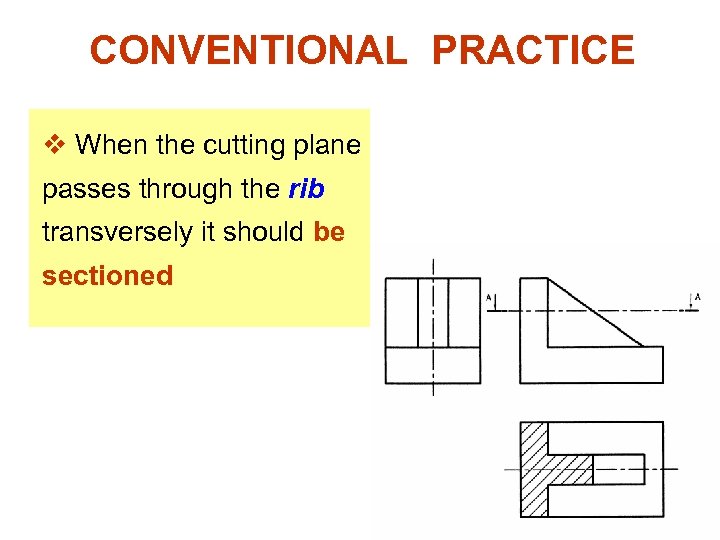 CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE v When the cutting plane passes through the rib transversely it should be sectioned
CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE v When the cutting plane passes through the rib transversely it should be sectioned
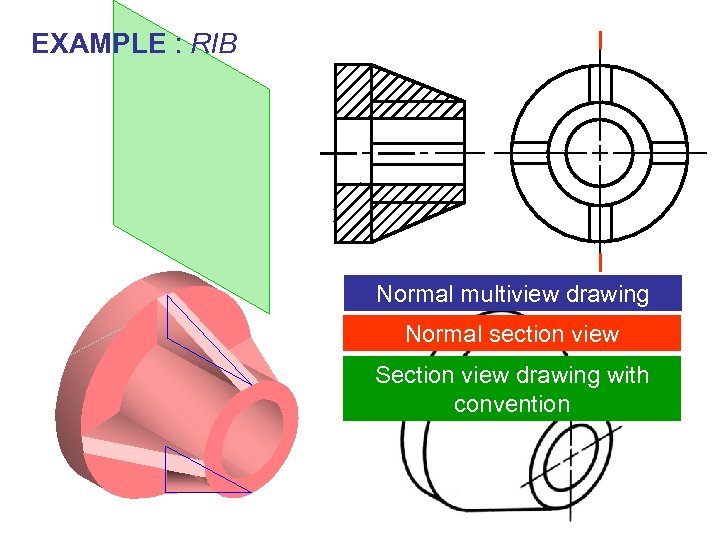 EXAMPLE : RIB Normal multiview drawing Normal section view Section view drawing with convention
EXAMPLE : RIB Normal multiview drawing Normal section view Section view drawing with convention
