b797a962f0a5c7800d5898056724ae2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Chapter 1 – The First Civilizations: The Peoples of Western Asia and Egypt
Chapter 1 – The First Civilizations: The Peoples of Western Asia and Egypt
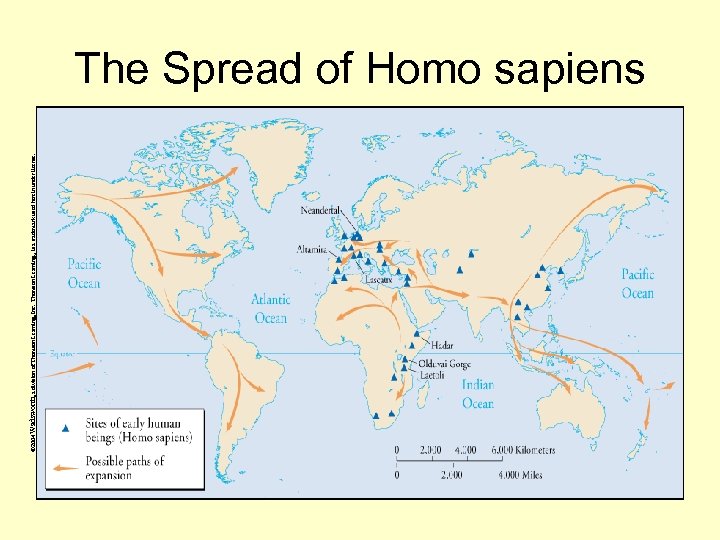 © 2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. The Spread of Homo sapiens
© 2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. The Spread of Homo sapiens
 How do we know what we know? • New evidences always forthcoming • Much of what we know is based on conjecture
How do we know what we know? • New evidences always forthcoming • Much of what we know is based on conjecture
 1 st Humans - Australopithecines • Hominids – lived 3 to 4 million years ago – Eastern and Southern Africa – Bipedal (walk upright) • Allowed them to move/travel – 1 st to make stone tools • Homo habilis discovered by the Leakeys – Larger brain and walked upright – Able to search for food better – Lived 1 to 4 million years ago
1 st Humans - Australopithecines • Hominids – lived 3 to 4 million years ago – Eastern and Southern Africa – Bipedal (walk upright) • Allowed them to move/travel – 1 st to make stone tools • Homo habilis discovered by the Leakeys – Larger brain and walked upright – Able to search for food better – Lived 1 to 4 million years ago
 1 st Humans - Australopithecines • Homo erectus – 100, 000 to 1 million years ego – used more tools – Left Africa and moved into Europe and Asia
1 st Humans - Australopithecines • Homo erectus – 100, 000 to 1 million years ego – used more tools – Left Africa and moved into Europe and Asia
 Homo sapiens • Means wise human – Two types: • Neanderthal 100, 000 -30, 000 B. C. E. – – Found in Europe and Middle East Buried dead – 1 st to do so Question of afterlife? Made clothes and killed for food • Homo sapiens 200, 000 B. C. E. – Anatomically modern humans – Africa
Homo sapiens • Means wise human – Two types: • Neanderthal 100, 000 -30, 000 B. C. E. – – Found in Europe and Middle East Buried dead – 1 st to do so Question of afterlife? Made clothes and killed for food • Homo sapiens 200, 000 B. C. E. – Anatomically modern humans – Africa
 Why move? • Theory 1 states that people outgrew their hunting grounds • Theory 2 states that humans developed in other places outside of Africa – Most believe that life began in Africa and then migrated out of it
Why move? • Theory 1 states that people outgrew their hunting grounds • Theory 2 states that humans developed in other places outside of Africa – Most believe that life began in Africa and then migrated out of it
 Hunter-Gathers of Paleolithic Age • Paleolithic 2, 500, 000 to 10, 000 BCE – Means old stone – Humans began to build tools • Became more sophisticated (spears, bow/arrows, harpoons, and fishhooks) – Nomadic - People gathered nuts, berries, fruits, and grains and hunted animals • Because of this, it is speculated that people lived in groups of 20 to 30 – Division of labor • Some argue that this means there was equality between men and women – Shelter – caves, animal hides with poles – Fire – allowed to stay warm and cook fire