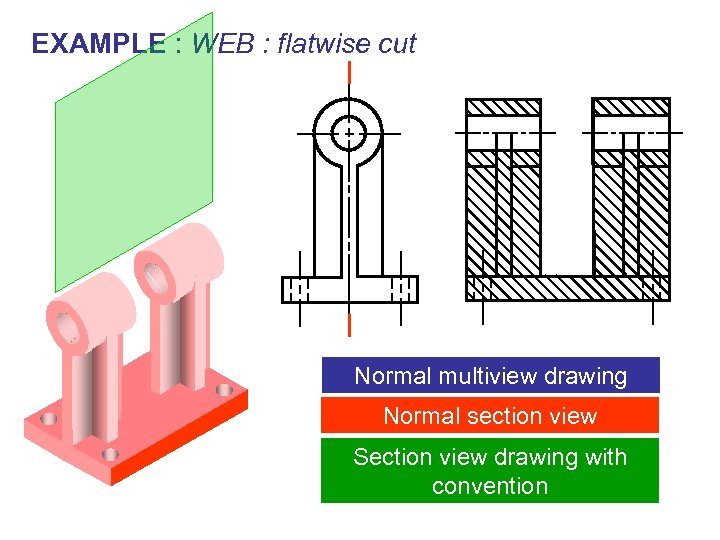 EXAMPLE : WEB : flatwise cut Normal multiview drawing Normal section view Section view drawing with convention
EXAMPLE : WEB : flatwise cut Normal multiview drawing Normal section view Section view drawing with convention
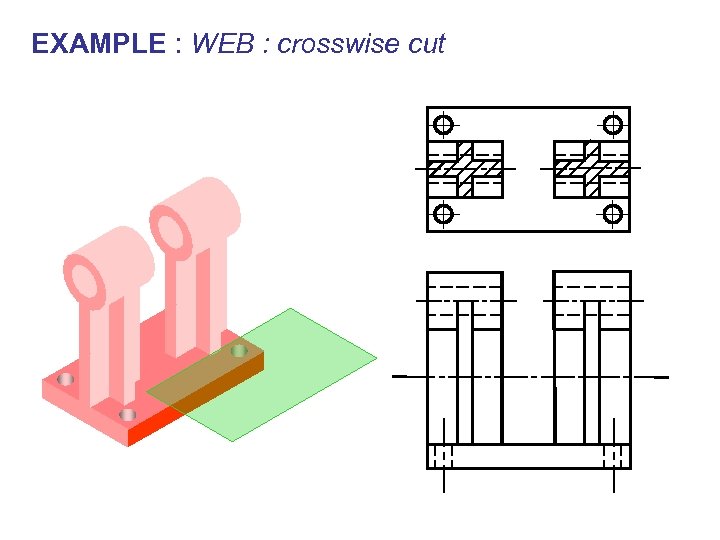 EXAMPLE : WEB : crosswise cut
EXAMPLE : WEB : crosswise cut
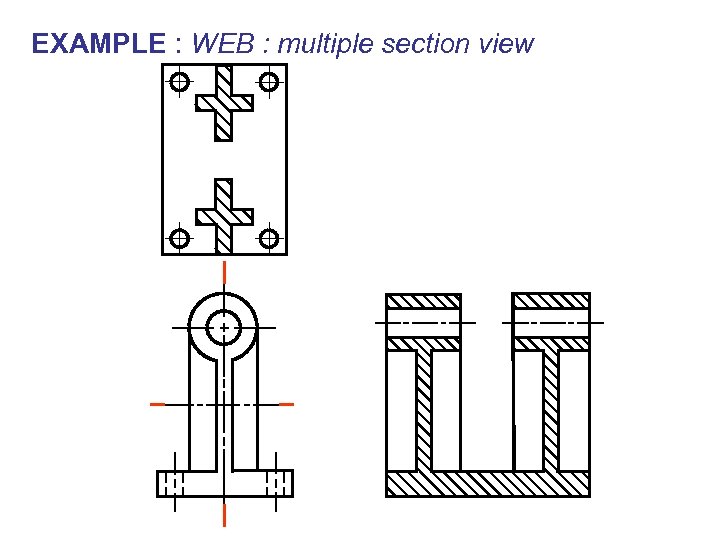 EXAMPLE : WEB : multiple section view
EXAMPLE : WEB : multiple section view
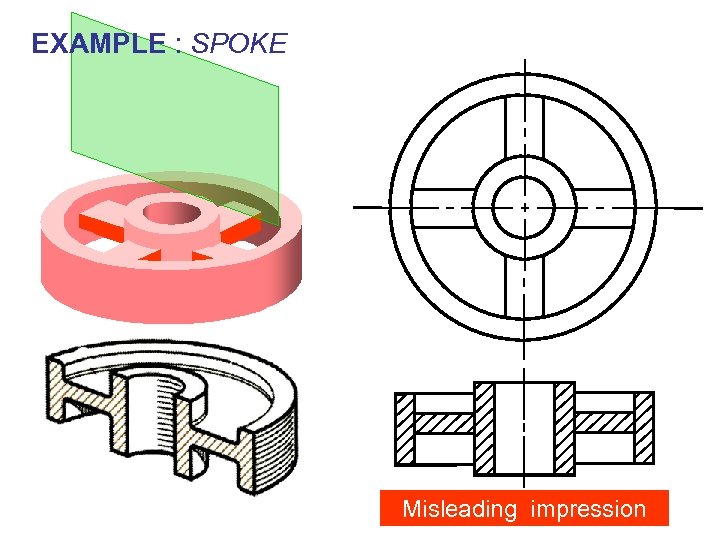 EXAMPLE : SPOKE Misleading impression