Hunter-Gathers of Paleolithic Age • Paleolithic 2, 500, 000 to 10, 000 BCE – Means old stone – Humans began to build tools • Became more sophisticated (spears, bow/arrows, harpoons, and fishhooks) – Nomadic - People gathered nuts, berries, fruits, and grains and hunted animals • Because of this, it is speculated that people lived in groups of 20 to 30 – Division of labor • Some argue that this means there was equality between men and women – Shelter – caves, animal hides with poles – Fire – allowed to stay warm and cook fire
 Hunter-Gathers of Paleolithic Age • Two most important technological innovations 1. Fire 2. Tools • Why? – Human ability to change environment – Ability to change physically to survive
Hunter-Gathers of Paleolithic Age • Two most important technological innovations 1. Fire 2. Tools • Why? – Human ability to change environment – Ability to change physically to survive
 The Neolithic Revolution • Neolithic Revolution means new stone age • 10, 000 BCE • Revolution = agriculture – Planted grains and tamed animals – Gave up nomadic lifestyle and settled down • Mesolithic Age (middle stone age) – 10, 000 to 7000 BCE – Really the transitional period for agriculture
The Neolithic Revolution • Neolithic Revolution means new stone age • 10, 000 BCE • Revolution = agriculture – Planted grains and tamed animals – Gave up nomadic lifestyle and settled down • Mesolithic Age (middle stone age) – 10, 000 to 7000 BCE – Really the transitional period for agriculture
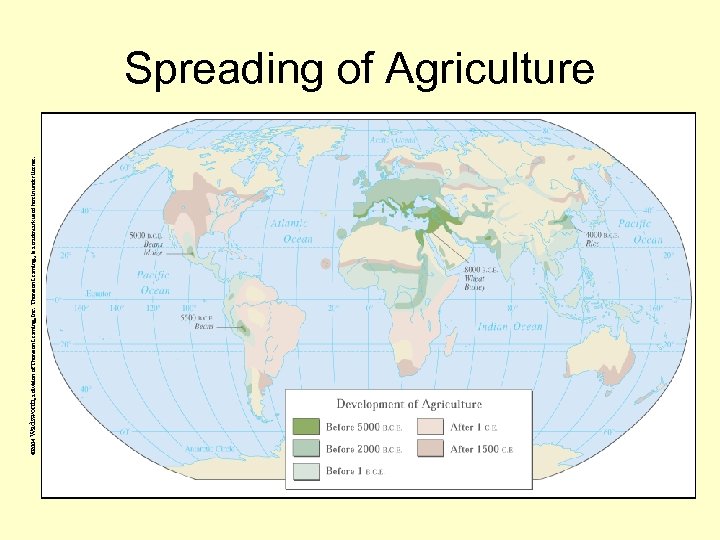 © 2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Spreading of Agriculture
© 2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Spreading of Agriculture
 Areas of Agriculture • Middle East – barley, oats, pigs, cattle, goats • Europe – Middle East farming spread into Europe • Egypt – barley and oats • Central Africa – root crops (yams ) and tree crops (bananas) • China – rice • Mesoamerica – beans, squash, maize (corn)
Areas of Agriculture • Middle East – barley, oats, pigs, cattle, goats • Europe – Middle East farming spread into Europe • Egypt – barley and oats • Central Africa – root crops (yams ) and tree crops (bananas) • China – rice • Mesoamerica – beans, squash, maize (corn)
 Neolithic Farming Villages • Oldest in Middle East • Catal Hüyük (in modern Turkey) – Walled city – Mud brick homes – no streets because close together – Cultivated 12 products (fruits, nuts, three kinds of wheat) – Domesticated animals – Hunted but did not rely on it for survival – Food surpluses allowed for occupations to develop • Caused trade to develop – Religious - earth mothers
Neolithic Farming Villages • Oldest in Middle East • Catal Hüyük (in modern Turkey) – Walled city – Mud brick homes – no streets because close together – Cultivated 12 products (fruits, nuts, three kinds of wheat) – Domesticated animals – Hunted but did not rely on it for survival – Food surpluses allowed for occupations to develop • Caused trade to develop – Religious - earth mothers
 Consequences of Neolithic Revolution • Built homes for protection and storage – Development of armies • Division of labor – Artisans, farmers – Women and men • Men in fields away from home • Women at home raising family and caring for them • Importance of working outside the home became dominate (so men became dominate) • • Trade Cloth developed due to planting Invention of writing – records Metal working – tools, weapons – Bronze Age 3000 to 1200 BCE (came from western Asia mixing copper and tin together)