EXAMPLE : SPOKE Misleading impression
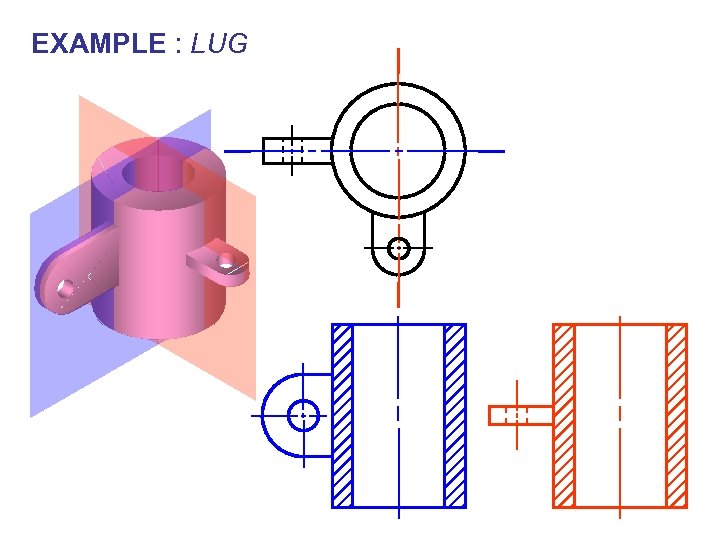 EXAMPLE : LUG
EXAMPLE : LUG
 Aligned Section
Aligned Section
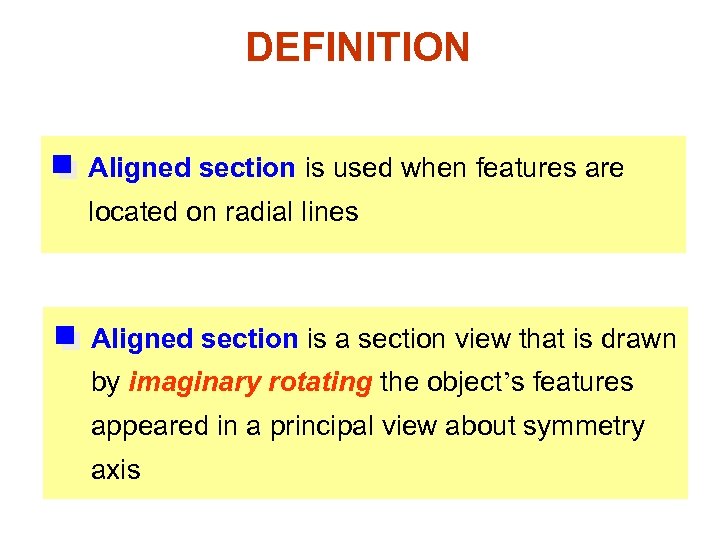 DEFINITION Aligned section is used when features are located on radial lines Aligned section is a section view that is drawn by imaginary rotating the object’s features appeared in a principal view about symmetry axis
DEFINITION Aligned section is used when features are located on radial lines Aligned section is a section