Consequences of Neolithic Revolution • Built homes for protection and storage – Development of armies • Division of labor – Artisans, farmers – Women and men • Men in fields away from home • Women at home raising family and caring for them • Importance of working outside the home became dominate (so men became dominate) • • Trade Cloth developed due to planting Invention of writing – records Metal working – tools, weapons – Bronze Age 3000 to 1200 BCE (came from western Asia mixing copper and tin together)
 Emergence of Civilization • Civilization – complex culture in large numbers of people that share common elements • Basic characteristics – Urban focus – political, economic, social, and religious centers – New political and military structures – organized – Social structure based on economic power – class structure – Complexity – trade – Religious structure – gods essential to city’s success – Writing – record keeping – Artistic and Intellectual Activity – architecture
Emergence of Civilization • Civilization – complex culture in large numbers of people that share common elements • Basic characteristics – Urban focus – political, economic, social, and religious centers – New political and military structures – organized – Social structure based on economic power – class structure – Complexity – trade – Religious structure – gods essential to city’s success – Writing – record keeping – Artistic and Intellectual Activity – architecture
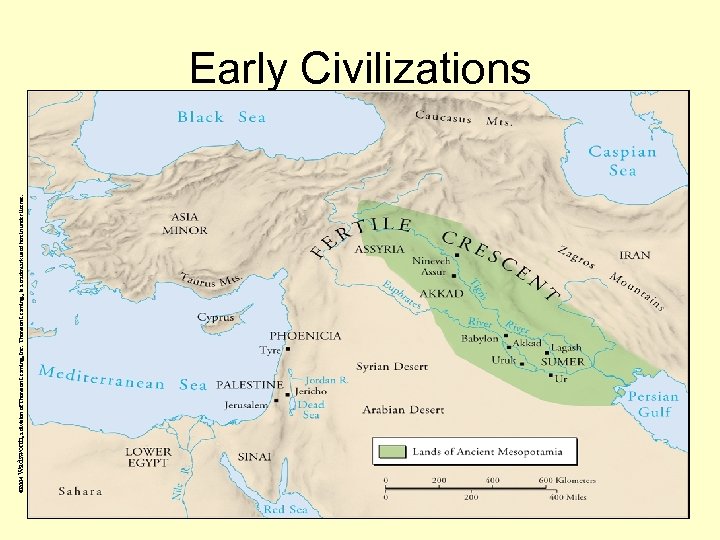 © 2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Early Civilizations
© 2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Early Civilizations
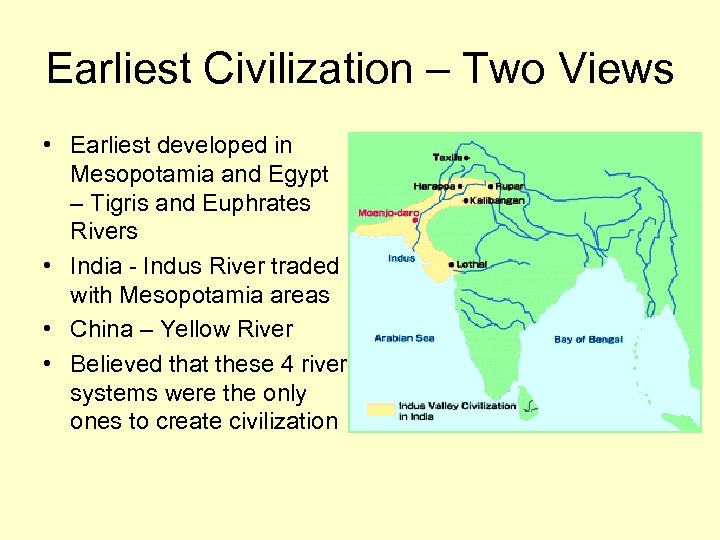 Earliest Civilization – Two Views • Earliest developed in Mesopotamia and Egypt – Tigris and Euphrates Rivers • India - Indus River traded with Mesopotamia areas • China – Yellow River • Believed that these 4 river systems were the only ones to create civilization
Earliest Civilization – Two Views • Earliest developed in Mesopotamia and Egypt – Tigris and Euphrates Rivers • India - Indus River traded with Mesopotamia areas • China – Yellow River • Believed that these 4 river systems were the only ones to create civilization
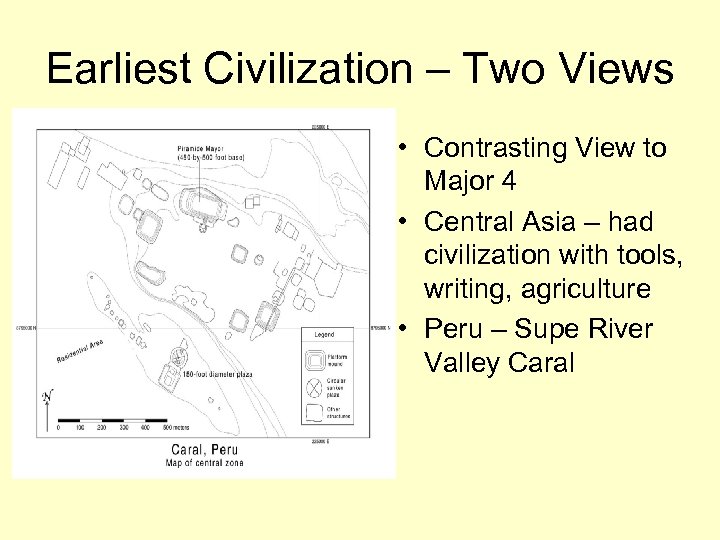 Earliest Civilization – Two Views • Contrasting View to Major 4 • Central Asia – had civilization with tools, writing, agriculture • Peru – Supe River Valley Caral
Earliest Civilization – Two Views • Contrasting View to Major 4 • Central Asia – had civilization with tools, writing, agriculture • Peru – Supe River Valley Caral
 Why did Civilization Develop? • Challenges faced by humans forced them to work together • Material wants and goods caused people to gather together • Nonmaterial goods caused unity (religion) • Who knows?
Why did Civilization Develop? • Challenges faced by humans forced them to work together • Material wants and goods caused people to gather together • Nonmaterial goods caused unity (religion) • Who knows?