view that is drawn by imaginary rotating the object’s features appeared in a principal view about symmetry axis
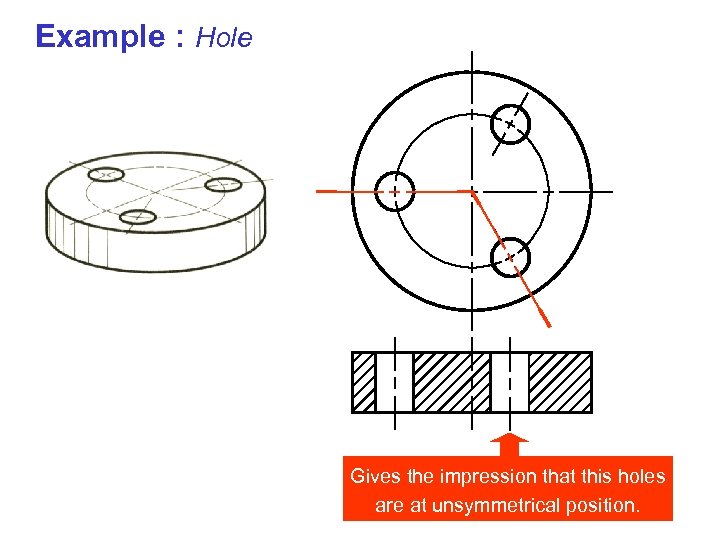 Example : Hole Gives the impression that this holes are at unsymmetrical position.
Example : Hole Gives the impression that this holes are at unsymmetrical position.
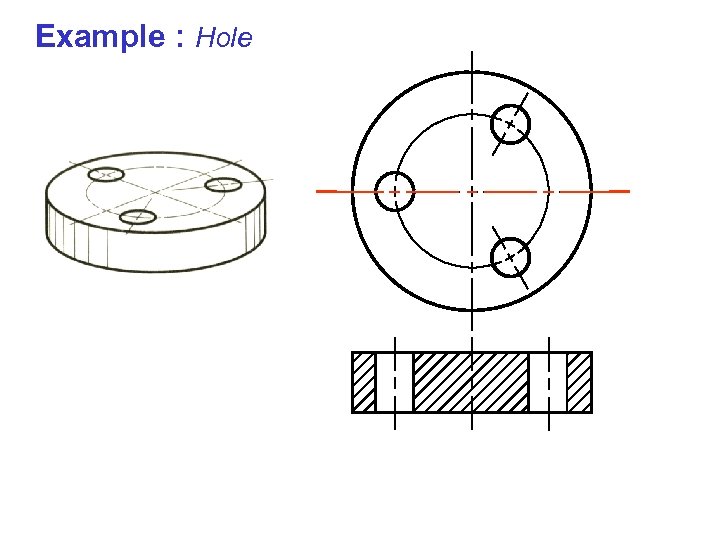 Example : Hole
Example : Hole
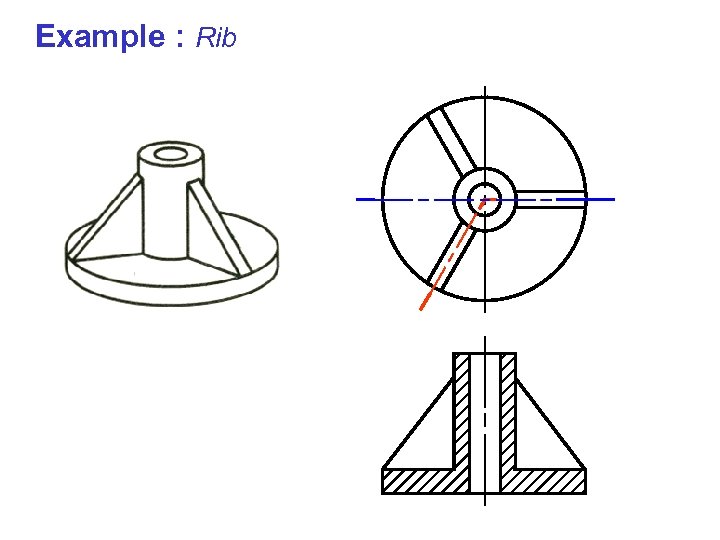 Example : Rib
Example : Rib
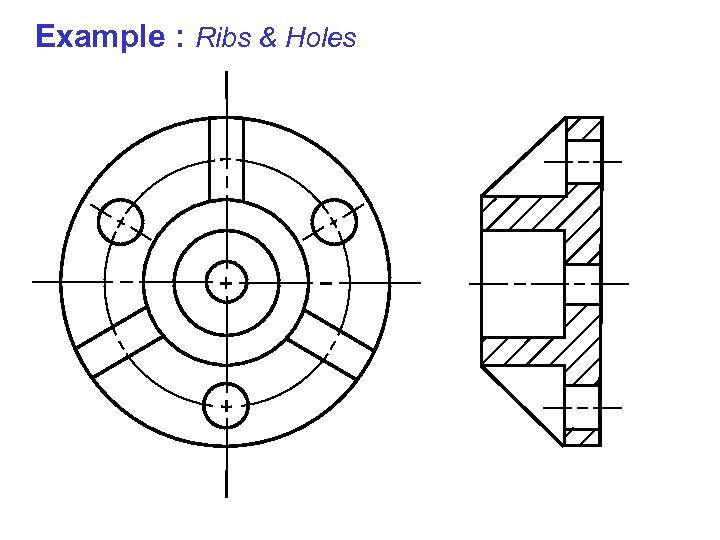 Example : Ribs & Holes
Example : Ribs & Holes