 Mesopotamia • Tigris and Euphrates Rivers overflowed and provided silt for land – Caused land to be rich • People manipulated the rivers • Sumerians – cities were Eridu, Uruk, Umma, and Lagash
Mesopotamia • Tigris and Euphrates Rivers overflowed and provided silt for land – Caused land to be rich • People manipulated the rivers • Sumerians – cities were Eridu, Uruk, Umma, and Lagash
 Sumerians • City-states • Cities had walls and mud bricks • Ziggurat – religious center of city-state – Gods owned city and provided all wealth to it – Priests had great power maybe even ruled • Theocracy
Sumerians • City-states • Cities had walls and mud bricks • Ziggurat – religious center of city-state – Gods owned city and provided all wealth to it – Priests had great power maybe even ruled • Theocracy
 Sumerians • Divine right to rule – kings were agents of the gods • Economy was agricultural – Did produce things like woolen textiles, pottery, metalwork – Imported tin, copper, and timber – Wheel invented which ease transportation 3000 BCE
Sumerians • Divine right to rule – kings were agents of the gods • Economy was agricultural – Did produce things like woolen textiles, pottery, metalwork – Imported tin, copper, and timber – Wheel invented which ease transportation 3000 BCE
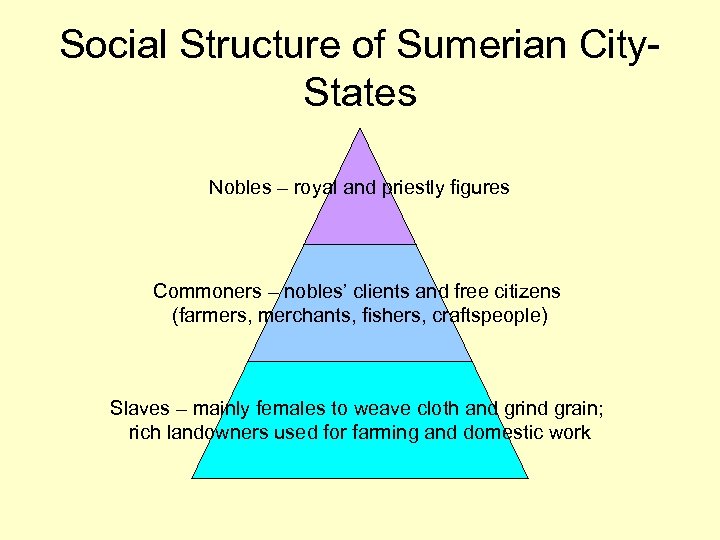 Social Structure of Sumerian City. States Nobles – royal and priestly figures Commoners – nobles’ clients and free citizens (farmers, merchants, fishers, craftspeople) Slaves – mainly females to weave cloth and grind grain; rich landowners used for farming and domestic work
Social Structure of Sumerian City. States Nobles – royal and priestly figures Commoners – nobles’ clients and free citizens (farmers, merchants, fishers, craftspeople) Slaves – mainly females to weave cloth and grind grain; rich landowners used for farming and domestic work
 Akkadian Empire • Semitic people • Sargon, 2340 BCE, leader conquered Sumerian city-states • Controlled most of Mesopotamia until 1792 BCE when the Amorites controlled the area
Akkadian Empire • Semitic people • Sargon, 2340 BCE, leader conquered Sumerian city-states • Controlled most of Mesopotamia until 1792 BCE when the Amorites controlled the area
 Culture of Mesopotamia • Harsh climate and constant death = religious zealousness – Polytheism – Divination allowed humans to figure out what the gods wanted – Epic of Gilgamesh • Cuneiform writing – Scribal education – males, from wealthier families – Number system – geometry, astronomy
Culture of Mesopotamia • Harsh climate and constant death = religious zealousness – Polytheism – Divination allowed humans to figure out what the gods wanted – Epic of Gilgamesh • Cuneiform writing – Scribal education – males, from wealthier families – Number system – geometry, astronomy
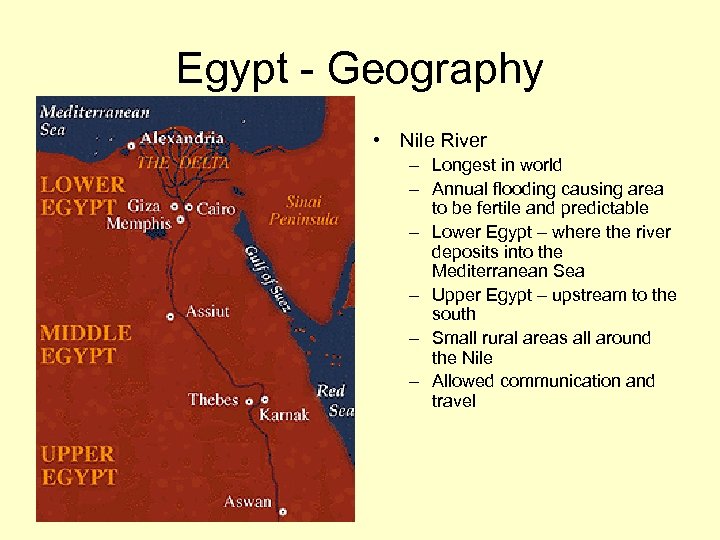 Egypt - Geography • Nile River – Longest in world – Annual flooding causing area to be fertile and predictable – Lower Egypt – where the river deposits into the Mediterranean Sea – Upper Egypt – upstream to the south – Small rural areas all around the Nile – Allowed communication and travel
Egypt - Geography • Nile River – Longest in world – Annual flooding causing area to be fertile and predictable – Lower Egypt – where the river deposits into the Mediterranean Sea – Upper Egypt – upstream to the south – Small rural areas all around the Nile – Allowed communication and travel
 Egypt - Geography • Natural barriers to invasions – Deserts to the east and west – Cataracts (rapids on southern part of Nile) – Mediterranean Sea to the north – Trade did develop
Egypt - Geography • Natural barriers to invasions – Deserts to the east and west – Cataracts (rapids on southern part of Nile) – Mediterranean Sea to the north – Trade did develop
 Old Kingdom 2686 to 2125 BCE White – upper Red – lower Together = Double Crown of Egypt • Menes first king of a royal dynasty united Upper and Lower Egypt • Built largest pyramid • Capital was Memphis • Pharaoh was ruling figure
Old Kingdom 2686 to 2125 BCE White – upper Red – lower Together = Double Crown of Egypt • Menes first king of a royal dynasty united Upper and Lower Egypt • Built largest pyramid • Capital was Memphis • Pharaoh was ruling figure
 Pharaoh • Absolute power but limited because of religion – Ma’at – truth and justice • Families originally helped but a bureaucracy developed – Vizier in charge of bureaucracy • Egypt divided into nomes/provides – Nomarch head of nome and reported to Vizier and Pharaoh
Pharaoh • Absolute power but limited because of religion – Ma’at – truth and justice • Families originally helped but a bureaucracy developed – Vizier in charge of bureaucracy • Egypt divided into nomes/provides – Nomarch head of nome and reported to Vizier and Pharaoh
 Middle Kingdom 2055 to 1650 BCE • Viewed as the Golden Age • Nomes were reorganized and rules stated • Pharaoh was viewed as a shepherd of the people and not an inaccessible god – Public works – Public welfare
Middle Kingdom 2055 to 1650 BCE • Viewed as the Golden Age • Nomes were reorganized and rules stated • Pharaoh was viewed as a shepherd of the people and not an inaccessible god – Public works – Public welfare
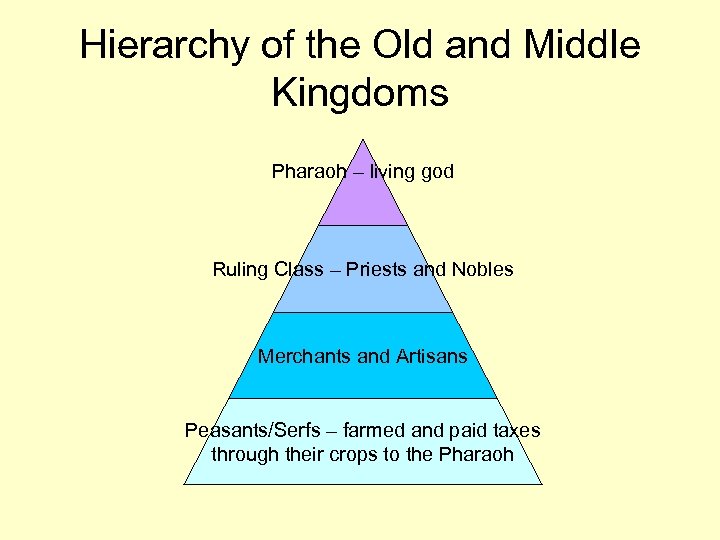 Hierarchy of the Old and Middle Kingdoms Pharaoh – living god Ruling Class – Priests and Nobles Merchants and Artisans Peasants/Serfs – farmed and paid taxes through their crops to the Pharaoh
Hierarchy of the Old and Middle Kingdoms Pharaoh – living god Ruling Class – Priests and Nobles Merchants and Artisans Peasants/Serfs – farmed and paid taxes through their crops to the Pharaoh
 Culture of Egypt • Spiritual life – Polytheistic – Pharaoh was the son of sun god, Ra/Re – Osiris and Isis – resurrection – Mummification of dead – People had two bodies – one physical and spiritual called ka – By supplying the mummified body with material goods, the ka could come alive again
Culture of Egypt • Spiritual life – Polytheistic – Pharaoh was the son of sun god, Ra/Re – Osiris and Isis – resurrection – Mummification of dead – People had two bodies – one physical and spiritual called ka – By supplying the mummified body with material goods, the ka could come alive again
 Culture of Egypt • Pyramids – 1 st done in Old Kingdom – Only for pharaohs – King Khufu built the Great Pyramid at Giza
Culture of Egypt • Pyramids – 1 st done in Old Kingdom – Only for pharaohs – King Khufu built the Great Pyramid at Giza
 Culture of Egypt • Hieroglyphics – form of writing for Egyptians • Paper was papyrus • Statues and writing had purpose for afterlife
Culture of Egypt • Hieroglyphics – form of writing for Egyptians • Paper was papyrus • Statues and writing had purpose for afterlife
 From the Book of the Dead Anubis wears the Jackal head Green man is Osiris
From the Book of the Dead Anubis wears the Jackal head Green man is Osiris
 New Kingdom • Middle Kingdom ended with the invasion of the Hyksos (from western Asia) – Used horse drawn chariots with wheels – Hyksos ruled for 100 years – Egyptians took bronze to make weapons and tools and war chariots
New Kingdom • Middle Kingdom ended with the invasion of the Hyksos (from western Asia) – Used horse drawn chariots with wheels – Hyksos ruled for 100 years – Egyptians took bronze to make weapons and tools and war chariots

 New Kingdom 1550 to 1085 BCE Temple at Deir el Bahri near Thebes • Used Hyksos technology to build a stronger and more massive Egypt • Queen Hatshepsut – 1 st female ruler – Expanded economy – Dressed as male pharaoh – Thutmosis III destroyed her images after her death –