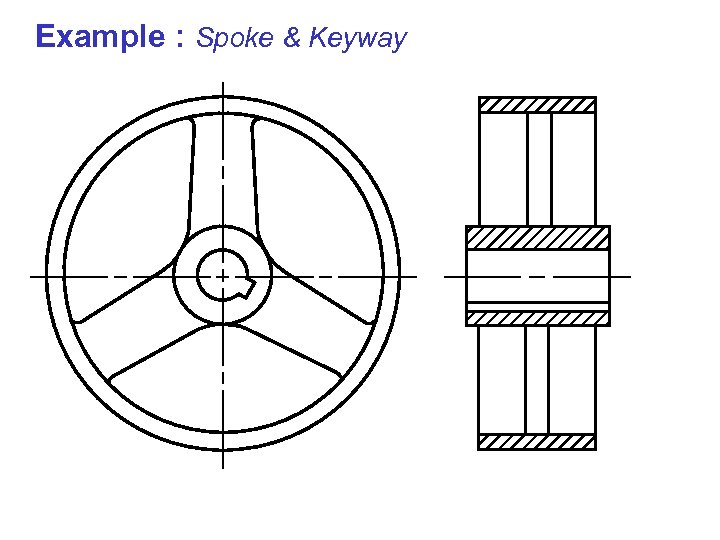 Example : Aligned section& Keyway Example : Spoke of keyway
Example : Aligned section& Keyway Example : Spoke of keyway
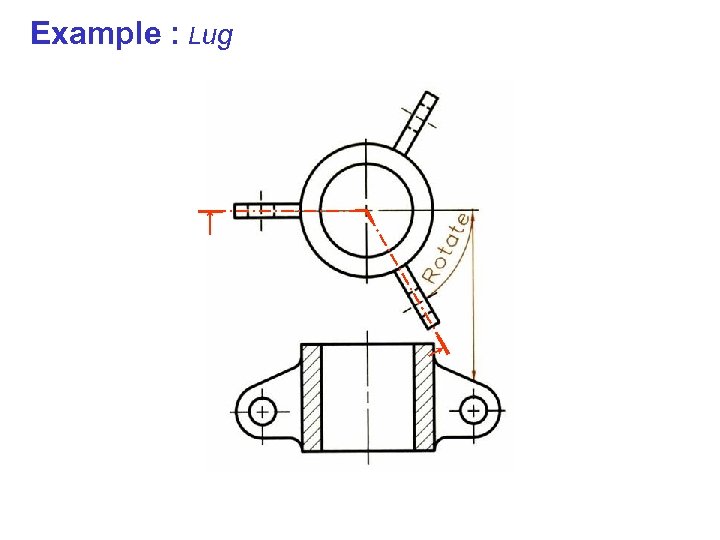 Example : Lug
Example : Lug
 Conventional Break
Conventional Break
 CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE For long objects that have to draw in a small scale to fit them on the paper, it is recommended to remove its long portion (which contains no important information) and draw the break lines at the broken ends.