New Kingdom 1550 to 1085 BCE Temple at Deir el Bahri near Thebes • Used Hyksos technology to build a stronger and more massive Egypt • Queen Hatshepsut – 1 st female ruler – Expanded economy – Dressed as male pharaoh – Thutmosis III destroyed her images after her death –
 Akhenaton/Akhenaten • Really Amehotep IV introduced the religion of Aten, worship of the sun disk – Attempt to decrease the power of the priests of Amon-Ra at Thebes – New capital Akhetaten – Religious changed failed – Akhenaton lost Syria and Palestine while trying to convert Egypt to the new religion – Akhenaton died and his religious changes were undone by his successor, Tutankhamen
Akhenaton/Akhenaten • Really Amehotep IV introduced the religion of Aten, worship of the sun disk – Attempt to decrease the power of the priests of Amon-Ra at Thebes – New capital Akhetaten – Religious changed failed – Akhenaton lost Syria and Palestine while trying to convert Egypt to the new religion – Akhenaton died and his religious changes were undone by his successor, Tutankhamen

 Decline of Egypt • Ramses II regained Palestine – Very powerful warrior king – Lived until his 80 s – Lots of construction projects – Battle of Kadesh – lost – Created peace treaties – Had at least 100 children
Decline of Egypt • Ramses II regained Palestine – Very powerful warrior king – Lived until his 80 s – Lots of construction projects – Battle of Kadesh – lost – Created peace treaties – Had at least 100 children
 Abu Simbel
Abu Simbel
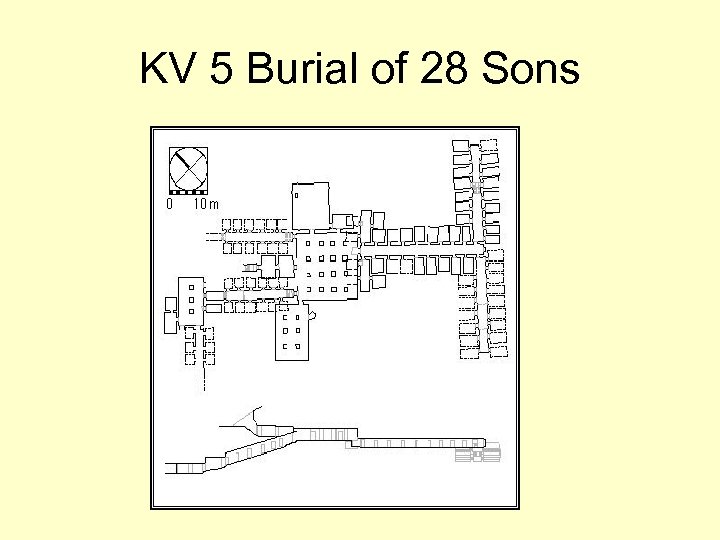 KV 5 Burial of 28 Sons
KV 5 Burial of 28 Sons
 Family and Marriage in Egypt • Pharaoh could have harem – Great Wife highest status • Original people were expected to marry young and maintain the home • Women could inherit and maintain property
Family and Marriage in Egypt • Pharaoh could have harem – Great Wife highest status • Original people were expected to marry young and maintain the home • Women could inherit and maintain property
 Europe • Along Balkan area settlements were established • Megalithic structures were built
Europe • Along Balkan area settlements were established • Megalithic structures were built
 Indo-Europeans • Indo-European refers to language – Greek, Latin, Persian, Sanskrit, Germanic and Slavic – Probably started in the Black Sea or in southwestern Asia (Iraq or Afghanistan) – Moved out into Europe (Greece and Italy) • Hittites 1 st of Indo-Europeans to make iron weapons – Destroyed by invading tribes
Indo-Europeans • Indo-European refers to language – Greek, Latin, Persian, Sanskrit, Germanic and Slavic – Probably started in the Black Sea or in southwestern Asia (Iraq or Afghanistan) – Moved out into Europe (Greece and Italy) • Hittites 1 st of Indo-Europeans to make iron weapons – Destroyed by invading tribes
 Phoenicians • Lived in Palestine • Fall of the Hittite and Egyptian empires let the Phoenicians expand their trade along Mediterranean • Produced purple dye, glass, wine, and cedar • Settled in southern Spain, Sicily, Sardinia, and Carthage • Phoenician Alphabet passed to Greeks
Phoenicians • Lived in Palestine • Fall of the Hittite and Egyptian empires let the Phoenicians expand their trade along Mediterranean • Produced purple dye, glass, wine, and cedar • Settled in southern Spain, Sicily, Sardinia, and Carthage • Phoenician Alphabet passed to Greeks
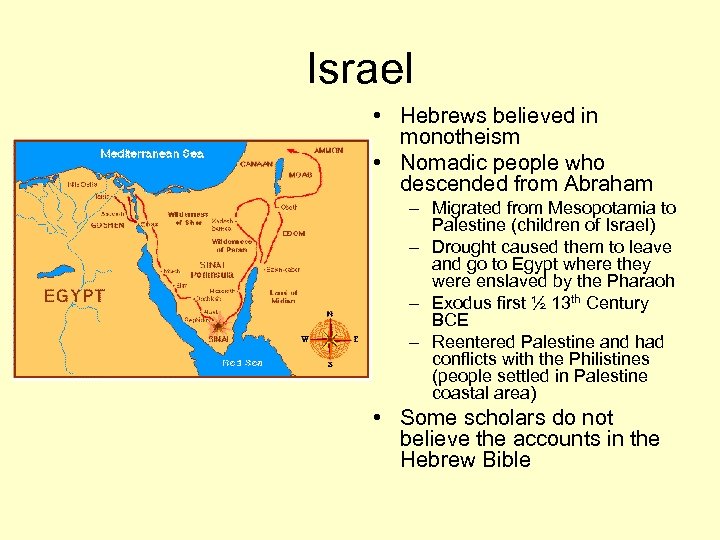 Israel • Hebrews believed in monotheism • Nomadic people who descended from Abraham – Migrated from Mesopotamia to Palestine (children of Israel) – Drought caused them to leave and go to Egypt where they were enslaved by the Pharaoh – Exodus first ½ 13 th Century BCE – Reentered Palestine and had conflicts with the Philistines (people settled in Palestine coastal area) • Some scholars do not believe the accounts in the Hebrew Bible