CONVENTIONAL PRACTICE For long objects that have to draw in a small scale to fit them on the paper, it is recommended to remove its long portion (which contains no important information) and draw the break lines at the broken ends.
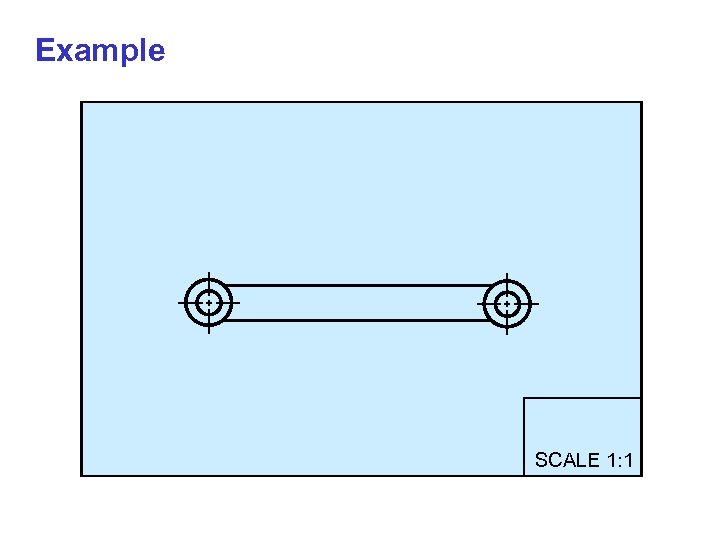 Example SCALE 1: 1
Example SCALE 1: 1
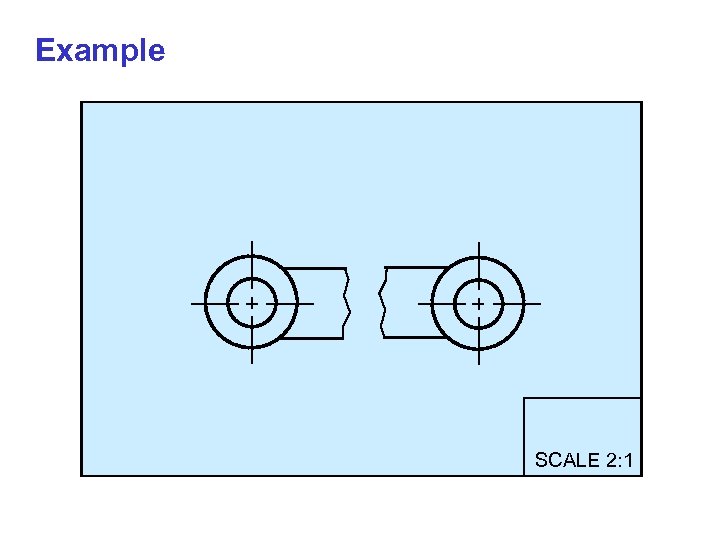 Example SCALE 2: 1
Example SCALE 2: 1
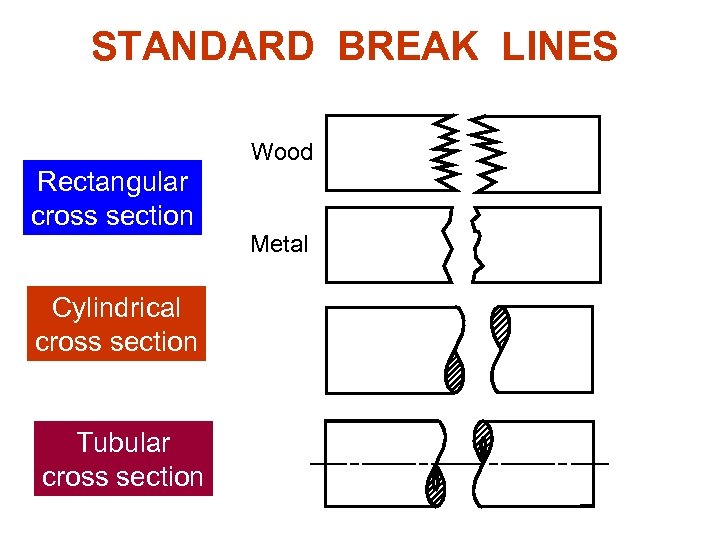 STANDARD BREAK LINES Wood Rectangular cross section Cylindrical cross section Tubular cross section Metal