Israel • Hebrews believed in monotheism • Nomadic people who descended from Abraham – Migrated from Mesopotamia to Palestine (children of Israel) – Drought caused them to leave and go to Egypt where they were enslaved by the Pharaoh – Exodus first ½ 13 th Century BCE – Reentered Palestine and had conflicts with the Philistines (people settled in Palestine coastal area) • Some scholars do not believe the accounts in the Hebrew Bible
 Kingdom of Israel • Saul 1 st king battled the Philistines and later died – Chaos • David reunited Israelites and defeated the Philistines to control all of Israel – Made Jerusalem the capital – New system based on farming and urban life
Kingdom of Israel • Saul 1 st king battled the Philistines and later died – Chaos • David reunited Israelites and defeated the Philistines to control all of Israel – Made Jerusalem the capital – New system based on farming and urban life
 David’s Successor • Solomon expanded political, military establishments, and trade – Built the Temple in Jerusalem housing the Ark of the Covenant – Solomon became unpopular
David’s Successor • Solomon expanded political, military establishments, and trade – Built the Temple in Jerusalem housing the Ark of the Covenant – Solomon became unpopular

 Divided Israel • • Two kingdoms established Northern tribes – Samaria Kingdom Southern tribes – Judah Kingdom Assyrians destroyed Samaria and sent Hebrews to other parts – 10 Lost Tribes of Israel • Judah also had to pay tribute to Assyria • Assyria was conquered by Chaldeans and they destroyed Jerusalem – Deported more Hebrews to Babylon – Persia conquered Chaldeans and allowed Hebrews to return to Jerusalem to rebuild temple – Alexander the Great will conquer this area
Divided Israel • • Two kingdoms established Northern tribes – Samaria Kingdom Southern tribes – Judah Kingdom Assyrians destroyed Samaria and sent Hebrews to other parts – 10 Lost Tribes of Israel • Judah also had to pay tribute to Assyria • Assyria was conquered by Chaldeans and they destroyed Jerusalem – Deported more Hebrews to Babylon – Persia conquered Chaldeans and allowed Hebrews to return to Jerusalem to rebuild temple – Alexander the Great will conquer this area
 Hebrew Religion • Yahweh – Hebrew God – All powerful, omnipresent • Three big concepts – covenant, law, and prophets – Covenant – Exodus – Law – Ten Commandments – Prophets – religious teachers – Because of these three things, they could not accept pagan gods
Hebrew Religion • Yahweh – Hebrew God – All powerful, omnipresent • Three big concepts – covenant, law, and prophets – Covenant – Exodus – Law – Ten Commandments – Prophets – religious teachers – Because of these three things, they could not accept pagan gods
 Assyrian Empire • Assyrians were Semitic speaking – Land covered Mesopotamia, Iranian Plateau, Asia Minor, Syria, Palestine, and Egypt • Too large led to decline • Used iron weapons • Leaders were absolute – Ashurbanipal greatest rule • Communication system efficient – posts with animals • Ninevah, capital, fell to Chaldeans in 612 BCE
Assyrian Empire • Assyrians were Semitic speaking – Land covered Mesopotamia, Iranian Plateau, Asia Minor, Syria, Palestine, and Egypt • Too large led to decline • Used iron weapons • Leaders were absolute – Ashurbanipal greatest rule • Communication system efficient – posts with animals • Ninevah, capital, fell to Chaldeans in 612 BCE
 Assyrian Empire • Conquests and maintenance of the empire – Military leaders and fighters • Well organized and discipline • Standing army • Use of guerilla and terror tactics • Ethnic differences did not matter because it was a polyglot society • Religion was a unifier • Economy – Mostly farms – no irrigation needed due to rain – Trade • Culture – hybrid of Sumerian and Babylonian
Assyrian Empire • Conquests and maintenance of the empire – Military leaders and fighters • Well organized and discipline • Standing army • Use of guerilla and terror tactics • Ethnic differences did not matter because it was a polyglot society • Religion was a unifier • Economy – Mostly farms – no irrigation needed due to rain – Trade • Culture – hybrid of Sumerian and Babylonian
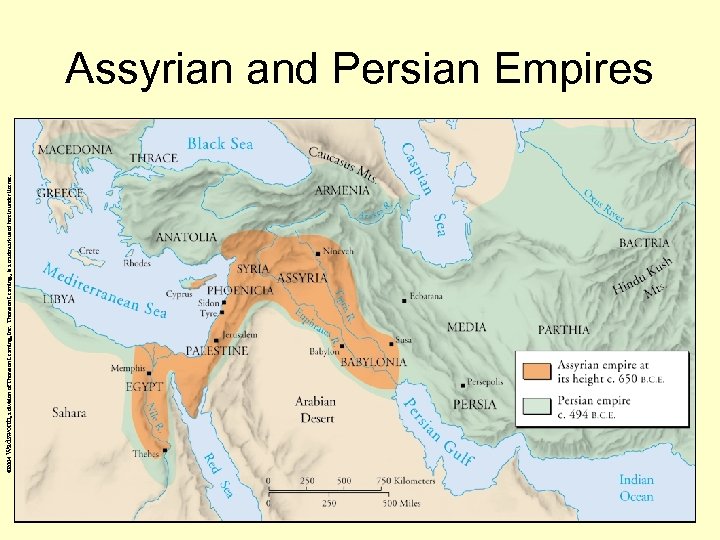 © 2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Assyrian and Persian Empires
© 2004 Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Assyrian and Persian Empires
 Persian Empire • Cyrus the Great – Controlled Medes (became satrapy/province) – Defeated Lydian Kingdom – Greek city-states on Ionian coast – Eastern part of the Iranian Plateau, Sogdia, and India – Captured Babylon and won the hearts of the people through vanity • Allowed Jews to leave and rebuild Temple – Used locals to help with running governments – Showed mercy to conquered
Persian Empire • Cyrus the Great – Controlled Medes (became satrapy/province) – Defeated Lydian Kingdom – Greek city-states on Ionian coast – Eastern part of the Iranian Plateau, Sogdia, and India – Captured Babylon and won the hearts of the people through vanity • Allowed Jews to leave and rebuild Temple – Used locals to help with running governments – Showed mercy to conquered
 Persian Empire • Cambyses invaded Egypt • Darius added western India – Ionian area revolted • Darius reestablished control despite the Greeks receiving help from Athens • Invaded mainland Greece – Battle of Marathon 490 BCE – Persians lost – Largest empire at this point in history • Empire divided into 20 satrapies – Paid tribute – Satraps (governors) were like minikings – Royal Road - connected empire • Kings hoarded wealth and overtaxed the people – Major reasons for the decline of the empire
Persian Empire • Cambyses invaded Egypt • Darius added western India – Ionian area revolted • Darius reestablished control despite the Greeks receiving help from Athens • Invaded mainland Greece – Battle of Marathon 490 BCE – Persians lost – Largest empire at this point in history • Empire divided into 20 satrapies – Paid tribute – Satraps (governors) were like minikings – Royal Road - connected empire • Kings hoarded wealth and overtaxed the people – Major reasons for the decline of the empire
 Persian Empire • Military – Standing army of different ethnicities – Immortals – elite force • Religion – Zoroastrian – monotheistic – Ahuramazda was the creator, gave free will – Ahriman was the evil spirit – Judgment at end of world
Persian Empire • Military – Standing army of different ethnicities – Immortals – elite force • Religion – Zoroastrian – monotheistic – Ahuramazda was the creator, gave free will – Ahriman was the evil spirit – Judgment at end of world
 Discussion Questions • Why is the term “Neolithic or new stone age” misleading? • How did the advent of settled agriculture change human society? • Why were city-states at the center of the early stages of civilization? • Compare and contrast the Assyrian and Persian approaches to governing an empire.
Discussion Questions • Why is the term “Neolithic or new stone age” misleading? • How did the advent of settled agriculture change human society? • Why were city-states at the center of the early stages of civilization? • Compare and contrast the Assyrian and Persian approaches to governing an empire.