STANDARD BREAK LINES Wood Rectangular cross section Cylindrical cross section Tubular cross section Metal
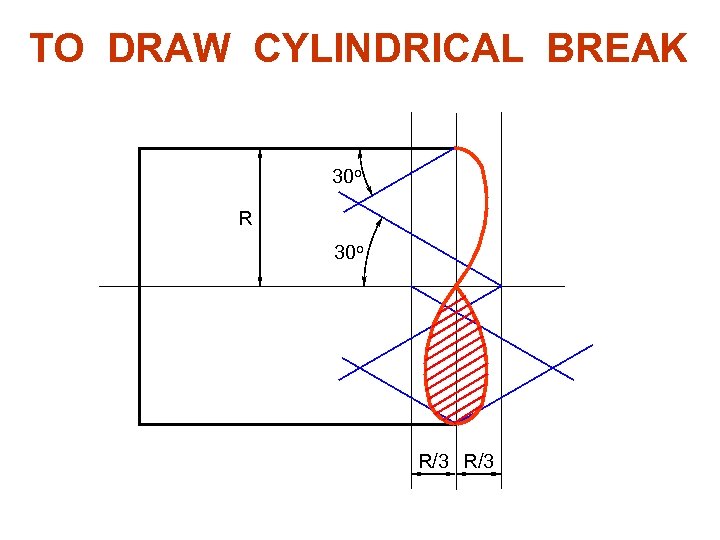 TO DRAW CYLINDRICAL BREAK 30 o R/3 R/3
TO DRAW CYLINDRICAL BREAK 30 o R/3 R/3
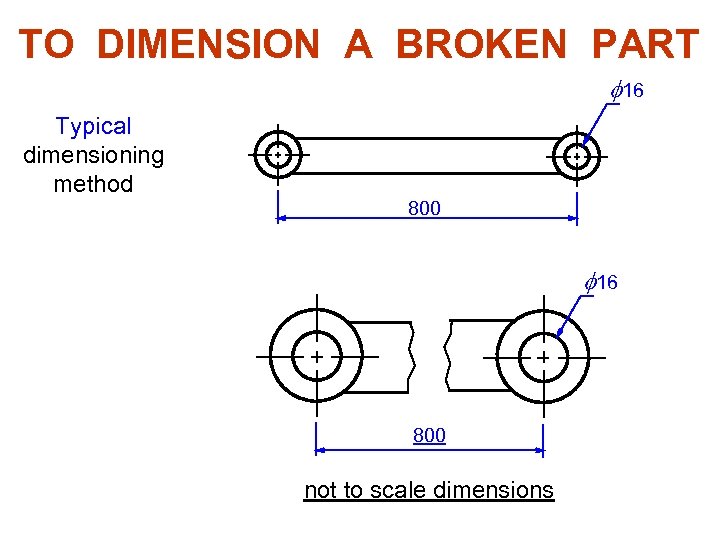 TO DIMENSION A BROKEN PART f 16 Typical dimensioning method 800 f 16 800 not to scale dimensions
TO DIMENSION A BROKEN PART f 16 Typical dimensioning method 800 f 16 800 not to scale dimensions